今天分享一篇文章,是關於如何使用 Manim 這個工具 Python 工具庫來製作視頻的。 據我所知,目前應該是沒有專門的書籍和教程來介紹這個工具的。至於教程,不同版本的Manim有一部分文檔,其中 Manim社區 版的文檔相對而言要完善些。 本次僅介紹 Manim 中 文本 的使用,使用的版本為 ...
今天分享一篇文章,是關於如何使用 Manim 這個工具 Python 工具庫來製作視頻的。
據我所知,目前應該是沒有專門的書籍和教程來介紹這個工具的。至於教程,不同版本的Manim有一部分文檔,其中 Manim社區
版的文檔相對而言要完善些。
本次僅介紹 Manim 中 文本 的使用,使用的版本為 Manim Community v0.14.0,本文內容主要如下: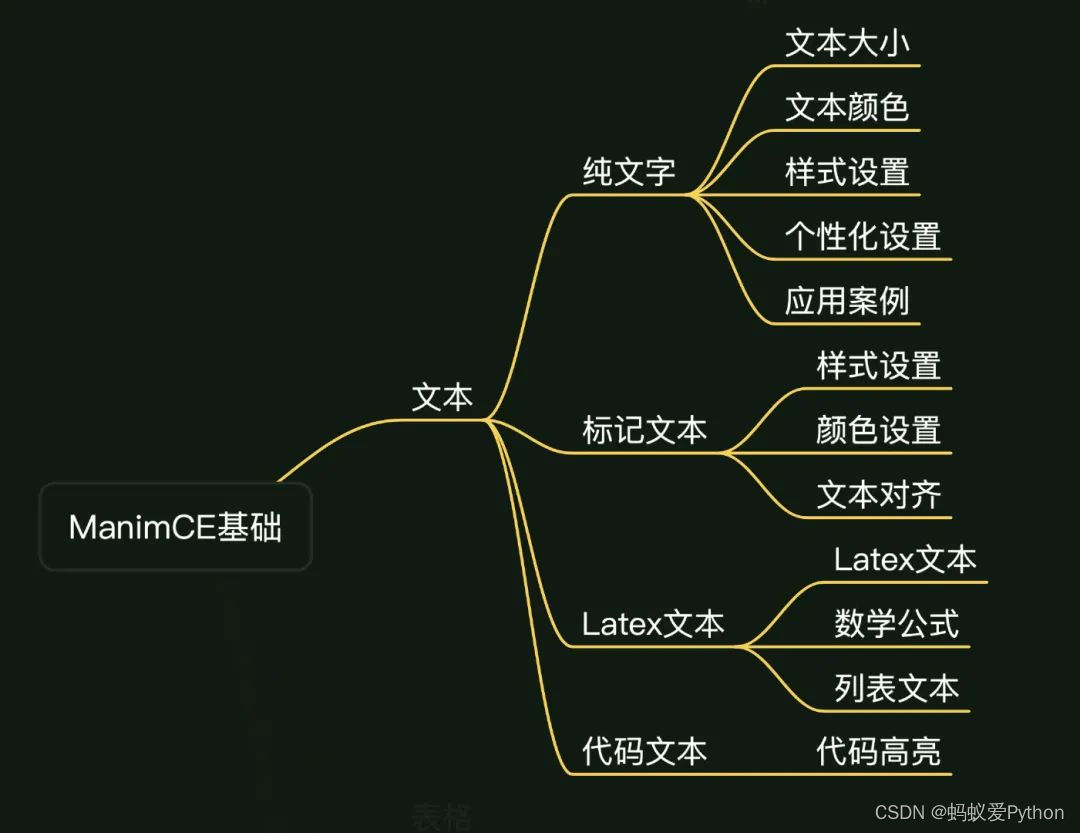
01Manim的安裝與運行
安裝
如何安裝Manim,參見下麵的官方鏈接:
https://docs.manim.community/en/stable/installation.html
如何運行 Manim
用 Manim 繪製圖形,首先需要引入 Manim 庫,然後將需要繪製的內容封裝到一個 類(class) 裡面。
社區版的導入代碼如下:
from manim import *
對於 編輯好的程式文件( XXXX.py 文件),需要在同一個文件夾下運行命令來運行程式,命令格式如下:
manim -pql XXXX.py DemoSquare
上面的命令行中:
•manim 是社區版Manim運行程式的主要標誌用語;
•p 表示程式運行後會進行預覽(圖片或視頻);
•ql 表示低質量(quality low), 其他的選項有 -ql, -qm, -qh, -qk, 分別表示 低質量、正常質量、高質量、4K質量;
•XXXX.py 是py代碼文件;
•DemoSquare 是 py代碼文件中的一個類;
演示過程錄屏如下: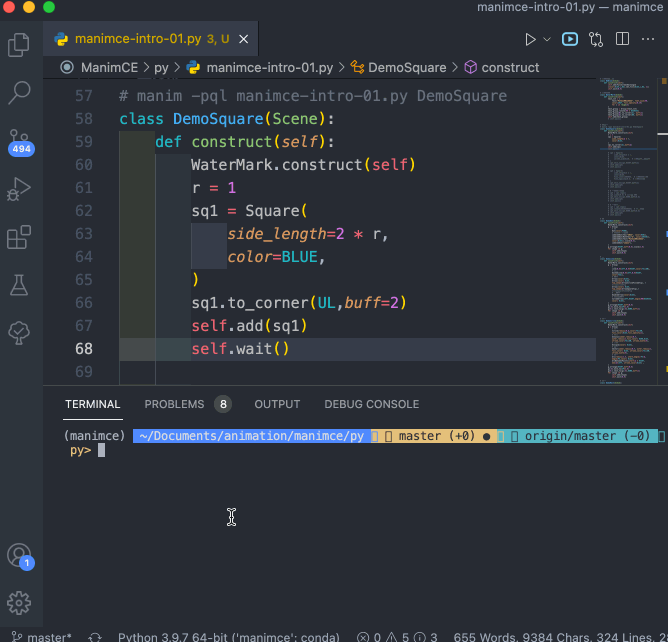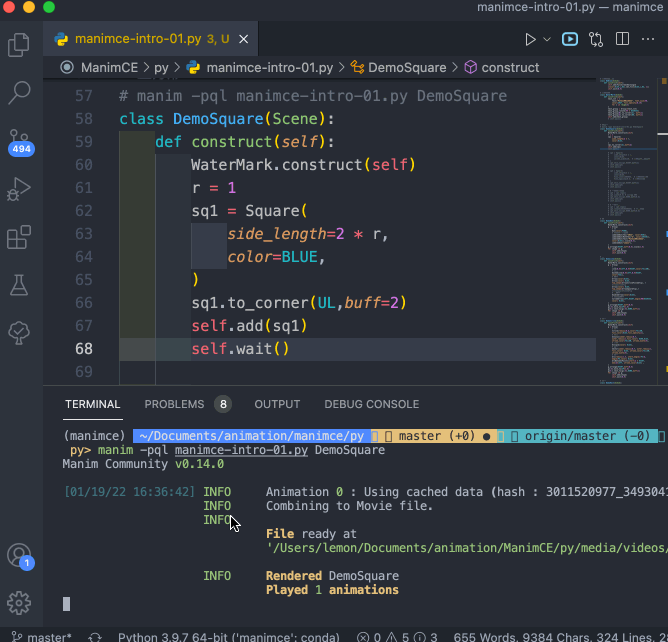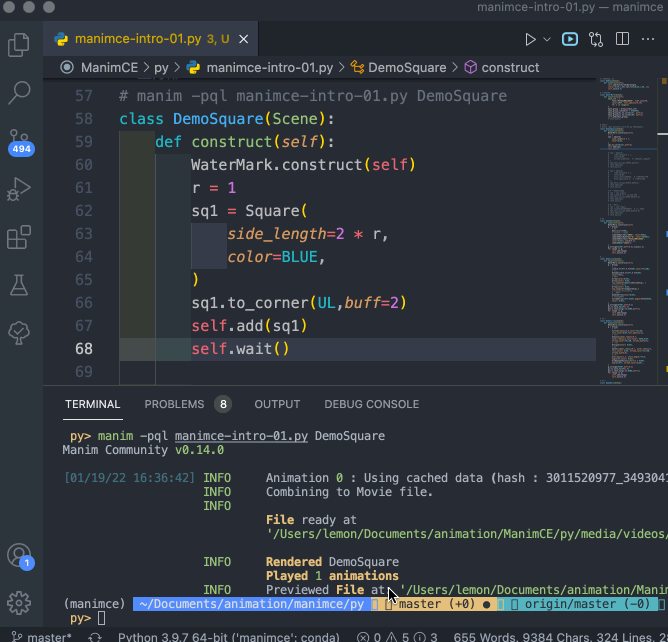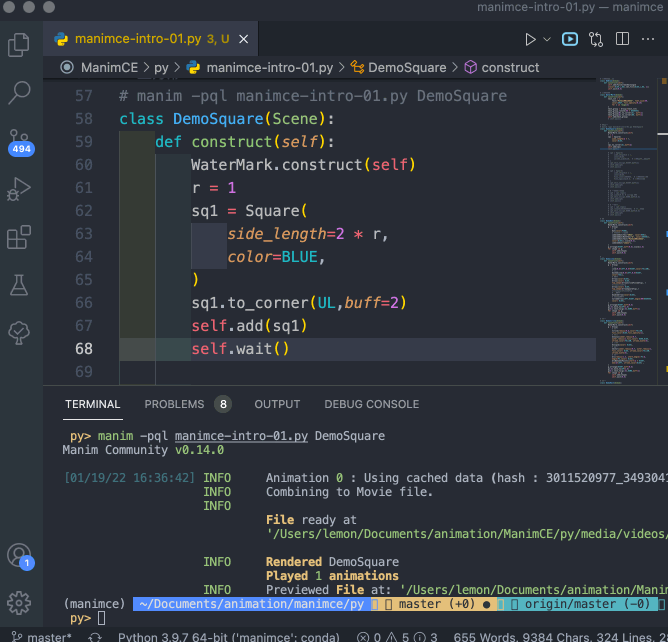
命令行中,還有其他許多參數可以設置,可以通過社區版的支持文檔來進一步瞭解:
https://docs.manim.community/en/stable/tutorials/configuration.html#command-line-arguments
02文本使用介紹
在 Manim社區版中,文本的使用可以分為幾個大類,分別是:
•純文本
•標記文本
•LaTex 文本
•代碼文本
2.1 純文本
純文本是最常見的一類文字,在視頻中使用的標題、正文等,都可以使用純文本,在Manim 中,純文本可以通過 Text() 對象來實現。
比如要輸出 文字 “Python數據之道”,核心代碼如下:
Text("Python數據之道")
效果如下:
設置文本大小
對於文本而言,設置文本在屏幕中顯示的大小,是經常要做的一個事情,Text() 對象可以通過多種方法來實現:
•設置 scale 屬性值;
•設置 set_width 屬性值;
•設置 font_size 參數值;
python學習交流Q群:906715085### # 設置文本大小 class Demo2(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) s = "Python數據之道" t1 = Text(s) t1.to_edge(UP,buff=0.5) t2 = Text(s).scale(2) t2.next_to(t1,DOWN) t3 = Text(s).set_width(10) t3.next_to(t2,DOWN) t4 = Text(s,font_size=40) t4.next_to(t3,DOWN) self.add(t1) self.play(Write(t2)) self.play(Create(t3)) self.play(Write(t4)) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
設置文本顏色
文本顏色設置包括指定某種顏色以及漸變顏色設置,通常情況下,顏色通過 color 參數來設置,漸變顏色通過 gradient 參數來設置。
演示案例的代碼如下:
