java8 (jdk 1.8) 新特性 ——初步認識 1. 什麼是lambda? 目前已知的是,有個箭頭 -> 說一大段官方話,也沒有任何意義 我們直接看代碼: 之前我們創建線程是這樣的 Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { @Override public vo ...
1. 什麼是lambda?
目前已知的是,有個箭頭 ->
說一大段官方話,也沒有任何意義
我們直接看代碼:
之前我們創建線程是這樣的
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("run。。。。。。"); } }; runnable.run();
用lambda:
Runnable run2 = () -> System.out.println("run。。。。。。");
run2.run();
是不是感覺特別離譜,看不懂
別急,還有更離譜的
很常見的一個例子,比較兩個整數的大小
之前是這樣寫的
Comparator<Integer> myCom = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1, o2);
}
};
int compare = myCom.compare(12, 20);
int compare1 = myCom.compare(20, 12);
int compare2 = myCom.compare(20, 20);
System.out.println(compare);
System.out.println(compare1);
System.out.println(compare2);
}
用lambda:
Comparator<Integer> myCom = (o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1, o2);
int compare = myCom.compare(12, 20);
int compare1 = myCom.compare(20, 12);
int compare2 = myCom.compare(20, 20);
System.out.println(compare);
System.out.println(compare1);
System.out.println(compare2);
甚至還可以這樣 (這個是方法引用)
Comparator<Integer> myCom = Integer::compare;
int compare = myCom.compare(12, 20);
int compare1 = myCom.compare(20, 12);
int compare2 = myCom.compare(20, 20);
System.out.println(compare);
System.out.println(compare1);
System.out.println(compare2);
第一個數比第二個數
大 :返回 1
小:返回 -1
相等:返回 0
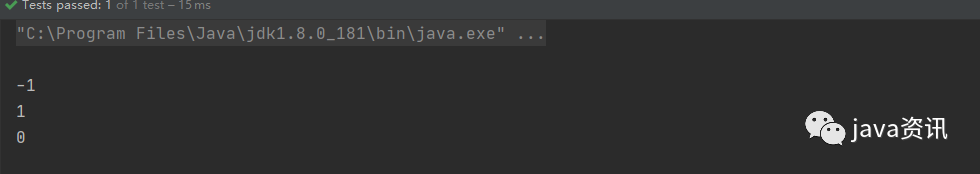
剛接觸是不是黑人問號,這是什麼玩意
很好,到這,你認識到了lambda 一個缺點,可閱讀性差 ,優點 代碼簡潔
小結:看到 -> lambda 看到 : : 方法引用
2. lamdba 語法
-
基本語法
1. 箭頭操作符 -> 或者叫做lambda 操作符
2. 箭頭操作符將lambda 表達式拆分成兩部分
左側:Lambda 表達式的參數列表
右側:Lambda 表達式中所需執行的功能 , 即 Lambda 體
3. 語法格式
語法格式1:無參數,無返回值
-
() -> system.out.println("Hello Lambda")前邊線程的那個例子就是
語法格式2:有一個參數 無返回值
(x)-> System.out.println(x);
若只有一個參數可以省略不寫
x-> System.out.println(x);
之前的寫法,沒有使用lambda
Consumer<String> consumer = new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println("輸出的值:"+s);
}
};
consumer.accept("今天不想emo了");
使用lambda
Consumer<String> consumer = s -> System.out.println("輸出的值:"+s);
consumer.accept("今天不想emo了");
語法格式3:有兩個以上參數 ,並且lambda體有多條語句,有返回值
Comparator<Integer> myCom = (o1, o2) -> {
System.out.println("其他語句");
return Integer.compare(o1, o2);
};
語法格式4 lambda體中只有一條語句,return 和 大括弧都可以省略不寫
Comparator<Integer> com =(x,y)-> Integer.compare(x,y);
有沒有發現所有的參數,都沒有參數類型,之前我們寫函數的時候可是要帶上參數類型的
語法格式5 lambda表達式參數列表的數據類型可以省略不寫,因為JVM編譯器通過上下文編譯推斷出數據類型——類型推斷
4. 函數式介面
不管上面哪一種語法格式,lambda都是需要函數式介面的支持
函數式介面:介面中只有一個抽象方法的介面 稱為函數式介面
可以使用一個註解@FunctionalInterface 修飾,可以檢查是否是函數式介面
我們可以看看Runnable 介面 的源碼
完成的介面類代碼如下
/*
* Copyright (c) 1994, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms
/
package java.lang;
/**
* The <code>Runnable</code> interface should be implemented by any
* class whose instances are intended to be executed by a thread. The
* class must define a method of no arguments called <code>run</code>.
* <p>
* This interface is designed to provide a common protocol for objects that
* wish to execute code while they are active. For example,
* <code>Runnable</code> is implemented by class <code>Thread</code>.
* Being active simply means that a thread has been started and has not
* yet been stopped.
* <p>
* In addition, <code>Runnable</code> provides the means for a class to be
* active while not subclassing <code>Thread</code>. A class that implements
* <code>Runnable</code> can run without subclassing <code>Thread</code>
* by instantiating a <code>Thread</code> instance and passing itself in
* as the target. In most cases, the <code>Runnable</code> interface should
* be used if you are only planning to override the <code>run()</code>
* method and no other <code>Thread</code> methods.
