之前的文章,在上面建立完config之後,UIl通過 來初始化ImageLoader對象,之後就可以用ImageLoader來載入圖片。 這裡,採用到單例模式來獲取ImageLoader對象,保證他全局初始化一次。再上面的分析中,我們可以看出單例模式的好處,創建ImageLoader對象的時候需要創 ...
之前的文章,在上面建立完config之後,UIl通過ImageLoader.getInstance().init(config.build());來初始化ImageLoader對象,之後就可以用ImageLoader來載入圖片。
這裡,採用到單例模式來獲取ImageLoader對象,保證他全局初始化一次。再上面的分析中,我們可以看出單例模式的好處,創建ImageLoader對象的時候需要創建Config,而Config裡面同樣初始化了一堆對象。如果每次用到都現初始化ImageLoader,消耗太大。我們看一下ImageLoader的init的源碼
public synchronized void init(ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration) {
if (configuration == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(ERROR_INIT_CONFIG_WITH_NULL);
}
if (this.configuration == null) {
L.d(LOG_INIT_CONFIG);
//創建圖片載入引擎
engine = new ImageLoaderEngine(configuration);
this.configuration = configuration;
} else {
L.w(WARNING_RE_INIT_CONFIG);
}
}
如果該對象還沒有config,則將傳入的config賦值給this.config。並且初始化圖片載入引擎。
我們繼續看圖片載入引擎主要執行的工作。
class ImageLoaderEngine {
/*ImageLoader載入配置*/
final ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration;
/*任務執行者*/
private Executor taskExecutor;
/*圖片緩存任務執行則*/
private Executor taskExecutorForCachedImages;
/*任務分配者*/
private Executor taskDistributor;
private final Map<Integer, String> cacheKeysForImageAwares = Collections
.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Integer, String>());
private final Map<String, ReentrantLock> uriLocks = new WeakHashMap<String, ReentrantLock>();
/*暫停*/
private final AtomicBoolean paused = new AtomicBoolean(false);
/*網路拒絕訪問*/
private final AtomicBoolean networkDenied = new AtomicBoolean(false);
/*網路慢*/
private final AtomicBoolean slowNetwork = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private final Object pauseLock = new Object();
/**
* ImageLoader引擎構造器
* @param configuration
*/
ImageLoaderEngine(ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration) {
//初始化ImageLoader配置參數
this.configuration = configuration;
//初始化三個不同任務的執行者
taskExecutor = configuration.taskExecutor;
taskExecutorForCachedImages = configuration.taskExecutorForCachedImages;
taskDistributor = DefaultConfigurationFactory.createTaskDistributor();
}
/** Submits task to execution pool */
/**
* 提交圖片載入和顯示任務到執行線程池中,進行運行
* @param task 具體需要執行的任務
*/
void submit(final LoadAndDisplayImageTask task) {
taskDistributor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//從文件系統緩存中獲取圖片文件
File image = configuration.diskCache.get(task.getLoadingUri());
//判斷是否已經取得了圖片
boolean isImageCachedOnDisk = image != null && image.exists();
initExecutorsIfNeed();
if (isImageCachedOnDisk) {
//如果當前圖片已經緩存在本地文件系統了,直接採用taskExecutorForCachedImages來進行執行任務
taskExecutorForCachedImages.execute(task);
} else {
//當天圖片在本地文件系統中沒有緩存,直接採用taskExecutor來進行執行任務
taskExecutor.execute(task);
}
}
});
}
/**
* Submits task to execution pool
* 提交圖片顯示任務並且執行 (該圖片從記憶體緩存中取得)
*/
void submit(ProcessAndDisplayImageTask task) {
initExecutorsIfNeed();
taskExecutorForCachedImages.execute(task);
}
/**
* 根據需要進行初始化執行者
*/
private void initExecutorsIfNeed() {
if (!configuration.customExecutor && ((ExecutorService) taskExecutor).isShutdown()) {
taskExecutor = createTaskExecutor();
}
if (!configuration.customExecutorForCachedImages && ((ExecutorService) taskExecutorForCachedImages)
.isShutdown()) {
taskExecutorForCachedImages = createTaskExecutor();
}
}
/**
* 進行創建任務執行者
* @return
*/
private Executor createTaskExecutor() {
return DefaultConfigurationFactory
.createExecutor(configuration.threadPoolSize, configuration.threadPriority,
configuration.tasksProcessingType);
}
/**
* 獲取當前被載入ImageAware到圖片的地址
* Returns URI of image which is loading at this moment into passed {@link com.nostra13.universalimageloader.core.imageaware.ImageAware}
*/
String getLoadingUriForView(ImageAware imageAware) {
return cacheKeysForImageAwares.get(imageAware.getId());
}
/**
*
* Associates <b>memoryCacheKey</b> with <b>imageAware</b>. Then it helps to define image URI is loaded into View at
* exact moment.