# 設置文本顏色 class Demo3(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) s = "Python數據之道" t1 = Text(s,color=BLUE) t1.to_edge(UP,buff=2) t2 = Text("一份價值,一份收穫",gradient=[BLUE,YELLOW,RED]).next_to(t1,DOWN) t3 = Text("Hello World",gradient=[BLUE,YELLOW,RED]).next_to(t2,DOWN) t4 = Text("@Python數據之道",gradient=[BLUE,YELLOW,RED],font_size=30,fill_opacity=0.8) t4.next_to(t3,DOWN) t5 = Text("Python數據之道",gradient=[BLUE,YELLOW,RED]).next_to(t4,DOWN) # 當英文和漢字混合時, 當前的manim社區版,使用 gradient 時會出現 bug self.add(t1) self.play(Write(t2)) self.play(Create(t3)) self.play(Write(t4)) self.play(Write(t5)) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
需要註意的是,當英文和漢字混合時, 當前的manim社區版,使用 gradient 時可能會出現 bug,沒有漸變的效果,上述案例中的
變數 t5 實例 就沒有實現漸變效果。
設置文本樣式
文本樣式的設置,包括文本加粗、斜體文本、文本字體設置、文本透明度設置、文本換行以及行距設置等。
演示案例的代碼如下:
python學習交流Q群:906715085### # 設置字體樣式 class Demo4(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) t1 = Text("Python數據之道",font="Alibaba PuHuiTi") t1.to_edge(UP,buff=0.5) t2 = Text("Python數據之道",color=BLUE,font="Times") t2.next_to(t1,DOWN) t3 = Text("Python數據之道", weight=BOLD) t3.next_to(t2,DOWN) t4 = Text("Python數據之道", slant=ITALIC) t4.next_to(t3,DOWN) t5 = Text("Python數據之道", fill_opacity=0.5) t5.next_to(t4,DOWN) t6 = Text("Hello\nPython", line_spacing=0.5) t6.next_to(t5,DOWN,buff=1).shift(LEFT) t7 = Text("Hello\nPython", line_spacing=2) t7.next_to(t6,RIGHT,buff=1) self.add(t1) self.play(Write(t2)) self.play(Write(t3)) self.play(Write(t4)) self.play(Write(t5)) self.add(t6,t7) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
需要主要的是,在選擇字體設置時,所選擇的字體需要在自己的電腦中已經安裝了對應的字體,才會有效果。
此外,在對於非英文字體的設置時,可能有些樣式設置會不起作用,具體的需要自己去根據實際情況測試下。
對於咱們而言,一般就是英文和中文的使用,常用的字體加粗、斜體文字、透明度等,是有效的。對於字體,我一般是使用 “Alibaba PuHuiTi” 字體,這個字體可以免費使用。
個性化設置部分文本
在控制顯示過程中,經常會遇到只需要顯示一段文本中一部分文本的情況,可以通過以下幾個參數來進行設置:
•t2c,全稱為 “text2color”,用來設置部分文字的顏色;
•t2f,全稱為 “text2font”,用來設置部分文字的字體;
•t2w,全稱為 “text2weight”,用來設置部分文字加粗;
•t2s,全稱為 “text2slant”,用來設置部分文字為斜體;
•t2g,全稱為 “text2gradient”,用來設置部分文字的漸變顏色;
演示案例的代碼如下:
# 個性化設置部分文本的樣式 class Demo5(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) t1 = Text("Python數據之道",t2c={"Python":RED,'[7:9]':YELLOW}) t1.to_edge(UP,buff=0.5) t2 = Text("Python數據之道",t2s={"Python":ITALIC}) t2.next_to(t1,DOWN) t3 = Text("Python數據之道", t2w={"Python":BOLD}) t3.next_to(t2,DOWN) t4 = Text("Python數據之道", t2f={"Python":"Times"}) t4.next_to(t3,DOWN) t5 = Text( "Hello,PyDataLab", t2g={ 'PyData':[BLUE,YELLOW,RED], # 'offset':"1", }, ) t5.next_to(t4,DOWN) t6 = Text( "Hello,Python數據之道", t2g={ 'Python':[BLUE,YELLOW,RED], }, ) t6.next_to(t5,DOWN) t7 = Text( "一份價值,一份收穫", t2g={ '一份價值':[BLUE,YELLOW,RED], }, ) t7.next_to(t6,DOWN) # "t2c"、"t2s"、"t2w"、"t2g"、"t2f" 參數設置,可以直接是 字元串,或者是 字元串的位置切片 self.add(t1) self.play(Write(t2)) self.play(Write(t3)) self.play(Write(t4)) self.play(Write(t5)) self.play(Write(t6)) self.play(Write(t7)) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
通過上面的代碼可以看出,“t2c”、“t2s”、“t2w”、“t2g”、“t2f” 參數設置,可以直接是 字元串,或者是 字元串的位置切片。
需要註意的是,當英文和漢字混合或者全部是中文時, 當前的manim社區版,使用 t2g 對部分文字進行漸變設置 時可能會出現
bug,會出現部分文字漸變效果不完整,或者全部文字都有漸變效果。
純文本應用案例
下麵咱們來看一個用純文本實現 “Google” 彩色 logo 的案例,如下:
class Demo6(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) text1 = Text( 'Google', t2c={'[:1]': '#3174f0', '[1:2]': '#e53125', '[2:3]': '#fbb003', '[3:4]': '#3174f0', '[4:5]': '#269a43', '[5:]': '#e53125'}, font_size=58).scale(3) self.play(Write(text1),run_time=3) self.wait() self.play(FadeOut(text1)) t2 = Text('Google',font_size=120) colors = [BLUE, ORANGE, PURPLE, PINK, TEAL,DARK_BROWN, RED,LIGHT_BROWN,GOLD,BLUE_L_C,ORANGE_L_A,PURPLE_E]*10 # for i in range(len(t2)): # t2[i].set_color(colors[i]) for letter in t2: letter.set_color(np.random.choice(colors,size=1)) self.play(Write(t2),run_time=3) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
2.2 標記文本
Manim社區版使用 Pango 來渲染非 LaTex 文本。
Pango標記語言是一種類似 html 的標記語言,可以使用一系列的標記符號。
PangoMarkup is a small markup language like html and it helps you avoid using “range of characters” while coloring or styling a piece a Text. You can use this language with MarkupText.
