今天我們來講解leetcode案例分析,如何動態規劃的解題套路,態規劃的核心思想,以前經常會遇到動態規劃類型題目。 ...
依賴
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpmime</artifactId>
<version>4.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.14</version>
</dependency>
調用
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClientProtocolException, URISyntaxException, IOException {
String s =
writeWordFile("d:/", "ab.doc", getHttpData(s));
System.out.println("ok");
}
獲取網頁
// 請求網路自考網數據
public static String getHttpData(String url) throws URISyntaxException, ClientProtocolException, IOException {
List<NameValuePair> nameValuePairList = Lists.newArrayList();
nameValuePairList.add(new BasicNameValuePair("q", "x"));
URI uri = new URIBuilder(url).addParameters(nameValuePairList).build();
List<Header> headerList = Lists.newArrayList();
headerList.add(new BasicHeader(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT_ENCODING, "gzip, deflate"));
headerList.add(new BasicHeader(HttpHeaders.CONNECTION, "keep-alive"));
HttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setDefaultHeaders(headerList).build();
HttpUriRequest httpUriRequest = RequestBuilder.get().setUri(uri).build();
HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpUriRequest);
HttpEntity entity = httpResponse.getEntity();
String rawHTMLContent = EntityUtils.toString(entity);
EntityUtils.consume(entity);
return rawHTMLContent;
}
寫入本地
public static void writeWordFile(String path, String fileName, String content) {
try {
if (!"".equals(path)) {
// 檢查目錄是否存在
File fileDir = new File(path);
if (fileDir.exists()) {
byte b[] = content.getBytes();
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(b);
POIFSFileSystem poifs = new POIFSFileSystem();
DirectoryEntry directory = poifs.getRoot();
DocumentEntry documentEntry = directory.createDocument("WordDocument", bais);
FileOutputStream ostream = new FileOutputStream(path + fileName);
poifs.writeFilesystem(ostream);
bais.close();
ostream.close();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
import
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.http.Header;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpUriRequest;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.RequestBuilder;
import org.apache.http.client.utils.URIBuilder;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicHeader;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.DirectoryEntry;
import org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.DocumentEntry;
import org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.POIFSFileSystem;
import org.assertj.core.util.Lists;
window.addEventListener來解決讓一個js事件執行多個函數
本篇文章來簡單介紹一下JS作用域,以及BOM對象中的三個基礎對象,分別是window對象、history對象和location對象。
一、JS作用域
1、函數嵌套作用域
//函數作用域
var place="Beijing"; //外部定義的變數
function outer()
{
var place="Chengdu"; //outer函數下的重新定義
function inner()
{
var place="Guangzhou"; //inner函數下的定義
console.log(place);
}
inner();
}
// //調用outer函數,同時會執行inner函數
outer();
執行結果:
Guangzhou
2、函數多調用
var name="路飛";
