摘要: 面試常問的知識點啊... 原文: "常見數據結構和Javascript實現總結" 作者:MudOnTire "Fundebug" 經授權轉載,版權歸原作者所有。 做前端的同學不少都是自學成才或者半路出家,電腦基礎的知識比較薄弱,尤其是數據結構和演算法這塊,所以今天整理了一下常見的數據結構和對 ...
摘要: 面試常問的知識點啊...
- 原文:常見數據結構和Javascript實現總結
- 作者:MudOnTire
Fundebug經授權轉載,版權歸原作者所有。
做前端的同學不少都是自學成才或者半路出家,電腦基礎的知識比較薄弱,尤其是數據結構和演算法這塊,所以今天整理了一下常見的數據結構和對應的Javascript的實現,希望能幫助大家完善這方面的知識體系。
1. Stack(棧)
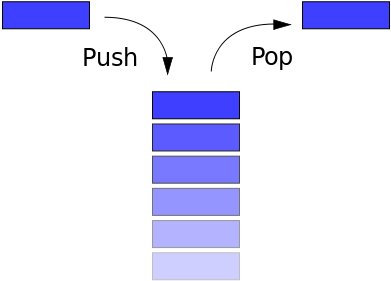
Stack的特點是後進先出(last in first out)。生活中常見的Stack的例子比如一摞書,你最後放上去的那本你之後會最先拿走;又比如瀏覽器的訪問歷史,當點擊返回按鈕,最後訪問的網站最先從歷史記錄中彈出。
Stack一般具備以下方法:
push:將一個元素推入棧頂pop:移除棧頂元素,並返回被移除的元素peek:返回棧頂元素length:返回棧中元素的個數
Javascript的Array天生具備了Stack的特性,但我們也可以從頭實現一個 Stack類:
function Stack() {
this.count = 0;
this.storage = {};
this.push = function (value) {
this.storage[this.count] = value;
this.count++;
}
this.pop = function () {
if (this.count === 0) {
return undefined;
}
this.count--;
var result = this.storage[this.count];
delete this.storage[this.count];
return result;
}
this.peek = function () {
return this.storage[this.count - 1];
}
this.size = function () {
return this.count;
}
}2. Queue(隊列)
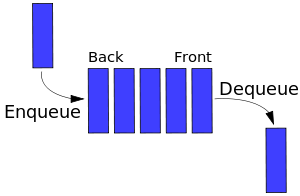
Queue和Stack有一些類似,不同的是Stack是先進後出,而Queue是先進先出。Queue在生活中的例子比如排隊上公交,排在第一個的總是最先上車;又比如印表機的列印隊列,排在前面的最先列印。
Queue一般具有以下常見方法:
enqueue:入列,向隊列尾部增加一個元素dequeue:出列,移除隊列頭部的一個元素並返回被移除的元素front:獲取隊列的第一個元素isEmpty:判斷隊列是否為空size:獲取隊列中元素的個數
Javascript中的Array已經具備了Queue的一些特性,所以我們可以藉助Array實現一個Queue類型:
function Queue() {
var collection = [];
this.print = function () {
console.log(collection);
}
this.enqueue = function (element) {
collection.push(element);
}
this.dequeue = function () {
return collection.shift();
}
this.front = function () {
return collection[0];
}
this.isEmpty = function () {
return collection.length === 0;
}
this.size = function () {
return collection.length;
}
}Priority Queue(優先隊列)
Queue還有個升級版本,給每個元素賦予優先順序,優先順序高的元素入列時將排到低優先順序元素之前。區別主要是enqueue方法的實現:
function PriorityQueue() {
...
