做過java開發的人都知道Spring,就算目前不知道,慢慢也會知道,由於spring體現龐大,模塊眾多,我就介紹下業務開發(以多年經歷的認識,90%的人都是做業務開發的)時用到的SpringMVC。 首先,讓我們從 Spring MVC 的四大組件:前端控制器(DispatcherServlet) ...
做過java開發的人都知道Spring,就算目前不知道,慢慢也會知道,由於spring體系龐大,模塊眾多,我就介紹下業務開發(以多年經歷的認識,90%的人都是做業務開發的)時用到的SpringMVC。
首先,讓我們從 Spring MVC 的四大組件:前端控制器(DispatcherServlet)、處理器映射器(HandlerMapping)、處理器適配器(HandlerAdapter)以及視圖解析器(ViewResolver) 的角度來看一下 Spring MVC 對用戶請求的處理過程,
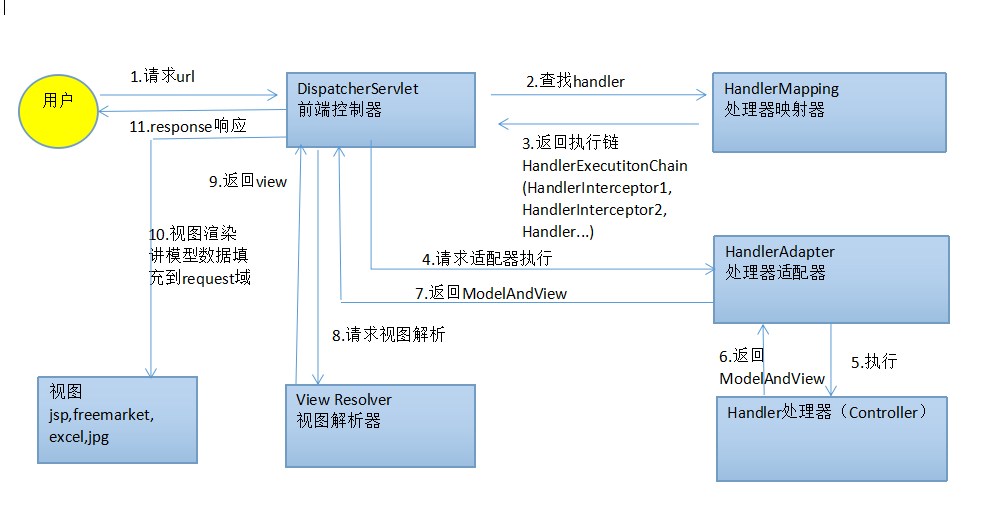
SpringMVC 執行過程
- 用戶請求發送到前端控制器 DispatcherServlet。
- 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 接收到請求後,DispatcherServlet 會使用 HandlerMapping 來處理,HandlerMapping 會查找到具體進行處理請求的 Handler 對象。
- HandlerMapping 找到對應的 Handler 之後,並不是返回一個 Handler 原始對象,而是一個 Handler 執行鏈(HandlerExecutionChain),在這個執行鏈中包括了攔截器和處理請求的 Handler。HandlerMapping 返回一個執行鏈給 DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet 接收到執行鏈之後,會調用 Handler 適配器去執行 Handler。
- HandlerAdapter執行完成 Handler之後會得到一個 ModelAndView,並返回給 DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet 接收到 HandlerAdapter 返回的 ModelAndView 之後,會根據其中的視圖名調用 ViewResolver。
- ViewResolver 根據邏輯視圖名解析成一個真正的 View 視圖,並返回給 DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet 接收到視圖之後,會根據上面的 ModelAndView 中的 model 來進行視圖中數據的填充,也就是所謂的視圖渲染。
- 渲染完成之後,DispatcherServlet 就可以將結果返回給用戶了。
在瞭解了大概的執行過程後,讓我們一起從源碼https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/角度去深入探索。
源碼解析
首先當我們訪問url的時候,將會把請求發送到前端控制器 DispatcherServlet,DispatcherServlet 是一個 Servlet,我們知道在 Servlet 在處理一個請求的時候會交給 service 方法進行處理,這裡也不例外,DispatcherServlet 繼承了 FrameworkServlet,首先進入 FrameworkServlet 的 service 方法:
1 protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 2 // 請求方法 3 HttpMethod httpMethod =HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod()); 4 // 若方法為 PATCH 方法或為空則單獨處理 5 if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) { 6 processRequest(request, response); 7 } else { 8 // 其他的請求類型的方法經由父類,也就是 HttpServlet 處理 9 super.service(request, response); 10 } 11 }
HttpServlet 中會根據請求類型的不同分別調用 doGet 或者 doPost 等方法,FrameworkServlet 中已經重寫了這些方法,在這些方法中會調用 processRequest 進行處理,在 processRequest 中會調用 doService 方法,這個 doService 方法就是在 DispatcherServlet 中實現的。下麵就看下 DispatcherServlet 中的 doService 方法的實現。
DispatcherServlet 收到請求
DispatcherServlet 中的 doService方法:
1 protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 logRequest(request); 3 // 給 request 中的屬性做一份快照,以便能夠恢複原始屬性 4 Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; 5 if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { 6 attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>(); 7 Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); 8 while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { 9 String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); 10 if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { 11 attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 // 如果沒有配置本地化或者主題的處理器之類的,SpringMVC 會使用預設的配置文件,即 DispatcherServlet.properties 16 request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); 17 request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); 18 request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); 19 request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); 20 if (this.flashMapManager != null) { 21 FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); 22 if (inputFlashMap != null) { 23 request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); 24 } 25 request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); 26 request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); 27 } 28 29 try { 30 // 開始真正的處理 31 doDispatch(request, response); 32 } 33 finally { 34 if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 35 // 恢複原始屬性快照 36 if (attributesSnapshot != null) { 37 restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 }
