io流主要應用在各種腳本的開發列如,一個目錄爬行要去使用字典文件,還可以用來進行文件加密。後面可以深入研究一下序列化漏洞 ...
java io流有四大家族分別是:
1.InputStream(位元組輸入流) 2.OutputStream(位元組輸入出流)3.Reader(字元輸入流)4.Writer(字元輸出流)四個類都是抽象類
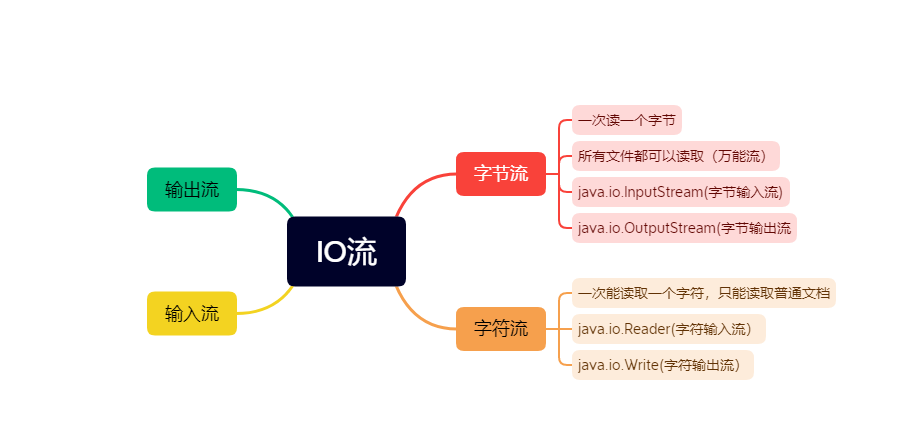
0x01位元組流的輸入和輸出
0x1FileInputStream
class FileInputStreamTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis=null;
try {
fis =new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\鐘林\\untitled\\src\\com\\zhonglin\\www\\TEset");//絕對路徑
while (true){
int data=fis.read();//read會依次向下讀沒有位元組的時候就會返回-1
if (data==-1){
break;
}System.out.println(data);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis!=null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
提高效率使用byet和while迴圈數組去讀取位元組
class FileInputStream_test02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis=null;
try {
fis=new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\鐘林\\untitled\\src\\com\\zhonglin\\www\\TEset");
byte[] bytes=new byte[ 4];
int flag=0;
while ((flag=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,flag));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
available()方法用法:
1.可以獲取文件還可以讀取的位元組數量
2.可以使用read(對象.available)一次性讀取完整個文件夾,但是不適用與大文件,因為byte數組不能太大
skip()方法:
1.跳過幾個位元組不讀取skip(int a)
class FileInputStream_test03{
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
try {
fileInputStream=new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\鐘林\\untitled\\src\\com\\zhonglin\\www\\TEset");
int flag=fileInputStream.read();
System.out.println("剩下多少個位元組key讀"+fileInputStream.available());//剩下多少個位元組key讀
byte[] bytes=new byte[fileInputStream.available()];//可以這樣一次讀取完不用迴圈
fileInputStream.read(bytes);
//不適用與大文件byte數組不能太大
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileInputStream != null) {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
0x2FileOutputStream
writre()方法:
1.在構造方法的後面加一個true代表文件追加,在文件後面繼續寫入
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("myfile",true);
2.寫入完成後一定要flush。
fileOutputStream.flush();
3.String對象轉成byte數組類型
String str1="我是以中國人";
byte[] bytes1=str1.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
fileOutputStream.write(bytes1,0,bytes1.length);`
fileOutputStream.flush();
看一下代碼
class FileOutputStream_test02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
try {
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("myfile",true);//在後面加一個ture代表追加寫入
byte[] bytes={88,66,52,99};
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,2);//從0到2
fileOutputStream.flush();//寫完一定要刷新
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
小結
------InputStream------
public void close() :關閉此輸入流並釋放與此流相關聯的任何系統資源。
public abstract int read() : 從輸入流讀取數據的下一個位元組。
public int read(byte[] b) : 從輸入流中讀取一些位元組數,並將它們存儲到位元組數組 b中 。public void close() :關閉此輸出流並釋放與此流相關聯的任何系統資源。
------OutputStream-----
public void flush() :刷新此輸出流並強制任何緩衝的輸出位元組被寫出。(寫完一定要執行)
public void write(byte[] b) :將 b.length位元組從指定的位元組數組寫入此輸出流。
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) :從指定的位元組數組寫入 len位元組,從偏移量 off開始輸
出到此輸出流。
public abstract void write(int b) :將指定的位元組輸出流。
0x02字元流的輸入和輸出
1.FileReader
a.大部分跟前面的差不多需要把原來的byte數組變成char數組
b.public void close() :關閉此流並釋放與此流相關聯的任何系統資源。
c.public int read() : 從輸入流讀取一個字元。
d.public int read(char[] cbuf) : 從輸入流中讀取一些字元,並將它們存儲到字元數組 cbuf中 。
char[] chars=new char[4];
int flag=0;
while ((flag=fileReader.read())!=0);
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,flag));
2.FileWriter
a.flush :刷新緩衝區,流對象可以繼續使用。
b.close :先刷新緩衝區,然後通知系統釋放資源。流對象不可以再被使用了。
c.大部分共性相同
void write(int c) 寫入單個字元。
void write(char[] cbuf) 寫入字元數組。
abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 寫入字元數組的某一部分,off數組的開始索引,len
寫的字元個數。
void write(String str) 寫入字元串。
void write(String str, int off, int len) 寫入字元串的某一部分,off字元串的開始索引,len寫的字元個
數。
void flush() 刷新該流的緩衝。
void close() 關閉此流,但要先刷新它。
0x03緩衝流的輸入和輸出
1.使用這個流的時候不需要自定義char/byte數組,此流自帶。
2.外部包裝的流叫包裝流(處理流),傳入的流叫節點流。
3.位元組緩衝流: BufferedInputStream , BufferedOutputStream
字元緩衝流: BufferedReader , BufferedWriter
4.看一下位元組緩衝構造方法:
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) :創建一個 新的緩衝輸入流。
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) : 創建一個新的緩衝輸出流。
5.字元緩衝流:
public BufferedReader(Reader in) :創建一個 新的緩衝輸入流。
public BufferedWriter(Writer out) : 創建一個新的緩衝輸出流。
需要參數Reader但是Reader是完全抽象的只能去尋找它的子類
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bis = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
String b = null ;
while ((b = bis.readLine())!=null){//讀取一行
System.out.println(b);
}
bis.close();
}
}
0x04其他流的使用
0x1數據流
1.DataOutputStram和DataInputStream,數據流對應的讀寫只能對應這兩個
2。write(數據類型)()會把對象的數據和類型一併傳過去
3.可以通過read(數據類型)()等方法讀取固定類型數據
class DataOutputStream_Test{
private static DataInputStream ios;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\鐘林\\untitled\\myfile"));
DataInputStream ios=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\鐘林\\untitled\\myfile"));
byte b=100;
int a=100;
dos.writeByte(a);//會把數據和類型一起傳過去
dos.writeByte(b);
ios.readByte();
dos.flush();
dos.close();
}
}
0x05File類
1.File類不屬於io流,不能完成文件數據的讀寫。
2.File對象帶包的是:文件目錄路徑名抽象的表示形式。
3.常用方法
public String getAbsolutePath() :返回此File的絕對路徑名字元串。
public String getPath() :將此File轉換為路徑名字元串。
public String getName() :返回由此File表示的文件或目錄的名稱。
public long length() :返回由此File表示的文件的長度。
public boolean exists() :此File表示的文件或目錄是否實際存在。
public boolean isDirectory() :此File表示的是否為目錄。
public boolean isFile() :此File表示的是否為文件。
public boolean createNewFile() :當前僅當具有該名稱的文件尚不存在時,創建一個新的空文件。
public boolean delete() :刪除由此File表示的文件或目錄。
public boolean mkdir() :創建由此File表示的目錄。//這個可以創建父目錄
public boolean mkdirs() :創建由此File表示的目錄,包括任何必需但不存在的父目錄。
public long lastModified():返回最後一次修改時間
4.看一下簡單的代碼
public class File_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file=new File("C:\\Users\\鐘林\\untitled\\myfile");
System.out.println(file.exists());//判斷是否存在。返回一個boolen值
if (file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();//文件的方式新建
file.mkdir();//以目錄的方式存在
file.getName();//獲取名字
file.isFile();
file.isDirectory();
long haomiao=file.lastModified();//最後一次修改時間.從1970年到現在的毫秒數
Date time=new Date(haomiao);//這樣就可以轉化成日期
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
String stdtiemSTR= simpleDateFormat.format(time);
System.out.println(stdtiemSTR);
}
}
}
0x06序列化和反序列化
1.java提供了一種對象序列化的機制,用一個位元組序列表示一個對象,該位元組包含對象的數據、對象的類型、對象的存儲屬性。位元組序列寫出到文件後,相當於可以持久報錯了一個對象信息,這過程叫做序列化
而反過來,將存儲在文件的位元組序列從文件中讀取出來,重構對象,重新用來創建對象,這步驟叫做反序列化。
2.public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out): 創建一個指定InputStream的ObjectOutputStream。
3.public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) : 創建一個指定InputStream的ObjectInputStream。
4.要實現序列化必須要去實現一個介面Serializable,implements Serializable,它只是一個標誌介面裡面沒有存在任何
看一下代碼(序列化)
class ObjectOutputStream_Test implements Serializable{
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
int id;
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public ObjectOutputStream_Test(int id,String name){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("XULIEHUAt"));
ObjectOutputStream_Test obj=new ObjectOutputStream_Test(10,"zl");
objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj);
objectOutputStream.flush();
objectOutputStream.close();
}
}
看一下反序列化
readObject()方法反序列化回來
public static void main(String[] args) {
Method e = null;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
e = (Method) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
fis.close();
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("name="+e.name);
System.out.println("address ="+e.address);
System.out.println("age="+e.age);
}
反序列化失敗——InvalidClassException
當你序列化class後class裡面的代碼發生了改變,源碼改動以後需要重新編譯,編譯以後變成了全新的位元組碼文件。
並且class文件再次運行的時候,java虛擬機生成的序列化版本號也會發生改變
Serializable 介面給需要序列化的類,提供了一個序列版本號。 serialVersionUID 該版本號的目的在於驗證序
列化的對象和對應類是否版本匹配。
我們可以給它一個固定不變的序列號private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
代碼
public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable {
// 加入序列版本號
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public String name;
public String address;
// 添加新的屬性 ,重新編譯, 可以反序列化,該屬性賦為預設值.
public int eid;
}
}
0x07總結
1.FileoutputStream/FileInputStream:位元組的方式輸入和輸出;
2.FileReade/FileWriter:位元組的方式輸入輸出;
3.位元組緩衝流: BufferedInputStream , BufferedOutputStream;
4.字元緩衝流: BufferedReader , BufferedWriter;
io流主要應用在各種腳本的開發列如,一個目錄爬行要去使用字典文件,還可以用來進行文件加密。後面可以深入研究一下序列化漏洞