function bar()
{
console.log(name);
}
function func()
{
var name="索隆";
return bar;
}
var ret=func(); //將func函數執行的返回結果賦值給ret變數,即ret將代表bar函數
ret(); //調用ret函數,即bar函數
//又因為bar函數的作用域在外部,與它同級的name變數值為“路飛”
執行結果:
路飛
二、window視窗
1、BOM簡介
BOM(瀏覽器對象模型),可以對瀏覽器視窗進行訪問和操作。使用 BOM,開發者可以移動視窗、改變狀態欄中的文本以及執行其他與頁面內容不直接相關的動作。使 JavaScript 有能力與瀏覽器“對話”。
2、window對象方法彙總
- alert() 顯示帶有一段消息和一個確認按鈕的警告框。
window.alert("歡迎訪問!");

- confirm() 顯示帶有一段消息以及確認按鈕和取消按鈕的對話框。
var ret= window.confirm("您確定要訪問嗎?"); //由用戶做出選擇,因此有一個返回值
console.log(ret);
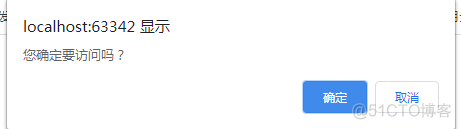
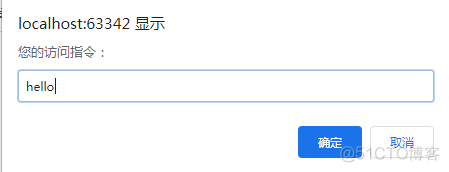
- prompt() 顯示可提示用戶輸入的對話框。
var ret= window.prompt("您的訪問指令:"); //要去用戶輸入內容,在控制台顯示
console.log(ret);
- open() 打開一個新的瀏覽器視窗或查找一個已命名的視窗。(不常用)
- close() 關閉瀏覽器視窗。(不常用)
- setInterval() 按照指定的周期(以毫秒計)來調用函數或計算表達式。
- clearInterval() 取消由 setInterval() 設置的 timeout。
setInterval(func,1000); //表示每隔1000毫秒(1秒)執行一次函數func()
function func()
{
console.log("Hello JavaScript!");
}
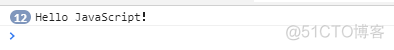
可以看到這個地方會一直有"Hello JavaScript!"的出現。
下麵是由setInterval和clearInterval實現的動態時間更新小案例…
JS(<script>標簽內的)代碼:
showTime();
function showTime()
{
var current_time=new Date().toLocaleString(); //獲取當前時間並將其轉化成字字元串顯示
// alert(current_time);
var ele=document.getElementById("id1"); //獲取id1這個標簽的內容
ele.value=current_time; //將獲取的id1標簽的內容設置為輸入框的值,實現動態更新時間
}
var click1
function begin()
{
if(click1==undefined) //防止多個click串列
{
showTime(); //實現無延遲效果
click1= setInterval(showTime,1000); //實現一秒更新一次時間
}
}
function end()
{
clearInterval(click1); //清除定時間隔
}
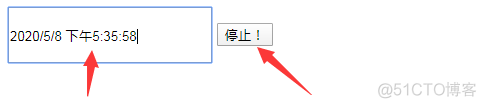
外部再加兩個標簽:
<input type="text" id="id1" onclick="begin()">
<button onclick="end()">停止!</button> <!-- 綁定一個end函數 -->
- setTimeout() 在指定的毫秒數後調用函數或計算表達式。
- clearTimeout() 取消由 setTimeout() 方法設置的 timeout。
function func()
{
console.log("別點我了!");
}
var c= setTimeout(func,3000); //三秒鐘之後只執行一次
//清除setTimeout 的內容
// clearTimeout(c);
scrollTo() 把內容滾動到指定的坐標。(少用)
三、history對象
1、簡介
History 對象包含用戶(在瀏覽器視窗中)訪問過的 URL。
History 對象是 window 對象的一部分,可通過 window.history 屬性對其進行訪問。
2、history對象的方法
- back() 載入 history 列表中的前一個 URL。
- forward() 載入 history 列表中的下一個 URL。
- go() 載入 history 列表中的某個具體頁面。
3、測試代碼例如:進口氣動球閥頁面
history1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="JS之history2.html">通往history2</a>
<button onclick="history.forward()"> >>>>>>>> </button>
<script>
</script>
</body>
</html>
history2:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="history.back()">Back</button>
</body>
</html>
這樣就可以實現一個基本的前進和返回的效果(這個其實也不太常用)
四、location對象
1、簡介
Location 對象包含有關當前 URL 的信息。
Location 對象是 Window 對象的一個部分,可通過 window.location 屬性來訪問。
2、location下的方法
- location.assign(URL)
- location.reload()
- location.replace(newURL)//註意與assign的區別
3、測試代碼
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="f()">點我!</button>
<script>
function f1()
{
// location.assign("www.baidu.com"); //預設跳轉的頁面
// location.reload(); //刷新當前頁面
location.replace("www.baidu.com"); //替換當前頁面
//assign可以後退,replace不行
}
</script>
</body>
</html>



