其他設計模式 JavaScript 中不常用 對應不到經典場景 原型模式 行為型 clone 自己,生成一個新對象 java 預設有 clone 介面,不用自己實現 對比 js 中的原型 prototype prototype 可以理解為 es6 class 的一種底層原理 而 class 是實現面 ...
其他設計模式
JavaScript 中不常用
對應不到經典場景
原型模式-行為型
- clone 自己,生成一個新對象
- java 預設有 clone 介面,不用自己實現
//'object.creat'用到了原型模式的思想(雖然不是java中的clone)
//基於一個原型創建一個對象
var prototype = {
gatName: function() {
return this.first + " " + this.last;
},
say: function() {
console.log("hello");
}
};
// 基於原型創建x
var x = Object.create(prototype);
x.first = "A";
x.last = "B";
console.log(x.gatName());
x.say();
//基於原型創建y
var y = Object.create(prototype);
y.first = "A";
y.last = "B";
console.log(y.gatName());
y.say();- 對比 js 中的原型 prototype
- prototype 可以理解為 es6 class 的一種底層原理
- 而 class 是實現面向對象的基礎,並不是服務於某個模式
- 若幹年後 es6 普及,大家可能會忽略掉 prototype
- 但是 Object.create 卻會長久存在
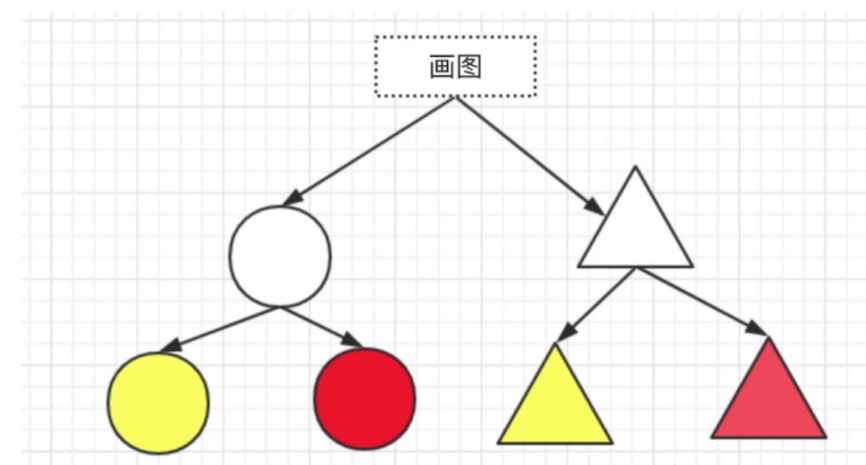
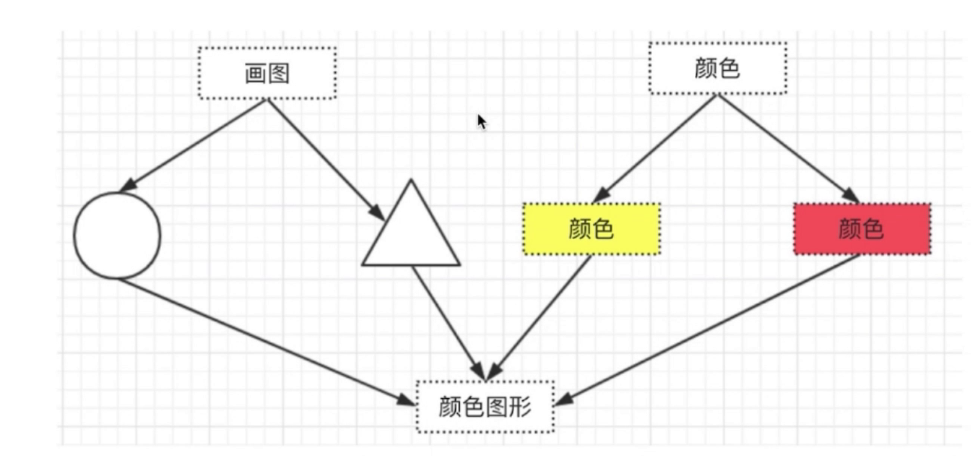
橋接模式-結構型
- 用於把抽象化與現實化解耦
- 使得二者可以獨立變化
- js 中未找到經典應用
class ColorShap {
yellowCircle() {
console.log("yellow circle");
}
redCircle() {
console.log("red circle");
}
yellowTriangle() {
console.log("yellow triangle");
}
redTriangle() {
console.log("red triangle");
}
}
// 測試
let cs = new ColorShap();
cs.yellowCircle();
cs.redCircle();
cs.yellowTriangle();
cs.redTriangle;上面代碼改進後
class Color {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Shap {
constructor(name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
draw() {
console.log(`${this.color.name} ${this.name}`);
}
}
// 測試代碼
let red = new Color("red");
let yellow = new Color("yellow");
let circle = new Shap("circle", red);
circle.draw();
let triabgle = new Shap("triangle", yellow);
triabgle.draw();- 設計原則驗證
- 抽象與實現分離,解耦
- 符合開放封閉原則
組合模式-結構型
- 生成樹形結構
- 讓整體和部分具有一致的操作方式
