MyBatis源碼解析 解析器模塊 1. 前言 在MyBatis中涉及多個xml文件,解析這些xml文件自然離不開解析器。本文就來分析一下解析器模塊。 2. 準備工作 xml常見的解析方式分為以下三種: DOM ( Document Object Model)解析方式 SAX (Simple API ...
MyBatis源碼解析 - 解析器模塊
1. 前言
在MyBatis中涉及多個xml文件,解析這些xml文件自然離不開解析器。本文就來分析一下解析器模塊。
2. 準備工作
xml常見的解析方式分為以下三種:
- DOM ( Document Object Model)解析方式
- SAX (Simple APIfor XML)解析方式
- StAX( Streaming API for XML)解析方式 - JDK 6.0版本開始,JDK開始支持
詳細的解析xml學習可以參考 Java解析XML 在這裡我們需要重點看下DOM解析,DOM解析主要的好處就是易於編程,可以跟根據需求在樹形結構的各個節點之間導航。
3. XPathParser
MyBatis 在初始化過程中處理mybatis-config.xml以及映射文件時使用的是DOM解析方式,並結合使用XPath解析XML配置文件。DOM會將整個XML文檔載入到記憶體中形成數據結構。
XPathParser類封裝了XPath 、Document和EntityResolver 依賴關係如圖所示
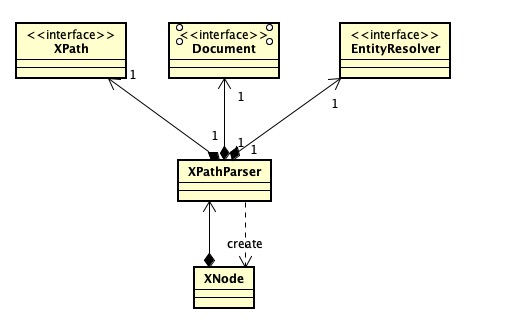
XPathParser中欄位含義和功能如下
private final Document document; //Document 對象
private boolean validation; //是否開啟校驗
private EntityResolver entityResolver; //用於載入本地DTD文件
private Properties variables; //mybatis-config.xml <properties> 標簽定義的鍵值對集合
private XPath xpath; //XPath對象- 預設情況下,對XML文檔驗證的時候,會根據XML文檔指定的網址載入對應的DTD文件或者XSD文件。
- 解析
mybatis-config.xml文件時,預設聯網載入http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd這個DTD文檔,當網路比較慢會使載入變緩慢。其實在MyBatis中已經配置了關於DTD文件的映射關係。 XMLMapperEntityResolver中實現了EntityResolver介面,並配置載入本地的DTD文件。關係如圖所示:

EntityResolver介面的核心是resolveEntity() 方法,XMLMapperEntityResolver的實現如下:
public class XMLMapperEntityResolver implements EntityResolver {
// 指定mybatis-config.xml 文件和映射文件對應的dtd的SystemId
private static final String IBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM = "ibatis-3-config.dtd";
private static final String IBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM = "ibatis-3-mapper.dtd";
private static final String MYBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM = "mybatis-3-config.dtd";
private static final String MYBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM = "mybatis-3-mapper.dtd";
// 指定指定mybatis-config.xml 文件和映射文件對應的dtd的具體位置
private static final String MYBATIS_CONFIG_DTD = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-config.dtd";
private static final String MYBATIS_MAPPER_DTD = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd";
/**
* Converts a public DTD into a local one.
*
* @param publicId The public id that is what comes after "PUBLIC"
* @param systemId The system id that is what comes after the public id.
