3.1.如何實現可迭代對象和迭代器對象 結果 3.2如何使用生成器函數實現可迭代對象 3.3.如何進行反向迭代以及如何實現反向迭代 反向迭代 要想實現反向迭代必須實現__reversed__方法 ...
3.1.如何實現可迭代對象和迭代器對象
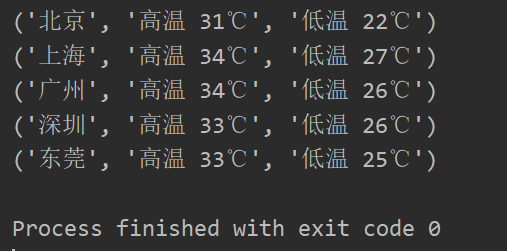
#3.1 如何實現可迭代對象和迭代器對象 import requests from collections.abc import Iterable,Iterator class WeatherIterator(Iterator): def __init__(self,cities): self.cities = cities #從列表中迭代一個city,index就+1 self.index = 0 def __next__(self): #如果所有的城市都迭代完了,就拋出異常 if self.index == len(self.cities): raise StopIteration #當前迭代的city city = self.cities[self.index] #迭代完當前city,index就+1 self.index += 1 return self.get_weather(city) def get_weather(self,city): url = 'http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=' + city r = requests.get(url) #獲取當天的天氣信息 data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0] #返回城市名字、最高和最低氣溫 return city, data['high'], data['low'] class WeatherIterable(Iterable): def __init__(self,cities): self.cities = cities def __iter__(self): return WeatherIterator(self.cities) def show(w): for x in w: print(x) weather = WeatherIterable(['北京','上海','廣州','深圳','東莞']) show(weather)
結果
3.2如何使用生成器函數實現可迭代對象
#3.2如何使用生成器函數實現可迭代對象 from collections.abc import Iterable class PrimeNumbers(Iterable): def __init__(self,a,b): self.a = a self.b = b def __iter__(self): for k in range(self.a,self.b): if self.is_prime(k): yield k def is_prime(self,k): return False if k < 2 else all(map(lambda x : k % x, range(2, k))) #列印1到30直接的素數 pn = PrimeNumbers(1, 30) for n in pn: print(n)
3.3.如何進行反向迭代以及如何實現反向迭代
反向迭代
In [75]: l = [1,2,3,4,5] In [76]: for x in l: ...: print(x) ...: 1 2 3 4 5 In [77]: for x in reversed(l): ...: print(x) ...: 5 4 3 2 1
要想實現反向迭代必須實現__reversed__方法
#3.3.如何進行反向迭代以及如何實現反向迭代 class IntRange: def __init__(self,a,b,step): self.a = a self.b = b self.step = step def __iter__(self): t = self.a while t <= self.b: yield t t += self.step def __reversed__(self): t = self.b while t >= self.a: yield t t -= self.step fr = IntRange(1, 10, 2) for x in fr: print(x) print('=' * 30) #反向迭代 for y in reversed(fr): print(y)
3.4.如何對迭代器做切片操作
(1)切片的實質是__getitem__方法
In [9]: l = list(range(10)) In [10]: l[3] Out[10]: 3 In [11]: l.__getitem__(3) Out[11]: 3 In [12]: l[2:6] Out[12]: [2, 3, 4, 5] In [13]: l.__getitem__(slice(2,6)) Out[13]: [2, 3, 4, 5]
(2)列印文件第2~5行
islice能返回一個迭代對象切片的生成器
#3.4.如何對迭代器做切片操作 from itertools import islice f= open('iter_islice') #列印文件的第2~5行內容 for line in islice(f, 1, 5): print(line)
(3)自己實現islice功能
#自己實現一個類似islice的功能 def my_slice(iterable, start, end, step=1): for i, x in enumerate(iterable): if i >= end: break if i >= start: yield x print(list(my_slice(range(1,20), 4, 10))) #[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] from itertools import islice print(list(islice(range(1,20),4, 10))) #[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
(4)加step
#3.4.如何對迭代器做切片操作 from itertools import islice f= open('iter_islice') #列印文件的第2~5行內容 for line in islice(f, 1, 5): print(line) #自己實現一個類似islice的功能 def my_slice(iterable, start, end, step=1): tmp = 0 for i, x in enumerate(iterable): if i >= end: break if i >= start: if tmp == 0: tmp = step yield x tmp -= 1 print(list(my_slice(range(1,20), 4, 10))) #[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] print(list(my_slice(range(1,20), 4, 10,2))) #[5, 7, 9] from itertools import islice print(list(islice(range(1,20),4, 10))) #[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] print(list(islice(range(1,20),4, 10,2))) #[5, 7, 9]
3.5.如何在一個for語句中迭代多個可迭代對象
計算學生的三科成績總分,用zip()函數
In [25]: from random import randint In [26]: chinese = [randint(60,100) for _ in range(10)] In [27]: math = [randint(60,100) for _ in range(10)] In [28]: english = [randint(60,100) for _ in range(10)] In [29]: chinese Out[29]: [70, 63, 85, 74, 70, 96, 60, 69, 62, 83] In [30]: math Out[30]: [76, 81, 86, 93, 74, 83, 69, 63, 60, 80] In [31]: english Out[31]: [100, 96, 83, 89, 71, 79, 82, 87, 81, 71] In [32]: t = [] In [33]: for s1, s2, s3 in zip(chinese, math, english): ...: t.append(s1 + s2 +s3) ...: In [34]: t Out[34]: [246, 240, 254, 256, 215, 258, 211, 219, 203, 234]
求三個班級中分數高於90分的總人數,用chain
In [53]: c1 = [randint(60,100) for _ in range(1,10)] In [54]: c2 = [randint(60,100) for _ in range(1,10)] In [55]: c3 = [randint(60,100) for _ in range(1,10)] In [56]: c1 Out[56]: [60, 79, 89, 84, 68, 68, 89, 68, 82] In [57]: c2 Out[57]: [69, 64, 87, 89, 60, 77, 89, 81, 90] In [58]: c3 Out[58]: [80, 92, 64, 73, 68, 84, 97, 71, 65] In [59]: from itertools import chain In [60]: len([ x for x in chain(c1, c2, c3) if x > 90]) Out[60]: 2