*/
void prepareDisplayTaskFor(ImageAware imageAware, String memoryCacheKey) {
cacheKeysForImageAwares.put(imageAware.getId(), memoryCacheKey);
}
/**
* Cancels the task of loading and displaying image for incoming <b>imageAware</b>.
*
* @param imageAware {@link com.nostra13.universalimageloader.core.imageaware.ImageAware} for which display task
* will be cancelled
*/
void cancelDisplayTaskFor(ImageAware imageAware) {
cacheKeysForImageAwares.remove(imageAware.getId());
}
/**
* Denies or allows engine to download images from the network.<br /> <br /> If downloads are denied and if image
* isn't cached then {@link ImageLoadingListener#onLoadingFailed(String, View, FailReason)} callback will be fired
* with {@link FailReason.FailType#NETWORK_DENIED}
*
* @param denyNetworkDownloads pass <b>true</b> - to deny engine to download images from the network; <b>false</b> -
* to allow engine to download images from network.
*/
void denyNetworkDownloads(boolean denyNetworkDownloads) {
networkDenied.set(denyNetworkDownloads);
}
/**
* Sets option whether ImageLoader will use {@link FlushedInputStream} for network downloads to handle <a
* href="http://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=6066">this known problem</a> or not.
*
* @param handleSlowNetwork pass <b>true</b> - to use {@link FlushedInputStream} for network downloads; <b>false</b>
* - otherwise.
*/
void handleSlowNetwork(boolean handleSlowNetwork) {
slowNetwork.set(handleSlowNetwork);
}
/**
* Pauses engine. All new "load&display" tasks won't be executed until ImageLoader is {@link #resume() resumed}.<br
* /> Already running tasks are not paused.
* 暫停任務運行
*/
void pause() {
paused.set(true);
}
/**
* Resumes engine work. Paused "load&display" tasks will continue its work.
* 任務恢復運行
*/
void resume() {
paused.set(false);
synchronized (pauseLock) {
pauseLock.notifyAll();
}
}
/**
* 停止ImageLoader引擎,取消所有正在運行或者掛起的圖片顯示任務,並且清除內部的數據
* Stops engine, cancels all running and scheduled display image tasks. Clears internal data.
* <br />
* <b>NOTE:</b> This method doesn't shutdown
* {@linkplain com.nostra13.universalimageloader.core.ImageLoaderConfiguration.Builder#taskExecutor(java.util.concurrent.Executor)
* custom task executors} if you set them.