* @return The InputSource for the DTD
*
* @throws org.xml.sax.SAXException If anything goes wrong
*/
//實現EntityResolver介面的resolveEntity方法
@Override
public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, String systemId) throws SAXException {
try {
if (systemId != null) {
String lowerCaseSystemId = systemId.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
//查找systemId指定的dtd文件,並調用getInputSource發放讀取dtd文檔
if (lowerCaseSystemId.contains(MYBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM) || lowerCaseSystemId.contains(IBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM)) {
return getInputSource(MYBATIS_CONFIG_DTD, publicId, systemId);
} else if (lowerCaseSystemId.contains(MYBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM) || lowerCaseSystemId.contains(IBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM)) {
return getInputSource(MYBATIS_MAPPER_DTD, publicId, systemId);
}
}
return null;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SAXException(e.toString());
}
}
// getInputSource()方法負責讀取DTD文件形成InputSource對象
private InputSource getInputSource(String path, String publicId, String systemId) {
InputSource source = null;
if (path != null) {
try {
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(path);
source = new InputSource(in);
source.setPublicId(publicId);
source.setSystemId(systemId);
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore, null is ok
}
}
return source;
}
}介紹完XMLMapperEntityResolver之後,我們回到XPathParser這個類上接下來我們按照組成部分挨個拆分出來。
XPathParser構造
XPathParser構造方法有16種,應該是滿足各種各樣不同使用場景下的需求吧。

createDocument方法
private void commonConstructor(boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
this.validation = validation;
this.entityResolver = entityResolver;
this.variables = variables;
XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance();
this.xpath = factory.newXPath();
}
//調用createDocument發放之前一定要先調用 commonConstructor() 方法完成初始化
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
// 創建 DocumentBuilderFactory 對象
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//對 DocumentBuilderFactory 對象一系列配置
factory.setFeature(XMLConstants.FEATURE_SECURE_PROCESSING, true);
factory.setValidating(validation);
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
//創建 DocumentBuilder 對象併進行配置
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
//設置 entityResolver 介面對象
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver);
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {
@Override
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
// NOP
}
});
//載入 xml 文件
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}- 在
XPathParser.createDocument()方法中封裝了創建Document對象的過程並觸發了載入XML文檔的過程。
eval*()系列方法
XPathParser中提供了一系列的eval*()方法用於解析boolean、short、Integer、Long、Float、Sting、Double、Node等類型的信息。- 通過調用
XPath.evaluate()方法查找指定路徑的節點霍屬性,併進行相應的類型轉換。 - 註意:
XPathParser.evalString()方法會調用PropertyParser.parse()方法處理節點中相應的預設值,具體實現代碼如下:
public String evalString(Object root, String expression) {
String result = (String) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.STRING);
result = PropertyParser.parse(result, variables);
return result;
}PropertyParser```中指定了是否開啟使用預設值的功能以及預設的分隔符,相關代碼如下:
private static final String KEY_PREFIX = "org.apache.ibatis.parsing.PropertyParser.";
//在 mybatis-config.xml 中<properties>節點下配置是否開啟預設值功能的對應配置項
public static final String KEY_ENABLE_DEFAULT_VALUE = KEY_PREFIX + "enable-default-value";
//配置占位符與預設值之間的預設分隔符的對應配置項
public static final String KEY_DEFAULT_VALUE_SEPARATOR = KEY_PREFIX + "default-value-separator";
//預設情況下關閉預設值的功能
private static final String ENABLE_DEFAULT_VALUE = "false";
//預設分隔符是冒號
private static final String DEFAULT_VALUE_SEPARATOR = ":";
private PropertyParser() {
// Prevent Instantiation
}
public static String parse(String string, Properties variables) {
VariableTokenHandler handler = new VariableTokenHandler(variables);
//創建 GenericTokenParser 解析器對象 並制定其占位符為 ${}
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
return parser.parse(string);
}- PropertyParser.parse()
方法創建GenericTokenParser解析器,並將預設值的處理委托給GenericTokenParser.parse()```方法。
4. GenericTokenParser
GenericTokenParser是通用的占位符解析器,具體代碼如下:
package org.apache.ibatis.parsing;
/**
* 通用的占位符解析器
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class GenericTokenParser {
private final String openToken; //占位符的開始標記
private final String closeToken; //占位符的結束標記
private final TokenHandler handler; //TokenHandler介面的實現會按照一定的邏輯解析占位符
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
public String parse(String text) {
//檢測 text 是否為空
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
// 查找開始標記
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
