acwing學習筆記,記錄容易忘記的知識點和難題。數組實現單鏈表、雙鏈表、棧、單調棧、隊列、單調隊列、KMP、字典樹 Trie、並查集、數組實現堆、哈希表(拉鏈法、開放定址法、字元串首碼哈希法)、STL常用容器 ...
筆試用數組模擬而不是結構體
使用結構體指針,new Node() 非常慢,創建10萬個節點就超時了,做筆試題不會用這種方式(優化是提前初始化好數組,但這樣跟數組模擬沒區別了,而且代碼量很長)
單鏈表(數組)
使用兩個數組,e存儲val,ne存儲next。空節點next用-1表示
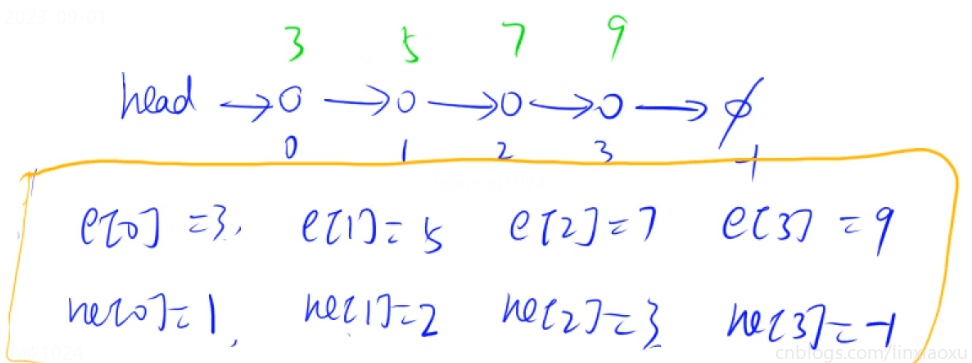
826 ⭐
第1個插入的點下標為0,第5個插入點下標為4,第k個插入點下標為k-1;
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
// head指向頭結點,e[i]表示節點值,ne[i]表示節點next
// idx指向可用空間(當前可以用的最新點下標)
// 演算法題不用考慮浪費的空間
int head, e[N], ne[N], idx;
void init() {
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
// x 插到頭結點後面
void add_to_head(int x) {
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx++;
}
// x 插到下標k的點後面
void add(int k, int x) {
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
// 將下標 k 後面點刪掉
void remove(int k) {
// if (ne[k] == -1) return; 題目保證合法不考慮邊界情況
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
int main() {
int m;
cin >> m;
init();
while (m--) {
char c;
int k, x;
cin >> c;
if (c == 'H') {
cin >> x;
add_to_head(x);
} else if (c == 'D') {
cin >> k;
if (!k)
head = ne[head]; // 特判刪除頭結點(鏈表第一個有效元素)
else
remove(k - 1);
} else if (c == 'I') {
cin >> k >> x;
add(k - 1, x);
}
}
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
cout << e[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
鄰接表
本質是一堆單鏈表,head[i]->x->x->-1 意思第i個點的鄰邊存起來了
最大用途:存儲圖、樹 (內容在第三章)
雙鏈表(數組)
用於優化某些題,每個節點有兩個指針,一個指向前,一個指向後
需要3個數組,l 數組表示before,r 數組表示next,e 數組表示val,idx指向可用空間
下標0為head,指向頭結點(左端點);下標1為tail,指向尾結點(右端點)
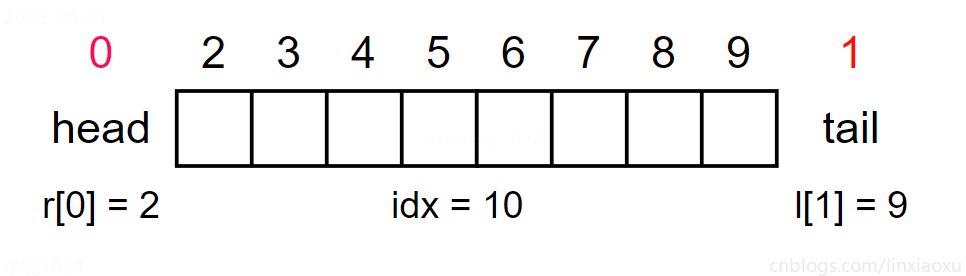
827 ⭐
因為提前用掉了數組中的兩個,所以第k個插入元素下標是 k - 1 + 2
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int e[N], l[N], r[N], idx;
void init() {
r[0] = 1;
l[1] = 0;
idx = 2;
}
// 在下標k點的右邊插入x(可以轉化成左邊)
void add(int k, int x) {
e[idx] = x;
r[idx] = r[k];
l[idx] = k;
r[k] = idx;
l[r[idx]] = idx;
idx++;
}
// 刪除下標k的點
void remove(int k) {
l[r[k]] = l[k];
r[l[k]] = r[k];
}
int main() {
int m;
cin >> m;
init();
while (m--) {
string s;
int k, x;
cin >> s;
if (s == "L") {
cin >> x;
add(0, x);
} else if (s == "R") {
cin >> x;
add(l[1], x);
} else if (s == "D") {
cin >> k;
remove(k - 1 + 2);
} else if (s == "IL") {
cin >> k >> x;
add(l[k - 1 + 2], x);
} else if (s == "IR") {
cin >> k >> x;
add(k - 1 + 2, x);
}
}
for (int i = r[0]; i != 1; i = r[i]) {
cout << e[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
棧
830
先進後出。數據存儲區間為[1,M],tt為棧頂指針
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int stk[N], tt;
