通俗理解spring源碼(四)—— 獲取Docment 上節講到了xmlBeanDefinitionReader.doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)方法: protected Document doLoadDocume ...
通俗理解spring源碼(四)—— 獲取Docment
上節講到了xmlBeanDefinitionReader.doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)方法:
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception { return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware()); }
getValidationModeForResource(resource)在這裡,看看getEntityResolver():
protected EntityResolver getEntityResolver() { if (this.entityResolver == null) { // Determine default EntityResolver to use. ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); if (resourceLoader != null) { this.entityResolver = new ResourceEntityResolver(resourceLoader); } else { this.entityResolver = new DelegatingEntityResolver(getBeanClassLoader()); } } return this.entityResolver; }
這裡有兩種類型的entityResolver,對於xmlBeanDefinitionReader來說,會new一個ResourceEntityResolver,後面會解釋什麼是EntityResolver。
然後將EntityResolver返回作為loadDocument()的參數。
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception { return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware()); }
調用DefaultDocumentLoader的loadDocument方法
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver, ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception { DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]"); } DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler); return builder.parse(inputSource); } protected DocumentBuilder createDocumentBuilder(DocumentBuilderFactory factory, @Nullable EntityResolver entityResolver, @Nullable ErrorHandler errorHandler) throws ParserConfigurationException { DocumentBuilder docBuilder = factory.newDocumentBuilder(); if (entityResolver != null) { docBuilder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver); } if (errorHandler != null) { docBuilder.setErrorHandler(errorHandler); } return docBuilder; }
在loadDocument方法中,使用的DocumentBuilderFactory 、DocumentBuilder 等都是jdk中的類,載入xml資源也是調用的java中的方法,這裡就不多說了,重點是docBuilder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver)方法,該方法將得到的entityResolver放到docBuilder中,也就是DocumentBuilder ,然後調用docBuilder.parse()。
那麼EntityResolver在生成document過程中起到什麼作用呢?
1、EntityResolver
EntityResolver不是屬於spring定義的,是jdk中org.xml.sax下的一個介面。
官方是這樣解釋EntityResolver的:如果SAX應用程式實現自定義處理外部實體,則必須實現此介面,並使用setEntityResolver方法向SAX 驅動器註冊一個實例。
也就是說,對於解析一個xml,sax首先會讀取該xml文檔上的聲明,根據聲明去尋找相應的dtd定義,以便對文檔的進行驗證,預設的尋找規則,(即:通過網路,實現上就是聲明DTD的地址URI地址來下載DTD聲明),併進行認證,下載的過程是一個漫長的過程,而且當網路不可用時,就會找不到相應的dtd,就會報錯。
EntityResolver 的作用就是項目本身就可以提供一個如何尋找DTD 的聲明方法,即:由程式來實現尋找DTD聲明的過程,比如我們將DTD放在項目的某處在實現時直接將此文檔讀取並返回個SAX即可,這樣就避免了通過網路來尋找DTD的聲明。
首先看看EntityResolver 介面聲明的方法:
public abstract InputSource resolveEntity (String publicId, String systemId) throws SAXException, IOException;
接收2個參數,publicId ,systemId ,並返回一個InputStream對象
如果我們在解析驗證模式為xsd的配置文件,代碼如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> ... </beans>
讀取得到以下參數
publicId : null
systemId : http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
如果我們解析的是DTD的配置文件,代碼如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN//EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd"> <beans> ... </beans>
上面說過,EntityResolver 會被set到DocumentBuilder 對象中,也就是說,在 DocumentBuilder .parse()過程中,EntityResolver 對象的resolveEntity會得到相應的參數publicId 和systemId ,然後調用其resolveEntity ()方法,返回的流InputSource 就是相應的DTD文件流或者XSD文件流,然後完成校驗工作。
所以,現在重點就是,不同的EntityResolver實現是以何種方式返回DTD或XSD文件流的。來看具體實現。
2、DelegatingEntityResolver
public InputSource resolveEntity(@Nullable String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws SAXException, IOException { if (systemId != null) { if (systemId.endsWith(DTD_SUFFIX)) { return this.dtdResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId); } else if (systemId.endsWith(XSD_SUFFIX)) { return this.schemaResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId); } } // Fall back to the parser's default behavior. return null; }