* This is important because classes should not be subclassed
* unless the programmer intends on modifying or enhancing the fundamental
* behavior of the class.
*
* @author Arthur van Hoff
* @see java.lang.Thread
* @see java.util.concurrent.Callable
* @since JDK1.0
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}
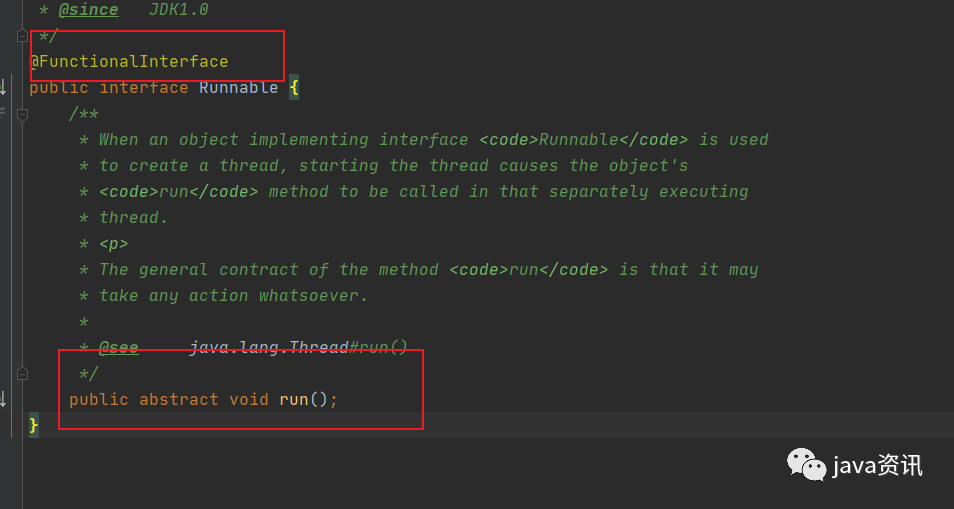
可以看到這裡面就只有一個實現,有一個註解@FunctionalInterface ,說明它就是一個函數式介面,就可以進行lambda簡寫
來看 Comparator 也是一樣 有@FunctionalInterface註解
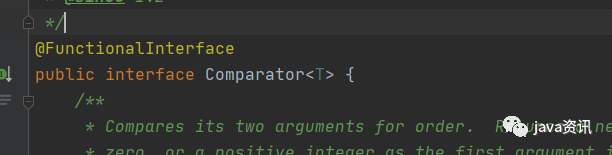
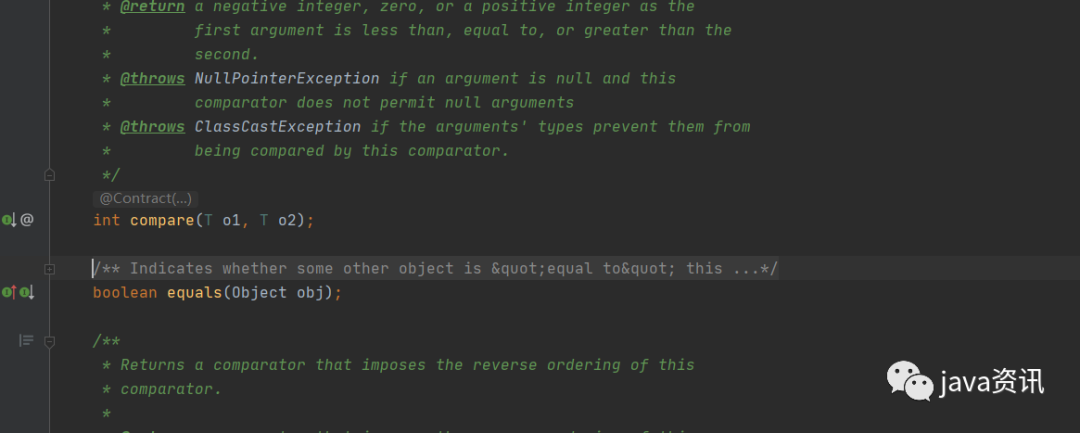
這裡可能就會有疑問,這邊明明是有兩個抽象方法,怎麼是函數式介面呢?