*/
void stop() {
if (!configuration.customExecutor) {
((ExecutorService) taskExecutor).shutdownNow();
}
if (!configuration.customExecutorForCachedImages) {
((ExecutorService) taskExecutorForCachedImages).shutdownNow();
}
cacheKeysForImageAwares.clear();
uriLocks.clear();
}
void fireCallback(Runnable r) {
taskDistributor.execute(r);
}
ReentrantLock getLockForUri(String uri) {
ReentrantLock lock = uriLocks.get(uri);
if (lock == null) {
lock = new ReentrantLock();
uriLocks.put(uri, lock);
}
return lock;
}
AtomicBoolean getPause() {
return paused;
}
Object getPauseLock() {
return pauseLock;
}
boolean isNetworkDenied() {
return networkDenied.get();
}
boolean isSlowNetwork() {
return slowNetwork.get();
}
}上面的代碼中,核心的部分就是創建了任務執行器和圖片緩存執行器,並且在submit方法中針對提交的任務,選擇不同的執行器執行。
ImageLoader關於載入顯示圖片,有如下幾種用法,我們依次分析一下。
displayImage(), loadImage()先看loadImage()
下麵的loadImage所有的重載方法。
public void loadImage(String uri, ImageLoadingListener listener) {
loadImage(uri, null, null, listener, null);
}
public void loadImage(String uri, ImageSize targetImageSize, ImageLoadingListener listener) {
loadImage(uri, targetImageSize, null, listener, null);
}
public void loadImage(String uri, DisplayImageOptions options, ImageLoadingListener listener) {
loadImage(uri, null, options, listener, null);
}
public void loadImage(String uri, ImageSize targetImageSize, DisplayImageOptions options,
ImageLoadingListener listener) {
loadImage(uri, targetImageSize, options, listener, null);
}
public void loadImage(String uri, ImageSize targetImageSize, DisplayImageOptions options,
ImageLoadingListener listener, ImageLoadingProgressListener progressListener) {
}不管是幾個參數的loadImage,最後都會重載下麵的方法。
public void loadImage(String uri, ImageSize targetImageSize, DisplayImageOptions options,
ImageLoadingListener listener, ImageLoadingProgressListener progressListener) {
checkConfiguration();
if (targetImageSize == null) {
targetImageSize = configuration.getMaxImageSize();
}
if (options == null) {
options = configuration.defaultDisplayImageOptions;
}
NonViewAware imageAware = new NonViewAware(uri, targetImageSize, ViewScaleType.CROP);
displayImage(uri, imageAware, options, listener, progressListener);
}如果沒有指定targetImageSize以及options就會採用config預設的提供,然後根據targetImageSize以及uri生成一個NonViewAware,最終通過displayImage來載入。
targetImageSize是一個ImageSize對象,該類是image尺寸的封裝類,config的預設值是屏幕的寬高。
options是採用config預設創建,config的預設值是faultDisplayImageOptions = DisplayImageOptions.createSimple();
這個初始化都是創建的DisplayImageOptions都是預設值,基本什麼屬性都是false或者null或者0
接下來,我們看一下NonViewAware類,NonViewAware是實現了ImageAware介面的一個類,ImageAware介面主要定義了圖片處理和顯示所需要的方法和屬性。所以NonViewAware也只是對傳入的參數進行封裝,來提供一個外部訪問的介面。
真正顯示圖片的方法都是displayImage,displayImage方法和loadImage一樣,提供了多種參數,displayImage的重載方法要多一些,因為displayImage方法有一類是接受ImageView而另一類是接受ImageAware。
下麵是無論如何都是最終調用的方法:
代碼如下:
public void displayImage(String uri, ImageAware imageAware, DisplayImageOptions options,