int main() {
int m;
cin >> m;
while (m--) {
string s;
int x;
cin >> s;
if (s == "push") {
cin >> x;
stk[++tt] = x;
} else if (s == "pop") {
tt--;
} else if (s == "empty") {
if (tt > 0)
puts("NO");
else
puts("YES");
} else if (s == "query") {
cout << stk[tt] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
3302 ⭐⭐數組
中綴轉尾碼的重要規則(強行記憶)。轉換與計算可以同步進行(各自需要一個棧)
- 當前運算符優先順序<=棧頂元素,則棧頂元素依次輸出直到不滿足條件,並當前符號進棧
- 遇到右括弧,則棧頂元素依次輸出直到左括弧
- 遍歷完成後彈出棧內剩餘運算符
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int op[N], num[N], opt = -1, numt = -1;
unordered_map<char, int> priority;
// 計算尾碼表達式
void eval() {
auto b = num[numt--];
auto a = num[numt--];
auto c = op[opt--];
int res;
if (c == '-')
res = a - b;
else if (c == '+')
res = a + b;
else if (c == '*')
res = a * b;
else if (c == '/')
res = a / b;
num[++numt] = res;
}
int main() {
priority = {{'-', 1}, {'+', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}};
string str;
cin >> str;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
if (isdigit(str[i])) {
int j = i, res = 0;
while (isdigit(str[j])) res = res * 10 + str[j++] - '0';
num[++numt] = res;
i = j - 1;
} else if (str[i] == '(')
op[++opt] = str[i];
else if (str[i] == ')') {
while (op[opt] != '(') eval();
opt--;
} else {
while (opt >= 0 && priority[str[i]] <= priority[op[opt]]) eval();
op[++opt] = str[i];
}
}
while (opt >= 0) eval();
cout << num[numt];
return 0;
}
3302 ⭐⭐STL
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
stack<int> num;
stack<char> op;
void eval() {
auto b = num.top();
num.pop();
auto a = num.top();
num.pop();
auto c = op.top();
op.pop();
int x;
if (c == '+')
x = a + b;
else if (c == '-')
x = a - b;
else if (c == '*')
x = a * b;
else
x = a / b;
num.push(x);
}
int main() {
unordered_map<char, int> pr{{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}};
string str;
cin >> str;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
auto c = str[i];
if (isdigit(c)) {
// 第一類雙指針
int x = 0, j = i;
while (j < str.size() && isdigit(str[j]))
x = x * 10 + str[j++] - '0';
i = j - 1; // 考慮i++
num.push(x);
} else if (c == '(')
op.push(c);
else if (c == ')') {
while (op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop();
} else {
while (op.size() && pr[op.top()] >= pr[c]) eval();
op.push(c);
}
}
while (op.size()) eval();
cout << num.top() << endl;
return 0;
}
隊列
829
829. 模擬隊列 - AcWing題庫 隊尾插入,隊頭輸出
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int que[N], st = -1, ed = -1;
