本文主要講解Spring載入xml配置文件的方式,跟蹤載入BeanDefinition的全過程。 源碼分析 源碼的入口 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext構造函數 new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“spring.xml”)用於載入CLA ...
本文主要講解Spring載入xml配置文件的方式,跟蹤載入BeanDefinition的全過程。
源碼分析
源碼的入口

ClassPathXmlApplicationContext構造函數
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“spring.xml”)用於載入CLASSPATH下的Spring配置文件,將配置文件傳給構造函數,然後調用類內部的另外一個重載方法。

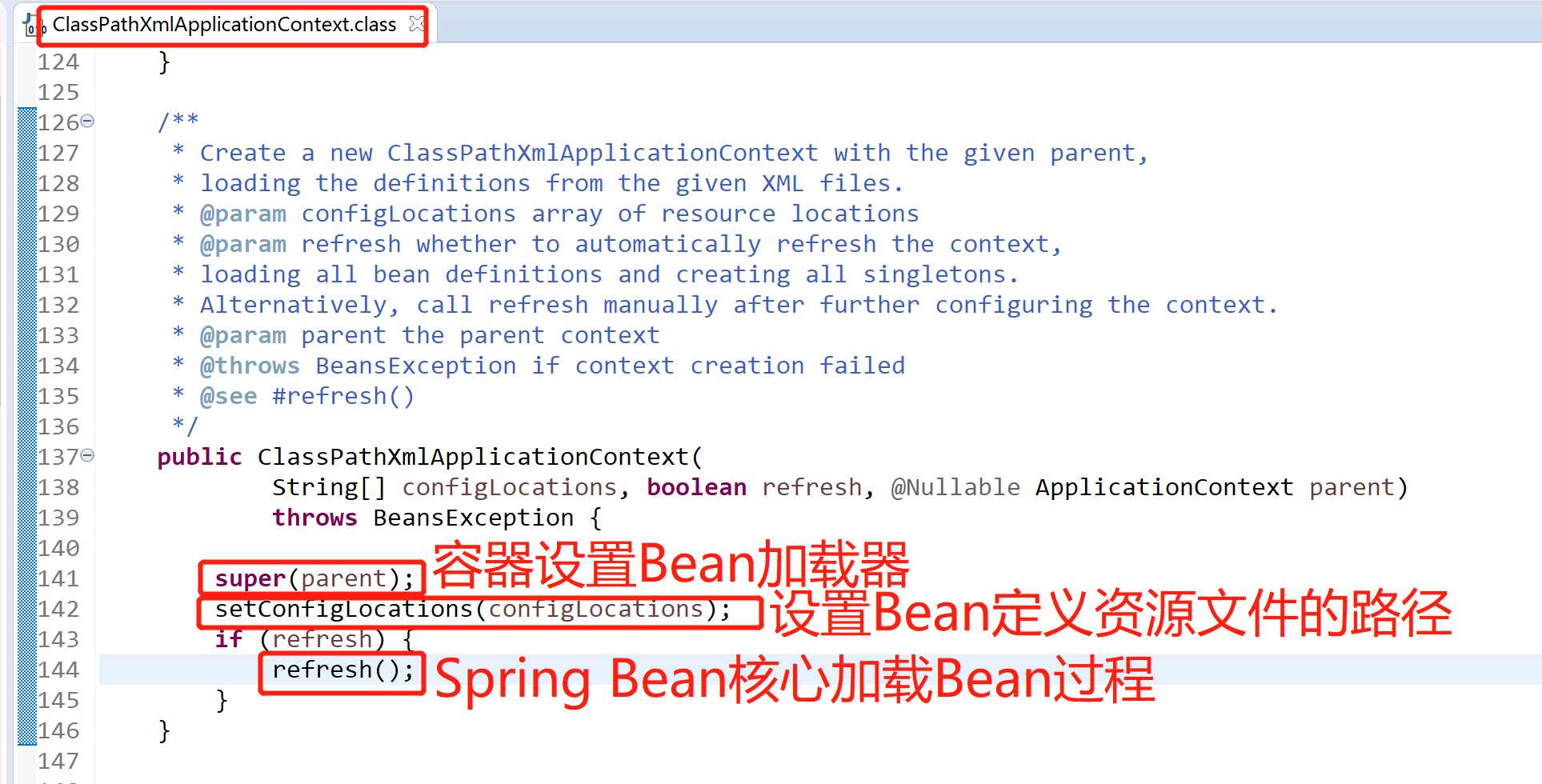
從構造函數中,可以看到一共做了3件事
super(parent)
super(parent)的作用是為容器設置Bean資源載入器,層層跟蹤,可知實際是由其父類AbstractApplicationContext完成設置的,parent為null,setParent(parent)就不繼續跟蹤了,這裡需要註意的是,該類繼承了DefaultResourceLoader,所以該類也作為資源載入器
AbstractApplicationContext.java
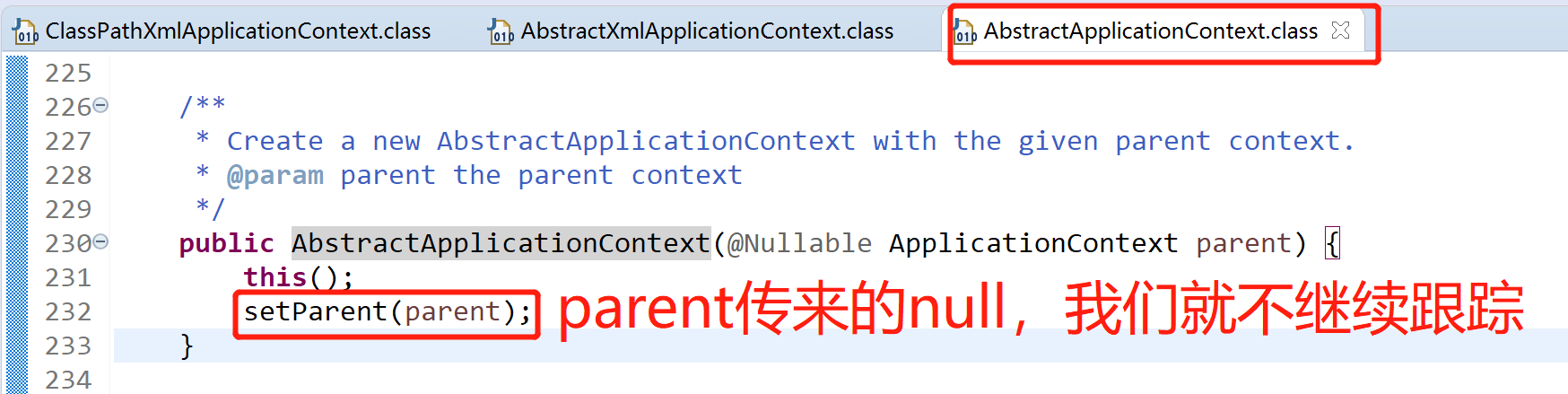
跟蹤該類this()無參構造函數進去看看
AbstractApplicationContext.java

AbstractApplicationContext.java
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.java

setConfigLocations(configLocations)
設置Bean定義資源的路徑,由其父類AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext完成,resolvePath解析路徑,一直跟蹤到底層是調用PropertyPlaceholderHelper的parseStringValue完成設置的

refresh()
這個就是整個Spring Bean載入的核心裡面十二大步,用於刷新整個Spring上下文信息,定義了整個Spring上下文載入的流程。
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { //1、 Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); //創建DefaultListableBeanFactory(真正生產和管理bean的容器) //載入BeanDefition並註冊到BeanDefitionRegistry //通過NamespaceHandler解析自定義標簽的功能(比如:context標簽、aop標簽、tx標簽) //2、 Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); //3、 Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { //4、 Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); //實例化並調用實現了BeanFactoryPostProcessor介面的Bean //比如:PropertyPlaceHolderConfigurer(context:property-placeholer) //就是此處被調用的,作用是替換掉BeanDefinition中的占位符(${})中的內容 //5、 Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); //創建並註冊BeanPostProcessor到BeanFactory中(Bean的後置處理器) //比如:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(實現@Autowired註解功能) // RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(實現@d註解功能) //這些註冊的BeanPostProcessor //6、 Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); //7、 Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); //8、 Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); //9、 Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); //10、 Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); //創建非懶載入方式的單例Bean實例(未設置屬性) //填充屬性 //初始化實例(比如調用init-method方法) //調用BeanPostProcessor(後置處理器)對實例bean進行後置處理 //11、 Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); //12、 Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
總結:
- 方法加了個類鎖,避免了多線程同時刷新Spring上下文。
- 鎖的這個對象為this.startupShutdownMonitor,有兩個好處
- refresh()方法和close()方法都使用了this.startupShutdownMonitor,保證了在調用refresh()方法的時候無法使用close()方法,反之亦然,避免了衝突
- 使用對象鎖可以減少同步的範圍,只對不能併發的代碼塊進行加鎖,提高了整體代碼的運行效率。
- refresh()函數是一個模板方法,執行多個方法,而且提供了各個protected方法(預設實現),其子類可以重寫他們。
- 模板方法模式:在一個方法中定義一個演算法的骨架,而將一些步驟延遲到子類中。模板方法使得子類(protected方法)可以在不改變演算法結構的情況下,重新定義演算法中的某些步驟。
refresh()核心調用obtainFreshBeanFactory()
obtainFreshBeanFactory()函數調用,完成了容器初始化的最基礎的功能,Bean定義資源的Resource定位、載入解析和註冊
AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { //使用的委派模式,調用2個抽象方法,定義了obtainFreshBeanFactory的演算法骨架,實際的行為交給了子類AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext實現 refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); } return beanFactory; }
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
/** * This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying * bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and * initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle. */ @Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //若有容器,銷毀容器中的bean,關閉容器,以此保證refresh()之後使用的是新建立起來的IoC容器 if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //創建IoC容器 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); //調用載入bean定義的方法,使用了委派模式,在當前類中定義了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具體實現交給子類 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }st
在這個方法中,先判斷BeanFactory是否存在,若存在,則先銷毀並關閉BeanFactory接著創建DefaultListableBeanFactory,並調用loadBeanDefinitions裝在bean使用了委派模式,在當前類中只定義了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具體的實現交給子類AbstractXmlApplicationContext
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
/** * Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader. * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader * @see #initBeanDefinitionReader * @see #loadBeanDefinitions */ @Override protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // 為給定的bean工廠創建一個新的xmlbeanfinitionReader XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); //使用此上下文的bean定義讀取器配置 // 資源載入環境 beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // 允許子類提供讀取器的自定義初始化,然後繼續實際載入bean定義 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
看下new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory)做了哪些工作,底層初始化了BeanDefinitionRegistry=BeanDefinitionRegistry也就是this.registry = registry
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/** * Create new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory. * @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into, * in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry */ public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { super(registry); }
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java
/** * Create a new AbstractBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory. * <p>If the passed-in bean factory does not only implement the BeanDefinitionRegistry * interface but also the ResourceLoader interface, it will be used as default * ResourceLoader as well. This will usually be the case for * {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} implementations. * <p>If given a plain BeanDefinitionRegistry, the default ResourceLoader will be a * {@link org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver}. * <p>If the passed-in bean factory also implements {@link EnvironmentCapable} its * environment will be used by this reader. Otherwise, the reader will initialize and * use a {@link StandardEnvironment}. All ApplicationContext implementations are * EnvironmentCapable, while normal BeanFactory implementations are not. * @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into, * in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry * @see #setResourceLoader * @see #setEnvironment */ protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null"); this.registry = registry; // Determine ResourceLoader to use. if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) { this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry; } else { this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(); } // Inherit Environment if possible if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) { this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment(); } else { this.environment = new StandardEnvironment(); } }
接著看AbstractXmlApplicationContext下的loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)方法,看最下麵一行的loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader)
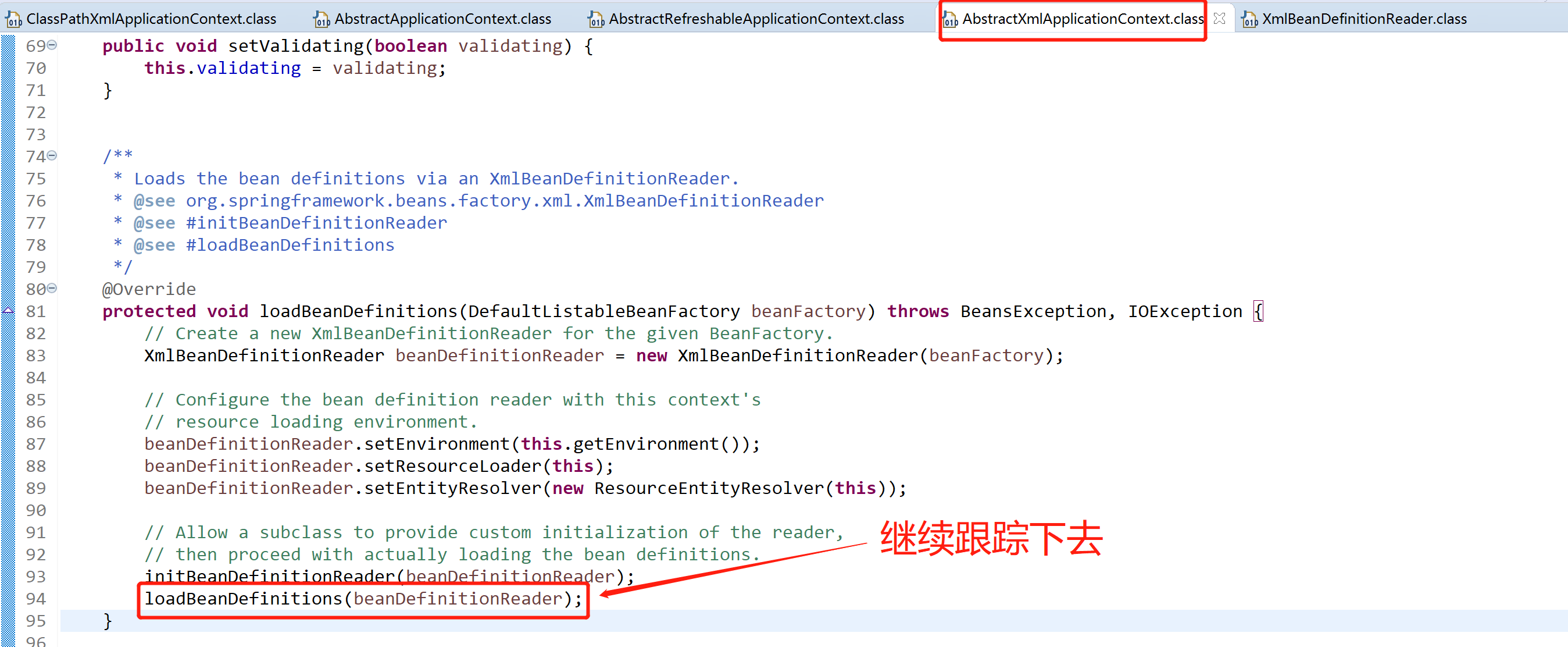
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
/** * Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader. * <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory} * method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions. * @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use * @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors * @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found * @see #refreshBeanFactory * @see #getConfigLocations * @see #getResources * @see #getResourcePatternResolver */ protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
接著跟蹤第一個reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources)
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java
@Override public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null"); int counter = 0; for (Resource resource : resources) { counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } return counter; }
開始迴圈載入loadBeanDefinitions,繼續跟蹤loadBeanDefinitions方法
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ @Override public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); }
繼續跟蹤loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource))
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/** * Load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file, * allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); } Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (currentResources == null) { currentResources = new HashSet<>(4); this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); } if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } try { InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); try { InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } finally { inputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } }
利用currentResources.add(encodedResource)用set判斷,如果重覆載入資源就拋出異常,繼續跟蹤doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/** * Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file. * @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from * @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors * @see #doLoadDocument * @see #registerBeanDefinitions */ protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (SAXParseException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (SAXException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } }
doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource)將xml解析成org.w3c.dom,具體底層如何實現,自行跟蹤,主要看registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource)
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/** * Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document. * Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}. * <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes * {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it. * @param doc the DOM document * @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information) * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors * @see #loadBeanDefinitions * @see #setDocumentReaderClass * @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions */ public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; }
繼續跟蹤documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource))
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
/** * This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD * (or DTD, historically). * <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings * specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions. */ @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) { this.readerContext = readerContext; logger.debug("Loading bean definitions"); Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root); }
繼續跟蹤doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root)
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
/** * Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element. */ protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { // Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; //初始化bean預設的解析器BeanDefinitionParserDelegate this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + "] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource()); } return; } } } preProcessXml(root); //解析dom parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent; }
createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent)初始化bean預設的解析器,BeanDefinitionParserDelegate開始解析dom,前面各有一個預留的空方法,方便以後版本擴展,繼續跟蹤parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate)
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
/** * Parse the elements at the root level in the document: * "import", "alias", "bean". * @param root the DOM root element of the document */ protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
獲取節點的命名空間,判斷是不是spring預設的,是的話就執行parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate),不是的話,就執行delegate.parseCustomElement(root),跟蹤parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate)
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { //import importBeanDefinitionResource(ele); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { //alias processAliasRegistration(ele); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { //bean processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate); } else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { //beans // recurse doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele); } }
標簽分別是import、alias、bean、beans,至此BeanDefinition載入完成,這就是refresh()方法中的
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();