ImageSize targetSize, ImageLoadingListener listener, ImageLoadingProgressListener progressListener) {
//進行檢查ImageLoader全局相關配置
checkConfiguration();
if (imageAware == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(ERROR_WRONG_ARGUMENTS);
}
if (listener == null) {
listener = defaultListener;
}
//檢查圖片顯示配置
if (options == null) {
options = configuration.defaultDisplayImageOptions;
}
//==============圖片地址為空=================
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(uri)) {
engine.cancelDisplayTaskFor(imageAware);
//介面方法回調,當前圖片載入任務開始
listener.onLoadingStarted(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
//進行判斷是否給imageview添加一個空地址的資源圖片
if (options.shouldShowImageForEmptyUri()) {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(options.getImageForEmptyUri(configuration.resources));
} else {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(null);
}
//直接載入回調載入成功
listener.onLoadingComplete(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView(), null);
return;
}
//=============圖片地址存在=====================
if (targetSize == null) {
//如果圖片顯示的目標大小沒有設置的,那麼就使用預設大小尺寸即可
targetSize = ImageSizeUtils.defineTargetSizeForView(imageAware, configuration.getMaxImageSize());
}
//根據地址和圖片目標尺寸信息,生成緩存key
String memoryCacheKey = MemoryCacheUtils.generateKey(uri, targetSize);
engine.prepareDisplayTaskFor(imageAware, memoryCacheKey);
//開始進行載入圖片
listener.onLoadingStarted(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
//首先根據key去緩存中獲取是否還存在該圖片
Bitmap bmp = configuration.memoryCache.get(memoryCacheKey);
if (bmp != null && !bmp.isRecycled()) {
//緩存中該圖片存在
L.d(LOG_LOAD_IMAGE_FROM_MEMORY_CACHE, memoryCacheKey);
if (options.shouldPostProcess()) {
ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo = new ImageLoadingInfo(uri, imageAware, targetSize, memoryCacheKey,
options, listener, progressListener, engine.getLockForUri(uri));
ProcessAndDisplayImageTask displayTask = new ProcessAndDisplayImageTask(engine, bmp, imageLoadingInfo,
defineHandler(options));
//是否允許同步載入
if (options.isSyncLoading()) {
displayTask.run();
} else {
//提交進行顯示
engine.submit(displayTask);
}
} else {
options.getDisplayer().display(bmp, imageAware, LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE);
listener.onLoadingComplete(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView(), bmp);
}
} else {
//緩存中不存在該圖片 通過網路載入
if (options.shouldShowImageOnLoading()) {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(options.getImageOnLoading(configuration.resources));
} else if (options.isResetViewBeforeLoading()) {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(null);
}
//進行構造圖片載入任務相關的所有信息對象
ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo = new ImageLoadingInfo(uri, imageAware, targetSize, memoryCacheKey,
options, listener, progressListener, engine.getLockForUri(uri));
//分裝圖片載入和顯示任務對象 然後進行開啟執行任務
LoadAndDisplayImageTask displayTask = new LoadAndDisplayImageTask(engine, imageLoadingInfo,
defineHandler(options));