標記文本的基礎應用
一個簡單的應用案例如下:
class Markup01(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) t1 = MarkupText('<span foreground="yellow" size="x-large">Hello, </span> <i>Welcome to </i>ValueLab !"') t1.to_edge(UP,buff=2) self.add(t1) self.wait() t2 = MarkupText('<span foreground="yellow" size="x-large">一份價值,</span> 一份 <i>收穫</i>!"') t2.next_to(t1,DOWN,buff=1) self.add(t2) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
可以看到,對於 Markup 標記語言,在應用於英文文字的時候,應用效果是挺好的,但對於中文字體,上面的文字中,斜體效果
就沒有體現出來。不知道是 Pango本身渲染的問題還是 Manim社區版存在一些瑕疵。
當前,Manim中進行文字渲染,支持以下標簽:
標記文本的樣式設置
標記文本的樣式設置包括文字加粗、下劃線、斜體、上標、下表、刪除線等,演示案例的代碼如下:
# 樣式設置,加粗、下劃線、斜體等 class Markup02(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) text1 = MarkupText("<b>Hello</b> <i>welcome to</i> <b><i>ValueLab</i></b>") text2 = MarkupText("<s>foo</s> <u>bar</u> <big>big</big> <small>small</small>") text3 = MarkupText("H<sub>2</sub>O and H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>") text4 = MarkupText("type <tt>help</tt> for help") text5 = MarkupText( '<span underline="double">foo</span> <span underline="error">bar</span>' ) group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4, text5).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
標記文本的顏色設置
標記文本的顏色設置,主要是漸變色的設置比較複雜,仔細看下麵案例中漸變色設置時的各個參數:
python學習交流Q群:906715085### # 顏色設置,設置不同的顏色、漸變色等 class Markup03(Scene): def construct(self): text1 = MarkupText( f'all in red <span fgcolor="{YELLOW}">except this</span>', color=RED ) text2 = MarkupText("nice gradient", gradient=(BLUE, GREEN)) text3 = MarkupText( 'nice <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW">intermediate</gradient> gradient', gradient=(BLUE, GREEN), ) text4 = MarkupText( 'fl ligature <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW">causing trouble</gradient> here' ) text5 = MarkupText( 'fl ligature <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset="1">defeated</gradient> with offset' ) text6 = MarkupText( 'fl ligature <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset="1">floating</gradient> inside' ) text7 = MarkupText( 'fl ligature <gradient from="RED" to="YELLOW" offset="1,1">floating</gradient> inside' ) group = VGroup(text1, text2, text3, text4, text5, text6, text7).arrange(DOWN) self.add(group)
