前言 logistic回歸,是一個分類演算法,可以處理二元分類,多元分類。我們使用sklearn中的logistic對手寫數字識別進行實踐。 數據集 MNIST數據集來自美國國家標準與技術研究所,訓練集由250個不同人手寫數字構成,50%高中學生,50%來自人口普查局。 數據集展示 數據集下載 百度雲 ...
前言
logistic回歸,是一個分類演算法,可以處理二元分類,多元分類。我們使用sklearn中的logistic對手寫數字識別進行實踐。
數據集
MNIST數據集來自美國國家標準與技術研究所,訓練集由250個不同人手寫數字構成,50%高中學生,50%來自人口普查局。
數據集展示
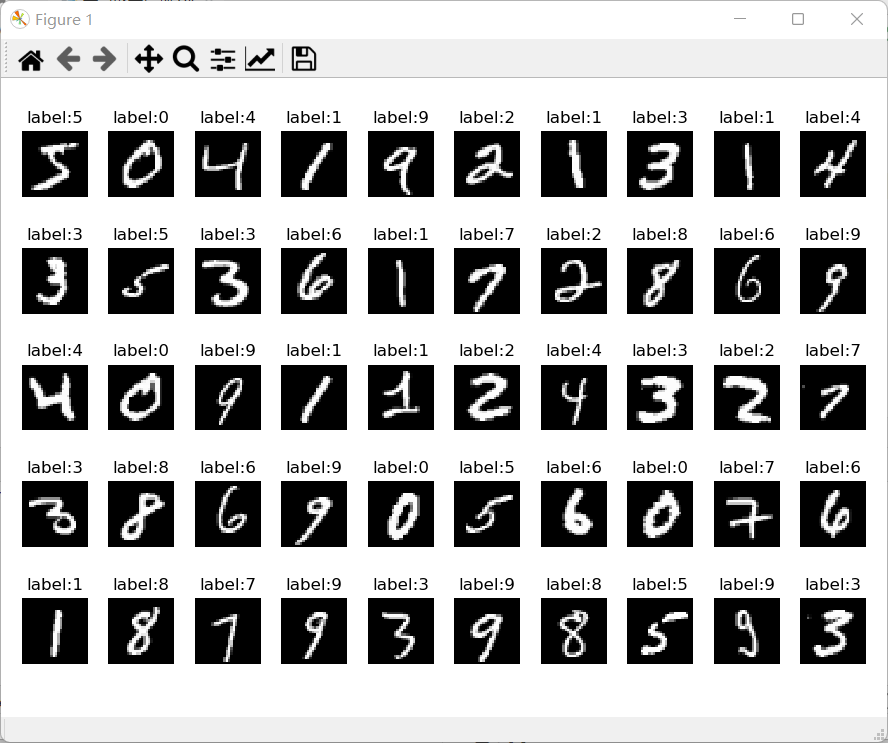
數據集下載
百度雲盤:
鏈接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ZBU8XBsx7lp7gdN4ySSIWg
提取碼:5mrf
關於使用pycharm圖片不顯示
pycharm預設會在右邊進行繪圖,由於某些原因導致圖片不能顯示,只能是白圖的解決辦法。
-
我們可以首先把圖片顯示調到獨立畫框顯示。file->settings->Tools->Python Scientific 取消勾選 show plots in tool window.