if (options.isSyncLoading()) {
displayTask.run();
} else {
engine.submit(displayTask);
}
}
}具體的執行過程已經通過代碼註釋了,下麵梳理下流程。
首先,針對為null的屬性,初始化這些屬性,然後判斷傳入的uri是不是為空,如果為空,則根據options.shouldShowImageForEmptyUri來判斷是否顯示先設置好的圖片。
如果傳入的uri是存在的,則根據地址和圖片目標尺寸的信息來生成緩存key,然後執行
prepareDisplayTaskFor方法。
再根據key來判斷緩存中是否存在該圖片,如果存在,就判斷options的shouldPostProcess,如果為true就創建一個ProcessAndDisplayImageTask對象,通過圖片載入引擎來載入。如果返回的值false,則調用options.getDisplayer().display(bmp, imageAware, LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE);
如果緩存不存在,則直接通過網路載入該圖片,載入的方式是構建LoadAndDisplayImageTask對象,通過圖片載入引擎來判斷。
在這裡,關於圖片的緩存相關的內容,先不分析。接下來主要分析的是圖片如何執行這兩種不同的任務的。
第一種,在有緩存的情況下,通過判斷shouldPostProcess為true來讓圖片引擎處理任務,這裡的shouldPostProcess是指在拿到bitmap之後是否進行後續的操作,判斷標準就是postProcess是否為null.
如果不為null,也就是shouldPostProcess為true,則執行下麵的代碼:
下麵,我們來看一下,圖片引擎是如何執行ProcessAndDisplayImageTask。
void submit(ProcessAndDisplayImageTask task) {
initExecutorsIfNeed();
taskExecutorForCachedImages.execute(task);
}內部直接調用taskExecutorForCachedImages去執行task,所以主要看ProcessAndDisplayImageTask的task構造。
final class ProcessAndDisplayImageTask implements Runnable {
private static final String LOG_POSTPROCESS_IMAGE = "PostProcess image before displaying [%s]";
/*ImageLoader引擎*/
private final ImageLoaderEngine engine;
private final Bitmap bitmap;
/*ImageLoader信息封裝對象*/
private final ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo;
private final Handler handler;
/**
* 圖片處理顯示任務構造器
* @param engine
* @param bitmap
* @param imageLoadingInfo
* @param handler
*/
public ProcessAndDisplayImageTask(ImageLoaderEngine engine, Bitmap bitmap, ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo,
Handler handler) {
this.engine = engine;
this.bitmap = bitmap;
this.imageLoadingInfo = imageLoadingInfo;
this.handler = handler;
}
@Override
public void run() {
L.d(LOG_POSTPROCESS_IMAGE, imageLoadingInfo.memoryCacheKey);
//獲取圖片處理器 然後取得載入的圖片
BitmapProcessor processor = imageLoadingInfo.options.getPostProcessor();
Bitmap processedBitmap = processor.process(bitmap);
//封裝圖片顯示任務 其中圖片來源設置成-來自記憶體緩存
DisplayBitmapTask displayBitmapTask = new DisplayBitmapTask(processedBitmap, imageLoadingInfo, engine,
LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE);
//執行任務
LoadAndDisplayImageTask.runTask(displayBitmapTask, imageLoadingInfo.options.isSyncLoading(), handler, engine);
}
}這邊可以看出,task內部run方法裡面,首先得到一個BitmapProcessor,然後通過該processor去處理bitmap,然後將處理後的bitmap以及其他信息封裝成了DisplayBitmapTask,然後最終還是執行了LoadAndDisplayImageTask的runTask方法
下麵將看LoadAndDisplayImageTask.runTask方法
static void runTask(Runnable r, boolean sync, Handler handler, ImageLoaderEngine engine) {
if (sync) {
//如果同步 任務直接運行
r.run();
} else if (handler == null) {
engine.fireCallback(r);
} else {
//任務通過Handler分發到主線程執行
handler.post(r);
}
}這邊,直接在UI線程displayBitmapTask,後面再看displayBitmapTask的內部實現。
回到shouldPostProcess的判斷那裡,如果為false,則直接調用BitmapDisplay顯示圖片,這裡傳入的是SimpleBitmapDisplayer
再回到緩存判斷那裡,上面的代碼都是在有記憶體緩存的情況下,執行的。看一下在無記憶體緩存時,執行的細節。
