本文深入介紹了Java 8的Stream API,包括創建、中間操作、終端操作等,強調了並行流在大數據處理中的性能提升。提供清晰實用的示例,為讀者理解流式計算提供有益指導。 ...
Java 8 引入的Stream API提供了一種新的數據處理方式,它以聲明式、函數式的編程模型,極大地簡化了對集合、數組或其他支持數據源的操作。Stream可以被看作是一系列元素的流水線。允許你高效地對大量數據執行複雜的過濾、映射、排序、聚合等操作,而無需顯式地使用迴圈或者臨時變數。Stream API的設計理念主要包括兩個方面:鏈式調用和惰性求值。鏈式調用允許我們將多個操作連接在一起,形成一個流水線,而惰性求值意味著只有在真正需要結果的時候才執行計算,從而避免了不必要的計算開銷。
接下來我們就來盤點一下日常開發中常用的一些Stream API。
創建Stream
- 集合創建
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 串列流
Stream<String> stream = list.stream();
// 並行流
Stream<String> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();
- 數組創建
String[] strs = new String[3];
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(strs);
- 使用
Stream.of(T...values)創建
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("Apple", "Orange", "Banana");
- 使用Stream.generate()創建流
// 生成一個無限流,通過limit()限制元素個數
Stream<Double> randomStream = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(5);
- 使用Stream.iterate()創建流
// 生成一個等差數列,通過limit()限制元素個數
Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.iterate(0, n -> n + 2).limit(5);
- 使用IntStream、LongStream、DoubleStream創建原始類型流
// 使用IntStream創建
IntStream intStream = IntStream.range(1, 5); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 使用LongStream創建
LongStream longStream = LongStream.rangeClosed(1, 5); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
IntStream我們使用的地方還是比較多的,比如我們按照下標遍歷一個集合時,同常的做法是:for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){},我們可以使用IntStream去改造一下,IntStream.rangeClosed(0, list.size()).forEach();
中間操作
中間操作是構建流水線的一部分,用於對流進行轉換和處理,但它們並不會觸發實際的計算。
- 過濾操作(filter)
過濾操作用於篩選流中的元素,保留滿足指定條件的元素。Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate),filter接受一個謂詞Predicate,我們可以通過這個謂詞定義篩選條件,Predicate是一個函數式介面,其包含一個test(T t)方法,該方法返回boolean。
private static void filterTest(){
List<String> fruits = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange", "grape");
// 過濾長度大於5的水果
List<String> filteredFruits = fruits.stream().filter(fruit -> fruit.length() > 5).collect(Collectors.toList());
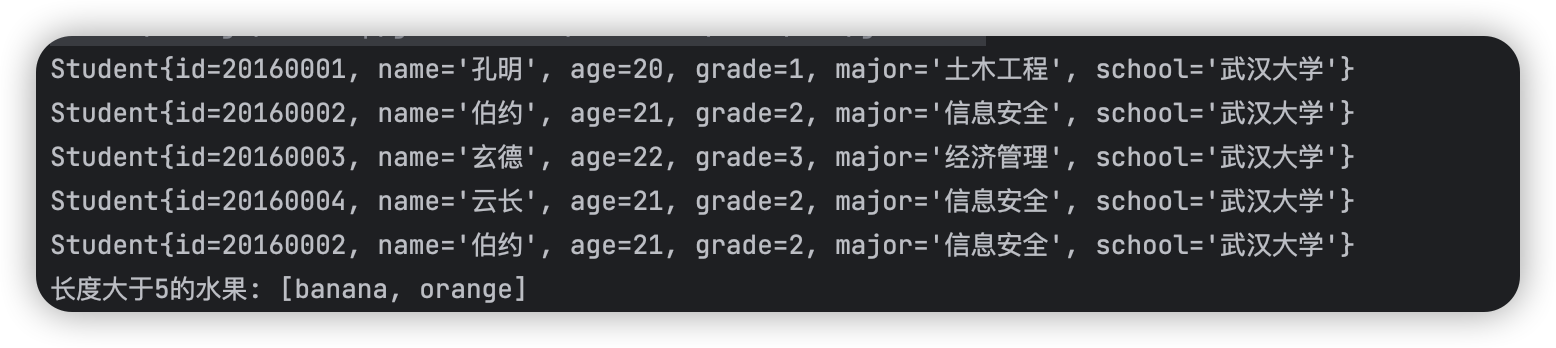
System.out.println("長度大於5的水果: "+ filteredFruits);
}
private static void filterTest(List<Student> students){
List<Student> filterStudents = students.stream()
.filter(student -> Objects.equals("武漢大學", student.getSchool()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
filterStudents.forEach(System.out::println);
}
列印結果:
- 映射操作(map/flatMap)
映射操作用於對流中的每個元素進行轉換。他有map以及flatMap兩種操作。map就是基本的映射操作,對每個元素進行提取轉換。
// 將實體層映射成學生姓名字元串
List<String> names = students.stream()
.map(Student::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 將字元串轉大寫。
List<String> upperList = Lists.newArrayList("hello", "world", "stream", "api").stream().map(String::toUpperCase).collect(Collectors.toList());
日常開發中map操作我們用的非常多,比如資料庫中查詢出來的DO實體,我們需要轉換為VO返回給前端頁面展示,這時候我們可以使用map進行轉換操作:
List<StudentDO> studentDOList = studentMapper.listStudents();
List<StudentVO> studentVOList = studentDOList.stream().map(studentDO -> {
StudentVO studentVO = StudentVO.builder().studentNo(studentDO.getId())
.studentName(studentDO.getName()).build();
return studentVO;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
而flatMap的作用略微特殊,它用於將一個元素映射為一個流,然後將所有流連接成一個流。這在處理嵌套結構或集合中的元素是另一個集合的情況下非常有用。
List<List<String>> nestedWords = Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList("Java", "Kotlin"),
Arrays.asList("Python", "Ruby"),
Arrays.asList("JavaScript", "TypeScript")
);
// 使用 flatMap 將嵌套的 List<String> 轉換為一個扁平的 List<String>, 結果將是包含所有單詞的扁平流
List<String> wordList = nestedWords.stream()