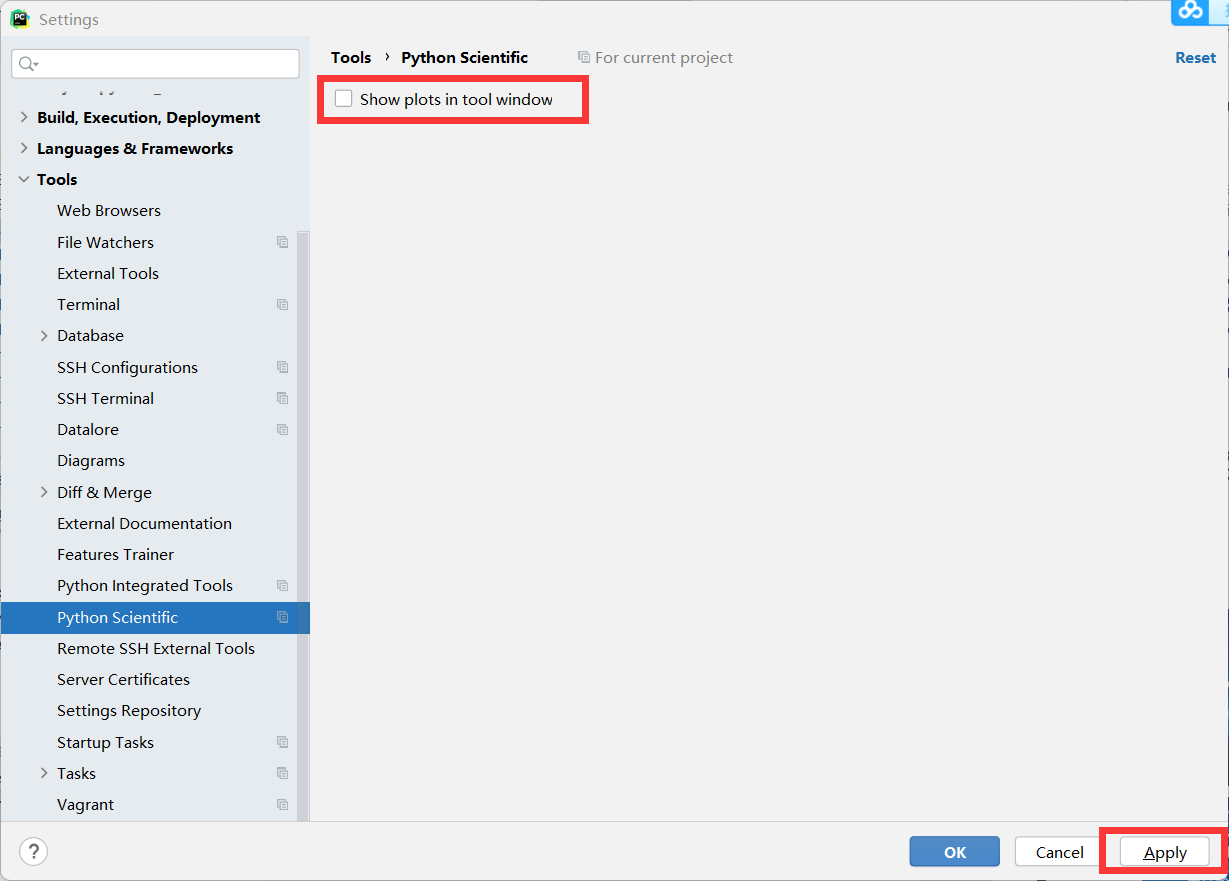
-
進行上述操作之後會獨立彈出畫框進行畫圖,如果仍然不能顯示可以進行下麵操作。
-
找到Configure subplots
-
點擊緊湊佈局,就能顯示,之前不能顯示可能是因為圖太大,導致我們沒有看到。
- 當然你也可以自己調整佈局,行距列距什麼的。
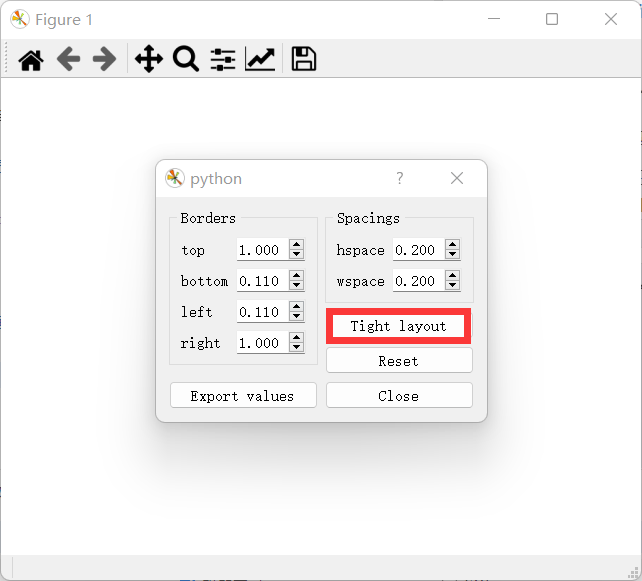
- 當然你也可以自己調整佈局,行距列距什麼的。
-
邏輯回歸手寫數字識別
## logistis回歸,是一個分類演算法,可以處理二元分類,多元分類。
## 首先邏輯回歸構造冠以的線性回歸函數,然後使用sigmoid函數將回歸值映射到散列類別
## sklearn 分類演算法與手寫數字識別
## 數據介紹
## MNIST數據集來自美國國家標準與技術研究所,訓練集由250個不同人手寫數字構成,50%高中學生,50%來自人口普查局
## 導包
import struct,os
import numpy as np
from array import array as pyarray
from numpy import append,array,int8,uint8,zeros
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
## 載入數據集
def load_mnist(image_file,label_file,path="mnist"):
digits=np.arange(10)
fname_image = os.path.join(path,image_file)
fname_label = os.path.join(path, label_file)
flbl = open(fname_label,'rb')
magic_nr, size = struct.unpack(">II", flbl.read(8))
lbl = pyarray("b",flbl.read())
flbl.close()
fimg = open(fname_image,'rb')
magic_nr, size, rows, cols = struct.unpack(">IIII", fimg.read(16))