this.enqueue = function (element) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
collection.push(element);
} else {
var added = false;
for (var i = 0; i < collection.length; i++) {
if (element[1] < collection[i][1]) {
collection.splice(i, 0, element);
added = true;
break;
}
}
if (!added) {
collection.push(element);
}
}
}
}
測試一下:
var pQ = new PriorityQueue();
pQ.enqueue(['gannicus', 3]);
pQ.enqueue(['spartacus', 1]);
pQ.enqueue(['crixus', 2]);
pQ.enqueue(['oenomaus', 4]);
pQ.print();結果:
[
[ 'spartacus', 1 ],
[ 'crixus', 2 ],
[ 'gannicus', 3 ],
[ 'oenomaus', 4 ]
]3. Linked List(鏈表)
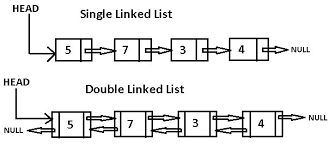
顧名思義,鏈表是一種鏈式數據結構,鏈上的每個節點包含兩種信息:節點本身的數據和指向下一個節點的指針。鏈表和傳統的數組都是線性的數據結構,存儲的都是一個序列的數據,但也有很多區別,如下表:
| 比較維度 | 數組 | 鏈表 |
|---|---|---|
| 記憶體分配 | 靜態記憶體分配,編譯時分配且連續 | 動態記憶體分配,運行時分配且不連續 |
| 元素獲取 | 通過Index獲取,速度較快 | 通過遍歷順序訪問,速度較慢 |
| 添加刪除元素 | 因為記憶體位置連續且固定,速度較慢 | 因為記憶體分配靈活,只有一個開銷步驟,速度更快 |
| 空間結構 | 可以是一維或者多維數組 | 可以是單向、雙向或者迴圈鏈表 |
一個單向鏈表通常具有以下方法:
size:返回鏈表中節點的個數head:返回鏈表中的頭部元素add:向鏈表尾部增加一個節點remove:刪除某個節點indexOf:返回某個節點的indexelementAt:返回某個index處的節點addAt:在某個index處插入一個節點removeAt:刪除某個index處的節點
單向鏈表的Javascript實現:
/**
* 鏈表中的節點
*/
function Node(element) {
// 節點中的數據
this.element = element;
// 指向下一個節點的指針
this.next = null;
}
function LinkedList() {
var length = 0;
var head = null;
this.size = function () {
return length;
}
this.head = function () {
return head;
}
this.add = function (element) {
var node = new Node(element);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
} else {
var currentNode = head;
while (currentNode.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
currentNode.next = node;
}
length++;
}
this.remove = function (element) {
var currentNode = head;
var previousNode;
if (currentNode.element === element) {
head = currentNode.next;
} else {
while (currentNode.element !== element) {
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
}
length--;
}
this.isEmpty = function () {
return length === 0;
}
this.indexOf = function (element) {
var currentNode = head;
var index = -1;
while (currentNode) {
index++;
if (currentNode.element === element) {
return index;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return -1;
}
this.elementAt = function (index) {
var currentNode = head;
var count = 0;
while (count < index) {
count++;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return currentNode.element;
}
this.addAt = function (index, element) {
var node = new Node(element);
var currentNode = head;
var previousNode;
var currentIndex = 0;
if (index > length) {
return false;