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
文字對齊
在書寫英文文字時,為了排版效果好看,經常需要將文字進行對齊顯示,這個在 Manim中,也可以實現。
演示案例的代碼如下:
# 文字對齊 class Markup05(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) ipsum_text = ( "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit." "Praesent feugiat metus sit amet iaculis pulvinar. Nulla posuere " "quam a ex aliquam, eleifend consectetur tellus viverra. Aliquam " "fermentum interdum justo, nec rutrum elit pretium ac. Nam quis " "leo pulvinar, dignissim est at, venenatis nisi. Quisque mattis " "dolor ut euismod hendrerit. Nullam eu ante sollicitudin, commodo " "risus a, vehicula odio. Nam urna tortor, aliquam a nibh eu, commodo " "imperdiet arcu. Donec tincidunt commodo enim a tincidunt." ) justified_text = MarkupText(ipsum_text, justify=True).scale(0.4) not_justified_text = MarkupText(ipsum_text, justify=False).scale(0.4) just_title = Title("Justified") njust_title = Title("Not Justified") self.add(njust_title, not_justified_text) self.play( Transform( not_justified_text, justified_text, ), Transform( njust_title, just_title, ), run_time=2, ) self.wait(1)
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
2.3 LaTex 文本
LaTeX(LATEX,音譯“拉泰赫”)是一種基於ΤΕΧ的排版系統,由美國電腦學家萊斯利·蘭伯特(Leslie Lamport)在20世紀80年
代初期開發,利用這種格式,即使使用者沒有排版和程式設計的知識也可以充分發揮由TeX所提供的強大功能,能在幾天、甚至
幾小時內生成很多具有書籍質量的印刷品。
對於生成複雜表格和數學公式,這一點表現得尤為突出。因此它非常適用於生成高印刷質量的科技和數學類文檔。這個系統同樣
適用於生成從簡單的信件到完整書籍的所有其他種類的文檔。
在 Manim 中使用 latex 文本,需要你的電腦環境中已經安裝了 latex的相關軟體和支持工具。
在 Manim 中,可以通過以下幾種方法來使用 latex 文本,如下:
•Tex
•MathTex
•Title
•BulletedList
文本型的 LaTex 可以通過 Tex、Title、BulletedList 來實現,數學公式類型的文本,可以通過 Tex 或 MathTex 來實現。
基礎應用
先來看一個 latex 的基礎應用案例,如下:
class DemoTex01(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) tex1 = Tex(r"\LaTeX", font_size=144) tex1.to_edge(UP,buff=1) self.add(tex1) self.wait() tex2 = Tex(r'$x^2 + y^2 = z^2$', font_size=144) tex2.next_to(tex1,DOWN,buff=0.5) tex3 = MathTex(r'x^2 + y^2 = z^2', font_size=144,color=BLUE) tex3.next_to(tex2,DOWN,buff=0.5) self.add(tex2) self.wait() self.add(tex3) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下: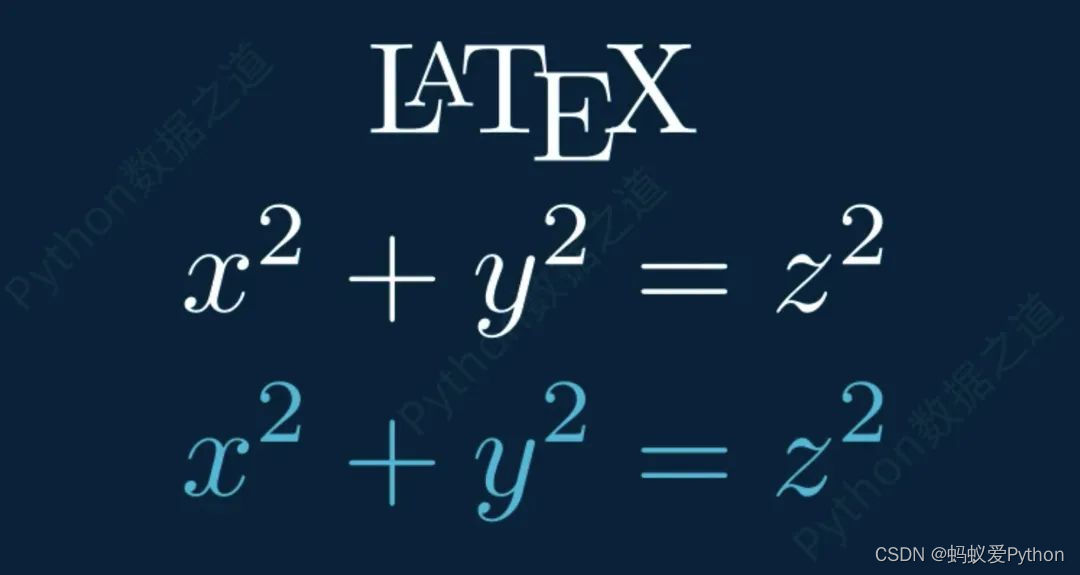