int main() {
int m;
cin >> m;
while (m--) {
string str;
int x;
cin >> str;
if (str == "push") {
cin >> x;
que[++ed] = x;
} else if (str == "pop") {
st++;
} else if (str == "empty") {
if (st == ed)
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
} else if (str == "query") {
cout << que[st + 1] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
單調棧
830 ⭐⭐
朴素做法是兩層迴圈。
使用棧,滿足情況:當下標為 i,棧內元素為 \(a_1,a_2...a_i\)
單調棧要求遍曆數組過程中,維護棧,滿足棧底至棧頂元素呈單調性(依次遞增)
- 棧內 \(a_1\)~\(a_i\) 遞增,此時遍歷至 \(a_{i+1}\),將小於 \(a_{i+1}\) 的棧內元素刪除,再插入 \(a_{i+1}\)
- 每個元素一次,出棧一次,\(O(n)\)
scanf 與 cin 速度差了十倍左右,使用 cin.tie(0) 或 ios::sync_with_stdio(false) 加速
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int stk[N], tt;
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
while (tt && stk[tt] >= x) tt--;
if (tt)
cout << stk[tt] << " ";
else
cout << -1 << " ";
stk[++tt] = x;
}
return 0;
}
單調隊列
154 ⭐⭐
朴素演算法是 \(O(n^2)\)
單調隊列要求滑動視窗每滑動一次時,將視窗內 >= \(a_i\) 的元素從隊尾刪除(類似單調棧),\(a_i\) 入隊,該隊列將保持單調遞增,此時對頭點為最小值。註意隊列里存的是下標
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N], q[N], st = 0, ed = -1;
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 移動隊頭
if (st <= ed && i - k + 1 > q[st]) st++;
// 移動隊尾
while (st <= ed && a[q[ed]] >= a[i]) ed--;
// ^ 先插入
q[++ed] = i;
// 每次滑動輸出
if (i >= k - 1) printf("%d ", a[q[st]]);
}
cout << endl;
st = 0;
ed = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (st <= ed && i - k + 1 > q[st]) st++;
while (st <= ed && a[q[ed]] <= a[i]) ed--;
q[++ed] = i;
if (i >= k - 1) printf("%d ", a[q[st]]);
}
return 0;
}
KMP
一個人能走多遠不在於他在順境時能走的多快,而在於他在逆境時多久能找到曾經的自己
強烈建議看 胡凡 演算法筆記 P455
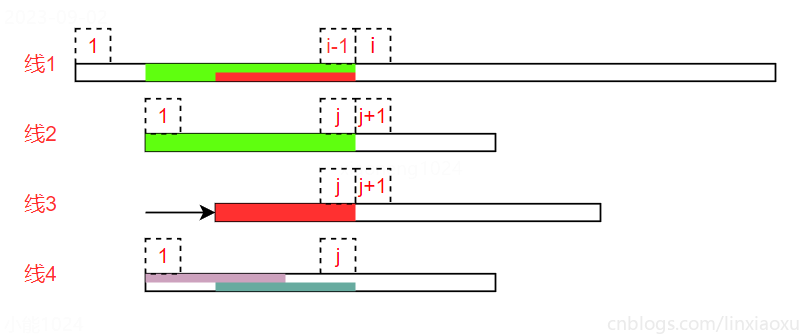
假設下標從1開始。字元串 S[1,N],子串 P[1,M],S 指針 i-1,P 指針 j
next[j]
- 子串中,以 j 為終點的尾碼 與 從1開始的首碼相等的最長長度 x
- \(P[1,x] = P[j-x+1,j]\)
kmp 建議看演算法筆記
- i-1 與 j 對應字元相同;i 與 j+1 對應字元不同。此時需要把紅顏色子串往後移動,為了移動最少需要 next[j]
- 讓 j = next[j],從線2變為線3(線1紅色部分 等於 線3紅色部分)
- 繼續匹配 i 與 j+1,若發現不匹配,再 j = next[j] (遞歸進行)
- 當 j = m,意味著找到子串,然後 j = next[j] 繼續尋找
時間複雜度計算
- 生成next數組 \(O(m)\)
- 字元串每個字元被遍歷一次,\(O(n)\)
- j++ 最多 n 次,最多減 n 次,\(O(n)\)
831 ⭐⭐⭐
next 在某些頭文件里有定義,最好換個變數名;另外KMP演算法還可以進一步優化,以下是優化後的演算法
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int M = 1e6 + 10;
int next_val[N];
int main() {
int n, m;
char p[N], s[M];
cin >> n >> p + 1 >> m >> s + 1;
// ^ 生成 next_val 數組
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i++) {
while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = next_val[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) j++;