}
if (index === 0) {
node.next = currentNode;
head = node;
} else {
while (currentIndex < index) {
currentIndex++;
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
node.next = currentNode;
previousNode.next = node;
}
length++;
}
this.removeAt = function (index) {
var currentNode = head;
var previousNode;
var currentIndex = 0;
if (index < 0 || index >= length) {
return null;
}
if (index === 0) {
head = currentIndex.next;
} else {
while (currentIndex < index) {
currentIndex++;
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
}
length--;
return currentNode.element;
}
}4. Set(集合)
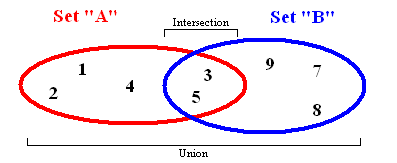
集合是數學中的一個基本概念,表示具有某種特性的對象彙總成的集體。在ES6中也引入了集合類型Set,Set和Array有一定程度的相似,不同的是Set中不允許出現重覆的元素而且是無序的。
一個典型的Set應該具有以下方法:
values:返回集合中的所有元素size:返回集合中元素的個數has:判斷集合中是否存在某個元素add:向集合中添加元素remove:從集合中移除某個元素union:返回兩個集合的並集intersection:返回兩個集合的交集difference:返回兩個集合的差集subset:判斷一個集合是否為另一個集合的子集
使用Javascript可以將Set進行如下實現,為了區別於ES6中的Set命名為MySet:
function MySet() {
var collection = [];
this.has = function (element) {
return (collection.indexOf(element) !== -1);
}
this.values = function () {
return collection;
}
this.size = function () {
return collection.length;
}
this.add = function (element) {
if (!this.has(element)) {
collection.push(element);
return true;
}
return false;
}
this.remove = function (element) {
if (this.has(element)) {
index = collection.indexOf(element);
collection.splice(index, 1);
return true;
}
return false;
}
this.union = function (otherSet) {
var unionSet = new MySet();
var firstSet = this.values();
var secondSet = otherSet.values();
firstSet.forEach(function (e) {
unionSet.add(e);
});
secondSet.forEach(function (e) {
unionSet.add(e);
});
return unionSet;
}
this.intersection = function (otherSet) {
var intersectionSet = new MySet();
var firstSet = this.values();
firstSet.forEach(function (e) {
if (otherSet.has(e)) {
intersectionSet.add(e);
}
});
return intersectionSet;
}
this.difference = function (otherSet) {
var differenceSet = new MySet();
var firstSet = this.values();
firstSet.forEach(function (e) {
if (!otherSet.has(e)) {
differenceSet.add(e);
}
});
return differenceSet;
}
this.subset = function (otherSet) {
var firstSet = this.values();
return firstSet.every(function (value) {
return otherSet.has(value);
});
}
}最後,推薦大家使用Fundebug,一款很好用的BUG監控工具~
5. Hash Table(哈希表/散列表)
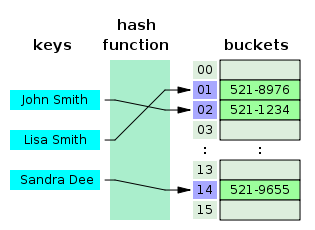
Hash Table是一種用於存儲鍵值對(key value pair)的數據結構,因為Hash Table根據key查詢value的速度很快,所以它常用於實現Map、Dictinary、Object等數據結構。如上圖所示,Hash Table內部使用一個hash函數將傳入的鍵轉換成一串數字,而這串數字將作為鍵值對實際的key,通過這個key查詢對應的value非常快,時間複雜度將達到O(1)。Hash函數要求相同輸入對應的輸出必須相等,而不同輸入對應的輸出必須不等,相當於對每對數據打上唯一的指紋。
