前言 亂碼是我們在程式開發中經常碰到且讓人頭疼的一件事,尤其是我們在做javaweb開發,如果我們沒有清楚亂碼產生的原理,碰到亂碼問題了就容易摸不著頭腦,無從下手。 亂碼主要出現在兩部分,如下: 第一,瀏覽器通過表單提交到後臺,如果表單內容有中文,那麼後臺收到的數據可能會出現亂碼。 第二,後端伺服器 ...
前言
亂碼是我們在程式開發中經常碰到且讓人頭疼的一件事,尤其是我們在做javaweb開發,如果我們沒有清楚亂碼產生的原理,碰到亂碼問題了就容易摸不著頭腦,無從下手。
亂碼主要出現在兩部分,如下:
第一,瀏覽器通過表單提交到後臺,如果表單內容有中文,那麼後臺收到的數據可能會出現亂碼。
第二,後端伺服器需要返回給瀏覽器數據,如果數據中帶有中文,那麼瀏覽器上可能會顯示亂碼。
接下來我們逐一分析亂碼產生的原因,以及如何解決亂碼問題。
一、後端收到瀏覽器提交的中文亂碼
這裡又分為get請求和post請求。
get請求
get請求,請求參數中帶有中文,後臺接收會出現亂碼,原因是tomcat預設編碼是“ISO-8859-1”,所以tomcat會使用“ISO-8859-1”對中文進行編碼,該編碼不支持中文,所以後臺接收到就亂碼了。解決方式有兩種。
param = new String(param.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"),"utf-8");- 修改tomcat編碼為"utf-8",不建議使用這種方式。
post請求
post請求,出現亂碼的原因同get請求,解決方式比較簡單,如下:
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");設置請求參數的編碼格式為“utf-8”,這樣就不會有問題了。
二、後端返回中文給瀏覽器發生亂碼
後端返回數據給瀏覽器,一般也有兩種形式,一種是response.getOutputStream(),一種是response.getWriter()。
兩者區別以及使用規則
- getOutputStream()就是得到了OutputStream,用來向客戶端(瀏覽器)輸出任何數據,如果輸出的是字元,會被轉換成二進位輸出,如果字元中出現中文,那麼會出現“java.io.CharConversionException:Not an ISO 8859-1 character:”異常
- getWriter()是對outputStream進行了包裝,用來輸出字元用的。
因此,調用requonse.getWriter()方法時可實現文本字元串數據輸出,調用response.getOutputStream()方法可現實位元組流數據的輸出。所以,如果要輸出圖片等二進位數據時,需要使用response.getOutputStream。
註意,getOutputStream()和getWriter()不能同時使用,否則會拋出”getWriter() has already been called for this response“異常。
區別講完了,下麵我們主要還是通過實踐分析下亂碼產生的原理。
response.getOutputStream().print()
返回英文數據就不說了,沒什麼問題,看下返回中文是什麼效果;
@RequestMapping("/helloworld.do")
public void helloworld(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String str = "中國加油,武漢加油";
response.getOutputStream().print(str);
}結果如下:
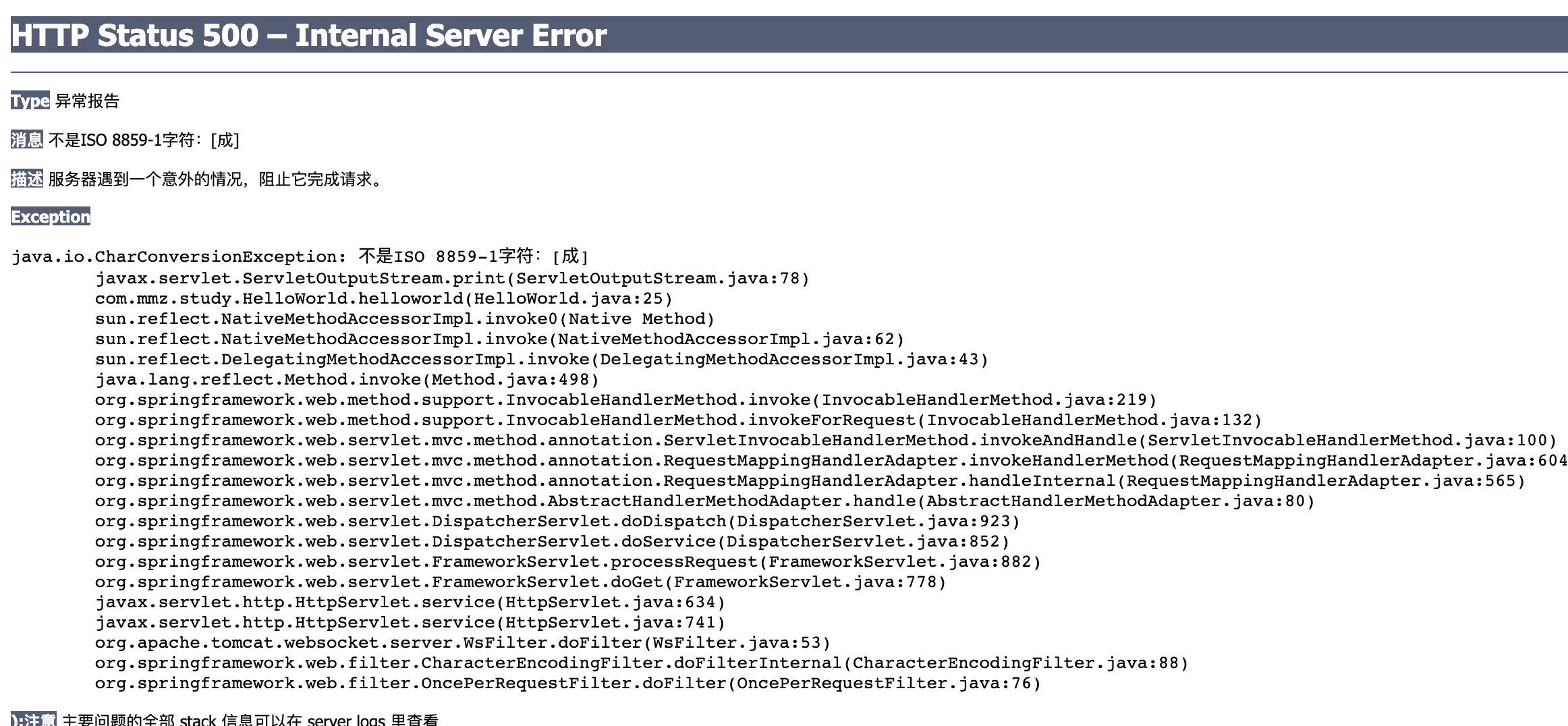
分析:
OutPutStream是輸出二進位數據的,所以需要對字元串改成二進位輸出,Tomcat使用的是"ISO8859-1"編碼對其進行轉換,而中文對”ISO859-1“不支持,所以就拋異常了。
response.getOutputStream.write()
同樣的,我們再來看下輸出中文會怎麼樣。
@RequestMapping("/helloworld.do")
public void helloworld(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String str = "中國加油,武漢加油";
response.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes());
}頁面輸出結果如下:
涓浗鍔犳補錛屾奼夊姞娌�分析:
在java中,String的getBytes()方法是得到一個操作系統預設的編碼格式的位元組數組,我電腦的系統是macos,預設編碼格式是utf-8,返回給瀏覽器是utf-8編碼格式的位元組數組,但是瀏覽器預設是"gbk"編碼解析,所以就亂碼了。
既然這樣,那我們換成“gb2312”編碼(gb2312編碼是gbk編碼的一種)試試呢?
@RequestMapping("/helloworld.do")
public void helloworld(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String str = "中國加油,武漢加油";
response.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes());
