spring中bean的細節之作用範圍 bean對象的生命周期 單例對象: 出生:當容器創建是對象出生 活著:只要容器還在,對象一直活著 死亡:容器銷毀,對象消亡 多例對象: 出生:當我們使用對象時spring框架為我們創建 活著:對象只要是在使用過程中就一直活著 死亡:當對象長時間不用,且沒有別的 ...
spring中bean的細節之作用範圍**
<!--<bean的作用範圍
bean標簽的scope屬性:
作用;用於指定bean的作用範圍
取值:
singleton:單例的(預設值)
prototype:多例的
request:作用於web應用的請求範圍
session:作用於web應用的會話範圍
global-session:作用於集群環境的會話範圍(全局會話範圍),當不是集群環境時,他是session
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService" scope="prototype"></bean>
bean對象的生命周期
單例對象:
出生:當容器創建是對象出生
活著:只要容器還在,對象一直活著
死亡:容器銷毀,對象消亡
多例對象:
出生:當我們使用對象時spring框架為我們創建
活著:對象只要是在使用過程中就一直活著
死亡:當對象長時間不用,且沒有別的對象引用是,由Java的垃圾回收器回收
spring的依賴註入
<!--spring中的依賴註入-->
<!--依賴註入:-->
<!--Dependenccy Injection-->
<!--IOC的作用:-->
<!--降低程式間的耦合(依賴關係)-->
<!--依賴關係的管理:-->
<!--以後都交給spring來維護-->
<!--在當前類需要用到其他類對象,由spring為我們提供,我們只需在配置文件中說明-->
<!--依賴關係的維護:-->
<!--就稱為依賴註入-->
<!--依賴註入:-->
<!--能註入的數據:有三類-->
<!--基本類型和String-->
<!--其他bean類型(在配置文件或者註解配置過的bean)-->
<!--複雜類型/集合類型-->
<!--註入的方式:-->
<!--第一種:使用構造函數提供-->
<!--第二種:使用set方法提供-->
<!--第三種:使用註解提供-->1.構造函數註入
首先定義可註入的變數
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
public AccountServiceImpl(String name,Integer age,Date birthday){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public void saveAccount(){
System.out.println(name+":"+age+":"+birthday);
}
}<!--構造函數註入
使用標簽:constructor-arg
標簽中的屬性:
type:用於指定要註入的數據的數據類型,該數據類型也是構造函數中某個或某些參數的類型
index:用於指定要註入的數據給構造函數中指定索引位置的參數賦值,索引的位置從0開始
name:用於指定給構造函數中指定名稱的參數賦值(常用)
=======================================
以上三個用於指定給構造函數的哪個參數賦值
=======================================
value:用於提供基本類型和String類型的數據
ref:用於指定其他的bean類型,他指的就是spring的Ioc核心容器中出現過的bean對象
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="迪麗熱巴"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="now"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--配置日期對象-->
<bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean>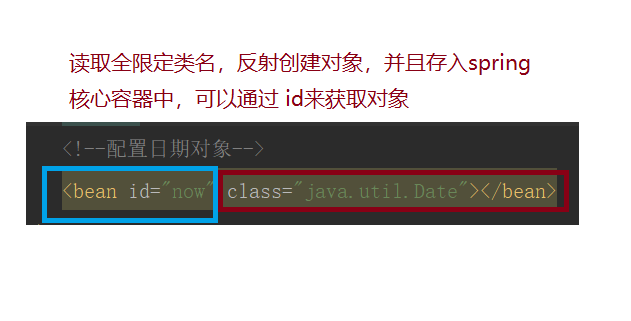
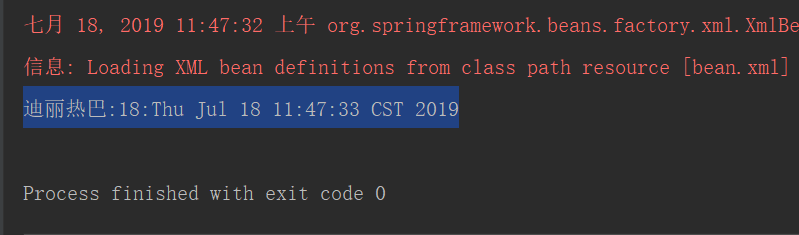
創建測試類調用對象方法,查看註入是否成功
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//獲取核心容器對象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根據id(唯一標識)獲取Bean對象
IAccountService as = (IAccountService)ac.getBean("accountService");
System.out.println(as);
}
}
set方法註入:
1.給屬性提供set,get方法
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 賬戶的業務層實現類
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl2 implements IAccountService {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public void saveAccount(){
System.out.println(name+":"+age+":"+birthday);
}
}
2.XML配置
<bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<!--set方法註入
涉及的標簽:property
標簽的屬性
name:用於指定註入時所調用的set方法名稱
value:用於提供基本類型和String類型的數據
ref:用於指定其他的bean類型,他指的就是spring的Ioc核心容器中出現過的bean對象
-->
