面試最常問的問題 1、equals比較的什麼? 2、有沒有重寫過equals? 3、有沒有重寫過hashCode? 4、什麼情況下需要重寫equals()和hashCode()? 1) equals源碼 **目標:**如果不做任何處理(可能絕大大大多數場景的對象都是這樣的),jvm對同一個對象的判斷 ...

面試最常問的問題
1、equals比較的什麼?
2、有沒有重寫過equals?
3、有沒有重寫過hashCode?
4、什麼情況下需要重寫equals()和hashCode()?
1) equals源碼
目標:如果不做任何處理(可能絕大大大多數場景的對象都是這樣的),jvm對同一個對象的判斷邏輯是怎樣的
我們先讀一下Object里的源碼:
/**
* Indicates whether some other object is "equal to" this one.
* <p>
* The {@code equals} method implements an equivalence relation
* on non-null object references:
* <ul>
* <li>It is <i>reflexive</i>: for any non-null reference value
* {@code x}, {@code x.equals(x)} should return
* {@code true}.
* <li>It is <i>symmetric</i>: for any non-null reference values
* {@code x} and {@code y}, {@code x.equals(y)}
* should return {@code true} if and only if
* {@code y.equals(x)} returns {@code true}.
* <li>It is <i>transitive</i>: for any non-null reference values
* {@code x}, {@code y}, and {@code z}, if
* {@code x.equals(y)} returns {@code true} and
* {@code y.equals(z)} returns {@code true}, then
* {@code x.equals(z)} should return {@code true}.
* <li>It is <i>consistent</i>: for any non-null reference values
* {@code x} and {@code y}, multiple invocations of
* {@code x.equals(y)} consistently return {@code true}
* or consistently return {@code false}, provided no
* information used in {@code equals} comparisons on the
* objects is modified.
* <li>For any non-null reference value {@code x},
* {@code x.equals(null)} should return {@code false}.
* </ul>
* <p>
* 該方法用於識別兩個對象之間的相似性
* 也就是說,對於一個非null值,x和y,當且僅當它們指向同一個對象時才會返回true
* 言外之意,和==沒啥兩樣。
* The {@code equals} method for class {@code Object} implements
* the most discriminating possible equivalence relation on objects;
* that is, for any non-null reference values {@code x} and
* {@code y}, this method returns {@code true} if and only
* if {@code x} and {@code y} refer to the same object
* ({@code x == y} has the value {@code true}).
* <p>
* Note that it is generally necessary to override the {@code hashCode}
* method whenever this method is overridden, so as to maintain the
* general contract for the {@code hashCode} method, which states
* that equal objects must have equal hash codes.
*
* @param obj the reference object with which to compare.
* @return {@code true} if this object is the same as the obj
* argument; {@code false} otherwise.
* @see #hashCode()
* @see java.util.HashMap
*/
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
猜想:如果我們不做任何操作,equals將繼承object的方法,那麼它和==也沒啥區別!
下麵一起做個面試題,驗證一下這個猜想:
package com.eq;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class DefaultEq {
String name;
public DefaultEq(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultEq eq1 = new DefaultEq("張三");
DefaultEq eq2 = new DefaultEq("張三");
DefaultEq eq3 = eq1;
//雖然倆對象外面看起來一樣,eq和==都不行
//因為我們沒有改寫equals,它使用預設object的,也就是記憶體地址
System.out.println(eq1.equals(eq2));
System.out.println(eq1 == eq2);
System.out.println("----");
//1和3是同一個引用
System.out.println(eq1.equals(eq3));
System.out.println(eq1 == eq3);
System.out.println("===");
//以上是對象,再來看基本類型
int i1 = 1;
Integer i2 = 1;
Integer i = new Integer(1);
Integer j = new Integer(1);
Integer k = new Integer(2);
//只要是基本類型,不管值還是包裝成對象,都是直接比較大小
System.out.println(i.equals(i1)); //比較的是值
System.out.println(i==i1); //拆箱 ,
// 封裝對象i被拆箱,變為值比較,1==1成立
//相當於 System.out.println(1==1);
System.out.println(i.equals(j)); //
System.out.println(i==j); // 比較的是地址,這是倆對象
System.out.println(i2 == i); // i2在常量池裡,i在堆里,地址不一樣
System.out.println(i.equals(k)); //1和2,不解釋
}
}
結論:
-
“==”比較的是什麼?
用於基本數據(8種)類型(或包裝類型)相互比較,比較二者的值是否相等。
用於引用數據(類、介面、數組)類型相互比較,比較二者地址是否相等。
-
equals比較的什麼?
預設情況下,所有對象繼承Object,而Object的equals比較的就是記憶體地址
所以預設情況下,這倆沒啥區別
2) 記憶體地址生成與比較
tips:既然沒區別,那我們看一下,記憶體地址到底是個啥玩意
目標:記憶體地址是如何來的?
