1. 概述 在本教程中,我們將探討如何使用兩種不同的策略改進客戶端重試:指數後退和抖動。 2. 重試 在分散式系統中,多個組件之間的網路通信隨時可能發生故障。 客戶端應用程式通過實現重試來處理這些失敗。 設想我們有一個調用遠程服務的客戶端應用程式—— PingPongService 。 如果 Pin ...
1. 概述
在本教程中,我們將探討如何使用兩種不同的策略改進客戶端重試:指數後退和抖動。
2. 重試
在分散式系統中,多個組件之間的網路通信隨時可能發生故障。
客戶端應用程式通過實現重試來處理這些失敗。
設想我們有一個調用遠程服務的客戶端應用程式—— PingPongService 。
interface PingPongService {
String call(String ping) throws PingPongServiceException;
}如果 PingPongService 返回一個 PingPongServiceException ,則客戶端應用程式必須重試。在以下選項當中,我們將考慮實現客戶端重試的方法。
3. Resilience4j 重試
在我們的例子中,我們將使用 Resilience4j 庫,特別是它的 retry 模塊。我們需要將添加 resilience4j-retry 模塊到 pom.xml :
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.resilience4j</groupId>
<artifactId>resilience4j-retry</artifactId>
</dependency>關於重試的複習,不要忘記查看我們的 Resilience4j 指南。
4. 指數後退
客戶端應用程式必須負責地實現重試。當客戶在沒有等待的情況下重試失敗的調用時,他們可能會使系統不堪重負,並導致已經處於困境的服務進一步降級。
指數回退是處理失敗網路調用重試的常用策略。簡單地說,客戶端在連續重試之間等待的時間間隔越來越長:
wait_interval = base * multiplier^n其中,
- base 是初始間隔,即等待第一次重試
- n 是已經發生的故障數量
- multiplier 是一個任意的乘法器,可以用任何合適的值替換
通過這種方法,我們為系統提供了喘息的空間,以便從間歇性故障或更嚴重的問題中恢復過來。
我們可以在 Resilience4j 重試中使用指數回退演算法,方法是配置它的 IntervalFunction ,該函數接受 initialInterval 和 multiplier。
重試機制使用 IntervalFunction 作為睡眠函數:
IntervalFunction intervalFn =
IntervalFunction.ofExponentialBackoff(INITIAL_INTERVAL, MULTIPLIER);
RetryConfig retryConfig = RetryConfig.custom()
.maxAttempts(MAX_RETRIES)
.intervalFunction(intervalFn)
.build();
Retry retry = Retry.of("pingpong", retryConfig);
Function<String, String> pingPongFn = Retry
.decorateFunction(retry, ping -> service.call(ping));
pingPongFn.apply("Hello");讓我們模擬一個真實的場景,假設我們有幾個客戶端同時調用 PingPongService :
ExecutorService executors = newFixedThreadPool(NUM_CONCURRENT_CLIENTS);
List<Callable> tasks = nCopies(NUM_CONCURRENT_CLIENTS, () -> pingPongFn.apply("Hello"));
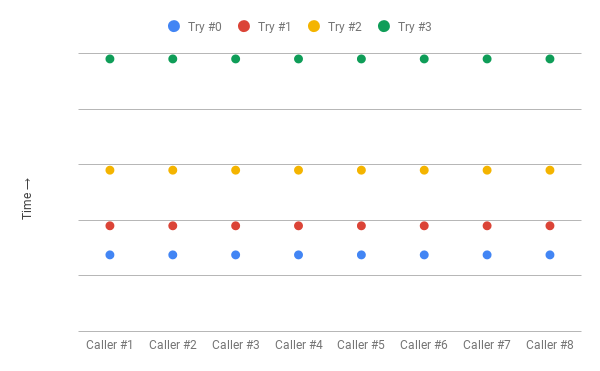
