本文主要分析 中 的載入,對於其解析我們在後面的文章中專門分析。 是屬於 模塊的,它是對 spring bean 的統一抽象描述定義介面,我們知道在spring中定義bean的方式有很多種,如XML、註解以及自定義標簽,同事Bean的類型也有很多種,如常見的工廠Bean、自定義對象、Advisor等 ...

本文主要分析 spring 中 BeanDefinition 的載入,對於其解析我們在後面的文章中專門分析。
BeanDefinition 是屬於 Spring Bean 模塊的,它是對 spring bean 的統一抽象描述定義介面,我們知道在spring中定義bean的方式有很多種,如XML、註解以及自定義標簽,同事Bean的類型也有很多種,如常見的工廠Bean、自定義對象、Advisor等等,我們在分析載入BeanDefinition之前,首先來瞭解它的定義和註冊設計。
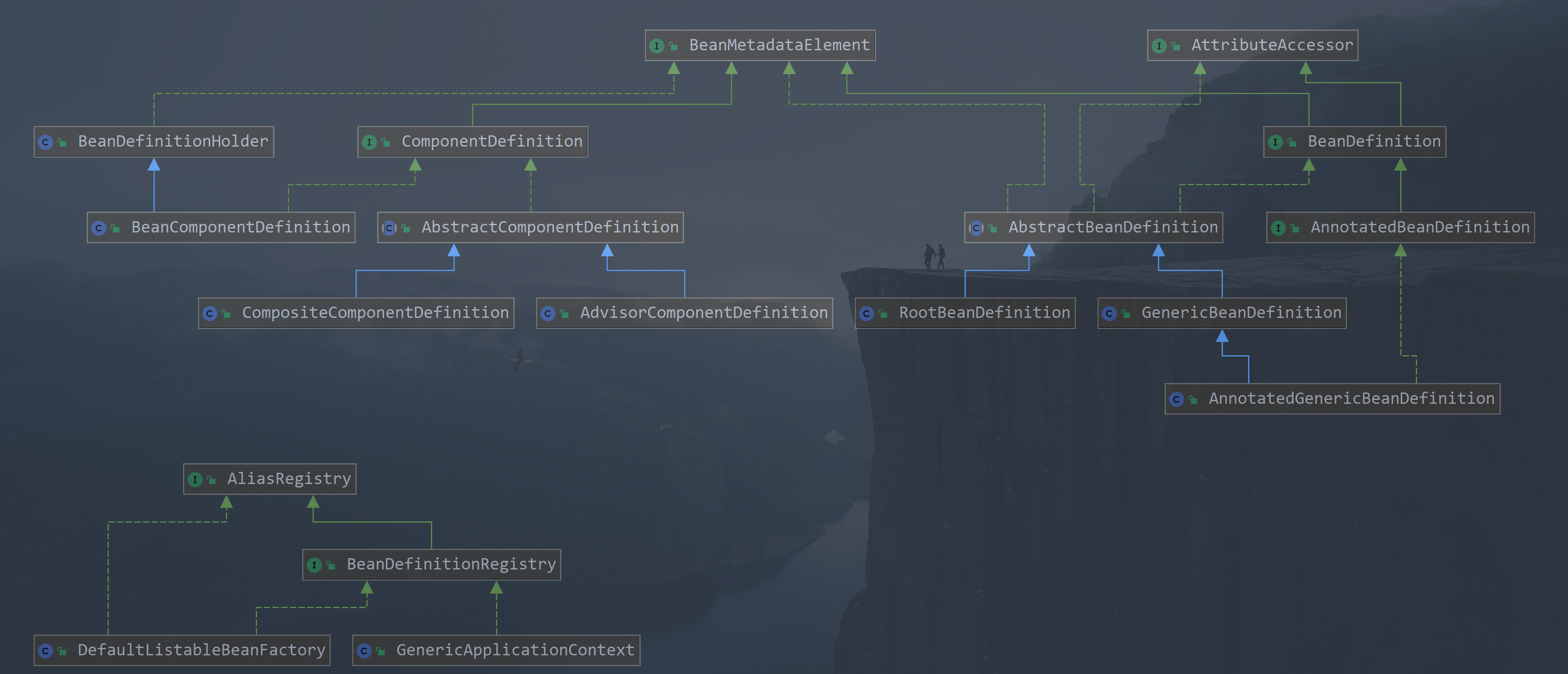
上面類圖我們做一個簡單介紹,具體詳細介紹在後面的相關文章說明
-
AliasRegistry為 Bean註冊一個別名的頂級介面 -
BeanDefinitionRegistry主要用來把bean的描述信息註冊到容器中,spring在註冊bean時一般是獲取到bean後通過BeanDefinitionRegistry來註冊噹噹前的BeanFactory中 -
BeanDefinition是用來定義描述 Bean的名字、作用域、角色、依賴、懶載入等基礎信息,以及包含與spring容器運行和管理Bean信息相關的屬性。spring中通過它實現了對bean的定製化統一,這也是一個核心介面層 -
AnnotatedBeanDefinition是一個介面,繼承了BeanDefinition, 對其做了一定的擴展,主要用來描述註解Bean的定義信息 -
AttributeAccessor主要用來設置 Bean配置信息中的屬性和屬性值的介面,實現key-value的映射關係 -
AbstractBeanDefinition是對BeanDefintion的一個抽象化實現,是一個模板,具體的詳細實現交給子類
2. BeanDefinition
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("bean.xml"); // <1>
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); // <2>
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); // <3>
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
上面這段代碼是 spring 中從資源的定位到載入過程,我們可以簡單分析一下:
- 通過
ClassPathResource進行資源的定位,獲取到資源 - 獲取
BeanFactory,即上下文 - 通過工廠創建一個特定的
XmlBeanDefinitionReader對象,該Reader是一個資源解析器, 實現了BeanDefinitionReader介面 - 裝載資源
整個過程分為三個大步驟,示意圖:
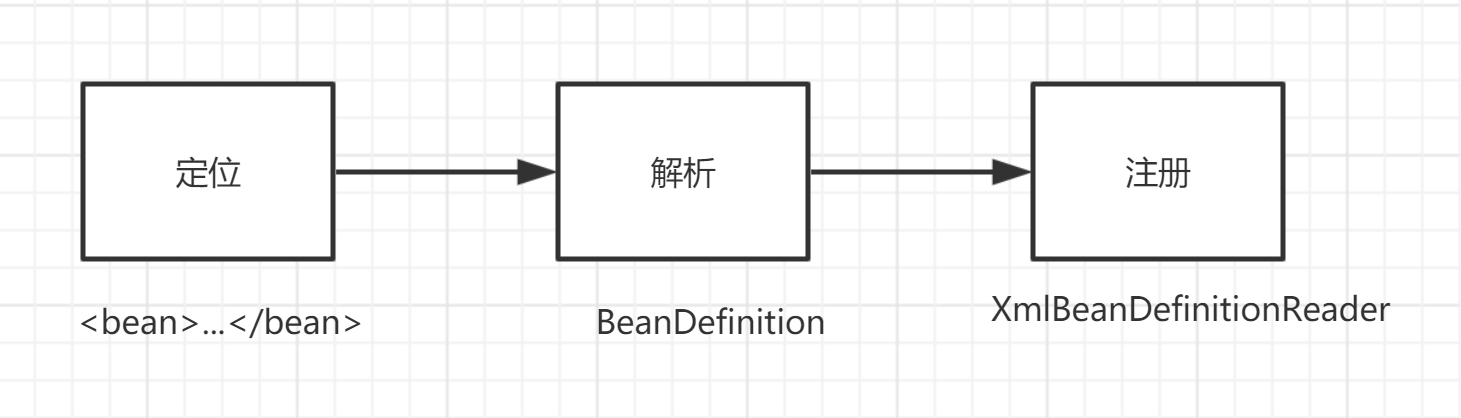
我們文章主要分析的就是第二步,裝載的過程,
3.loadBeanDefinitions
資源的定位我們之前文章分析過了,不在闡述,這裡我們關心 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 這句的具體實現,
通過代碼追蹤我們可以知道方法 #loadBeanDefinitions(...) 是定義在 BeanDefinitionReader 中的,而他的具體實現是在 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 類中,代碼如下:
/**
* 從指定的xml文件中載入bean的定義