<bean id="accountService2" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl2">
<property name="name" value="迪麗熱巴2"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
<property name="birthday" ref="now"></property>
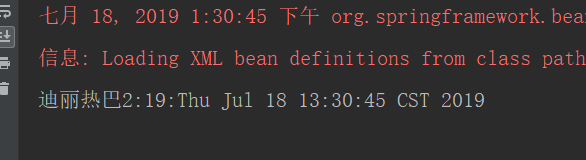
</bean>3.測試類
package com.itheima.ui;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 模擬一個表現層,用於調用業務層
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//獲取核心容器對象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根據id(唯一標識)獲取Bean對象
IAccountService as = (IAccountService)ac.getBean("accountService2");
as.saveAccount();
}
}
註入結合數據
1.類中添加集合屬性
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 賬戶的業務層實現類
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl3 implements IAccountService {
private String[] myStrs;
private List<String> myList;
private Set<String> mySet;
private Map<String,String> myMap;
private Properties myProps;
public String[] getMyStrs() {
return myStrs;
}
public void setMyStrs(String[] myStrs) {
this.myStrs = myStrs;
}
public List<String> getMyList() {
return myList;
}
public void setMyList(List<String> myList) {
this.myList = myList;
}
public Set<String> getMySet() {
return mySet;
}
public void setMySet(Set<String> mySet) {
this.mySet = mySet;
}
public Map<String, String> getMyMap() {
return myMap;
}
public void setMyMap(Map<String, String> myMap) {
this.myMap = myMap;
}
public Properties getMyProps() {
return myProps;
}
public void setMyProps(Properties myProps) {
this.myProps = myProps;
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myStrs));
System.out.println(myList);
System.out.println(mySet);
System.out.println(myMap);
System.out.println(myProps);
}
}
3.配置xml
數組中的元素使用value標簽提供
<!--複雜類型的註入/集合類型的註入
用於給List結構集合註入的標簽
list array set
用於給Map結構集合註入的標簽有
map props
結構相同,標簽可以互換
-->
<bean id="accountService3" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl3">
<property name="myStrs">
<array>
<value>李白</value>
<value>蘇軾</value>
<value>辛棄疾</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="myList">
<list>
<value>李白</value>
<value>蘇軾</value>
<value>辛棄疾</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="mySet">
<set>
<value>李白</value>
<value>蘇軾</value>
<value>辛棄疾</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--===============上面三個是單列集合=====================-->
<property name="myMap">
<map>
<entry key="李白" value="李清照"></entry>
<entry key="蘇軾" value="蘇東坡"></entry>
<entry key="迪麗熱巴" value="古娜力扎"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="myProps">
<props>
<prop key="古娜力扎">迪麗熱巴</prop>
<prop key="佟麗婭">賈靜雯</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
4.測試數據是否註入集合
package com.itheima.ui;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 模擬一個表現層,用於調用業務層