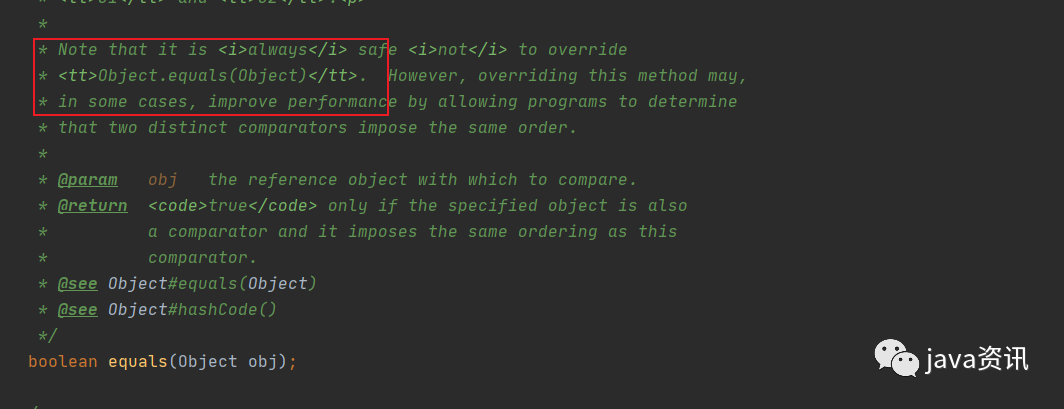
別急 !!可以看到這邊的註釋, 說明這個equals 是 重寫了超類 的 equals,本質上是對object 的重寫,官方定義這樣的抽象方法是不會被定義到 抽象介面數的 ,因此實際上只有一個抽象方法
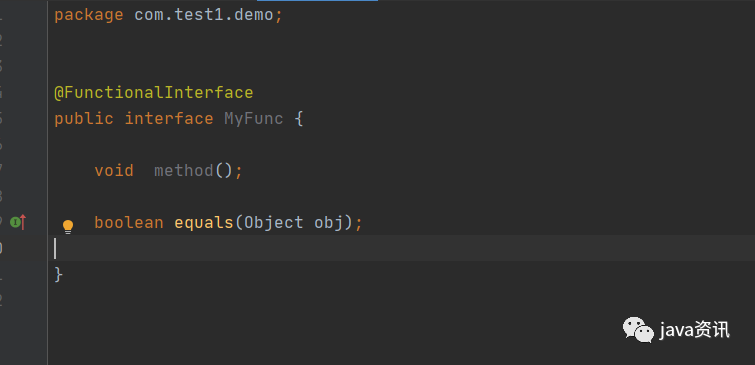
我們自己可以試著定義 函數式介面,很簡單
package com.test1.demo;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyFunc {
void method();
}
好了,如果,寫兩個抽象介面會怎樣?
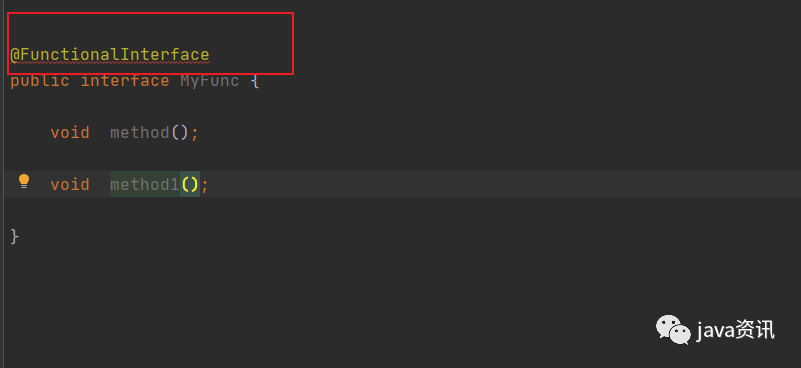
可以看到註解報錯了,所以註解用來校驗作用就在這
重申一遍,函數式介面:介面中只有一個抽象方法的介面 稱為函數式介面
註解只是拿來校驗的,方便我們一看就知道這是一函數式介面類,不然還得數個數,驗證一下是不是只有一個
現在我也重寫 equals ,可以看到並沒有報錯
5. java8 中內置四大核心函數式介面
-
Consumer<T> 消費型介面
//Consumer 消費型介面
@Test
public void testConsumer() {
cosumer(1000, (m) -> System.out.println("星期一" + m));
// 星期一1000.0
}
public void cosumer(double m, Consumer<Double> con) {
con.accept(m);
}
-
供給型介面 supplier<T>
@Test
public void testSupplier() {
List<Integer> numList = getNumList(10, () -> (int) (Math.random() * 100));
for (Integer integer : numList) {
System.out.println(integer); //100 以內10位隨機整數
}
}
// 需求:產生指定個數的整數放入集合中
public List<Integer> getNumList(int num, Supplier<Integer> su) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
Integer integer = su.get();
list.add(integer);
}
return list;
}
-
Function<T,R> 函數型介面
@Test
public void FunctioStr(){
String c = getFunction("sbjikss", str -> str.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(c); //SBJIKSS
String sub = getFunction("sbjikss", str -> str.substring(2, 3));
System.out.println(sub);//j
}
public String getFunction( String str, Function<String,String> f) {
return f.apply(str);
}
-
斷言型介面 Predicate<T>
public void tetPre(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Hello","sss","xxxx","sjjss");
List<String> list1 = filterStr(list, (pre) -> pre.length() > 3);
for (String s : list1) {
System.out.println(s); // Hello xxxx sjjss
}
}
//需求:將滿足條件字元串放入集合中
public List<String> filterStr(List<String> old , Predicate<String> pre ){
List<String> newList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : old) {
if (pre.test(str)){
newList.add(str);
}
}
return newList;
}
感謝閱讀!!!