一個Hash Table通常具有下列方法:
add:增加一組鍵值對remove:刪除一組鍵值對lookup:查找一個鍵對應的值
一個簡易版本的Hash Table的Javascript實現:
function hash(string, max) {
var hash = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < string.length; i++) {
hash += string.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % max;
}
function HashTable() {
let storage = [];
const storageLimit = 4;
this.add = function (key, value) {
var index = hash(key, storageLimit);
if (storage[index] === undefined) {
storage[index] = [
[key, value]
];
} else {
var inserted = false;
for (var i = 0; i < storage[index].length; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
storage[index][i][1] = value;
inserted = true;
}
}
if (inserted === false) {
storage[index].push([key, value]);
}
}
}
this.remove = function (key) {
var index = hash(key, storageLimit);
if (storage[index].length === 1 && storage[index][0][0] === key) {
delete storage[index];
} else {
for (var i = 0; i < storage[index]; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
delete storage[index][i];
}
}
}
}
this.lookup = function (key) {
var index = hash(key, storageLimit);
if (storage[index] === undefined) {
return undefined;
} else {
for (var i = 0; i < storage[index].length; i++) {
if (storage[index][i][0] === key) {
return storage[index][i][1];
}
}
}
}
}6. Tree(樹)
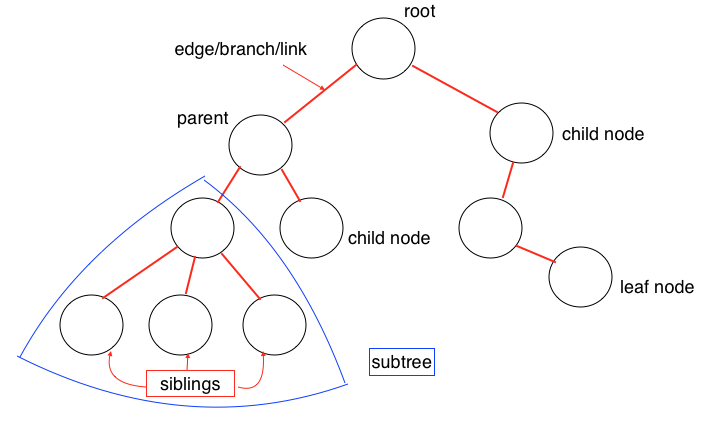
顧名思義,Tree的數據結構和自然界中的樹極其相似,有根、樹枝、葉子,如上圖所示。Tree是一種多層數據結構,與Array、Stack、Queue相比是一種非線性的數據結構,在進行插入和搜索操作時很高效。在描述一個Tree時經常會用到下列概念:
- Root(根):代表樹的根節點,根節點沒有父節點
- Parent Node(父節點):一個節點的直接上級節點,只有一個
- Child Node(子節點):一個節點的直接下級節點,可能有多個
- Siblings(兄弟節點):具有相同父節點的節點
- Leaf(葉節點):沒有子節點的節點
- Edge(邊):兩個節點之間的連接線
- Path(路徑):從源節點到目標節點的連續邊
- Height of Node(節點的高度):表示節點與葉節點之間的最長路徑上邊的個數
- Height of Tree(樹的高度):即根節點的高度
- Depth of Node(節點的深度):表示從根節點到該節點的邊的個數
- Degree of Node(節點的度):表示子節點的個數
我們以二叉查找樹為例,展示樹在Javascript中的實現。在二叉查找樹中,即每個節點最多只有兩個子節點,而左側子節點小於當前節點,而右側子節點大於當前節點,如圖所示:
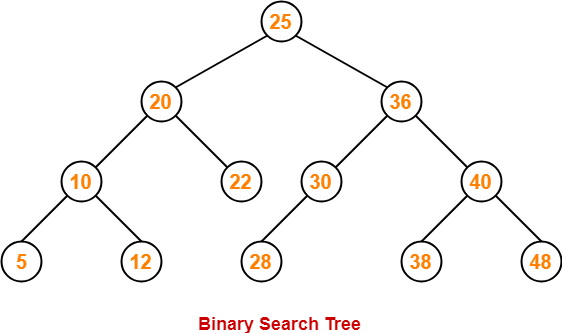
一個二叉查找樹應該具有以下常用方法:
add:向樹中插入一個節點findMin:查找樹中最小的節點findMax:查找樹中最大的節點find:查找樹中的某個節點isPresent:判斷某個節點在樹中是否存在remove:移除樹中的某個節點
以下是二叉查找樹的Javascript實現:
class Node {
constructor(data, left = null, right = null) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
add(data) {
const node = this.root;
if (node === null) {
this.root = new Node(data);
return;
} else {
const searchTree = function (node) {
if (data < node.data) {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = new Node(data);
return;
