分享一下 Idea 的 scope 功能 事情的起因是我在使用 idea 的call hierarchy功能時,覺得它沒有像find usage那樣有排除功能,並且如果點擊了展開全部,當代碼中使用了某些框架導致調用層級非常深時,idea 會占用非常高的 CPU。 於是我去 jetbrains 的缺陷 ...
![]() 容器(可以用來管理所有的組件(類))
容器(可以用來管理所有的組件(類))
核心關註:IOC和AOP
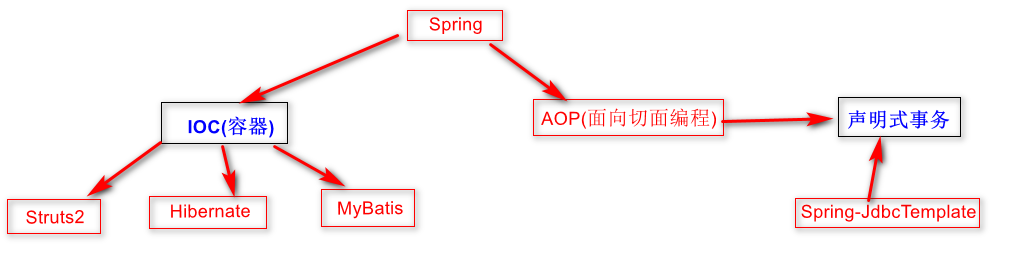
1.IOC
Inversion(反轉) Of Control:控制反轉
控制:資源的獲取方式
1.主動式(要什麼資源自己創建)
Person{
Book book=new Book();
Dog dog=new Dog();
//複雜對象的創建時比較龐大的工程
}
2.被動式:資源的獲取不是自己創建,而是交給一個容器創建和設置
Person{
Book book;
public void test(){
book.read();
}
}
容器:管理所有的組件(有功能的類),主動的new資源改為被動的接受資源1.1 DI(Dependency Injection)依賴註入
容器能知道哪個組件(類)運行的時候,需要另外一個組件(類);
容器通過反射的形式,將容器中準備好的Book對象註入(利用反射給屬性賦值)到Person中代碼實現:
1.實體類
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String email;
public Person() {
System.out.println("person的構造器!");
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("設置pserson的name");
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
System.out.println("設置person的age");
this.age = age;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
System.out.println("設置person的gender");
this.gender = gender;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
System.out.println("設置person的email");
this.email = email;
}
....
...get()
}
2.spring的配置文件ioc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--註冊person對象,spring會自動創建這個person對象-->
<bean class="com.Person" id="person01">
<property name="age" value="18"></property>------------->name是bean中的屬性,通過set方法反射註入
<property name="email" value="[email protected]"/>
<property name="gender" value="男"/>
<property name="name" value="吳孟達"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3.測試類:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("啟動spring容器....");
ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");--------->啟動spring的配置文件
System.out.println("spring容器啟動成功!");
Person person= (Person) ioc.getBean("person01");----------->此處的person01為spring配置文件中的bean的id
System.out.println(person);
}
}
輸出:
啟動spring容器....
person的構造器!
設置person的age
設置person的email
設置person的gender
設置pserson的name
spring容器啟動成功!
Person{name='吳孟達', age=18, gender='男', email='[email protected]'}
結論:------>發現其執行順序為:
1.<bean...>元素驅動spring容器調用構造器創建對象
2.<property...>元素驅動spring執行setter方法1.第一種情況:範圍大的(person引用book)在範圍小的前面
spring配置文件內容:
<bean id="person01" class="entity.Person">
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="吳孟達"></property>
<property name="book" ref="book"/>
</bean>
<bean id="book" class="entity.Book">
<property name="name" value="java分析"/>
<property name="price" value="32"/>
</bean>
實體類信息:
。。。
測試類信息:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("載入spring....");
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
System.out.println("spring容器啟動成功!");
Person person= (Person) ac.getBean("person01");
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
輸出:
載入spring....
person實例化!
Book實例化!
Book執行set name方法
Book執行set price方法
person執行set age方法
person執行set name方法
spring容器啟動成功!
發現執行順序為:
1.先實例化兩個對象
2.在執行小的set方法
3.再執行大的set方法
第二種情況:小範圍的在上
spring配置文件內容:
<bean id="book" class="entity.Book">
<property name="name" value="java分析"/>
<property name="price" value="32"/>
</bean>
<bean id="person01" class="entity.Person">
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="吳孟達"></property>
<property name="book" ref="book"/>
</bean>
輸出:
Book實例化!
Book執行set name方法
Book執行set price方法
person實例化!
person執行set age方法
person執行set name方法
spring容器啟動成功!
執行順序為:
1.小範圍對象實例化
2.小範圍對象set方法
3.大範圍對象實例化
4.大範圍對象set方法
2.源碼解析
1.