接下來 DispatcherServlet 開始真正的處理,讓我們來看下 doDispatch 方法,首先會獲取當前請求的 Handler 執行鏈,然後找到合適的 HandlerAdapter,接著調用 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 的 handle 方法,如下為 doDispatch 方法:
1 protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; 3 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; 4 boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; 5 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); 6 try { 7 ModelAndView mv = null; 8 Exception dispatchException = null; 9 try { 10 // 先檢查是不是 Multipart 類型的,比如上傳等;如果是 Multipart 類型的,則轉換為 MultipartHttpServletRequest 類型 11 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); 12 multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); 13 14 // 獲取當前請求的 Handler 執行鏈 15 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); 16 if (mappedHandler == null) { 17 noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); 18 return; 19 } 20 21 // 獲取當前請求的 Handler 適配器 22 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); 23 24 // 對於 header 中 last-modified 的處理 25 String method = request.getMethod(); 26 boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); 27 if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { 28 long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 29 if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { 30 return; 31 } 32 } 33 34 // 遍歷所有定義的 interceptor,執行 preHandle 方法 35 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { 36 return; 37 } 38 39 // 實際調用 Handler 的地方 40 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 41 42 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 43 return; 44 } 45 // 處理成預設視圖名,也就是添加首碼和尾碼等 46 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); 47 // 攔截器postHandle方法進行處理 48 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); 49 } 50 catch (Exception ex) { 51 dispatchException = ex; 52 } 53 catch (Throwable err) { 54 dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); 55 } 56 // 處理最後的結果,渲染之類的都在這裡 57 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); 58 } 59 catch (Exception ex) { 60 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); 61 } 62 catch (Throwable err) { 63 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, 64 new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); 65 } 66 finally { 67 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 68 if (mappedHandler != null) { 69 mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); 70 } 71 } 72 else { 73 if (multipartRequestParsed) { 74 cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 }
查找對應的 Handler 對象
查找對應的 Handler 對象
讓我們去探索下是如何獲取當前請求的 Handler 執行鏈,對應著這句代碼 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);,看下 DispatcherServlet 具體的 getHandler 方法,該方法主要是遍歷所有的 handlerMappings 進行處理,handlerMappings 是在啟動的時候預先註冊好的,在迴圈中會調用 AbstractHandlerMapping 類中的 getHandler 方法來獲取 Handler 執行鏈,若獲取的 Handler 執行鏈不為 null,則返回當前請求的 Handler 執行鏈,DispatcherServlet 類的 getHandler 方法如下:
1 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 2 if (this.handlerMappings != null) { 3 // 遍歷所有的 handlerMappings 進行處理,handlerMappings 是在啟動的時候預先註冊好的 4 for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { 5 HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); 6 if (handler != null) { 7 return handler; 8 } 9 } 10 } 11 return null; 12 }
在迴圈中,根據 mapping.getHandler(request);,繼續往下看 AbstractHandlerMapping 類中的 getHandler 方法:
1 public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 2 // 根據 request 獲取 handler 3 Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); 4 if (handler == null) { 5 // 如果沒有找到就使用預設的 handler 6 handler = getDefaultHandler(); 7 } 8 if (handler == null) { 9 return null; 10 } 11 // 如果 Handler 是 String,表明是一個 bean 名稱,需要尋找對應 bean 12 if (handler instanceof String) { 13 String handlerName = (String) handler; 14 handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); 15 } 16 // 封裝 Handler 執行鏈 17 return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); 18 }View Code