executors.invokeAll(tasks);讓我們看看 NUM_CONCURRENT_CLIENTS = 4 的遠程調用日誌:
[thread-1] At 00:37:42.756
[thread-2] At 00:37:42.756
[thread-3] At 00:37:42.756
[thread-4] At 00:37:42.756
[thread-2] At 00:37:43.802
[thread-4] At 00:37:43.802
[thread-1] At 00:37:43.802
[thread-3] At 00:37:43.802
[thread-2] At 00:37:45.803
[thread-1] At 00:37:45.803
[thread-4] At 00:37:45.803
[thread-3] At 00:37:45.803
[thread-2] At 00:37:49.808
[thread-3] At 00:37:49.808
[thread-4] At 00:37:49.808
[thread-1] At 00:37:49.808我們可以在這裡看到一個清晰的模式——客戶機等待指數級增長的間隔,但是在每次重試(衝突)時,它們都在同一時間調用遠程服務。
我們只解決了問題的一部分 - 我們不再重新啟動遠程服務,但是,取而代之的是隨著時間的推移分散工作量,我們在工作時間間隔更多,空閑時間更長。此行為類似於驚群問題。
5. 介紹抖動
在我們前面的方法中,客戶機等待時間逐漸變長,但仍然是同步的。添加抖動提供了一種方法來中斷跨客戶機的同步,從而避免衝突。在這種方法中,我們給等待間隔增加了隨機性。
wait_interval = (base * 2^n) +/- (random_interval)其中,random_interval 被添加(或減去)以打破客戶端之間的同步。
我們不會深入研究隨機區間的電腦制,但是隨機化必須將峰值空間分離到更平滑的客戶端調用分佈。
我們可以通過配置一個指數隨機回退 IntervalFunction,它也接受一個 randomizationFactor,從而在 Resilience4j 重試中使用帶有抖動的指數回退:
IntervalFunction intervalFn =
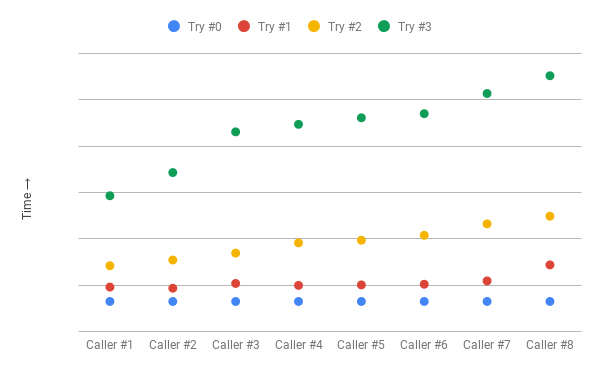
IntervalFunction.ofExponentialRandomBackoff(INITIAL_INTERVAL, MULTIPLIER, RANDOMIZATION_FACTOR);讓我們回到我們的真實場景,並查看帶抖動的遠程調用日誌:
[thread-2] At 39:21.297
[thread-4] At 39:21.297
[thread-3] At 39:21.297
[thread-1] At 39:21.297
[thread-2] At 39:21.918
[thread-3] At 39:21.868
[thread-4] At 39:22.011
[thread-1] At 39:22.184
[thread-1] At 39:23.086
[thread-5] At 39:23.939
[thread-3] At 39:24.152
[thread-4] At 39:24.977
[thread-3] At 39:26.861
[thread-1] At 39:28.617
[thread-4] At 39:28.942
[thread-2] At 39:31.039現在我們有了更好的傳播。我們已經消除了衝突和空閑時間,並以幾乎恆定的客戶端調用率結束,除非出現最初的激增。
註意:我們誇大了插圖的間隔時間,在實際情況中,我們會有較小的差距。
6. 結論
在本教程中,我們探討瞭如何通過使用抖動增加指數回退來改進客戶端應用程式重試失敗調用的方法。本教程中使用的示例的源代碼可以在 GitHub 上找到。
原文:https://www.baeldung.com/resilience4j-backoff-jitter
譯者:Queena
9月福利,關註公眾號
後臺回覆:004,領取8月翻譯集錦!
往期福利回覆:001,002, 003即可領取!