golang支持兩種隨機數生成方式: math/rand // 偽隨機 crypto/rand // 真隨機 math/rand的用法:rand.Intn(100)。這個起始位置是由一個seed決定的,預設是從1開始。為了儘量隨機性,那麼我們可以每次使用不同的seed來啟動程式,就可以保證每次啟動都 ...
golang支持兩種隨機數生成方式:
math/rand // 偽隨機
crypto/rand // 真隨機
math/rand的用法:rand.Intn(100)。這個起始位置是由一個seed決定的,預設是從1開始。為了儘量隨機性,那麼我們可以每次使用不同的seed來啟動程式,就可以保證每次啟動都產生新的隨機數,聰明的你肯定想到了使用時間戳
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
rand.Intn(100)
crypto/rand是為了提供更好的隨機性滿足密碼對隨機數的要求,在linux上已經有一個實現就是/dev/urandom,crypto/rand 就是從這個地方讀“真隨機”數字返回,但性能比較慢
go的一種輸入方式
reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
input, err := reader.ReadString('\n')
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
input = strings.Trim(input, "\r\n")
num, err := strconv.Atoi(input)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
bufio 包實現了緩存IO。它包裝了 io.Reader 和 io.Writer 對象,創建了另外的Reader和Writer對象,它們也實現了 io.Reader 和 io.Writer 介面,不過它們是有緩存的。該包同時為文本I/O提供了一些便利操作。