AbstractHandlerMapping 類中的 getHandler 方法中首先根據 requrst 獲取 handler,主要是調用了 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 類中的 getHandlerInternal 方法,該方法首先獲取 request 中的 url,即 /testSpringMvc,用來匹配 handler 並封裝成 HandlerMethod,然後根據 handlerMethod 中的 bean 來實例化 Handler 並返回。
1 protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 2 // 獲取 request 中的 url,用來匹配 handler 3 String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); 4 request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath); 5 this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); 6 try { 7 // 根據路徑尋找 Handler,並封裝成 HandlerMethod 8 HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); 9 // 根據 handlerMethod 中的 bean 來實例化 Handler,並添加進 HandlerMethod 10 return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); 11 } 12 finally { 13 this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); 14 } 15 }View Code
接下來,我們看 lookupHandlerMethod 的邏輯,主要邏輯委托給了 mappingRegistry 這個成員變數來處理:
1 protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 2 List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>(); 3 // 通過 lookupPath 屬性中查找。如果找到了,就返回對應的RequestMappingInfo 4 List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath); 5 if (directPathMatches != null) { 6 // 如果匹配到了,檢查其他屬性是否符合要求,如請求方法,參數,header 等 7 addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); 8 } 9 if (matches.isEmpty()) { 10 // 沒有直接匹配到,則遍歷所有的處理方法進行通配符匹配 11 addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request); 12 } 13 14 if (!matches.isEmpty()) { 15 // 如果方法有多個匹配,不同的通配符等,則排序選擇出最合適的一個 16 Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); 17 matches.sort(comparator); 18 Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); 19 // 如果有多個匹配的,會找到第二個最合適的進行比較 20 if (matches.size() > 1) { 21 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 22 logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches); 23 } 24 if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) { 25 return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH; 26 } 27 Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1); 28 if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { 29 Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); 30 Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); 31 String uri = request.getRequestURI(); 32 // 不能有相同的最優 Match 33 throw new IllegalStateException( 34 "Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}"); 35 } 36 } 37 request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod); 38 // 設置 request 參數(RequestMappingHandlerMapping 對其進行了覆寫) 39 handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); 40 // 返回匹配的 url 的處理的方法 41 return bestMatch.handlerMethod; 42 } 43 else { 44 // 調用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 類的 handleNoMatch 方法再匹配一次 45 return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request); 46 } 47 }View Code
通過上面的過程,我們就獲取到了 Handler,就開始封裝執行鏈了,就是將我們配置的攔截器加入到執行鏈中去,getHandlerExecutionChain 方法如下:

1 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { 2 // 如果當前 Handler 不是執行鏈類型,就使用一個新的執行鏈實例封裝起來 3 HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)); 4 5 String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH); 6 // 遍歷攔截器,找到跟當前 url 對應的,添加進執行鏈中去 7 for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) { 8 if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) { 9 MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor; 10 if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) { 11 chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); 12 } 13 } 14 else { 15 chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); 16 } 17 } 18 return chain; 19 }View Code