img = pyarray("B",fimg.read())
fimg.close()
ind = [ k for k in range(size) if lbl[k] in digits ]
N = len(ind)
images = zeros((N, rows*cols),dtype = uint8)
labels = zeros((N,1), dtype = int8)
for i in range(len(ind)):
images[i] = array(img[ind[i]*rows*cols : (ind[i]+1)*rows*cols]).reshape((1,rows*cols))
labels[i] = lbl[ind[i]]
return images,labels
train_image, train_label = load_mnist('train-images.idx3-ubyte', 'train-labels.idx1-ubyte')
test_image, test_label = load_mnist('t10k-images.idx3-ubyte','t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte')
## 數據展示
## 28*28
def show_image(imgdata, imgtarget, show_column, show_row,titlename):
for index, (im, it) in enumerate(list(zip(imgdata, imgtarget))):
xx = im.reshape(28,28)
plt.subplots_adjust(left=1, bottom=None, right=3,top=2, wspace=None, hspace=None)
plt.subplot(show_row,show_column,index+1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(xx, cmap='gray', interpolation='nearest')
plt.title(titlename+':%i' % it)
# plt.savefig(titlename+'.png')
# 這個地方可能會有一個警告,可能因為圖太大了,不過沒關係,代碼正常運行
plt.show()
show_image(train_image[:50], train_label[:50],10,5,'label')
## sklearn 分類模型
## 數據歸一化
train_image = [im/255.0 for im in train_image]
test_image = [im/255.0 for im in test_image]
print(len(train_image))
print(len(test_image))
print(len(train_label))
print(len(test_label))
## 模型分類
## 模型實例化
lr = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)
## 模型訓練
lr.fit(train_image,train_label.ravel())
## 模型驗證
predict = lr.predict(test_image)
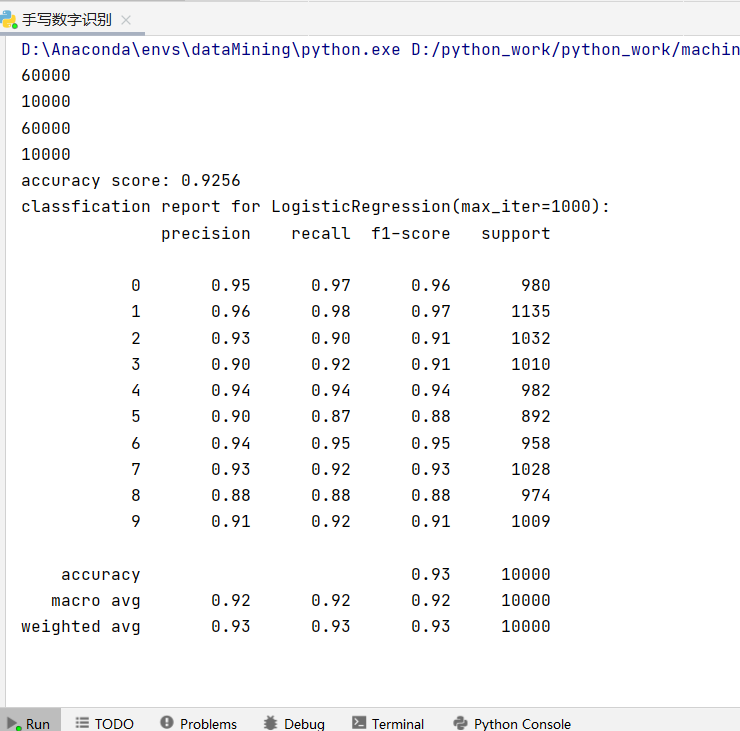
print("accuracy score: %.4lf"% accuracy_score(predict,test_label))
print("classfication report for %s:\n%s\n"%(lr, classification_report(test_label, predict)))
show_image(test_image[:100],predict,10,10,'predict')
結果展示
- 模型訓練信息
- 可以看到
- 準確度:0.9256
- 訓練次數最大1000次
- 精度、平均值、加權平均值等
- 識別效果展示
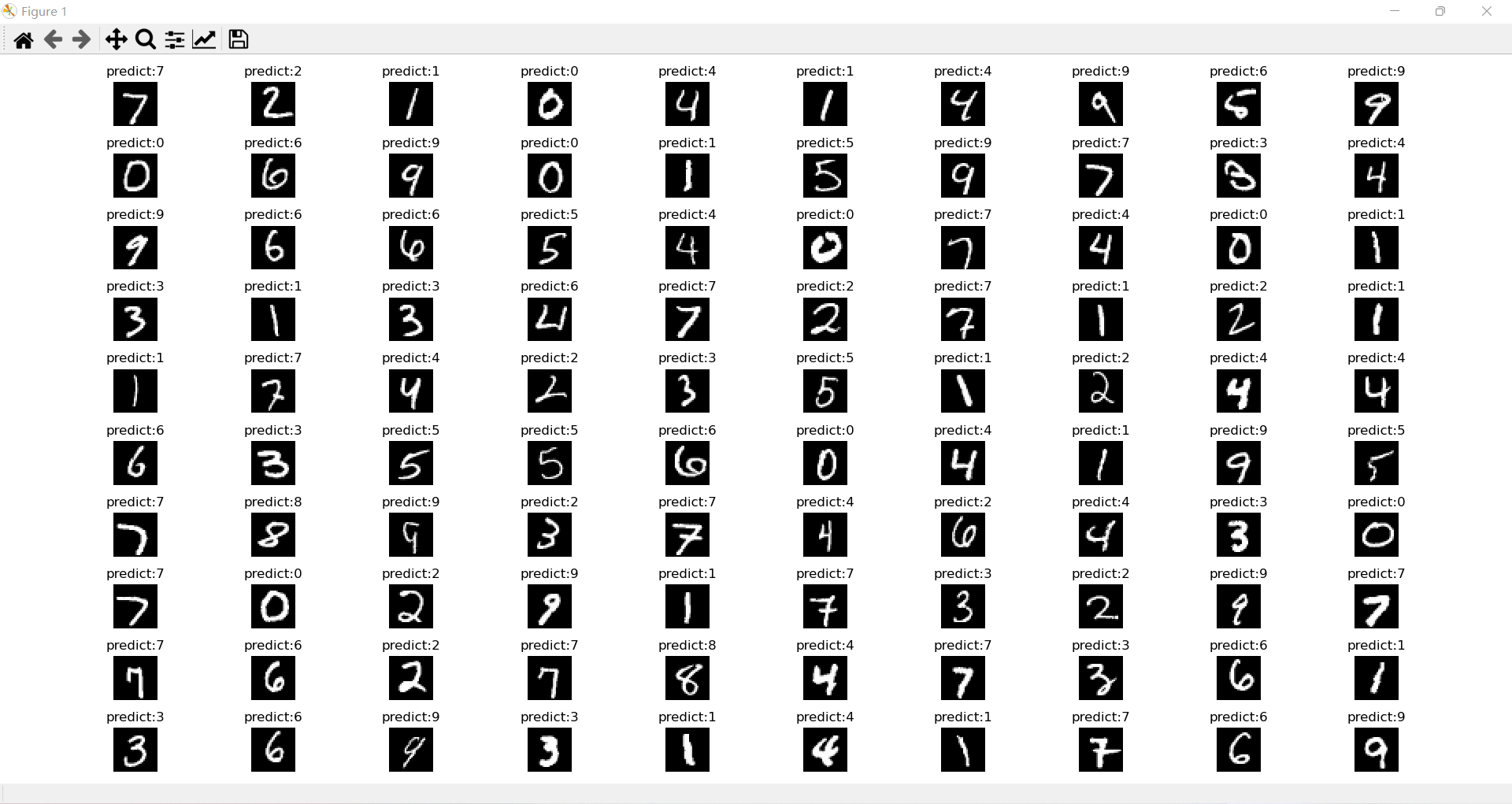
分析
我們展示了100張圖片的識別效果,可以找到3張明顯的識別錯誤,和模型的評估結果相似。

總結
我們可以多重覆運行幾次發現結果並沒有變化,這可能也是logistic回歸的缺點吧,我們也可以使用神經網路進行手寫數字識別,但那是深度學習的內容,我們後續會對其進行實現。