.flatMap(List::stream).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(wordList);
// 列印結果: [Java, Kotlin, Python, Ruby, JavaScript, TypeScript]
flatMap在使用時,通常會涉及到處理複雜的數據結構,比如處理嵌套的對象集合或者進行數據的扁平化。
@Data
@Builder
class Student {
private String name;
private List<Integer> grades;
}
@Data
@Builder
class ClassRoom {
private List<Student> studentList;
}
@Data
@Builder
class School {
private List<ClassRoom> classRoomList;
}
School school = School.builder()
.classRoomList(Lists.newArrayList(
ClassRoom.builder().studentList(Lists.newArrayList(
Student.builder().name("Alice").gradeList(Lists.newArrayList(90, 85, 88)).build(),
Student.builder().name("Bob").gradeList(Lists.newArrayList(78, 92, 80)).build()
)).build(),
ClassRoom.builder().studentList(Lists.newArrayList(
Student.builder().name("Charlie").gradeList(Lists.newArrayList(95, 89, 91)).build(),
Student.builder().name("David").gradeList(Lists.newArrayList(82, 87, 79)).build()
)).build()
))
.build();
// 使用 flatMap 扁平化處理獲取所有學生的所有課程成績
List<Integer> allGrades = school.getClassRoomList().stream()
.flatMap(classroom -> classroom.getStudentList().stream())
.flatMap(student -> student.getGradeList().stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(allGrades);
// 列印結果:[90, 85, 88, 78, 92, 80, 95, 89, 91, 82, 87, 79]
- mapToInt操作
mapToInt是 Stream API 中的一種映射操作,專門用於將元素映射為IntStream。通過mapToInt,你可以將流中的元素映射為int類型,從而進行更專門化的操作,例如數值計算。
int totalAge2 = students.stream().mapToInt(Student::getAge).sum();
類似的還有mapToLong和mapToDouble 操作,這兩個操作類似於 mapToInt,分別用於將流中的元素映射為 LongStream 和 DoubleStream。
- 排序操作(sorted)
排序操作用於對流中的元素進行排序。
List<String> cities = Lists.newArrayList("New York", "Tokyo", "London", "Paris");
// 對城市按字母順序排序
List<String> sortedStream = cities.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
對於集合中對象的排序,sorted要求待比較的元素必須實現Comparable介面。
@Data
@Builder
static class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Override
public int compareTo(Student other) {
return other.getAge()-this.getAge();
}
}
List<String> sortedList = students.stream()
.sorted()
.map(Student::getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
如果沒有實現,就需要將比較器作為參數傳遞給sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator)。
@Data
@Builder
static class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
List<String> sortedList = students.stream()
.sorted((student1,student2) -> student2.getAge() - student1.getAge())
.map(Student::getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
- 去重操作(distinct)
去重操作用於去除流中的重覆元素。distinct基於Object.equals(Object)實現。
List<Integer> numbers = Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6);
// 去除重覆的數字
List<Integer> distinctList = numbers.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// 或者去除學生中姓名相同的
List<String> studentNameList = students.stream()
.map(Student::getName())
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
- 截斷操作(limit)
截斷操作用於限制流中元素的數量。limit返回包含前n個元素的流,當集合大小小於n時,則返回實際長度。
List<Integer> numbers = Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6);
// 只取前三個數字
List<Integer> limitedList = numbers.stream().limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 取土工工程專業的年齡最小的前兩名學生
List<Student> limitStu = students.stream()
.filter(student -> Objects.equals("土木工程", student.getMajor()))
.sorted((student1,student2) -> student2.getAge() - student1.getAge())
.limit(2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
- 跳過操作(skip)
跳過操作用於跳過流中的前幾個元素,返回由後面所有元素構造的流,如果n大於滿足條件的集合的長度,則會返回一個空的集合。作用上跟limit相反。