//用來標記解析後的字元串
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
// 遇到轉義的開始標記 則直接將前面的字元串以及開始標記追加到builder中
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
//查找到開始標記,且未轉義
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
//將前面的字元串追加到builder中
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
//修改offset位置
offset = start + openToken.length();
// 從offset後繼續查找結束標記
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
//處理轉義的結束標記
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
//將開始標記和結束標記之間的字元串追加到expression中保存
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
//未找到結束標記
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
//將占位符的字面值交給TokenHandler處理,並將處理結果追加到builder中保存
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
//最終拼湊出解析後完整的內容
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset); //移動start
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
}GenericTokenParser.parse()方法比較簡單,具體實現就是順序查找openToken和closeToken,解析得到占位符的字面值- 解析出來的結果交給
Tokenhandler處理,然後將解析結果重新拼裝成字元串返回。
5. TokenHandler
<img src="http://qiniu-cdn.janker.top/oneblog/20200105225624602.png" style="zoom:67%;" />
## 6. PropertyParser
PropertyParser是使用VariableTokenHandler和GenericTokenParser配合完成占位符解析。代碼如下:
------
package org.apache.ibatis.parsing;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
- @author Clinton Begin
- @author Kazuki Shimizu
*/
public class PropertyParser {
private static final String KEY_PREFIX = "org.apache.ibatis.parsing.PropertyParser.";
//在 mybatis-config.xml 中
public static final String KEY_ENABLE_DEFAULT_VALUE = KEY_PREFIX + "enable-default-value";
//配置占位符與預設值之間的預設分隔符的對應配置項
public static final String KEY_DEFAULT_VALUE_SEPARATOR = KEY_PREFIX + "default-value-separator";
//預設情況下關閉預設值的功能
private static final String ENABLE_DEFAULT_VALUE = "false";
//預設分隔符是冒號
private static final String DEFAULT_VALUE_SEPARATOR = ":";
private PropertyParser() {
// Prevent Instantiation
}
public static String parse(String string, Properties variables) {
VariableTokenHandler handler = new VariableTokenHandler(variables);
//創建 GenericTokenParser 解析器對象 並制定其占位符為 ${}
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
return parser.parse(string);
}
private static class VariableTokenHandler implements TokenHandler {
private final Properties variables;
private final boolean enableDefaultValue;
private final String defaultValueSeparator;
private VariableTokenHandler(Properties variables) {
this.variables = variables;
this.enableDefaultValue = Boolean.parseBoolean(getPropertyValue(KEY_ENABLE_DEFAULT_VALUE, ENABLE_DEFAULT_VALUE));
this.defaultValueSeparator = getPropertyValue(KEY_DEFAULT_VALUE_SEPARATOR, DEFAULT_VALUE_SEPARATOR);
}
private String getPropertyValue(String key, String defaultValue) {
return (variables == null) ? defaultValue : variables.getProperty(key, defaultValue);
}
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
// 檢測 variables 集合是否為空
if (variables != null) {
String key = content;
//檢測是否支持占位符中使用預設值的功能
if (enableDefaultValue) {
// 查找分隔符
final int separatorIndex = content.indexOf(defaultValueSeparator);
String defaultValue = null;
if (separatorIndex >= 0) {
// 獲取占位符的名稱
key = content.substring(0, separatorIndex);
//獲取預設值
defaultValue = content.substring(separatorIndex + defaultValueSeparator.length());
}
if (defaultValue != null) {
//在variable集合中查找指定占位符
return variables.getProperty(key, defaultValue);
}
}
// 不支持預設值的功能,直接查找variables集合
if (variables.containsKey(key)) {
return variables.getProperty(key);
}
}
return "${" + content + "}"; //variables集合為空 直接返回
}}
}
------
- VariableTokenHandler```是```PropertyParser```類中的一個靜態內部類。
- ```VariableTokenHandler```實現了```TokenHandler```介面中的```handlerToken()```方法
- 該實現首先按照defaultValueSeparator欄位指定的分隔符對整個占位符進行切分,得到占位符的名稱和預設值,然後按照切分得到的占位符名稱查找對應的值
- 如果在```<properties>```節點下未定義相應的鍵值對,則將切分得到額預設值作為解析結果返回。
## 7. XNode
XPathParser.evalNode()方法返回的類型為XNode,他對org.w3c.dom.Node對象驚醒了封裝和解析,具體代碼如下:
------
public class XNode {
private final Node node; //org.w3c.dom.Node對象
private final String name; //Node節點名稱
private final String body; //節點內容
private final Properties attributes; //節點屬性集合
private final Properties variables; //mybatis-config.xml配置文件中
private final XPathParser xpathParser; //xpathParser對象 xNode由XPathParser對象生成
public XNode(XPathParser xpathParser, Node node, Properties variables) {
this.xpathParser = xpathParser;
this.node = node;
this.name = node.getNodeName();
this.variables = variables;
this.attributes = parseAttributes(node);
this.body = parseBody(node);
}
public XNode newXNode(Node node) {
return new XNode(xpathParser, node, variables);
}
public XNode getParent() {
Node parent = node.getParentNode();