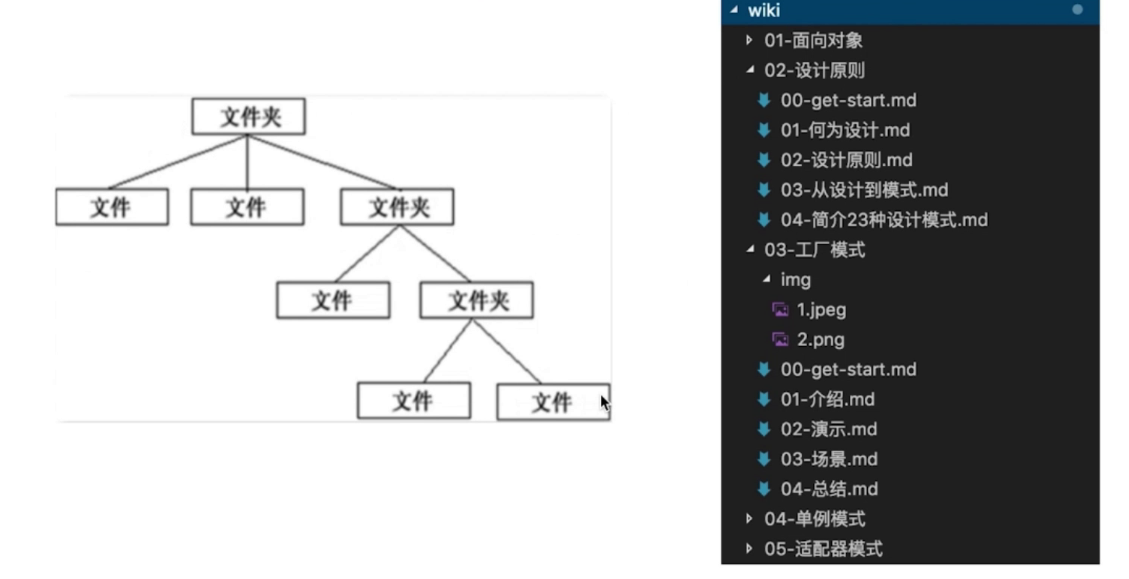
- js 經典應用中,未找到這嗎複雜的數據結構
- 虛擬 DOM 中的 vnode 是這種形式,但數據結構類型簡單
- 用 js 實現一個菜單,不算經典應用,與業務相關
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1" class="container">
<p>123</p>
<p>456</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script>
var 組合模式 = {
tag: "div",
attr: {
id: "div1",
className: "container"
},
children: [
{
tag: "p",
attr: {},
children: ["123"]
},
{
tag: "p",
attr: {},
children: ["456"]
}
]
};
</script>- 整體和單個節點的操作是一致的
整體和單個節點的數據結構也一致
- 設計原則驗證
- 將整體和單個節點的操作抽象出來
- 符合開放封閉原則
享元模式-結構型
- 共用記憶體(主要考慮記憶體,而非效率)
- 相同數據,共用記憶體
- js 中未找到經典應用場景
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 無限下拉列表,將事件代理到高層節點上 -->
<!-- 如果都綁定到`<a>`標簽,對記憶體開銷太大 -->
<div id="div1">
<a href="#">a1</a>
<a href="#">a2</a>
<a href="#">a3</a>
<a href="#">a4</a>
<!-- 無限下拉列表 -->
</div>
<script>
var div1 = document.getElementById("div1");
div1.addEventListener("clink", function(e) {
var target = e.target;
if (e.nodeName === "A") {
alert(target.innerHrml);
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>- 設計原則驗證
- 將相同的部分抽象出來
- 符合開封閉原則
策略模式-行為型
- 不同策略分開處理
- 避免出現大量
if...else或者switch..case - js 中未找到經典應用場景
class User {
constructor(type) {
this.type = type;
}
buy() {
if (this.type === "ordinary") {
console.log("普通用戶購買");
} else if (this.type === "member") {
console.log("會員購買");
} else if (this.type === "vip") {
console.log("vip 用戶購買");
}
}
}
// 測試代碼
var u1 = new User("ordinary");
u1.buy();
var u2 = new User("member");
u2.buy();
var u3 = new User("vip");
u3.buy();上面代碼改進後
class OridinaryUser {
buy() {
console.log("普通用戶購買");
}
}
class MemberUser {
buy() {
console.log("會員用戶購買");
}
}
class vipUser {
buy() {
console.log("vip用戶購買");
}
}
// 測試代碼
var u1 = new OridinaryUser("ordinary");