bufio.Reader 結構包裝了一個 io.Reader 對象,提供緩存功能,同時實現了 io.Reader 介面。Reader 結構沒有任何導出的欄位,結構定義如下:
type Reader struct {
buf []byte // 緩存
rd io.Reader // 底層的io.Reader
// r:從buf中讀走的位元組(偏移);w:buf中填充內容的偏移;
// w - r 是buf中可被讀的長度(緩存數據的大小),也是Buffered()方法的返回值
r, w int
err error // 讀過程中遇到的錯誤
lastByte int // 最後一次讀到的位元組(ReadByte/UnreadByte)
lastRuneSize int // 最後一次讀到的Rune的大小 (ReadRune/UnreadRune)
}
Reader一共封裝了ReadSlice、ReadBytes、ReadString 和 ReadLine四種方法
去掉字元串s中首部以及尾部與字元串cutset中每個相匹配的字元,如:s="hello yes",cutset="he",那麼s的結果為:"ello yes"
正文開始
線上翻譯
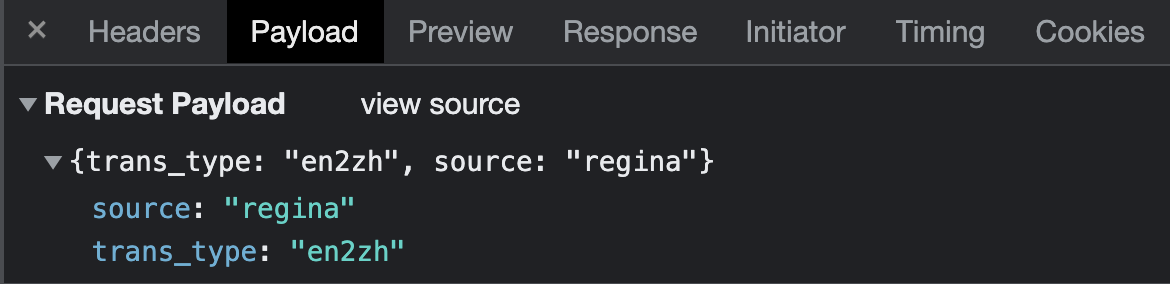
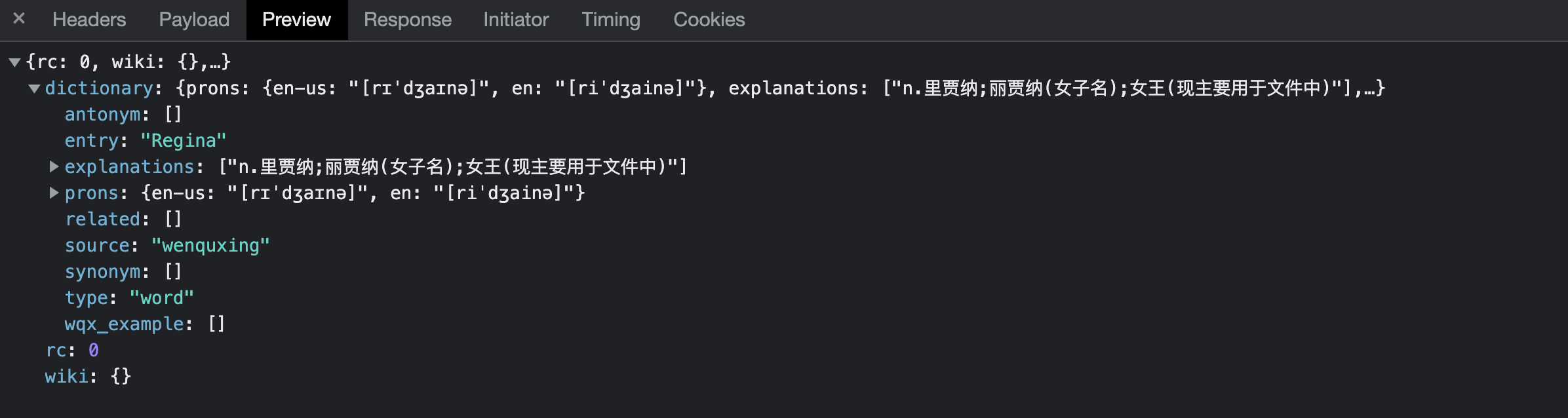
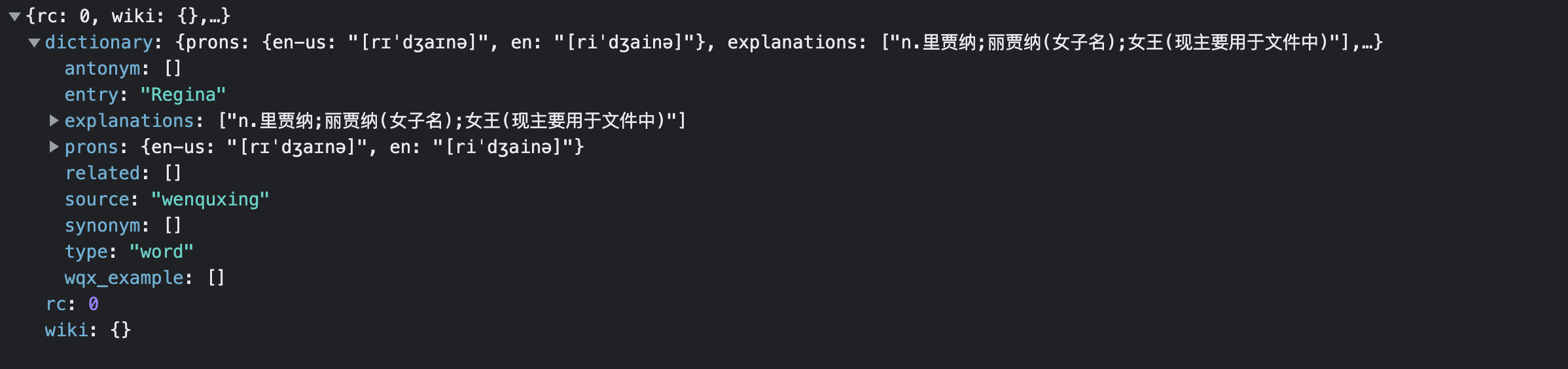
首先我們從網頁中找到這兩個模塊,這是一個http的post請求,請求頭裡面有兩個json欄位。一個是代表從A語言轉化為B語言,另一個是翻譯結果。裡面會有wiki和dictionary兩個欄位,我沒需要的是dictionary.explanations和prons欄位.