// ^ 繼續優化,選擇回退的最佳位置
if (j && p[i + 1] == p[j + 1]) {
next_val[i] = next_val[j];
} else
next_val[i] = j;
}
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// cout << next_val[i] << endl;
// }
// ^ KMP 匹配過程
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i++) {
while (j && p[j + 1] != s[i]) j = next_val[j];
if (p[j + 1] == s[i]) j++;
if (j == n) {
cout << i - n << " ";
j = next_val[j];
}
}
return 0;
}
字典樹 Trie
用於高效存儲和查找字元串集合的數據結構
835
son[N][26] 存的是每個節點所有的兒子是什麼,cnt[N] 存的是單詞的數量,idx與數組模擬單鏈表裡的idx相同
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx; // ^ 下標是0的點,既是根節點又是空節點
void insert(char str[]) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++) {
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
cnt[p]++;
}
int query(char str[]) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++) {
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
char a, b[N];
cin >> a >> b;
if (a == 'I')
insert(b);
else
cout << query(b) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
143 ⭐⭐
朴素演算法是兩層迴圈並滿足 j<i(避免重覆, \(C^2_n = n*(n-1)/2\) );時間複雜度 \(O(n^2)\) ,題目給的 n 是 1e5,則 1e10 超時
可以使用 trie tree 優化,每插入一個元素 x,在字典樹中查找滿足與該元素異或最大值的元素(儘可能反著取,每次查找只要遍歷31位),時間複雜度 \(O(n)\)
可以先插入再遍歷(少個判斷),第一個插入的元素與自身異或為 0
每個節點個數長31,最多1e5個,那麼idx最大可以到 31 * 1e5
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 31 * N;
int son[M][2], idx;
void insert(int x) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {
int bit = x >> i & 1;
if (!son[p][bit]) son[p][bit] = ++idx;
p = son[p][bit];
}
}
int query(int x) {
int res = 0, p = 0;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {
int bit = x >> i & 1;
if (son[p][!bit]) {
bit = !bit;
}
p = son[p][bit];
res = (res << 1) + bit;
}
return res;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int m = 0;
while (n--) {
int x;
cin >> x;
insert(x);
m = max(x ^ query(x), m);
}
cout << m;
return 0;
}
並查集
操作
- 將兩個集合合併
- 詢問兩個元素是否在一個集合當中
朴素演算法下,合併兩個集合需要執行\(O(n+m)\)次;並查集可以近乎\(O(1)\)合併兩個集合
基本原理
- 用樹的形式維護所有集合;根節點是集合編號
- 每個節點存儲父節點,p[x] 表示x的父節點
如何判斷樹根
if (p[x] == x),根節點的父節點是它本身
如何求x的集合編號
while(p[x] != x) x = p[x]- 路徑壓縮⭐ :往上走找到根節點把路徑所有點都指向跟節點
如何合併兩個集合 ⭐ 記住模板
p[x] = y,將一顆樹根節點插到另一棵樹的某個位置
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
如何維護集合元素個數(攜帶額外信息)
- 見837題
836 ⭐
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int p[N];
// ^ 返回x祖宗節點 + 路徑壓縮
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
while (m--) {
char op;
int a, b;
cin >> op >> a >> b;