到此為止,我們就獲取了當前請求的 Handler 執行鏈,接下來看下是如何獲取請求的 Handler 適配器,主要依靠 DispatcherServlet 類的 getHandlerAdapter 方法,該方法就是遍歷所有的 HandlerAdapter,找到和當前 Handler 匹配的就返回,在這裡匹配到的為 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
DispatcherServlet 類的 getHandlerAdapter 方法如下:

1 protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { 2 if (this.handlerAdapters != null) { 3 // 遍歷所有的 HandlerAdapter,找到和當前 Handler 匹配的就返回 4 for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) { 5 if (adapter.supports(handler)) { 6 return adapter; 7 } 8 } 9 } 10 throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + 11 "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); 12 }View Code
HandlerAdapter 執行當前的 Handler
再獲取完當前請求的 Handler 適配器後,接著進行緩存處理,也就是對 last-modified 的處理,然後調用 applyPreHandle 方法執行攔截器的 preHandle 方法,即遍歷所有定義的 interceptor,執行 preHandle 方法,然後就到了實際執行 handle 的地方,doDispatch 方法中 handle 方法是執行當前 Handler,我們這裡使用的是 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,首先會進入 AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter 的 handle 方法:
1 public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
2 return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
3 }
在 AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter 的 handle 方法中又調用了 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 類的 handleInternal 方法:
1 protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { 2 ModelAndView mav; 3 checkRequest(request); 4 if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { 5 HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); 6 if (session != null) { 7 Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); 8 synchronized (mutex) { 9 mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); 10 } 11 } 12 else { 13 mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); 14 } 15 } 16 else { 17 // 執行方法,封裝 ModelAndView 18 mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); 19 } 20 if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) { 21 if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) { 22 applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers); 23 } 24 else { 25 prepareResponse(response); 26 } 27 } 28 return mav; 29 }View Code
在執行完 handle 方法後,然後調用 applyDefaultViewName 方法組裝預設視圖名稱,將首碼和尾碼名都加上,接著調用 applyPostHandle 方法執行攔截器的 preHandle 方法,也就是遍歷所有定義的 interceptor,執行preHandle 方法。處理最終結果以及渲染
最終調用 DispatcherServlet 類中的 processDispatchResult 方法,此方法主要是處理最終結果的,包括異常處理、渲染頁面和發出完成通知觸發攔截器的 afterCompletion() 方法執行等。processDispatchResult()方法代碼如下:

1 private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception { 2 boolean errorView = false; 3 if (exception != null) { 4 if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { 5 logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); 6 mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); 7 } 8 else { 9 Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); 10 mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); 11 errorView = (mv != null); 12 } 13 } 14 if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { 15 // 渲染 16 render(mv, request, response); 17 if (errorView) { 18 WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); 19 } 20 } 21 else { 22 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 23 logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned."); 24 } 25 } 26 if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 27 return; 28 } 29 if (mappedHandler != null) { 30 mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); 31 } 32 }View Code
接下來讓我們看下 DispatcherServlet 類的 render 方法是如何完成渲染的,DispatcherServlet 類的 render 方法渲染過程如下:- 判斷 M