//緩存中不存在該圖片 通過網路載入
if (options.shouldShowImageOnLoading()) {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(options.getImageOnLoading(configuration.resources));
} else if (options.isResetViewBeforeLoading()) {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(null);
}
//進行構造圖片載入任務相關的所有信息對象
ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo = new ImageLoadingInfo(uri, imageAware, targetSize, memoryCacheKey,
options, listener, progressListener, engine.getLockForUri(uri));
//分裝圖片載入和顯示任務對象 然後進行開啟執行任務
LoadAndDisplayImageTask displayTask = new LoadAndDisplayImageTask(engine, imageLoadingInfo,
defineHandler(options));
if (options.isSyncLoading()) {
displayTask.run();
} else {
engine.submit(displayTask);
}通過源碼可以看出,首先判斷要不要進行顯示載入中的View,然後構建圖片載入信息,通過圖片載入信息構建LoadAndDisplayImageTask對象,執行去run方法。
上面,我們已經分析了其runTask方法,該方法比較簡單,這次我們看一下run方法。
public void run() {
//如果當前狀態是暫停 當前任務直接返回
if (waitIfPaused()) return;
//如果當前狀態需要等待 當前任務直接返回
if (delayIfNeed()) return;
ReentrantLock loadFromUriLock = imageLoadingInfo.loadFromUriLock;
L.d(LOG_START_DISPLAY_IMAGE_TASK, memoryCacheKey);
if (loadFromUriLock.isLocked()) {
L.d(LOG_WAITING_FOR_IMAGE_LOADED, memoryCacheKey);
}
//任務加鎖
loadFromUriLock.lock();
Bitmap bmp;
try {
//進行檢查任務 判斷當前要顯示的引用對象是否已經被回收了
checkTaskNotActual();
//先從緩存中獲取圖片
bmp = configuration.memoryCache.get(memoryCacheKey);
if (bmp == null || bmp.isRecycled()) {
//進行嘗試獲取載入圖片(去文件中,文件中不存在去網路下載,然後緩存到文件)
bmp = tryLoadBitmap();
if (bmp == null) return; // listener callback already was fired
checkTaskNotActual();
checkTaskInterrupted();
if (options.shouldPreProcess()) {
L.d(LOG_PREPROCESS_IMAGE, memoryCacheKey);
bmp = options.getPreProcessor().process(bmp);
if (bmp == null) {
L.e(ERROR_PRE_PROCESSOR_NULL, memoryCacheKey);
}
}
if (bmp != null && options.isCacheInMemory()) {
L.d(LOG_CACHE_IMAGE_IN_MEMORY, memoryCacheKey);
configuration.memoryCache.put(memoryCacheKey, bmp);
}
} else {
//從緩存中獲取到圖片信息
//設置圖片來源信息 --Memory Cache
loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE;
L.d(LOG_GET_IMAGE_FROM_MEMORY_CACHE_AFTER_WAITING, memoryCacheKey);
}
if (bmp != null && options.shouldPostProcess()) {
L.d(LOG_POSTPROCESS_IMAGE, memoryCacheKey);
bmp = options.getPostProcessor().process(bmp);
if (bmp == null) {
L.e(ERROR_POST_PROCESSOR_NULL, memoryCacheKey);
}
}
checkTaskNotActual();
checkTaskInterrupted();
} catch (TaskCancelledException e) {
fireCancelEvent();
return;
} finally {
//任務取消鎖
loadFromUriLock.unlock();
}
//封裝圖片顯示任務對象
DisplayBitmapTask displayBitmapTask = new DisplayBitmapTask(bmp, imageLoadingInfo, engine, loadedFrom);
//進行任務運行
runTask(displayBitmapTask, syncLoading, handler, engine);
}其流程圖如下:
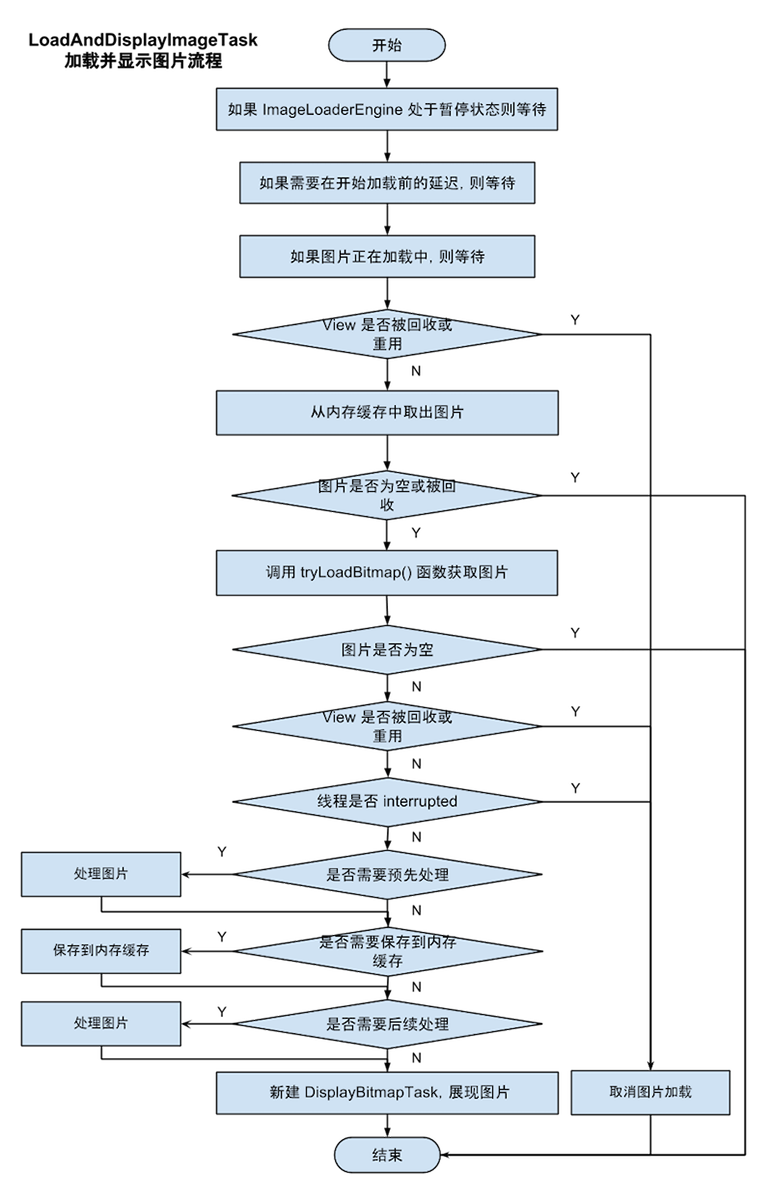
可以看到這邊,利用的圖片三級緩存,第一級是記憶體緩存,如果記憶體緩存沒有則利用二級緩存,從文件中去讀取,如果文件中有,則從文件中取出bitmap,如果沒有則從網路下載。
這邊從文件中bitmap的方法是tryLoadBitmap,下麵主要看一下這個方法
private Bitmap tryLoadBitmap() throws TaskCancelledException {
Bitmap bitmap = null;
try {
//從本地文件緩存中獲取圖片