List<Integer> numbers = Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6);
// 跳過前三個數字,返回後面的數字
List<Integer> limitedList = numbers.stream().skip(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 跳過土工工程專業的年齡最小的前兩名學生,取後面的學生
List<Student> limitStu = students.stream()
.filter(student -> Objects.equals("土木工程", student.getMajor()))
.sorted((student1,student2) -> student2.getAge() - student1.getAge())
.skip(2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
- peek操作
peek方法對每個元素執行操作並返回一個新的 Stream。peek的主要目的是用於調試和觀察流中的元素,通常用於列印調試信息、記錄日誌或其他類似的目的,而不會改變流中元素的結構。
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange", "grape");
List<String> modifiedWords = words.stream()
.filter(word -> word.length() > 5)
.peek(word -> System.out.println("Filtered Word: " + word))
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.peek(word -> System.out.println("Uppercase Word: " + word))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
Stream的終端操作
終端操作是對流進行最終計算的操作,執行終端操作後,流將被消耗,不能再被使用。
- 迭代forEach操作
forEach迭代操作,用於對流中的每個元素執行指定的操作。
List<String> fruits = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange", "grape");
// 使用 forEach 輸出每個水果
fruits.stream().forEach(fruit -> System.out.println(fruit));
// 執行forEach時可省略 stream(),即
fruits.forEach(fruit -> System.out.println(fruit));
// 或
fruits.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
- 收集操作(collect)
通過collect()方法結合java.util.stream.Collectors工具類將Stream轉換為另一種形式,例如列表、集合(toList, toSet, toMap)、映射或歸約結果。如上述示例中的:
- 收集到List
使用Collectors.toList()。
// 跳過土工工程專業的年齡最小的前兩名學生,取後面的學生
List<Student> limitStu = students.stream()
.filter(student -> Objects.equals("土木工程", student.getMajor()))
.sorted((student1,student2) -> student2.getAge() - student1.getAge())
.skip(2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
- 收集到Set
使用Collectors.toSet()。
// 將學生姓名收集到Set
Set<String> studentNameSet = students.stream().map(Student::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
- List轉Map
使用Collectors.toMap。日常開發中使用很多。
// 轉換為年齡對應的學生信息
Map<Integer, Student> studentMap = students.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(
Student::getAge,
Function.identity(),
(e1,e2) -> e1));
這段代碼代表,我們使用年齡作為Map的key,對應學生信息作為value。Function.identity():這是一個提取元素自身的映射函數。(e1, e2) -> e1:這是一個合併衝突的操作。如果在流中存在相同的年齡(相同的鍵),這個函數定義了當出現重覆鍵時應該如何處理。在這裡,我們選擇保留第一個出現的元素,即保留先出現的 Student 對象。當然我們還可以這樣(e1, e2) -> {...}自定義合併衝突策略,例如:
// 轉換為年齡對應的學生信息,如果年齡相同,則取名字較長的
Map<Integer, Student> studentMap = students.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getAge, Function.identity(), (e1,e2) -> {
return e1.getName().length() > e2.getName().length() ? e1 : e2;
}));
如果value的值是一些number,我們也可以做一些加減乘除之類的合併。
日常開發中,這個用法很頻繁。
- 字元串拼接:
使用Collectors.joining(拼接符)。
List<Student> students = Lists.newArrayList(
Student.builder().name("Alice").gradeList(Lists.newArrayList(90, 85, 88)).build(),
Student.builder().name("Bob").gradeList(Lists.newArrayList(78, 92, 80)).build()
);
String studentName = students.stream().map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
// 列印出來:Alice,Bob
- 分組
即按照集合中的元素的某個屬性進行分組,轉換為Map<Object, List<Object>>:
List<String> fruits = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange", "grape");
Map<Integer, List<String>> lengthToNamesMap = fruits.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(String::length));
// 按照年齡分組
Map<Integer, List<Student>> studentMap = students.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge));
// 連續進行分組
Map<String,Map<String,List<Student>>> groupsStudent = students.stream()
// 先按照學校分組