u1.buy();
var u2 = new MemberUser("member");
u2.buy();
var u3 = new vipUser("vip");
u3.buy();- 設計原則驗證
- 不同策略,分開處理,而不是混合在一起
- 符合開放封閉原則
模板方法模式-行為型
class Action {
handle() {
handle1();
handle2();
handle3();
}
handle1() {
console.log("1");
}
handle2() {
console.log("2");
}
handle3() {
console.log("3");
}
}職責連接模式-行為型
- 一步操作可能分為多個職責角色來完成
- 把這些角色都分開,然後用一個鏈串起來
- 將發起者和各個處理者隔離
class Action {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
this.nextAction = null;
}
setNextAction(action) {
this.nextAction = action;
}
handle() {
console.log(`${this.name} 審批`);
if (this.nextAction != null) {
this.nextAction.handle();
}
}
}
let a1 = new Action("組長");
let a2 = new Action("經理");
let a3 = new Action("總監");
a1.setNextAction(a2);
a2.setNextAction(a3);
a1.handle();js 中的鏈式操作
- 職責鏈模式和業務結合較多,js 中能聯想到鏈式操作
- jQuery 的鏈式操作,promise.then 的鏈式操作
- 設計原則驗證
- 發起者與各個處理者隔離
- 符合開放封閉原則
命令模式-行為型
- 執行命令時,發佈者和執行者分開
- 中間加入命令對象,作為中轉站
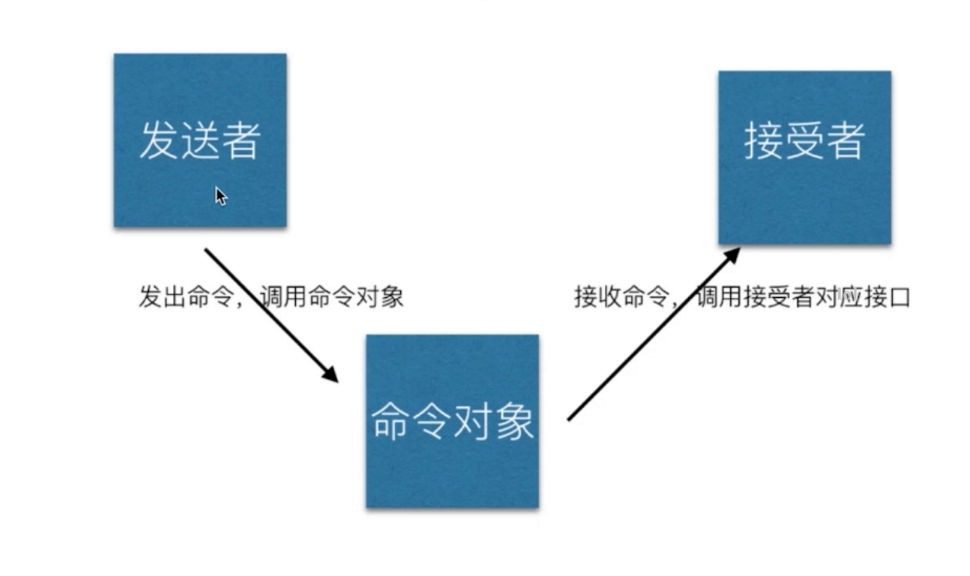
class Receive {
exec() {
console.log("執行");
}
}
class Command {
constructor(recever) {
this.receive = recever;
}
cmd() {
console.log("觸發命令");
this.receive.exec();
}
}
class Invoker {
constructor(command) {
this.command = command;
}
invoke() {
console.log("開始");
this.command.cmd();
}
}
//士兵
let solider = new Receive();
//小號手
let trumpter = new Command(solider);
//將軍
let general = new Invoker(trumpter);
general.invoke();js 中的應用
- 網頁富文本編輯器操作,瀏覽器封裝了一個命令對象
document.exeCommand('bold')document.exeCommand('undo')
- 設計原則驗證
- 命令對象與執行對象分開,解耦
- 符合開放封閉原則
備忘錄模式-行為型
- 隨時記錄一個對象的狀態變化
- 隨時可以恢復之前的某個狀態(如撤銷功能)
- 未找到 js 中經典應用,除了一些工具(編輯器)
// 狀態備忘
class Memento {
constructor(content) {
this.content = content;
}
getContent() {
return this.content;
}
}
// 備忘列表
class CareTaker {