在 Tex 或 MathTex 中使用字元串時,一般會使用 r"…" 的形式,而不是 ‘…’ 的形式,這是因為在 latex文本中,經常會涉及到一些
特殊的字元,比如 \ 。
在進行數學公式的表達時,使用 Tex 時需要在字元串前後添加符號 ,形式為 r",形式為r"…$“,使用 MathTex 時,形式為 r”…" 就可以
了。兩者之間的區別,需要註意下。
使用 latex 工具包
在 latex 中輸出特殊符號時,可以通過 latex 工具包來實現。
當然,需要你的電腦中已經安裝了對應的 latex 工具包。對於沒有使用過 latex 的同學來說,這個確實會有些繁瑣。
演示案例的代碼如下:
# 使用 latex 工具包 class DemoTex02(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) myTemplate = TexTemplate() myTemplate.add_to_preamble(r"\usepackage{mathrsfs}") tex = Tex(r'$\mathscr{H} \rightarrow \mathbb{H}$}', tex_template=myTemplate, font_size=144) self.add(tex)
上述代碼的實現效果如下: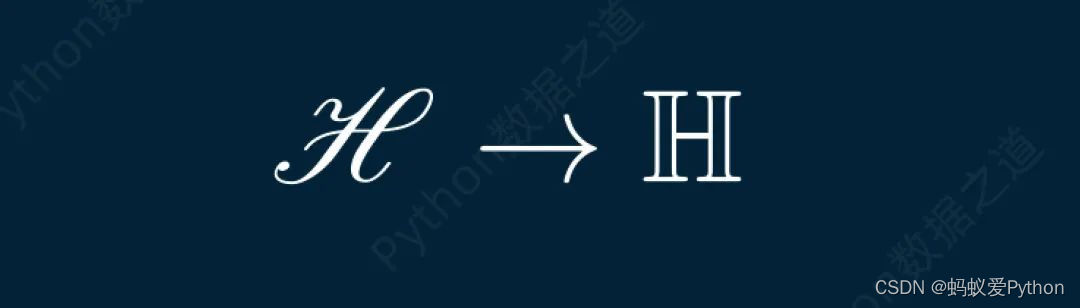
數學公式的顏色設置
在 Manim 中,對於數學公式中字元的顏色設置,可以通過參數 set_color_by_tex 和 substrings_to_isolate 的組合來實現不同的效
果。
演示案例的代碼如下:
# 數學公式的顏色設置 class DemoTex03(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) eq1 = MathTex( r"e^x = x^0 + x^1 + \frac{1}{2} x^2 + \frac{1}{6} x^3 + \cdots + \frac{1}{n!} x^n + \cdots" ) eq1.scale(1.2) eq1.set_color_by_tex("x", YELLOW) eq1.to_edge(UP,buff=2) self.add(eq1) self.wait() # self.play(FadeOut(eq1)) eq2 = MathTex( r"e^x = x^0 + x^1 + \frac{1}{2} x^2 + \frac{1}{6} x^3 + \cdots + \frac{1}{n!} x^n + \cdots", substrings_to_isolate="x", ) eq2.scale(1.2) eq2.set_color_by_tex("x", RED) eq2.next_to(eq1,DOWN,buff=1) self.add(eq2) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
在 eq1 中,僅設置參數 set_color_by_tex 時,是對於包含 “x” 的整個公式進行顏色設置;而在 eq2 中,同時設置參數
set_color_by_tex 和 substrings_to_isolate 時,僅僅對公式中的 “x” 字元進行顏色設置;這兩種是不一樣的應用場景,大家選擇合
適的去使用。
我在自己視頻中涉及數學公式的部分代碼如下:
class DemoTex04(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) equations = VGroup( MathTex( r"1.01^{365} = 37.8", # size=80, ), MathTex( r"1.00^{365} = 1.00", # size=80, ), MathTex( r"0.99^{365} = 0.03", # size=80, ), ) # 設置寬度 # equations.set_width(FRAME_WIDTH-4) equations.set_width(8) for equation in equations: equation.set_color_by_tex_to_color_map({ "1.01": BLUE, "0.99": RED, }) equations.arrange(DOWN, buff=0.7, aligned_edge=LEFT) self.play(Write(equations[0])) self.wait() self.play(Write(equations[2])) self.wait() self.play(Write(equations[1])) self.wait() self.play(equations[1].animate.set_opacity(0.2)) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