根據systemId尾碼,委派給dtdResolver和schemaResolver完成,dtdResolver和schemaResolver也是EntityResolver的實現,在 DelegatingEntityResolver構造中初始化。
public DelegatingEntityResolver(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { this.dtdResolver = new BeansDtdResolver(); this.schemaResolver = new PluggableSchemaResolver(classLoader); }
3、BeansDtdResolver
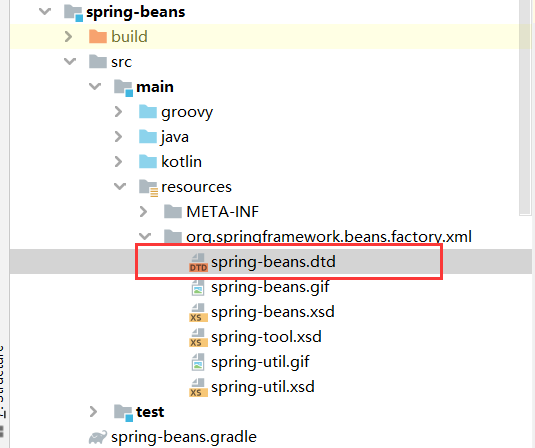
BeansDtdResolver負責找到classpath下spring-beans.dtd文件的位置,返迴文件流。
public InputSource resolveEntity(@Nullable String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws IOException { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Trying to resolve XML entity with public ID [" + publicId + "] and system ID [" + systemId + "]"); } if (systemId != null && systemId.endsWith(DTD_EXTENSION)) { int lastPathSeparator = systemId.lastIndexOf('/'); int dtdNameStart = systemId.indexOf(DTD_NAME, lastPathSeparator); if (dtdNameStart != -1) { String dtdFile = DTD_NAME + DTD_EXTENSION; //dtdFile="spring-beans.dtd" if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Trying to locate [" + dtdFile + "] in Spring jar on classpath"); } try { //定位classpath資源文件 Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(dtdFile, getClass()); InputSource source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream()); source.setPublicId(publicId); source.setSystemId(systemId); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Found beans DTD [" + systemId + "] in classpath: " + dtdFile); } return source; } catch (FileNotFoundException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not resolve beans DTD [" + systemId + "]: not found in classpath", ex); } } } } // Fall back to the parser's default behavior. return null; }
spring-beans.dtd文件在如下位置:
4、PluggableSchemaResolver
public static final String DEFAULT_SCHEMA_MAPPINGS_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.schemas"; private volatile Map<String, String> schemaMappings; public PluggableSchemaResolver(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { this.classLoader = classLoader; this.schemaMappingsLocation = DEFAULT_SCHEMA_MAPPINGS_LOCATION; }
PluggableSchemaResolver是重點,負責找到相對應的XSD文件,一般我們都是使用XSD作為檢驗文件。
DEFAULT_SCHEMA_MAPPINGS_LOCATION ,指明資源文件路徑。

可以看到,spring很貼心的將所有版本的xsd文件都準備了,即使沒有指定版本號,也會有預設的xsd文件。
schemaMappings負責保存資源路徑與校驗文件url的映射。即systemId為key,resourceLocation為value。
public InputSource resolveEntity(@Nullable String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws IOException { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Trying to resolve XML entity with public id [" + publicId + "] and system id [" + systemId + "]"); } if (systemId != null) { //根據systemId,也就是驗證文件的url,找到本地文件路徑 String resourceLocation = getSchemaMappings().get(systemId); //如果沒有找到,並且url是https開頭,就轉換為http開頭的url if (resourceLocation == null && systemId.startsWith("https:")) { // Retrieve canonical http schema mapping even for https declaration resourceLocation = getSchemaMappings().get("http:" + systemId.substring(6)); } //定位本地資源文件 if (resourceLocation != null) { Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(resourceLocation, this.classLoader); try { InputSource source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream()); source.setPublicId(publicId); source.setSystemId(systemId); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Found XML schema [" + systemId + "] in classpath: " + resourceLocation); } return source; } catch (FileNotFoundException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not find XML schema [" + systemId + "]: " + resource, ex); } } } } // Fall back to the parser's default behavior. return null; }