if (op == 'M') {
p[find(a)] = find(b);
} else {
if (find(a) == find(b))
puts("Yes");
else
puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
837 ⭐⭐
保證根節點的nums有意義
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int p[N], nums[N];
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
nums[i] = 1;
}
while (m--) {
string op;
int a, b;
cin >> op;
if (op == "C") {
cin >> a >> b;
// ^ 特判
if (find(a) == find(b)) continue;
// ^ 先算元素個數再合併
nums[find(b)] += nums[find(a)];
p[find(a)] = find(b);
} else if (op == "Q1") {
cin >> a >> b;
if (find(a) == find(b))
puts("Yes");
else
puts("No");
} else if (op == "Q2") {
cin >> a;
cout << nums[find(a)] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
240 ⭐⭐⭐
確定每個動物跟領袖(n對1)的關係,而不是動物跟動物(n對n)的關係
維護每個節點與根節點的距離(x吃y,y到x距離是1),然後 % 3 判斷類型。初始化每個節點都是0,各自一類。
- 餘1:可以吃根節點
- 餘2:可以被根節點吃
- 餘0:與根節點是同類
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int p[N], d[N];
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
// 遞歸處理所有祖宗節點,並更新到根的距離
int t = find(p[x]);
// d[x] 等於 x到父的距離 + 父到根的距離(遞歸處理完了)
d[x] += d[p[x]];
// x 的父修改為根節點,路徑優化
p[x] = t;
// // 記錄舊的父
// int u = p[x];
// // 路徑壓縮,新父根節點
// p[x] = find(p[x]);
// // x到根的距離等於x到舊父距離加上舊父到根的距離
// d[x] += d[u];
}
return p[x];
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
int count = 0;
while (k--) {
char t;
int x, y;
cin >> t >> x >> y;
if (x > n || y > n) {
count++;
} else {
int px = find(x), py = find(y);
if (t == '1') {
if (px == py && (d[x] - d[y]) % 3 != 0)
count++;
else if (px != py) {
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] - d[x]; // IMPORTANT
}
} else {
if (x == y || px == py && (d[x] - d[y] - 1) % 3 != 0) {
count++;
} else if (px != py) {
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] + 1 - d[x];
}
}
}
}
cout << count << endl;
return 0;
}
堆
小根堆
每個點 <= 左右兒子,根節點就是樹的最小值 。
完全二叉樹用一維數組存:x 的左兒子 2x,x 的右兒子 2x+1;下標從1開始
兩個操作 ⭐
- down(x) 往下調整 (x是坐標 1 ~ size) \(O(log_2n)\)
- 每次找{ x,x左子,x右子 }的最小值,進行交換
- up(x) 往上調整 \(O(log_2n)\)
- 每次找{ x,x父 }的最小值,進行交換
堆的功能
- 插入一個數 \(O(log_2n)\)
heap[++size] = x然後不斷往上移up(size)
- 求集合當中的最小值 \(O(1)\)
heap[1]
- 刪除最小值 \(O(log_2n)\)
heap[1] = heap[size--]堆最後一個元素覆蓋堆頂元素,然後down(1)- 因為刪除頭結點非常困難,刪除尾結點很easy
- 刪除任意一個元素(STL沒直接實現,優先隊列) \(O(log_2n)\)
heap[k] = heap[size--]有三種情況,可直接down(k)再up(k),只會執行一個
- 修改任意一個元素(STL沒直接實現,優先隊列) \(O(log_2n)\)
heap[k] = x再down(k)、up(k)
838 ⭐
一個一個往裡插是 \(O(nlog_2n)\) 。可以採用 \(O(n)\) 的方式,先全部讀入,除最後一層外反著down操作(倒第2層,倒第3層...第1層)(可用數列推導出,每個節點down的次數總和 < n)(記憶)