現在把這個數據包複製成curl模式,找到這個curl轉化為代碼的工具,進行轉化。得到一大串
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
func main() {
///創建請求頭
client := &http.Client{}
var data = strings.NewReader(`{"trans_type":"en2zh","source":"regina"}`)
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", "https://lingocloud.caiyunapp.com/v1/dict", data)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
///設置請求頭
req.Header.Set("Accept", "application/json, text/plain, */*")
req.Header.Set("Accept-Language", "en-GB,en-US;q=0.9,en;q=0.8,zh-CN;q=0.7,zh;q=0.6")
req.Header.Set("Connection", "keep-alive")
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
req.Header.Set("Cookie", "_gcl_au=1.1.1750352016.1683964760; _gid=GA1.2.1869393783.1683964761; _ga_B96YSRGWD1=GS1.1.1683964970.1.1.1683964990.0.0.0; _ga_65TZCJSDBD=GS1.1.1683964760.1.1.1683965034.0.0.0; _ga_R9YPR75N68=GS1.1.1683964760.1.1.1683965034.59.0.0; _ga=GA1.2.1571953844.1683964761; _gat_gtag_UA_185151443_2=1; amp_6e403e=6Ovk5-bjgwTIUa6Ae310zz.aXZhbmxlZXJ1aUBnbWFpbC5jb20=..1h0a1v3c6.1h0a26hdq.0.3.3")
req.Header.Set("Origin", "https://fanyi.caiyunapp.com")
req.Header.Set("Referer", "https://fanyi.caiyunapp.com/")
req.Header.Set("Sec-Fetch-Dest", "empty")
req.Header.Set("Sec-Fetch-Mode", "cors")
req.Header.Set("Sec-Fetch-Site", "same-site")
req.Header.Set("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/113.0.0.0 Safari/537.36")
req.Header.Set("X-Authorization", "token:qgemv4jr1y38jyq6vhvi")
req.Header.Set("app-name", "xy")
req.Header.Set("device-id", "fdbc32c472fb18c75038bbe17028bb97")
req.Header.Set("os-type", "web")
req.Header.Set("os-version", "")
req.Header.Set("sec-ch-ua", `"Google Chrome";v="113", "Chromium";v="113", "Not-A.Brand";v="24"`)
req.Header.Set("sec-ch-ua-mobile", "?0")
req.Header.Set("sec-ch-ua-platform", `"macOS"`)
//發起請求
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