if (!(parent instanceof Element)) {
return null;
} else {
return new XNode(xpathParser, parent, variables);
}
}
public String getPath() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
Node current = node;
while (current instanceof Element) {
if (current != node) {
builder.insert(0, "/");
}
builder.insert(0, current.getNodeName());
current = current.getParentNode();
}
return builder.toString();
}
public String getValueBasedIdentifier() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
XNode current = this;
while (current != null) {
if (current != this) {
builder.insert(0, "");
}
String value = current.getStringAttribute("id",
current.getStringAttribute("value",
current.getStringAttribute("property", null)));
if (value != null) {
value = value.replace('.', '');
builder.insert(0, "]");
builder.insert(0,
value);
builder.insert(0, "[");
}
builder.insert(0, current.getName());
current = current.getParent();
}
return builder.toString();
}
public String evalString(String expression) {
return xpathParser.evalString(node, expression);
}
public Boolean evalBoolean(String expression) {
return xpathParser.evalBoolean(node, expression);
}
public Double evalDouble(String expression) {
return xpathParser.evalDouble(node, expression);
}
public List
return xpathParser.evalNodes(node, expression);
}
public XNode evalNode(String expression) {
return xpathParser.evalNode(node, expression);
}
public Node getNode() {
return node;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getStringBody() {
return getStringBody(null);
}
public String getStringBody(String def) {
if (body == null) {
return def;
} else {
return body;
}
}
public Boolean getBooleanBody() {
return getBooleanBody(null);
}
public Boolean getBooleanBody(Boolean def) {
if (body == null) {
return def;
} else {
return Boolean.valueOf(body);
}
}
public Integer getIntBody() {
return getIntBody(null);
}
public Integer getIntBody(Integer def) {
if (body == null) {
return def;
} else {
return Integer.parseInt(body);
}
}
public Long getLongBody() {
return getLongBody(null);
}
public Long getLongBody(Long def) {
if (body == null) {
return def;
} else {
return Long.parseLong(body);
}
}
public Double getDoubleBody() {
return getDoubleBody(null);
}
public Double getDoubleBody(Double def) {
if (body == null) {
return def;
} else {
return Double.parseDouble(body);
}
}
public Float getFloatBody() {
return getFloatBody(null);
}
public Float getFloatBody(Float def) {
if (body == null) {
return def;
} else {
return Float.parseFloat(body);
}
}
public <T extends Enum
return getEnumAttribute(enumType, name, null);
}
public <T extends Enum
String value = getStringAttribute(name);
if (value == null) {
return def;
} else {
return Enum.valueOf(enumType, value);
}
}
// ** 省略 get*()方法
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
toString(builder, 0);
return builder.toString();}
private void toString(StringBuilder builder, int level) {
// ** 省略 toString **
}
private void indent(StringBuilder builder, int level) {
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
builder.append(" ");
}
}
private Properties parseAttributes(Node n) {
Properties attributes = new Properties();
// 獲取節點的屬性集合
NamedNodeMap attributeNodes = n.getAttributes();
if (attributeNodes != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < attributeNodes.getLength(); i++) {
Node attribute = attributeNodes.item(i);
//使用PropertyParser處理每個屬性中的占位符
String value = PropertyParser.parse(attribute.getNodeValue(), variables);
attributes.put(attribute.getNodeName(), value);
}
}
return attributes;
}
private String parseBody(Node node) {
String data = getBodyData(node);
if (data == null) { //當前節點不是文本節點
NodeList children = node.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
//處理子節點
Node child = children.item(i);
data = getBodyData(child);
if (data != null) {
break;
}
}
}
return data;
}
private String getBodyData(Node child) {
if (child.getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE
|| child.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) { //只處理文本內容
String data = ((CharacterData) child).getData();
// 使用 PropertyParser處理文本節點中的占位符
data = PropertyParser.parse(data, variables);
return data;
}
return null;
}
}
```
- XNode
的構造函數會調用其parseAttributes()方法和parseBody()方法解析org.w3c.dom.Node對象中的信息,初始化attributes集合和body```欄位。 XNode中提供了多種get*()方法獲取所需的節點信息,這些信息主要描述attributes集合、body欄位、node欄位。- 此外我們也可以使用XNode.eval()方法結合XPath查詢需要的信息,eval () 系列方法是通過調用其封裝的XPathParser對象的eval *()方法實現的。
- eval *() 系列方法的上下文節點是當前的
XNode.node。
8. 小結
以上就是MyBatis的解析器模塊的全部內容,下一篇博客我們繼續分析反射模塊。
本文由 Janker 創作,採用 CC BY 3.0 CN協議 進行許可。 可自由轉載、引用,但需署名作者且註明文章出處。如轉載至微信公眾號,請在文末添加作者公眾號二維碼。