for (int i = n / 2; i; i--) {
down(i);
}
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int h[N], idx;
void down(int u) {
int t = u;
if (u * 2 <= idx && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;
if (u * 2 + 1 <= idx && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;
if (u != t) {
swap(h[t], h[u]);
down(t);
}
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
int x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> h[i];
}
idx = n;
for (int i = n / 2; i; i--) {
down(i);
}
while (m--) {
cout << h[1] << " ";
h[1] = h[idx--];
down(1);
}
return 0;
}
839 ⭐⭐
存儲映射:ph 存第k個插入的點在堆里的下標,hp 存堆里點的坐標是第k個插入的,兩者互為相反關係。
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int h[N], hp[N], ph[N], idx;
void new_swap(int a, int b) {
swap(ph[hp[a]], ph[hp[b]]);
swap(hp[a], hp[b]);
swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
void up(int x) {
while (x / 2 && h[x / 2] > h[x]) {
new_swap(x / 2, x);
x /= 2;
}
}
void down(int x) {
int t = x;
if (2 * x <= idx && h[2 * x] < h[t]) t = 2 * x;
if (2 * x + 1 <= idx && h[2 * x + 1] < h[t]) t = 2 * x + 1;
if (t != x) {
new_swap(x, t);
down(t);
}
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
int count = 0;
while (n--) {
string s;
int k, x;
cin >> s;
if (s == "I") {
cin >> x;
idx++;
count++;
h[idx] = x;
hp[idx] = count;
ph[count] = idx;
up(idx);
} else if (s == "PM") {
cout << h[1] << endl;
} else if (s == "DM") {
// ^ h[1] = h[idx--]; // 這樣只交換點,沒交換ph hp
new_swap(1, idx--);
down(1);
} else if (s == "D") {
cin >> k;
// ^ h[ph[k]] = h[idx--]; // 這樣只交換點,沒交換ph hp
k = ph[k]; // 獲取第k個插入的數在堆中的坐標
new_swap(k, idx--);
down(k), up(k); // 只會執行其中一個
} else if (s == "C") {
cin >> k >> x;
k = ph[k];
h[k] = x;
down(k), up(k);
}
}
return 0;
}
哈希表
情景
- 把 1e5 個值域 -1e9~1e9 的數(值域大,個數少)映射到 1e5 的範圍的哈希函數
- \(h(x) \in (0,1e5) = x\ mod\ 1e5\) 模數一般要取質數,離2的整數冪儘可能遠
- 發生衝突:兩個不同值域的數映射成了同一個數
存儲結構-解決衝突的方式 ⭐
演算法題99%一般只有添加、查找,若要實現刪除不會真刪掉,開一個bool數組標記刪除
- 開放定址法(常用)
- 開一個一維數組,範圍是題目數據範圍的2~3倍,即 2e5 ~ 3e5 區間的質數,該數組存儲實際的 x 值
- 計算哈希值,如果哈希值已被占用,則移動到下一個位置,從前往後找
- h(11) = 3 在 數組[3] 存入 11,h(4) = 3 在數組[4] 存入 4
- 與拉鏈法不同,查詢函數返回 x 所在的位置,如果 x 不存在返回應該存儲的位置
- 需要約定一個標誌,不在 x 的值域範圍內,表示當前位置為空,如 0x3f3f3f3f
- 拉鏈法
- 開一個一維數組 \([0,大於1e5的最小質數]\) 存儲所有哈希值對應的鏈表
- h(11) = 3 在 數組[3] 開一條鏈,插入 11
- 若 h(4) = 3 在 數組[3] 已開的鏈插入 4
- 期望情況下,每條鏈長度 1,時間複雜度 \(O(1)\)
字元串哈希-字元串首碼哈希法(特殊)
應用:可以快速判斷一個字元串某兩段是否相同。KMP望而卻步(KMP擅長迴圈節),極困難題可用這種方法
-
先預處理所有首碼的哈希,h[0] = 0, h[1] = "A" 的hash,h[2] = "AB" 的hash...