tex 模板應用
在 LaTex 中,可以通過設置使用的模板,來設置使用的字體。此外,在使用中文字元時,經常需要設置中文的模板(一般使用 ctex)。
演示案例的代碼如下:
# tex 模板應用 class DemoTex05(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) tex1 = Tex(r'$x^2 + y^2 = z^2$', tex_template=TexFontTemplates.french_cursive, font_size=144) tex1.to_edge(UP,buff=1) self.add(tex1) self.wait() tex2 = Tex(r'Hello 你好 \LaTeX', tex_template=TexTemplateLibrary.ctex, font_size=144) tex2.next_to(tex1,DOWN,buff=0.5) self.add(tex2) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下: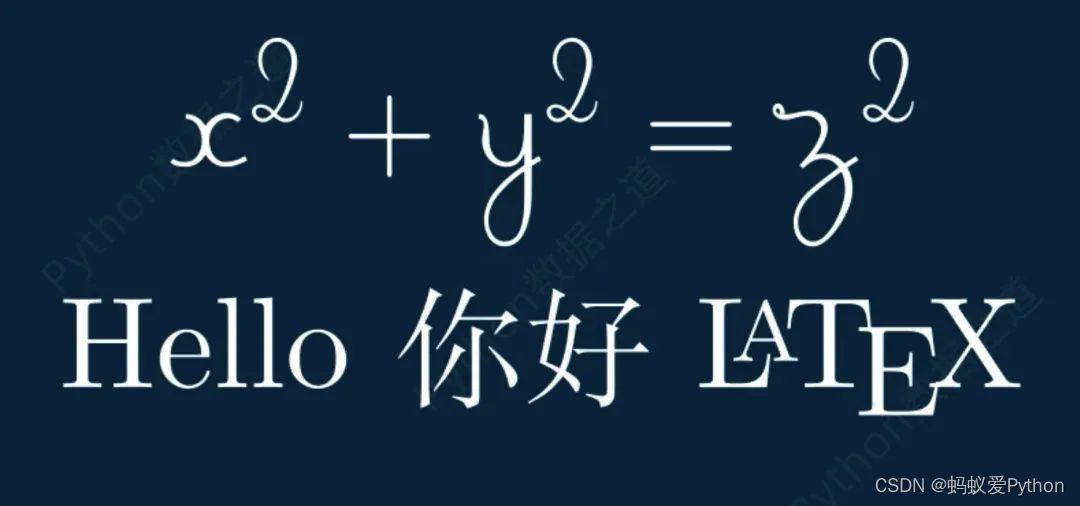
對於 TexFontTemplates,可以使用的模板說明如下:
A collection of TeX templates for the fonts described at http://jf.burnol.free.fr/showcase.html
公式換行
在數學公式中,可以實現換行效果,如下:
# 公式換行 class DemoTex06(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) tex1 = MathTex( r'f(x) &= 3 + 2 + 1\\ &= 5 + 1 \\ &= 6', font_size=96, ) self.add(tex1) self.wait() self.play(FadeOut(tex1)) tex2 = MathTex( r'f(x) &= 3 + 2 + 1\\ &= 5 + 1 \\ &= 6', font_size=96, substrings_to_isolate=['5','3'], ) tex2.set_color_by_tex_to_color_map({ "5": BLUE, "3": RED, }) self.add(tex2) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下: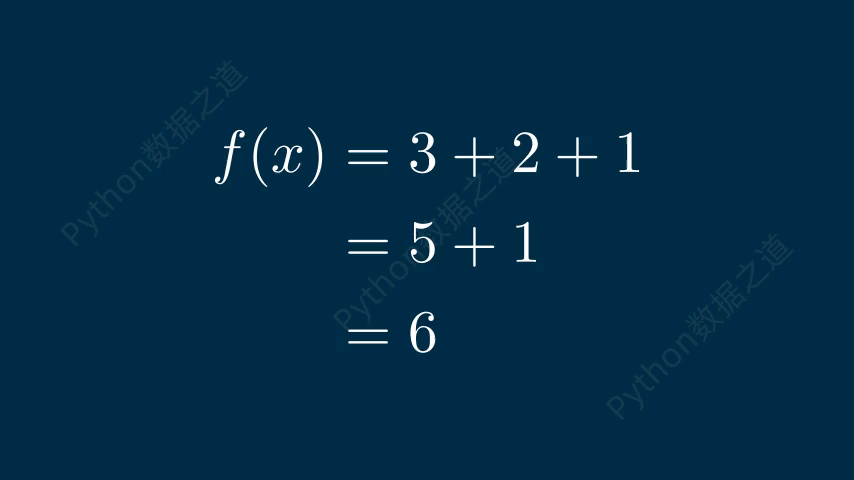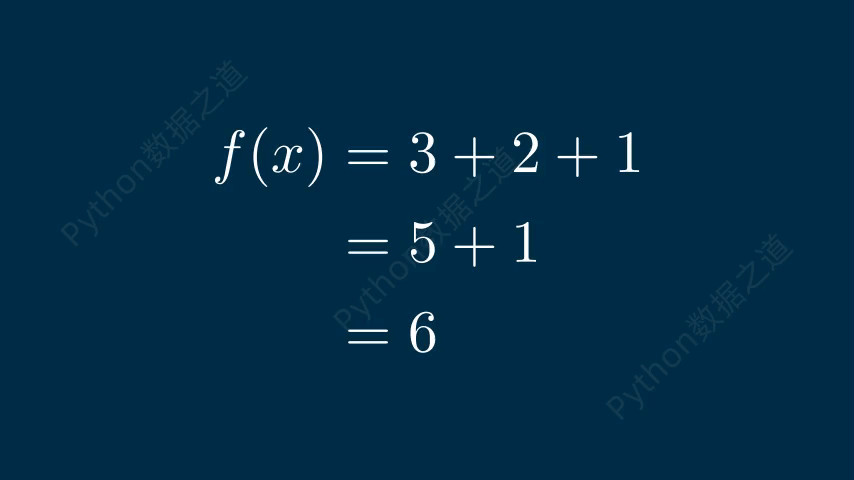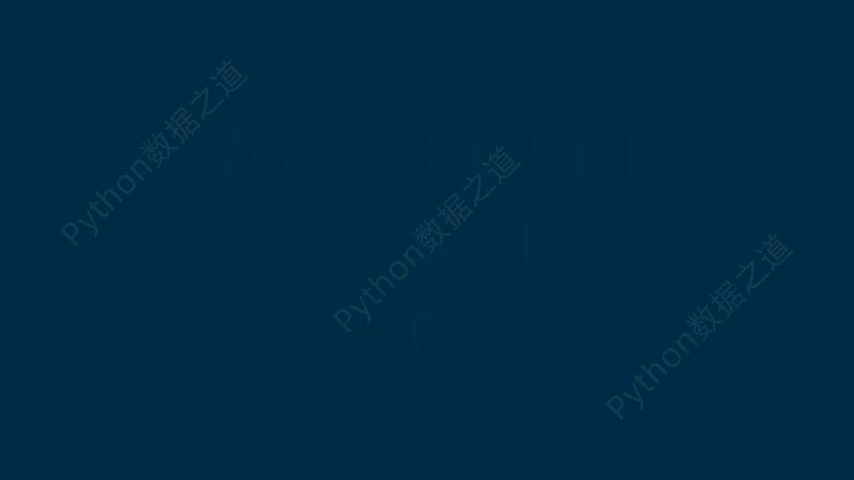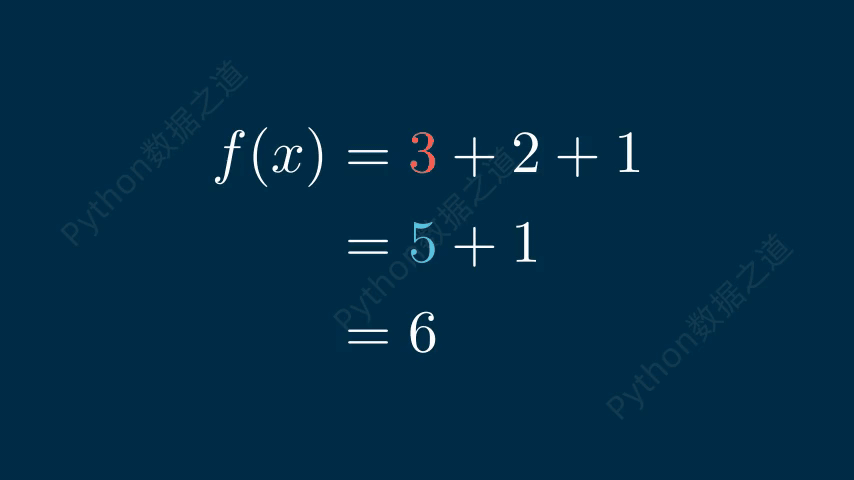
Title 對象應用
在視頻中設置文字標題時,可以直接使用 Title 對象,需要說明的是,Title 對象是基於 Tex 來實現的,在涉及中文輸出時,需要設置使用的模板為中文適用的模板。
演示案例的代碼如下:
# Title 對象應用 class DemoTex07(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) title1 = Title("Hello,title") self.add(title1) self.wait() self.play(FadeOut(title1)) # 使用 “Title” 對象,當有中文時,需要設置中文字體模板(電腦中需要安裝了 ctex) title2 = Title("你好,title",tex_template=TexTemplateLibrary.ctex) self.add(title2) self.wait()
上述代碼的實現效果如下:
列表類型的文本
在文本的使用過程中,會時不時涉及到 列表型文本,目前,在 Manim 中,可以直接實現無序號型的列表文本,通過 BulletedList
對象來實現。
演示案例的代碼如下:
# 列表類型的文本 class DemoTex08(Scene): def construct(self): blist = BulletedList("Python", "Java", "C++", height=2, width=2) blist.set_color_by_tex("Python", RED) blist.set_color_by_tex("Java", GREEN) blist.set_color_by_tex("C++", BLUE) self.add(blist)
上述代碼的實現效果如下: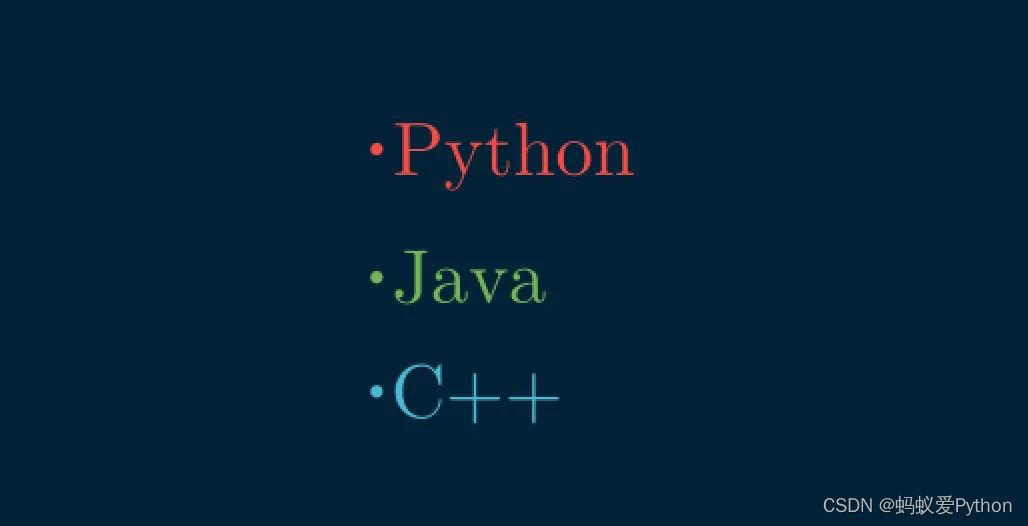
2.4 代碼文本
在 IT編程領域,代碼的高亮顯示是一個常見的需求,在 Manim 製作的視頻中,也可以實現代碼高亮的效果,主要是通過 Code() 對象來實現。
下麵以快速排序的Python代碼為例,來演示如何在視頻中進行代碼高亮顯示。
class Code1(Scene): def construct(self): WaterMark.construct(self) code_str_1 = """ def quickSort(Array): n = len(Array) if n <= 1: return Array baseline = Array[0] left = [Array[i] for i in range(1, len(Array)) if Array[i] < baseline] right = [Array[i] for i in range(1, len(Array)) if Array[i] >= baseline] return quickSort(left) + [baseline] + quickSort(right) """ code1 = Code( code=code_str_1, tab_width=4, background="window", language="Python", font="Monospace", insert_line_no=False, # 是否顯示代碼行數 style='monokai', ) code1.scale(0.8).to_edge(UP,buff=1) self.play(Write(code1)) self.wait()
代碼高亮效果如下: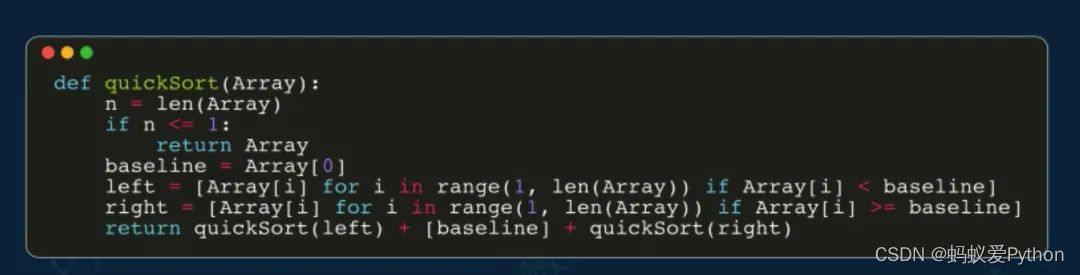
上述代碼中,變數 code_str_1 是快速排序演算法的Python實現代碼, 變數 code1 是 Code() 對象的實例, Code() 有許多參數可以
進行設置,這裡只對部分參數進行設置:
•background 參數,可以選擇 “rectangle” 或 “window”,預設是 “rectangle”,我自己一般喜歡用 “window”;
•language 參數是所用的編程語言,支持常用的編程語言;
•font 參數,代碼字體,預設為 “Monospac821 BT”,我一般用 “Monospace”;
•insert_line_no 參數,是否顯示代碼行數,預設是 True;需要註意的是,在顯示代碼行數時,有時行數與代碼的對齊效果不一定完美;
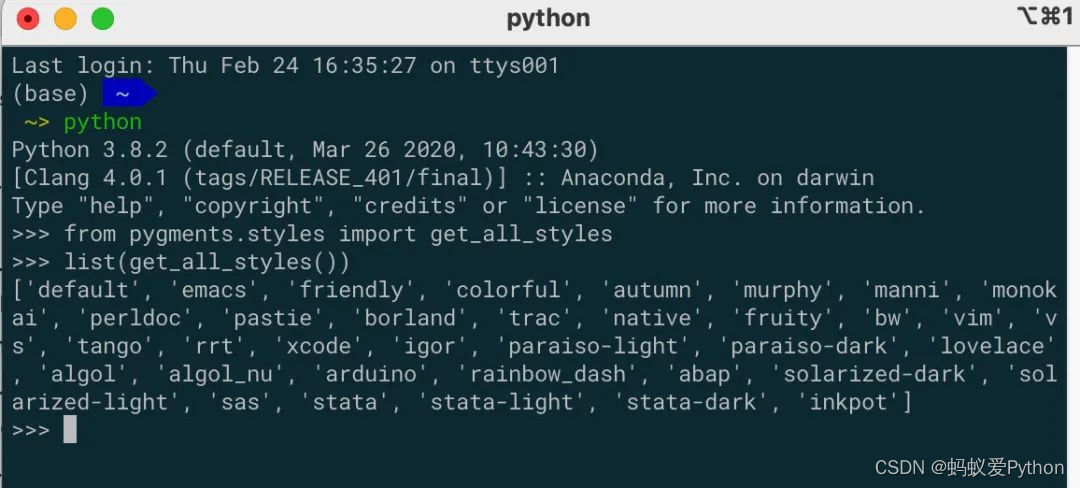
•style 參數,代碼顯示風格,有多種風格可以選擇,其可選代碼樣式來源於 “pygments” (https://pygments.org/docs/styles/)。可在Python中運行代碼來獲取支持的樣式。
from pygments.styles import get_all_styles styles = list(get_all_styles())
style支持的樣式如下:
['default', 'emacs', 'friendly', 'colorful', 'autumn', 'murphy', 'manni', 'monokai', 'perldoc', 'pastie', 'borland', 'trac', 'native', 'fruity', 'bw', 'vim', 'vs', 'tango', 'rrt', 'xcode', 'igor', 'paraiso-light', 'paraiso-dark', 'lovelace', 'algol', 'algol_nu', 'arduino', 'rainbow_dash', 'abap', 'solarized-dark', 'solarized-light', 'sas', 'stata', 'stata-light', 'stata-dark', 'inkpot'] 預設的樣式為 'vim',我一般喜歡用 'monokai' 樣式。
再選擇一款淺色的樣式(‘solarized-light’),並設置不同的參數值,來對比下效果,如下:
class