File imageFile = configuration.diskCache.get(uri);
if (imageFile != null && imageFile.exists() && imageFile.length() > 0) {
L.d(LOG_LOAD_IMAGE_FROM_DISK_CACHE, memoryCacheKey);
//文件存在設置圖片來源
loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.DISC_CACHE;
//檢查引用是否已經被回收了
checkTaskNotActual();
//圖片解碼,文件轉換成bitmap對象
bitmap = decodeImage(Scheme.FILE.wrap(imageFile.getAbsolutePath()));
}
if (bitmap == null || bitmap.getWidth() <= 0 || bitmap.getHeight() <= 0) {
L.d(LOG_LOAD_IMAGE_FROM_NETWORK, memoryCacheKey);
//本地文件系統中圖片解碼失敗,嘗試通過網路獲取
loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.NETWORK;
String imageUriForDecoding = uri;
//判斷圖片可以本地文件系統緩存以及嘗試本地文本系統緩存(網路下載圖片,下載成功圖片緩存本地文件系統)
if (options.isCacheOnDisk() && tryCacheImageOnDisk()) {
//從本地文件系統緩存中獲取圖片
imageFile = configuration.diskCache.get(uri);
if (imageFile != null) {
imageUriForDecoding = Scheme.FILE.wrap(imageFile.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
checkTaskNotActual();
//圖片解碼
bitmap = decodeImage(imageUriForDecoding);
if (bitmap == null || bitmap.getWidth() <= 0 || bitmap.getHeight() <= 0) {
//回調圖片解碼失敗
fireFailEvent(FailType.DECODING_ERROR, null);
}
}
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
fireFailEvent(FailType.NETWORK_DENIED, null);
} catch (TaskCancelledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (IOException e) {
L.e(e);
fireFailEvent(FailType.IO_ERROR, e);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
L.e(e);
fireFailEvent(FailType.OUT_OF_MEMORY, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
L.e(e);
fireFailEvent(FailType.UNKNOWN, e);
}
//圖片存在 返回
return bitmap;
}首先是從diskcache中,取出File,然後對file進行轉換。如果轉換後的bitmap為null,則從網路獲取圖片,獲取圖片的方法調用是在options.isCacheOnDisk() && tryCacheImageOnDisk() 該判斷首先判斷是否存儲在文件中,如果不存在文件中,就不執行後面的網路獲取。
private boolean tryCacheImageOnDisk() throws TaskCancelledException {
L.d(LOG_CACHE_IMAGE_ON_DISK, memoryCacheKey);
boolean loaded;
try {
//圖片下載並且保存本地
loaded = downloadImage();
if (loaded) {
int width = configuration.maxImageWidthForDiskCache;
int height = configuration.maxImageHeightForDiskCache;
if (width > 0 || height > 0) {
L.d(LOG_RESIZE_CACHED_IMAGE_FILE, memoryCacheKey);
//根據尺寸大小配置 進行圖片縮放和保存
resizeAndSaveImage(width, height); // TODO : process boolean result
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
L.e(e);
loaded = false;
}
return loaded;
}
downloadImage是執行網路請求的方法,其內部通過BaseImageDownloader進行下載,其內部的網路庫是HttpURLConnection,下載後的圖片,根據設定的文件存儲的最大寬高,進行縮放與保存。
這樣,就在文件緩存中緩存了圖片,在回到上面LoadAndDisplayTask的run方法,在得到bitmap之後,就會判斷是否要 對bitmap進行預處理,預處理完的bitmap全部會緩存到記憶體緩存中。上面的操作都是建立在bitmap中記憶體緩存中取沒有取出來的情況,如果取出來就直接得到bitmap,然後從bitmap判斷是否進行後續的處理。
這裡,簡單說一下 preProcessor以及postProcessor,preProcessor是指對圖片進行預處理,比如加水印,如果加水印的圖片都會緩存到記憶體,postProcessor是對取出的bitmap做一些後續的操作,操作後將顯示出來。
最後得到的Bitmap會封裝成DisplayBitmapTask,調用上面提到的runtask方法,進行處理。
這樣,到此,發起圖片獲取需求,到圖片經過記憶體緩存,文件緩存,網路獲取後得到,然後再通過Handler回到UI線程的流程就分析完畢了。
其實,整個流程非常的簡單,清晰。只不過在考慮到了多種情況,使得代碼看上去很多。
下麵,將分析圖片載入框架最重要的一部分,緩存的設計。