} else if (node.left !== null) {
return searchTree(node.left);
}
} else if (data > node.data) {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = new Node(data);
return;
} else if (node.right !== null) {
return searchTree(node.right);
}
} else {
return null;
}
};
return searchTree(node);
}
}
findMin() {
let current = this.root;
while (current.left !== null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
findMax() {
let current = this.root;
while (current.right !== null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current.data;
}
find(data) {
let current = this.root;
while (current.data !== data) {
if (data < current.data) {
current = current.left
} else {
current = current.right;
}
if (current === null) {
return null;
}
}
return current;
}
isPresent(data) {
let current = this.root;
while (current) {
if (data === current.data) {
return true;
}
if (data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return false;
}
remove(data) {
const removeNode = function (node, data) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
if (data == node.data) {
// node沒有子節點
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return null;
}
// node沒有左側子節點
if (node.left == null) {
return node.right;
}
// node沒有右側子節點
if (node.right == null) {
return node.left;
}
// node有兩個子節點
var tempNode = node.right;
while (tempNode.left !== null) {
tempNode = tempNode.left;
}
node.data = tempNode.data;
node.right = removeNode(node.right, tempNode.data);
return node;
} else if (data < node.data) {
node.left = removeNode(node.left, data);
return node;
} else {
node.right = removeNode(node.right, data);
return node;
}
}
this.root = removeNode(this.root, data);
}
}測試一下:
const bst = new BST();
bst.add(4);
bst.add(2);
bst.add(6);
bst.add(1);
bst.add(3);
bst.add(5);
bst.add(7);
bst.remove(4);
console.log(bst.findMin());
console.log(bst.findMax());
bst.remove(7);
console.log(bst.findMax());
console.log(bst.isPresent(4));列印結果:
1
7
6
false7. Trie(字典樹,讀音同try)
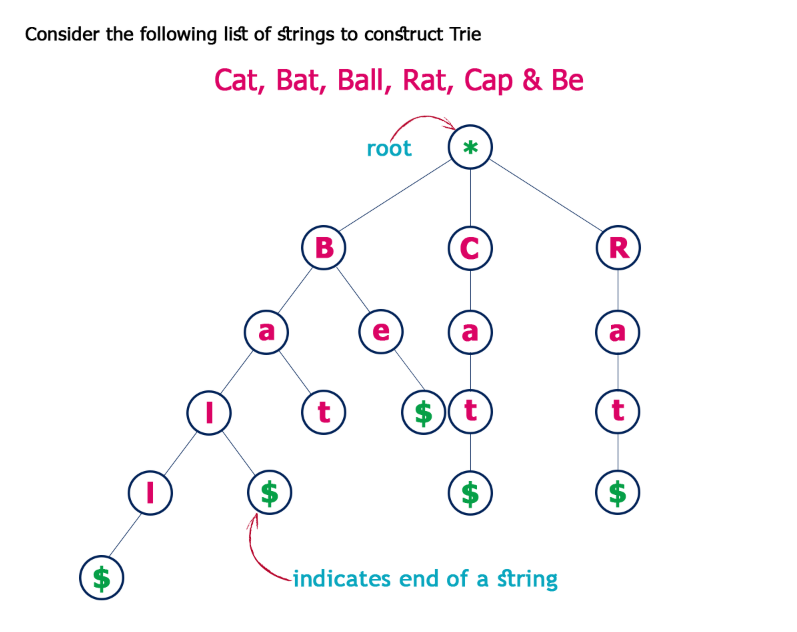
Trie也可以叫做Prefix Tree(首碼樹),也是一種搜索樹。Trie分步驟存儲數據,樹中的每個節點代表一個步驟,trie常用於存儲單詞以便快速查找,比如實現單詞的自動完成功能。 Trie中的每個節點都包含一個單詞的字母,跟著樹的分支可以可以拼寫出一個完整的單詞,每個節點還包含一個布爾值表示該節點是否是單詞的最後一個字母。
Trie一般有以下方法:
add:向字典樹中增加一個單詞isWord:判斷字典樹中是否包含某個單詞print:返回字典樹中的所有單詞
/**
* Trie的節點
*/
function Node() {
this.keys = new Map();
this.end = false;
this.setEnd = function () {
this.end = true;
};
this.isEnd = function () {
return this.end;
}
}
function Trie() {
this.root = new Node();
this.add = function (input, node = this.root) {
if (input.length === 0) {
node.setEnd();