以此為示例:
<bean id="book" class="entity.Book"></bean>
實際上<bean.../>元素預設一反射的方式來調用該類的無參構造器
底層簡單源碼如下:
String idStr=...;//解析<bean。。。。/>元素的id屬性得到該欄位的字元串值為"book"
String classStr=...;//解析class屬性得到該欄位的值為:entity.Book
Class clazz=Class.forName(classStr);
Object object=clazz.newInstance();//通過反射示例化對象
container.put(idstr,obj);//將對象放入容器給中,container為spring容器
2.
<bean id="person01" class="entity.Person">
<property name="book" ref="book"/>
</bean>
底層的簡單源碼如下:
String nameStr=...;解析<property.../>元素的name屬性得到該字元串的值為book
String refStr=..;解析<property.../>元素的ref屬性得到該字元串的值為book
String setterName-"set"+nameStr.subString(0,1).toUpperCase()+name.subString(1);//生成將要調用的setter方法】
Object paramBean=container.get(refStr);//從容器中取到refStr的bean,作為傳入參數
Method setter=clazz.getMethod(setterName,parmBean.getClass())//此處的clazz和1的對應起來
setter.incoke(obj,parmBean);//此處的obj和1的對應起來
3.組件在spring容器中是單例的
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("載入spring....");
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
System.out.println("spring容器啟動成功!");
Person person1= (Person) ac.getBean("person01");
Person person2= (Person) ac.getBean("person01");
System.out.println(person1==person2);------------------------->此時輸出為true;
}
4.使用構造器為bean的屬性賦值
spring配置文件為:
<bean id="book" class="entity.Book">
<property name="name" value="java分析"/>
<property name="price" value="32"/>
</bean>
<bean id="person01" class="entity.Person">-------------------------------->此處有兩個person的bean:這一個使用set方法給屬性賦值,調用的是無參構造器
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="吳孟達"></property>
<property name="book" ref="book"/>
</bean>
<bean id="person02" class="entity.Person">------------------------------>這裡調用的是有參構造器來進行屬性賦值
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="book" ref="book"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="吳孟達02"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
person類的代碼:
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Book book;
public Person() {
System.out.println("person執行無參構造器");
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Book book) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.book = book;
System.out.println("person執行有參構造器");
}
get/set方法
}
測試類方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("載入spring....");
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
System.out.println("spring容器啟動成功!");
Person person= (Person) ac.getBean("person02");
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
輸出:
載入spring...
Book實例化!
Book執行set name方法
Book執行set price方法
person執行無參構造器-------------->調用無參構造器實例化對象,然後調用set方法賦值
person執行set age方法
person執行set name方法
person執行有參構造器-------------->調用有參構造器,並且直接賦值
spring容器啟動成功!
Person{name='吳孟達02', age=18, book=Book{name='java分析', price=32}}
5.使用p名稱空間為bean屬性賦值
1.在spring的xml文件中加入這一句:xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"----------------------------------->加入這一句
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="book" class="entity.Book">
<property name="name" value="java分析"/>
<property name="price" value="32"/>
</bean>
<bean id="person03" class="entity.Person" p:age="18" p:name="吳孟達03" p:book-ref="book"></bean>------>此時可以通過p標簽進行賦值
</beans>
6.複雜賦值
1.給屬性賦值null
<bean id="person04" class="entity.Person">
<property name="name">
<null></null>---------------------------->使用null標簽進行賦值:不能使用<property name="name" value="null">這是付了一個null的字元串
</property>
</bean>
2.屬性是引用時
2.1引用外部bean
<bean id="book" class="entity.Book">
<property name="name" value="java分析"/>
<property name="price" value="32"/>
</bean>
<bean id="person04" class="entity.Person">
<property name="name">
<null></null>
</property>
<property name="book" ref="book"></property>------------->如果外邊已經有了像引用的Book bean,則使用ref引用:這裡意思是:book=ioc.getBean("book")
</bean>
測試代碼:
ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
Person person= (Person) ioc.getBean("person04");
System.out.println(ioc.getBean("book")==person.getBook());------------->此時輸出為true
2.2內部引用
<bean id="person04" class="entity.Person">
<property name="name">
<null></null>
</property>
<property name="book">
<!--對象我們可以使用bean標簽創建 book=new Book();引用內部bean-->
<bean class="entity.Book">---------------------------------------->此處需要註意的是:內部bean不能直接通過ioc容器獲取:
<property name="name" value="java"></property> ----->如<bean id="bookInner" class="entity.Book">內部bean加上id
<property name="price" value="25"></property> ------>ioc.getBean("bookInner")會獲取出錯!