Main.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user1=new User("張三");
User user2=new User("張三");
}
1、載入過程(回顧)
從java文件到jvm:
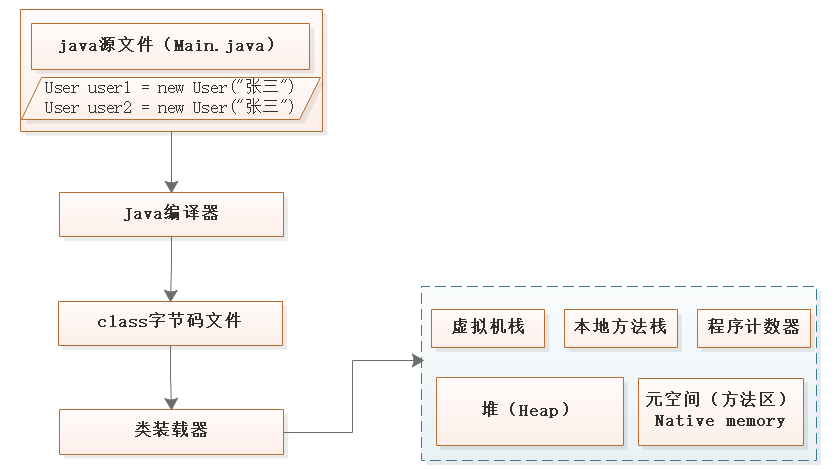
tips: 載入到方法區
這個階段只是User類的信息進入方法區,還沒有為兩個user來分配記憶體
2、分配記憶體空間
在main線程執行階段,指針碰撞(連續記憶體空間時),或者空閑列表(不連續空間)方式開闢一塊堆記憶體
每次new一個,開闢一塊,所以兩個new之間肯定不是相同地址,哪怕你new的都是同一個類型的class。
那麼它如何來保證記憶體地址不重覆的呢?(cas畫圖)
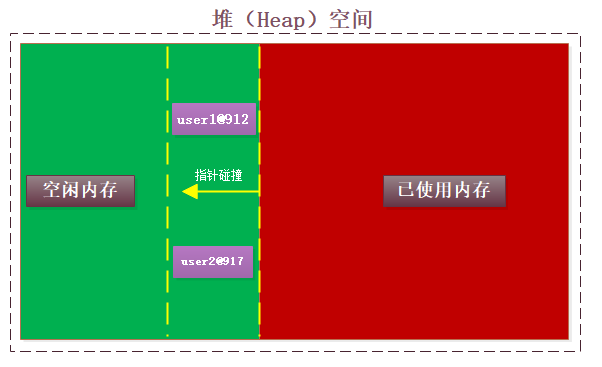
3、指向
在棧中創建兩個局部變數 user1,user2,指向堆里的記憶體
歸根到底,上面的==比較的是兩個對象的堆記憶體地址,也就是棧中局部變數表裡存儲的值。
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);//本類比較的是記憶體地址(引用)
}
3) 預設equals的問題
需求(or 目標):user1和user2,如果name一樣我們就認為是同一個人;如何處理?
tips:
面試最常問的問題
1、equals比較的什麼?
2、有沒有重寫過equals?
3、有沒有重寫過hashCode?
4、什麼情況下需要重寫equals()和hashCode()?
1、先拿User下手,看看它的預設行為(com.eq.EqualsObjTest)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求::user1和user2,在現實生活中是一個人;如何判定是一個人(相等)
User user1 = new User("張三");
User user2 = new User("張三");
System.out.println("是否同一個人:"+user1.equals(user2));
System.out.println("記憶體地址相等:"+String.valueOf(user1 == user2));//記憶體地址
System.out.println("user1的hashCode為>>>>" + user1.hashCode());
System.out.println("user2的hashCode為>>>>" + user2.hashCode());
}
輸出如下

結論:
很顯然,預設的User繼承了Object的方法,而object,根據上面的源碼分析我們知道,equals就是記憶體地址。
而你兩次new User,不管name怎麼一致,記憶體分配,肯定不是同一個地址!
怎麼破?
2、同樣的場景,我們把用戶名從User換成單純的字元串試試(com.eq.EqualsStrTest)
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "張三";//常量池
String str2 = new String("張三");//堆中
String str3 = new String("張三");//堆中
System.out.println("是否同一人:"+str1.equals(str2));//這個地方為什麼相等呢,重寫
System.out.println("是否同一人:"+str2.equals(str3));//這個地方為什麼相等呢,重寫
//如果相等,hashcode必須相等,重寫
System.out.println("str1的hashCode為>>" + str1.hashCode());
System.out.println("str2的hashCode為>>" + str2.hashCode());
}
}
輸出如下

達到了我們的逾期,相同的name,被判定為同一個人,為什麼呢?往下看!
String的源碼分析
/**
* Compares this string to the specified object. The result is {@code
* true} if and only if the argument is not {@code null} and is a {@code
* String} object that represents the same sequence of characters as this
* object.
*
* @param anObject
* The object to compare this {@code String} against
*
* @return {@code true} if the given object represents a {@code String}
* equivalent to this string, {@code false} otherwise
*
* @see #compareTo(String)
* @see #equalsIgnoreCase(String)
*/
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
//如果記憶體地址相等,那必須equal
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
//如果對象是String類型
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
//並且長度還相等!