- 把字元串看成 P 進位的數,然後模 Q

-
**某個字元不能映射成 0,否則 AA 跟 A 兩個哈希都是 0 **
-
該哈希法假定人品足夠好,不考慮衝突
-
經驗值:當 p = 131 或 13331,Q 取 \(2^{64}\) (用 unsinged long long可以不取模,溢出相當於取模)
⭐ 我們可以利用首碼哈希算出任意子段的哈希值
- 預處理首碼
h(i) = h(i-1) * p + str[i]
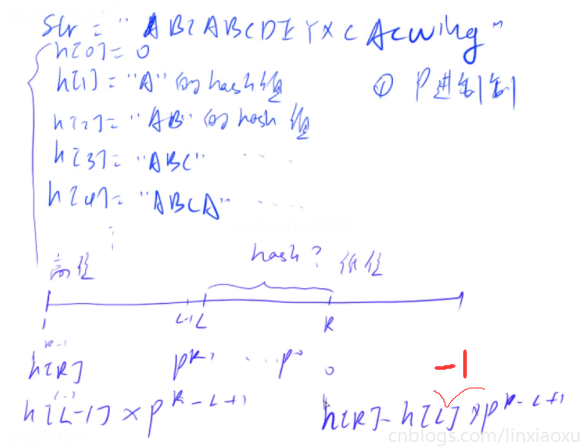
與整數離散化的區別
整數離散化需要保序,而且不會發生衝突,每一個元素都有唯一確定的位置(1 ~ n)
840 ⭐拉鏈法
h 數組維護 N 條鏈,空節點表示-1,e 數組與 ne 數組維護鏈上的每一個節點,idx為每個節點分配唯一標識符;插入操作從鏈表頭結點插入
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 3; // 質數
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
void insert(int x) {
// 第一次模餘數可能是負數,第二次模餘數絕對是正數
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k];
h[k] = idx++;
}
bool find(int x) {
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for (int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
if (e[i] == x) return true;
return false;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
string s;
int x;
cin >> s >> x;
if (s == "I")
insert(x);
else {
if (find(x))
puts("Yes");
else
puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
840 ⭐開放定址法
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 3, null = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 質數
int h[N];
int find(int x) {
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[k] != null && h[k] != x) {
k++;
if (k == N) k = 0; // 查到數組最後從開頭找
}
return k;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof h);
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
string s;
int x;
cin >> s >> x;
int k = find(x);
if (s == "I")
h[k] = x;
else {
if (h[k] != null)
puts("Yes");
else
puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
841 ⭐⭐ 字元串哈希
如下的朴素演算法會超時
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
string s;
int n, m, l1, l2, r1, r2;
cin >> n >> m >> s;
while (m--) {
cin >> l1 >> r1 >> l2 >> r2;
l1 -= 1, l2 -= 1, r1 -= 1, r2 -= 1;
if (s.substr(l1, r1 - l1 + 1) == s.substr(l2, r2 - l2 + 1))
puts("Yes");
else
puts("No");
}
return 0;
}
p 數組提前存儲預處理的 p 次方的值,減少計算量
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int N = 1e5, P = 131;
int n, m;
char str[N];
ULL h[N], p[N];
ULL get(int l, int r) { return h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1]; }
int main() {
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m >> str + 1;
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = p[i - 1] * P;
h[i] = h[i - 1] * P + str[i];
}
while (m--) {
int l1, r1, l2, r2;
cin >> l1 >> r1 >> l2 >> r2;
if (get(l1, r1) == get(l2, r2))
puts("Yes");
else
puts("No");
}
return 0;
}
STL
size()、empty() 所有容器都有,時間複雜度 \(O(1)\)
clear() 並不是所有容器都有,隊列、優先隊列、棧;範圍遍歷可以遍歷所有容器
⭐ 系統為某一個程式分配空間時,所需的時間與空間大小無關,與申請次數有關
vector
變長數組,倍增,支持比較運算(字典序(4個3小於3個4))。有erase但用得不多
插入操作\(O(1)\):插入1e6次,申請空間的次數 \(log_21e6\) ,拷貝的次數均攤是 1 (數組大小從1到1e6,總共拷貝次數是1e6(1+2+4+8+...))