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
測試代碼為:
ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
Person person= (Person) ioc.getBean("person04");
System.out.println(ioc.getBean("book")==person.getBook());------------->此時輸出為false
3.為list屬性賦值
為psrson新增屬性
private List<Book> library;
如何為library賦值
<property name="library">
<!--library=new ArrayLiast<Book>-->
<list>-------------------------------->使用過list標簽
<bean class="entity.Book" p:name="java" p:price="14"></bean>------>1.用bean標簽創建list元素
<ref bean="book"></ref>-------------------------------------------->2.用ref標簽引入外部bean
</list>
</property>
4.為map賦值
為person新增一個屬性
private Map map;
springxml中的配置
<property name="map">
<map>-------------------------------------------->使用map標簽:map=new HashMap<>();
<entry key="key01" value="張三"></entry>
<entry key="key02" value="18"></entry>
<entry key="book01" value-ref="book"></entry>----->可以使用value-ref引入外部bean
<entry key="key04">
<bean class="entity.Person" p:name="吳孟達" p:age="18" p:book-ref="book"></bean>------>也可以使用該方式引入內部bean
</entry>
<entry key="key05">---->map中嵌套map
<map>
</map>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
5.為Properties賦值
person新增一個屬性:
private Properties properties;
spring的配置文件中:
<property name="properties">
<!--properties=new Properties();所有的k=v都是String-->
<props>
<!--k=v都是string,值直接寫在標簽中-->
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
6.使用util名稱空間創建集合類型的bean
使用場景:如果相同的map或者list在多處都有引用
可以將map或list單獨拿出來做個bean
使用步驟
1.在spring的配置文件中加入:xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"---------------------->在spring的配置文件中加入這行
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
。。。。。
</bean>
2.
<!--相當於new LinkedHashMap<>()-->
<util:map id="mymap">
<!--往map中添加元素-->
<entry key="key01" value="張三"></entry>
<entry key="key02" value="18"></entry>
<entry key="book01" value-ref="book"></entry>
<entry key="key04">
<bean class="entity.Person" p:name="吳孟達" p:age="18" p:book-ref="book"></bean>
</entry>
<entry key="key05">
<map></map>
</entry>
</util:map>
3.其他地方的使用
<property name="map" ref="mymap"></property>----->直接根據引用獲取即可
也可以在代碼中直接獲取
Map<String,Object> map= (Map<String, Object>) ioc.getBean("mymap");
7.util:list的使用和list標簽類似
<util:list id="mylist">
<bean class="entity.Person" p:book="西游" p:name="吳孟達"></bean>
<ref bean="mymap"></ref>
<value>12</value>
</util:list>
8.級聯屬性:屬性的屬性
<bean id="book" class="entity.Book">
<property name="name" value="java分析"/>
<property name="price" value="32"/>
</bean>
<bean id="person05" class="entity.Person">
<property name="book" ref="book"></property>
<property name="book.price" value="1000"></property>
----->這裡通過book.price直接更改:person的book屬性的price屬性:但這裡註意的是這裡一改,容器中的book的bean的price屬性改為1000
</bean>
9.通過繼承實現bean屬性的重用
<bean id="person01" class="entity.Person">
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="吳孟達"></property>
<property name="book" ref="book"/>
</bean>
這裡需要一個personbean,其他屬性都一樣,只有age屬性變為19,則可以這樣
<bean id="person06" class="entity.Person" parent="person01">--------->使用parent屬性,指定需要繼承屬性的bean id,這裡的繼承只是當前bean的配置信息繼承,並不是真正的類繼承
<property name="name" value="劉丹"></property>
</bean>
結論:
1. 這裡的person01和pserson06在容器中是不同的組件(對象)
2.這兩個組件的屬性都相同,只有name屬性值不同
3.因為指定了要繼承配置信息的類,所以上述還可以這樣寫
<bean id="person06" parent="person01">-------------------------->省略了class,因為配置信息繼承於person01,所以class配置值可以繼承person01的class配置值值
<property name="name" value="劉丹"></property>
</bean>
4.父類的信息不會因為子類而更改!