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
//那我們就逐個字元的比較
while (n-- != 0) {
//從前往後,任意一個字元不匹配,直接返回false
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
//全部匹配結束,返回true
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
結論:
String類型改寫了equals方法,沒有使用Object的預設實現
它不管你是不是同一個記憶體地址,只要倆字元串里的字元都匹配上,那麼equals就認為它是true
3、據此,我們參照String,來重寫User的equals和hashCode(com.eq.User2)
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
//註意這些額外的判斷類操作
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
//比較值
return name != null ? name.equals(user.name) : user.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
//返回值的hashCode
return name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
}
換成User2 再來跑試試 (參考 com.eq.EqualsObjTest2)

目的達到!
4)hashCode與equals
為什麼說hashCode和equals是一對搭檔?他倆到底啥關係需要綁定到一塊?
看代碼說話:(com.eq.Contains)
package com.eq;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Contains {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user1 = new User("張三");
User user2 = new User("張三");
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(user1);
System.out.println(set.contains(user2));
User2 user3 = new User2("張三");
User2 user4 = new User2("張三");
Set set2 = new HashSet();
set2.add(user3);
System.out.println(set2.contains(user4));
}
}
結論:
hashCode是給java集合類的一些動作提供支撐,來判斷倆對象“是否是同一個”的標準
equals是給你編碼時判斷用的,所以,這倆必須保持一致的邏輯。
5)總結
1、特殊業務需求需要重寫,比如上面的
2、例如map,key放自定義對象也需要重寫
3、重寫equals後必須要重寫hashCode,要保持邏輯上的一致!
1.2.5 關於雙等(擴展)
equals被重寫後,雙等還留著幹啥用?
1)String的特殊性
tips:面試常問的問題
intern是做什麼的?
先來看一段代碼:(com.eq.Intern)
public class Intern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "張三";//常量池
String str2 = new String("張三");//堆中
//intern;記憶體地址是否相等(面試常問)
System.out.println("str1與str2是否相等>>" +(str1==str2)); // false
System.out.println("str1與str2是否相等>>" +(str1==str2.intern())); // true
}
}
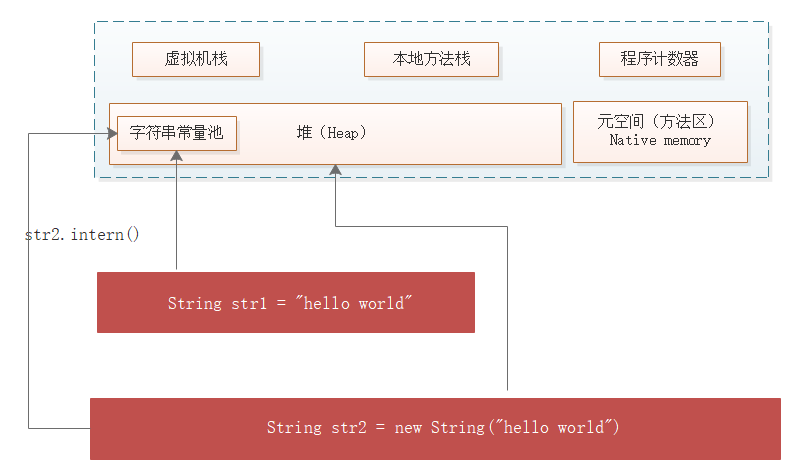
版本聲明:(JDK1.8)
new String是在堆上創建字元串對象。
當調用 intern() 方法時,
JVM會將字元串添加(堆引用指向常量池)到常量池中註意:
1、1.8版本只是將hello word在堆中的引用指向常量池,之前的版本是把hello word複製到常量池
2、堆(字元串常量值) 方法區(運行時常量池)不要搞反了
2)valueOf里的秘密
關於雙等號地址問題,除了String.intern() , 在基礎類型里,如Integer,Long等同樣有一個方法:valueOf需要註意
我們先來看一個小例子: 猜一猜結果?
package com.eq;
public class Valueof {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println( Integer.valueOf(127) == Integer.valueOf(127));
System.out.println( Integer.valueOf(128) == Integer.valueOf(128));
}
}
奇怪的結果……
源碼分析(以Integer為例子):
/**
* Returns an {@code Integer} instance representing the specified
* {@code int} value. If a new {@code Integer} instance is not
* required, this method should generally be used in preference to
* the constructor {@link #Integer(int)}, as this method is likely
* to yield significantly better space and time performance by
* caching frequently requested values.
*
* !在-128 到 127 之間會被cache,同一個地址下,超出後返回new對象!
*
* This method will always cache values in the range -128 to 127,
* inclusive, and may cache other values outside of this range.
*
* @param i an {@code int} value.
* @return an {@code Integer} instance representing {@code i}.
* @since 1.5
*/
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
本文由傳智教育博學谷 - 狂野架構師教研團隊發佈
如果本文對您有幫助,歡迎關註和點贊;如果您有任何建議也可留言評論或私信,您的支持是我堅持創作的動力
轉載請註明出處!