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// ^ 定義一個長度為10的vector,每個數都是3
vector<int> a(10, 3);
vector<int> b[10];
a.push_back(1);
cout << a.size() << endl;
cout << a.empty() << endl;
a.clear();
cout << a.front() << endl;
cout << a.back() << endl;
// a.begin(); // ^ 返回的是迭代器(指針),需要解引用
// a.end();
return 0;
}
pair
二元組,支持比較運算(字典序)。適用於某種東西有兩個屬性,也可以存儲三個屬性,任意嵌套
相比結構體:pair 幫我們實現了結構體,並實現了比較函數,省了點代碼
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
pair<int, pair<int, string>> a;
pair<int, string> p;
p = {20, "abc"};
p.first;
p.second;
return 0;
}
string
字元串,substr(起始位置,長度)、c_str()
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string a = "yxc";
a += "def";
a += "c";
// 從哪開始,返回多長(可省略)
cout << a.substr(1, 2) << endl;
printf("%s\n", a.c_str());
return 0;
}
queue
隊列,push()、front()、pop(),沒有 clear()
int main() {
queue<int> q;
// ^ 沒有clear的清空方法
q = queue<int>();
return 0;
}
deque
雙端隊列,支持隨機訪問 []。相當於加強版 vector。效率較低,不常用
front、back、push_back、pop_back、push_front、pop_front
priority_queue
優先隊列,預設是大根堆。push()、top()、pop()。頭文件queue
int main() {
priority_queue<int> heap;
// ^ 定義小根堆
// 方式 1 每次插入負數
// heap.push(-x);
// 方式 2 多加兩個參數
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> heap;
return 0;
}
stack
棧,push()、top()、pop();與隊列用法類似
set、map、multiset、multimap
基於平衡二叉樹(紅黑樹),動態維護有序序列。begin、end支持++、--操作,返回前驅後繼(有序序列的前一個數或後一個數)。增刪改查大部分 \(O(log_2n)\)
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
set<int> s;
multiset<int> ms;
s.insert(1);
// 找不到返回 end 迭代器
s.find(1);
// 返回某個數的個數
s.count(1);
// 刪除所有等於這個數的節點 O(k + logn) k是x的個數
ms.erase(1);
// 刪除這個迭代器
ms.erase(ms.find(1));
// 大於等於 x 的最小的數的迭代器,不存在返回end
s.lower_bound(0);
// 大於 x 的最小的數的迭代器,不存在返回end
s.upper_bound(0);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, int> a;
a.insert({"abc", 123});
// erase 跟 set 一樣
// 可以像數組一樣用 map,時間複雜度 O(logn)
count << a["abc"] << endl;
// 也支持 lower_bound、upper_bound
return 0;
}
unordered_
沒有順序,基於哈希表實現。與上面類似。但增刪改查時間複雜度是 \(O(1)\)
不支持 lower_bound、upper_bound;不支持迭代器 ++ --
bitset
壓位。C++里bool是1位元組,如果要開1024個bool數組需要1024個位元組,如果用壓位,只需要128B
1e4 * 1e4 布爾矩陣,需要 1e8B,約100MB,題目給的 64MB,用壓位可以縮小到12MB
int main() {
bitset<10000> s;
// ~ & | ^ >> << == != []
// count() 返回有多少個 1
// any() 判斷是否至少有1個 1
// none() 判斷是否全為 0
// set() 把所有位置1
// set(k,v) 將第k位變成v
// reset() 把所有位變成0
// flip() 等價於 ~
// flip(k) 把第k位取反
return 0;
}