constructor() {
this.list = [];
}
add(memento) {
this.list.push(memento);
}
get(index) {
return this.list[index];
}
}
//編輯器
class Editor {
constructor() {
this.content = null;
}
setContent(content) {
this.content = content;
}
getContent() {
return this.content;
}
saveContentToMemento() {
return new Memento(this.content);
}
getContentFromMemento(memento) {
this.content = memento.getContent();
}
}
//測試代碼
let editor = new Editor();
let careTaker = new CareTaker();
editor.setContent("111");
editor.setContent("222");
careTaker.add(editor.saveContentToMemento()); //存儲備忘錄
editor.setContent("333");
careTaker.add(editor.saveContentToMemento()); //存儲備忘錄
editor.setContent("444");
console.log(editor.getContent());
editor.getContentFromMemento(careTaker.get(1)); //撤銷
console.log(editor.getContent());
editor.getContentFromMemento(careTaker.get(0)); //撤銷
console.log(editor.getContent());- 設計原則驗證
- 狀態對象與使用者分開,解耦
- 符合開放封閉原則
中介者模式-行為型
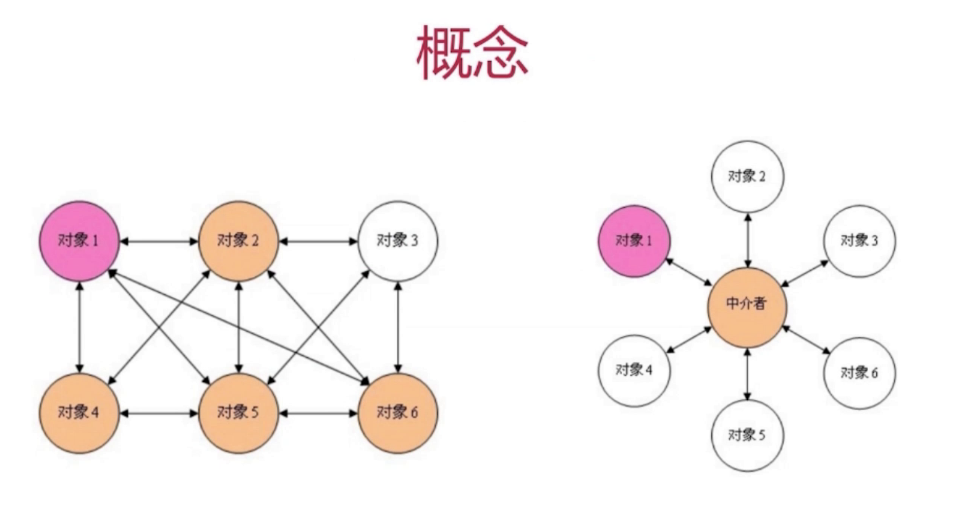
class Mediator {
constructor(a, b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
setA() {
let number = this.b.number;
this.a.setNumber(number * 100);
}
setB() {
let number = this.a.number;
this.b.setNumber(number / 100);
}
}
class A {
constructor() {
this.number = 0;
}
setNumber(num, m) {
this.number = num;
if (m) {
m.setB();
}
}
}
class B {
constructor() {
this.number = 0;
}
setNumber(num, m) {
this.number = num;
if (m) {
m.setA();
}
}
}
let a = new A();
let b = new B();
let m = new Mediator(a, b);
a.setNumber(100);
console.log(a.number, b.number); //100 1
b.setNumber(100);
console.log(a.number, b.number); //10000 100- 設計原則驗證
- 將各個關聯對象通過中介者隔離
- 符合開放封閉原則
訪問者模式-行為型
- 將數據操作和數據結構進行分離
- 使用場景不多
解釋器模式-行為型
- 描述語言語法如何定義,如何解釋和編譯
- 用於專業場景