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//調用私有方法處理 這裡將resource進行了編碼處理,保證瞭解析的正確性
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
/**
* 裝載bean定義的真實處理方法
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file,
* allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//1.對資源判空
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
//2.獲取當前線程中的 EncodedResource 集合 -> 已經載入過的資源
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
//3.若當前已載入資源為空,則創建並添加
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
//4.添加資源到集合如果已載入資源中存在 則拋出異常
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
//5.獲取 encodedResource 中的 Resource ,在獲取 intputSteram 對象
try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
//6. 真實執行載入beanDefinition業務邏輯的方法
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
//7.從已載入集合中去除資源
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
-
通過
resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get()代碼,來獲取已經載入過的資源,然後將encodedResource加入其中,如果resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded中已經存在該資源,則拋出BeanDefinitionStoreException異常。 -
為什麼需要這麼做呢?答案在 "Detected cyclic loading" ,避免一個
EncodedResource在載入時,還沒載入完成,又載入自身,從而導致死迴圈。也因此,,當一個EncodedResource載入完成後,需要從緩存中剔除。 -
從
encodedResource獲取封裝的Resource資源,並從Resource中獲取相應的InputStream,然後將InputStream封裝為InputSource,最後調用#doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)方法,執行載入BeanDefinition的真正邏輯
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//1. 獲取到 Document 實例
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//2. 註冊bean實列,通過document
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
上面 #registerBeanDefinitions(...) 方法是 beanDefinition 的具體載入過程, #doLoadDocument(...) 是解析 document 的方法內部包含 spring 的驗證模型與 document 解析兩塊,這些我們在後面專門進行分析
本文由AnonyStar 發佈,可轉載但需聲明原文出處。
仰慕「優雅編碼的藝術」 堅信熟能生巧,努力改變人生
歡迎關註微信公賬號 :雲棲簡碼 獲取更多優質文章
更多文章關註筆者博客 :雲棲簡碼