其中getSchemaMappings獲取或初始化map容器,這裡用到了懶載入
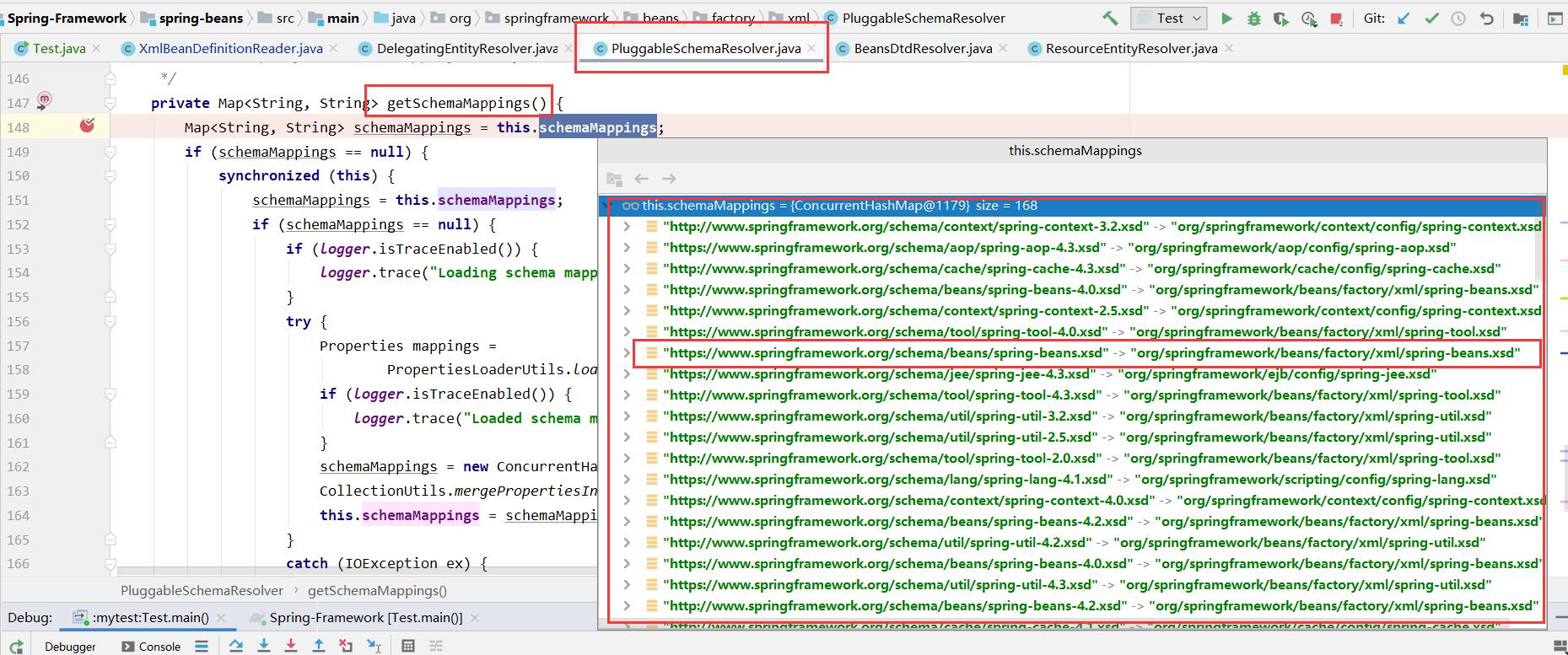
private Map<String, String> getSchemaMappings() { Map<String, String> schemaMappings = this.schemaMappings; if (schemaMappings == null) { synchronized (this) { schemaMappings = this.schemaMappings; if (schemaMappings == null) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Loading schema mappings from [" + this.schemaMappingsLocation + "]"); } try { //這裡負責初始化map Properties mappings = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties(this.schemaMappingsLocation, this.classLoader); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Loaded schema mappings: " + mappings); } schemaMappings = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(mappings.size()); CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(mappings, schemaMappings); this.schemaMappings = schemaMappings; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable to load schema mappings from location [" + this.schemaMappingsLocation + "]", ex); } } } } return schemaMappings; }
通過調試,可以看到map中的中的內容
4、ResourceEntityResolver
在xmlBeanDefinitionReader中,預設會用這種EntityResolver。
public class ResourceEntityResolver extends DelegatingEntityResolver { public InputSource resolveEntity(@Nullable String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws SAXException, IOException { InputSource source = super.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId); //調用父類DelegatingEntityResolver的方法,如果沒有,就從網路獲取 if (source == null && systemId != null) { String resourcePath = null; try { String decodedSystemId = URLDecoder.decode(systemId, "UTF-8"); String givenUrl = new URL(decodedSystemId).toString(); String systemRootUrl = new File("").toURI().toURL().toString(); // Try relative to resource base if currently in system root. if (givenUrl.startsWith(systemRootUrl)) { resourcePath = givenUrl.substring(systemRootUrl.length()); } } catch (Exception ex) { // Typically a MalformedURLException or AccessControlException. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not resolve XML entity [" + systemId + "] against system root URL", ex); } // No URL (or no resolvable URL) -> try relative to resource base. resourcePath = systemId; } if (resourcePath != null) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Trying to locate XML entity [" + systemId + "] as resource [" + resourcePath + "]"); } Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(resourcePath); source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream()); source.setPublicId(publicId); source.setSystemId(systemId); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Found XML entity [" + systemId + "]: " + resource); } } else if (systemId.endsWith(DTD_SUFFIX) || systemId.endsWith(XSD_SUFFIX)) { // External dtd/xsd lookup via https even for canonical http declaration String url = systemId; if (url.startsWith("http:")) { url = "https:" + url.substring(5); } try { source = new InputSource(new URL(url).openStream()); source.setPublicId(publicId); source.setSystemId(systemId); } catch (IOException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not resolve XML entity [" + systemId + "] through URL [" + url + "]", ex); } // Fall back to the parser's default behavior. source = null; } } } return source; } }
該類首先會調用父類DelegatingEntityResolver的方法獲取資源文件,如果沒有就會從網路獲取。不過一般都能從本地獲取到。
走的太遠,不要忘記為什麼出發!
再來看看這個方法,是不是清楚多了?
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception { return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware()); }
至此,document對象獲取完成。
參考:spring源碼深度解析。