return;
} else if (!node.keys.has(input[0])) {
node.keys.set(input[0], new Node());
return this.add(input.substr(1), node.keys.get(input[0]));
} else {
return this.add(input.substr(1), node.keys.get(input[0]));
}
}
this.isWord = function (word) {
let node = this.root;
while (word.length > 1) {
if (!node.keys.has(word[0])) {
return false;
} else {
node = node.keys.get(word[0]);
word = word.substr(1);
}
}
return (node.keys.has(word) && node.keys.get(word).isEnd()) ? true : false;
}
this.print = function () {
let words = new Array();
let search = function (node = this.root, string) {
if (node.keys.size != 0) {
for (let letter of node.keys.keys()) {
search(node.keys.get(letter), string.concat(letter));
}
if (node.isEnd()) {
words.push(string);
}
} else {
string.length > 0 ? words.push(string) : undefined;
return;
}
};
search(this.root, new String());
return words.length > 0 ? words : null;
}
}8. Graph(圖)
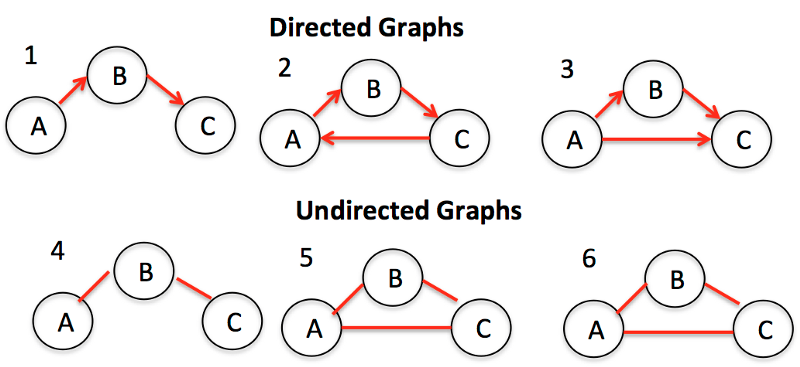
Graph是節點(或頂點)以及它們之間的連接(或邊)的集合。Graph也可以稱為Network(網路)。根據節點之間的連接是否有方向又可以分為Directed Graph(有向圖)和Undrected Graph(無向圖)。Graph在實際生活中有很多用途,比如:導航軟體計算最佳路徑,社交軟體進行好友推薦等等。
Graph通常有兩種表達方式:
Adjaceny List(鄰接列表):
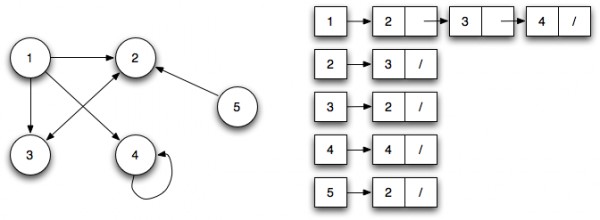
鄰接列表可以表示為左側是節點的列表,右側列出它所連接的所有其他節點。
和 Adjacency Matrix(鄰接矩陣):
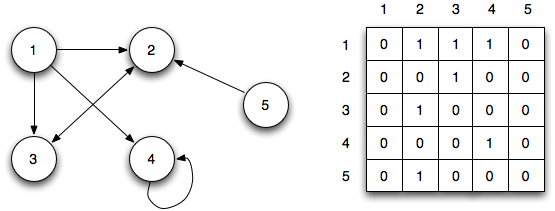
鄰接矩陣用矩陣來表示節點之間的連接關係,每行或者每列表示一個節點,行和列的交叉處的數字表示節點之間的關係:0表示沒用連接,1表示有連接,大於1表示不同的權重。
訪問Graph中的節點需要使用遍歷演算法,遍歷演算法又分為廣度優先和深度優先,主要用於確定目標節點和根節點之間的距離,
在Javascript中,Graph可以用一個矩陣(二維數組)表示,廣度優先搜索演算法可以實現如下:
function bfs(graph, root) {
var nodesLen = {};
for (var i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
nodesLen[i] = Infinity;
}
nodesLen[root] = 0;
var queue = [root];
var current;
while (queue.length != 0) {
current = queue.shift();
var curConnected = graph[current];
var neighborIdx = [];
var idx = curConnected.indexOf(1);
while (idx != -1) {
neighborIdx.push(idx);
idx = curConnected.indexOf(1, idx + 1);
}
for (var j = 0; j < neighborIdx.length; j++) {
if (nodesLen[neighborIdx[j]] == Infinity) {
nodesLen[neighborIdx[j]] = nodesLen[current] + 1;
queue.push(neighborIdx[j]);
}
}
}
return nodesLen;
}測試一下:
var graph = [
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
];
console.log(bfs(graph, 1));列印:
{
0: 2,
1: 0,
2: 1,
3: 3,
4: Infinity
}最後,推薦大家使用Fundebug,一款很好用的BUG監控工具~
本文旨在向廣大前端同學普及常見的數據結構,本人對這一領域也只是初窺門徑,說的有差池的地方歡迎指出。也希望大家能打牢基礎,在這條路上走的更高更遠!
關於Fundebug
Fundebug專註於JavaScript、微信小程式、微信小游戲、支付寶小程式、React Native、Node.js和Java線上應用實時BUG監控。 自從2016年雙十一正式上線,Fundebug累計處理了20億+錯誤事件,付費客戶有陽光保險、核桃編程、荔枝FM、掌門1對1、微脈、青團社等眾多品牌企業。歡迎大家免費試用!