10.專門建立一個供其他bean繼承的bean
<bean id="person01" class="entity.Person" abstract="true">----------------------->加入:abstract="true"
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="吳孟達"></property>
<property name="book" ref="book"/>
</bean>
abstract="true"這個bean的配置是一個抽象的,不能獲取他的實例,只能被別人繼承
此時:
ioc.getBean("person01");-------------------->此時獲取會報錯,因為這個是被其他bean繼承的
7.bean的作用域
1.單例:scope="singleton"
<bean id="person05" class="entity.Person" scope="singleton">
<property name="book" ref="book"></property>
<property name="book.price" value="1000"></property>
</bean>
2.多例:scope="prototype"
<bean id="person05" class="entity.Person" scope="prototype">
<property name="book" ref="book"></property>
<property name="book.price" value="1000"></property>
</bean>
結論:
1.scope="singleton"單例模式:預設
1.1在容器啟動完成前就已經創建好對象,保存在容器中
1.2任何獲取都是獲取之前創建好的對象
2.scope="prototype"多例模式
2.1容器啟動預設不會創建多例的bean
2.2每次獲取的時候創建這個bean(ioc.getBean("person05"))
2.3每次獲取都會創建一個新的對象
8.bean的生命周期(自定義初始化方法和銷毀方法)
1.當是單例模式
1.person實體類
public class Person {
//person的無參構造器
public Person() {
System.out.println("person的無參構造器方法...");
}
//自定義初始化方法
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("person的初始化方法");
}
//自定義對象銷毀方法
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("person的銷毀方法");
}
}
2.spring的配置文件
<bean id="person" class="entity.Person"
init-method="initMethod"--------------------------->指定自定義的初始化方法
destroy-method="destroyMethod"--------------------->指定自定義的銷毀方法
>
</bean>
3.測試類
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("spring容器啟動...");
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
System.out.println("spring容器啟動成功!");
System.out.println("關閉spring容器...");
ioc.close();---------------------------------------->調用容器的停止方法
System.out.println("關閉spring容器成功!");
}
輸出:
spring容器啟動...
person的無參構造器方法...
person的初始化方法
spring容器啟動成功!
關閉spring容器...
person的銷毀方法
關閉spring容器成功!
2.當是多例模式
2.1ioc的配置文件
<bean id="person" class="entity.Person"
scope="prototype"---------------------------->多例模式
init-method="initMethod"
destroy-method="destroyMethod"
>
</bean>
測試代碼:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("spring容器啟動...");
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
System.out.println("spring容器啟動成功!");
System.out.println("關閉spring容器...");
ioc.close();
System.out.println("關閉spring容器成功!");
}
輸出:
spring容器啟動...
spring容器啟動成功!
關閉spring容器...
關閉spring容器成功!
因為多例模式不是容器啟動的時候創創建,而是在ioc.getBean("id")時候創建該對象!
2.2當測試代碼為:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("spring容器啟動...");
ConfigurableApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
System.out.println("spring容器啟動成功!");
ioc.getBean("person");------------------------>多例模式獲取bean對象
System.out.println("關閉spring容器...");
ioc.close();
System.out.println("關閉spring容器成功!");
}
輸出:
spring容器啟動...
spring容器啟動成功!
person的無參構造器方法...
person的初始化方法
關閉spring容器...
關閉spring容器成功!
結論:
1.當是單例模式時:Bean的生命周期
(容器啟動)構造器方法---->初始化方法----->(容器關閉)銷毀方法
2.多實例
獲取bean(構造器------>初始化方法---->容器關閉(不會調用銷毀方法))
9.Bean的後置處理器
1.自定義一個類實現BeanPostProcessor介面
public class MyBeanPostProcess implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 自定義的初始化方法之前調用
* Object o是容器創建的bean
* String s是spring配置文件中配置的id
*/
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("bean的後置處理器Befor...方法");
System.out.println(s+":"+o);
return o;----->註意:這裡不能return null,要不會報錯
}
//自定義初始化方法之後執行
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("bean的後置處理器After...方法");
System.out.println(s+":"+o);
return o;------------------------->註意:這裡如果return null;則ioc.getBean也是為null;
}
}
2.在spring配置文件中配置後置處理器
<!--實體類配置-->
<bean id="person01" class="entity.Person"
init-method="initMethod"----------------------->perosn類的自定義初始化方法(person實例化時後會調用)
destroy-method="destroyMethod">----------------->person類的自定義銷毀方法(spring容器銷毀前會調用)
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="吳孟達"></property>
</bean>
<!--後置處理器配置-->
<bean id="myBeanPostProcess" class="Test.MyBeanPostProcess"></bean>
3.測試代碼如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("載入spring....");
ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioc.xml");
System.out.println("spring容器啟動成功!");
Object bean= ioc.getBean("person01");
System.out.println("容器獲取的bean:"+bean);
}
4.輸出:
person執行無參構造器
person執行set age方法
person執行set name方法
bean的後置處理器Befor...方法
person01:Person{name='吳孟達', age=18, book=null}
person自定義的初始化方法
bean的後置處理器After...方法
person01:Person{name='吳孟達', age=18, book=null}
spring容器啟動成功!
容器獲取的bean:Person{name='吳孟達', age=18, book=null}
結論:
發現帶後置處理器的執行流程如下: 執行順序:
- 1.bean實例化
- 2.執行bean的後置處理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
- 3.執行自定義的初始化方法
- 4.執行bean後置處理器的postProcessAfterInitialization方法