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getSchool
// 再按照專業分組
,Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getMajor)));
- counting()
counting()收集器用於計算流中元素的數量。等同於Stream的count()操作。
long studentCount = students.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
// 效果同等於
long studentCount = students.stream().count();
- maxBy()
maxBy()基於指定的比較器,用於找到流中的最大的元素。等同於Stream的max操作
// 年齡最大的學生
Student olderStudent = students.stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy((s1,s2) -> s1.getAge()- s2.getAge())).orElse(null);
Student olderStudent2 = students.stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge))).orElse(null);
// 等價於stram的max
Student olderStudent = students.stream()
.max(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge)).orElse(null);
- minBy()
minBy()基於指定的比較器,用於找到流中的最小的元素。等同於Stream的min操作。
// 年齡最小的學生
Student youngStudent = students.stream()
.collect(Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge))).orElse(null);
Student youngStudent = students.stream()
.min(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge)).orElse(null);
- averagingInt
averagingInt()收集器用於計算流中元素的平均值。
// 求學生平均年齡
double avgAge = students.stream()
.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Student::getAge));
- summarizingInt()
summarizingInt()收集器用於計算流中元素的彙總統計信息,包括總數、平均值、最大值和最小值。
// 一次性得到元素個數、總和、均值、最大值、最小值
IntSummaryStatistics summaryStatistics = students.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Student::getAge));
System.out.println("總數:" + summaryStatistics.getCount());
System.out.println("平均值:" + summaryStatistics.getAverage());
System.out.println("最大值:" + summaryStatistics.getMax());
System.out.println("最小值:" + summaryStatistics.getMin());
- partitioningBy()
將流中的元素按照指定的條件分成兩個部分。在分區中key只有兩種情況:true或false,目的是將待分區集合按照條件一分為二,分區相對分組的優勢在於,我們可以同時得到兩類結果,在一些應用場景下可以一步得到我們需要的所有結果,比如將數組分為奇數和偶數。
// 分為武漢大學學生,非武漢大學學生
Map<Boolean,List<Student>> partStudent = students.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(student -> Objects.equals("武漢大學",student.getSchool())));
- count操作
count用於計算流中的元素個數。效果等同於Collectors.counting()。
long studentCount = students.stream().count();
// 效果同等於
long studentCount = students.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
- max操作
基於指定比較器,max用於找到流中最大的元素。效果等同於Collectors.maxBy()。
Student olderStudent = students.stream()
.max(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge)).orElse(null);
Student olderStudent2 = students.stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge))).orElse(null);
- min操作
基於指定比較器,min用於找到流中最小的元素。效果等同於Collectors.minBy()。
Student youngStudent = students.stream()
.min(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge)).orElse(null);
// 年齡最小的學生
Student youngStudent = students.stream()
.collect(Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge))).orElse(null);
- reduce操作
reduce用於對流中的元素進行歸約操作,得到一個最終的結果。
// 計算學生的總年齡
int totalAge1 = students.stream()
.map(Student::getAge)
.reduce(0, (a,b) -> a+b);
// 也可以使用Integer.sum
int totalAge2 = students.stream()
.map(Student::getAge)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);
// 也可以不設置初始值0,直接Integer.sum,但是返回的是Optional
int totalAge3 = students.stream()
.map(Student::getAge)
.reduce(Integer::sum).orElse(0);
- findFirst操作
findFirst用於查找流中的第一個元素。也即list.get(0)。
Student firstStu = students.stream()
.filter(student -> Objects.equals("土木工程", student.getMajor()))
.findFirst().orElse(null);
曾經有個小兄弟問我,他有一段代碼類似 Student firstStu = students.get(0)。他們組長讓他優化優化,然後就用了這種方式優化的。