//讀取響應
bodyText, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%s\n", bodyText)
}

手寫結構體太複雜,再找一個把json轉換成go語言結構體的工具
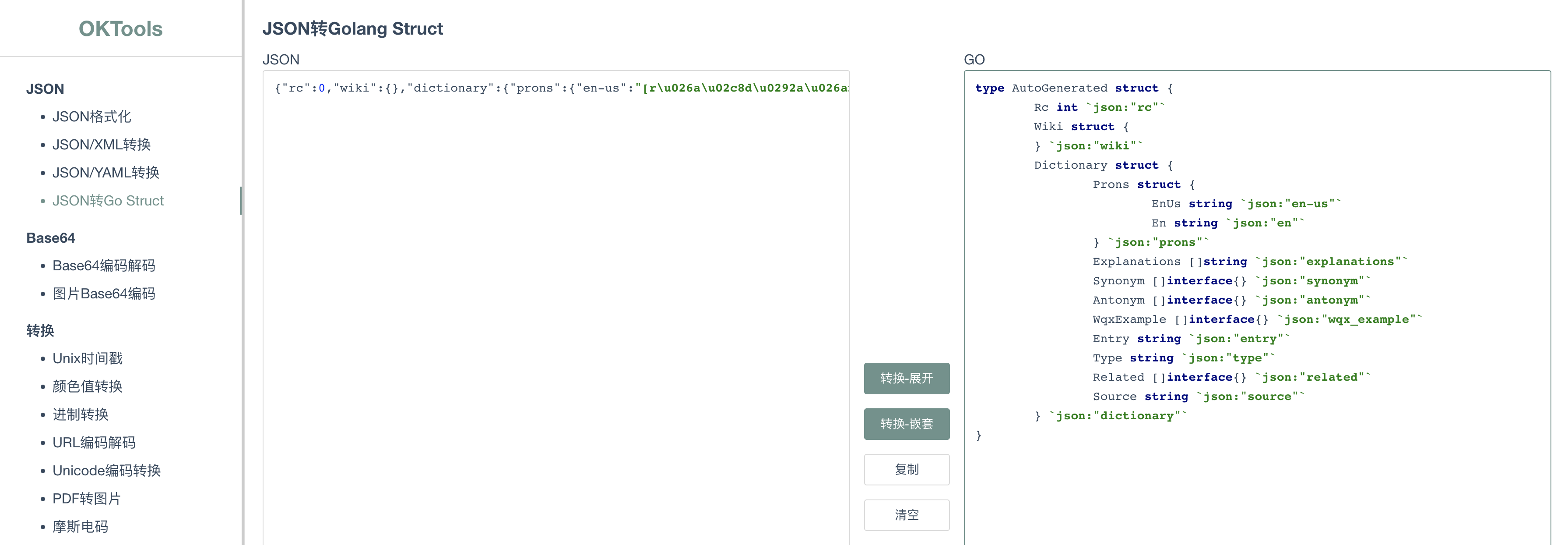
type DictResponse struct {
Rc int `json:"rc"`
Wiki struct {
} `json:"wiki"`
Dictionary struct {
Prons struct {
EnUs string `json:"en-us"`
En string `json:"en"`
} `json:"prons"`
Explanations []string `json:"explanations"`
Synonym []interface{} `json:"synonym"`
Antonym []interface{} `json:"antonym"`
WqxExample []interface{} `json:"wqx_example"`
Entry string `json:"entry"`
Type string `json:"type"`
Related []interface{} `json:"related"`
Source string `json:"source"`
} `json:"dictionary"`
}
//讀取響應文件,進行格式轉換
bodyText, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
var dictResponse DictResponse
err = json.Unmarshal(bodyText, &dictResponse) //把body內容json轉化後存到指針內
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", dictResponse)
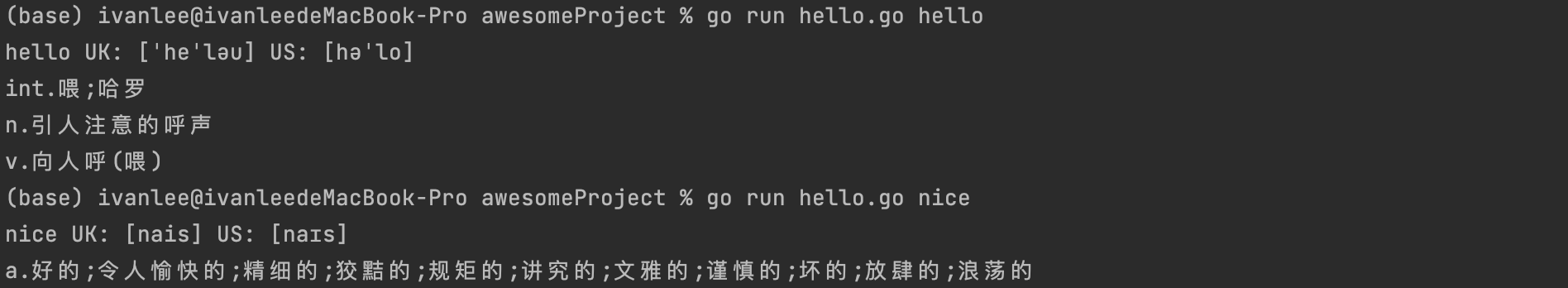
現在再挑我們需要的東西進行列印
fmt.Println("UK:", dictResponse.Dictionary.Prons.En, "US:", dictResponse.Dictionary.Prons.EnUs)
for _, item := range dictResponse.Dictionary.Explanations {
fmt.Println(item)
為了交互使用字典,要先定義一個輸入功能,然後再去發起請求
type DictRequest struct {
TransType string `json:"trans_type"`
Source string `json:"source"`
UserID string `json:"user_id"`
}
client := &http.Client{}
request := DictRequest{TransType: "en2zh", Source: word}
buf, err := json.Marshal(request)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
var data = bytes.NewReader(buf)
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", "https://api.interpreter.caiyunai.com/v1/dict", data)
要想把struct轉化成json,只要把結構體內的欄位名設置成導出狀態,也就是把首字母大寫就行了,預設情況下,轉化後的json中的key值和結構體中的欄位名是一樣的,如果我們期望轉化後的json欄位名和struct里的不一樣的話,就得用到tag了。tag在這裡的用途就是提供別名,讓兩者的轉化更加靈活。
本文來自博客園,作者:ivanlee717,轉載請註明原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ivanlee717/p/17397959.html