}頁面輸出:
中國加油,武漢加油原理我們弄清楚了,但是在項目開發中,我們需要編碼統一,最常用的就是中文字元編碼"UTF-8",可是按照我們的理解,如果我們直接response.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes("utf-8"));肯定會亂碼,我們需要用某種方式,告訴瀏覽器,你要用我指定的“utf-8”編碼接受我返回的中文。response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8")這樣就完事了,看看效果吧。
@RequestMapping("/helloworld.do")
public void helloworld(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String str = "中國加油,武漢加油";
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.getOutputStream().write(str.getBytes("utf-8"));
}頁面輸出:
中國加油,武漢加油response.getWriter()
前面已經總結過了,response.getWriter()跟response.getOutputStream()不一樣,outputStream是輸出二進位的,writer是輸出字元串的。response.getWriter()輸出也有兩種方法,一種是print(),一種是write(),其實兩者在處理亂碼這一塊沒有什麼區別,就不分開講述了。
示例:
@RequestMapping("/helloworld.do")
public void helloworld(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String str = "中國加油,武漢加油";
response.getWriter().print(str);
}頁面輸出:
?????????分析:
同樣的,Tomcat預設的編碼是ISO 8859-1,當我們輸出中文數據的時候,Tomcat會依據ISO 8859-1碼表給我們的數據編碼,中文不支持這個碼表呀,所以出現了亂碼。
這個時候response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8")又派上用場了。
@RequestMapping("/helloworld.do")
public void helloworld(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String str = "中國加油,武漢加油";
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().print(str);
}頁面輸出:
中國加油,武漢加油在這裡,response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8")做了兩件事,response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");和response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=UTF-8");具體就是,第一,輸出中文”中國加油,武漢加油“的時候,對中文進行”utf-8“編碼;第二,告訴瀏覽器,你也要用"utf-8"來顯示我返回的中文。
最後
對於springMVC項目,如何解決亂碼問題呢?項目中一般會在web.xml中配置編碼過濾器。配置如下:
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>這樣能保證請求的參數按照指定的編碼格式進行編碼,簡單翻看下過濾器源碼如下:
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
if (this.encoding != null && (this.forceEncoding || request.getCharacterEncoding() == null)) {
request.setCharacterEncoding(this.encoding);
if (this.forceEncoding) {
response.setCharacterEncoding(this.encoding);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}代碼中有兩處重要的地方值得註意,分別是request.setCharacterEncoding(this.encoding);和response.setCharacterEncoding(this.encoding);前者表示我們對請求過來的參數使用指定的"utf-8"進行編碼,後者便是,返回給瀏覽器時,後端返回字元的編碼是“utf-8”。
好了,經過以上分析是不是亂碼也沒有那麼可怕了。只要明白其中的緣由,解決起來就是一行代碼或者幾行配置的事兒了,如果大家覺得有幫助,不妨點贊支持一下?
如果大家覺得我寫的不錯、清晰易懂的話,可以關註我的公眾號“灰太狼學爪哇”,不定期分享原創技術文章,與君共勉。