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//獲取核心容器對象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根據id(唯一標識)獲取Bean對象
IAccountService as = (IAccountService)ac.getBean("accountService3");
as.saveAccount();
}
}

使用註解創建對象
1.配置xml,告知spring註解存在的位置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--告知spring在創建容器是要掃描的包,配置所需要的標簽在context名稱空間和約束中-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
</beans>2.加上註解:@Component
@Component
//作用:用於把當前類對象存入spring容器中
//屬性 value:用於指定bean的id,當我們不寫是,他的預設是當前類名,且首字母該小寫
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl();
public AccountServiceImpl(){
System.out.println("對象創建了");
}
public void saveAccount(){ accountDao.saveAccount();
}
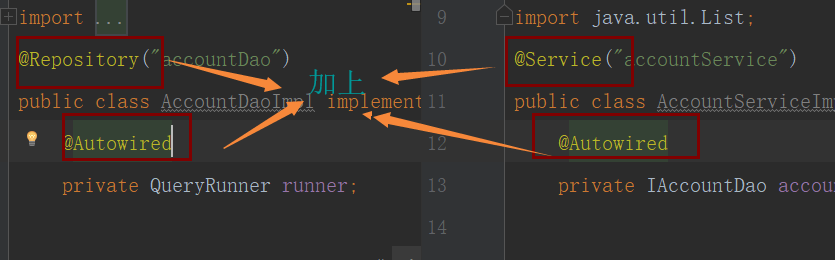
}由Component衍生的註解
Controller:一般用於表現層
Service:一般用在業務層
Repository:一般用在持久層
以上三個註解他們的作用和屬性與Component是一模一樣的,他們三個是spring框架為我們提供明確三層使用的註解,使我們的三層對象更加清晰
自動按照類型註入
Autowired註解:作用:自動按照類型註入,只要容器中有唯一的一個bean對象類型和要註入的變數類型匹配,就可以註入成功
出現位置:可以是變數上,也可以是方法上
細節:在使用註解註入時,set方法就不是必須的
Qualifier註解:作用:在按照類中註入的基礎之上再按照名稱註入。它在給類成員註入時不能單獨使用。但是在給方法參數註入時可以
屬性value:用於指定註入bean的id。
Resource註解:作用:直接按照bean的id註入。它可以獨立使用
屬性name:用於指定bean的id。
以上三個註入都只能註入其他bean類型的數據,而基本類型和String類型無法使用上述註解實。另外,集合類型的註入只能通過XML來實現。
Value註解:作用用於註入基本類型和String類型的數據;
屬性value:用於指定數據的值
Spring的新配置(取出xml的配置文件)
現在需要使用註解來去除 通過配置xml來獲取的兩個bean對象
<!--配置QueryRunner-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///eesy"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="12345"></property>
</bean>
實現方式
//Configuration 作用,指定當前類是一個配置類
//ComponentScan 作用,用於通過註解指定spring在創建容器是要掃描的包
//
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.itheima")//指定創建容器是要掃描的包
public class SpringConfiguration {
//用於創建一個QueryRunner對象
@Bean(name="runner")//用於把當前方法的返回值作為bean對象存入spring的IoC容器中
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(DataSource dataSource){
return new QueryRunner(dataSource);
}
// 創建數據源對象
@Bean(name="dataSource")
public DataSource createDataSource(){
ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
try {
ds.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (PropertyVetoException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ds.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql:///eesy");
ds.setUser("root");
ds.setPassword("12345");
return ds;
}
}
在使用xml配置是獲取容器是通過如下
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");那麼我們現在通過註解來獲取容器就應該使用另外一個類來獲取,如下
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);運行案例是報了錯誤:
NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of typeavailable: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations:
具體錯誤信息如下

關鍵字:NoSuchBeanDefinitionException,說沒有bean對象
原來是忘記在bean對象前加註解了dao層,和service層都要加