FUSE 倉庫 Wiki FUSE 性能評測 關於Fuse文件系統: FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace) is an interface for userspace programs to export a filesystem to the Linux kernel. T ...
關於Fuse文件系統:
FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace) is an interface for userspace programs to export a filesystem to the Linux kernel. The FUSE project consists of two components: the fuse kernel module (maintained in the regular kernel repositories) and the libfuseuserspace library (maintained in this repository). libfuse provides the reference implementation for communicating with the FUSE kernel module.
A FUSE file system is typically implemented as a standalone application that links with libfuse. libfuse provides functions to mount the file system, unmount it, read requests from the kernel, and send responses back. libfuse offers two APIs: a "high-level", synchronous API, and a "low-level" asynchronous API. In both cases, incoming requests from the kernel are passed to the main program using callbacks. When using the high-level API, the callbacks may work with file names and paths instead of inodes, and processing of a request finishes when the callback function returns. When using the low-level API, the callbacks must work with inodes and responses must be sent explicitly using a separate set of API functions.
FUSE 巨集觀調用:
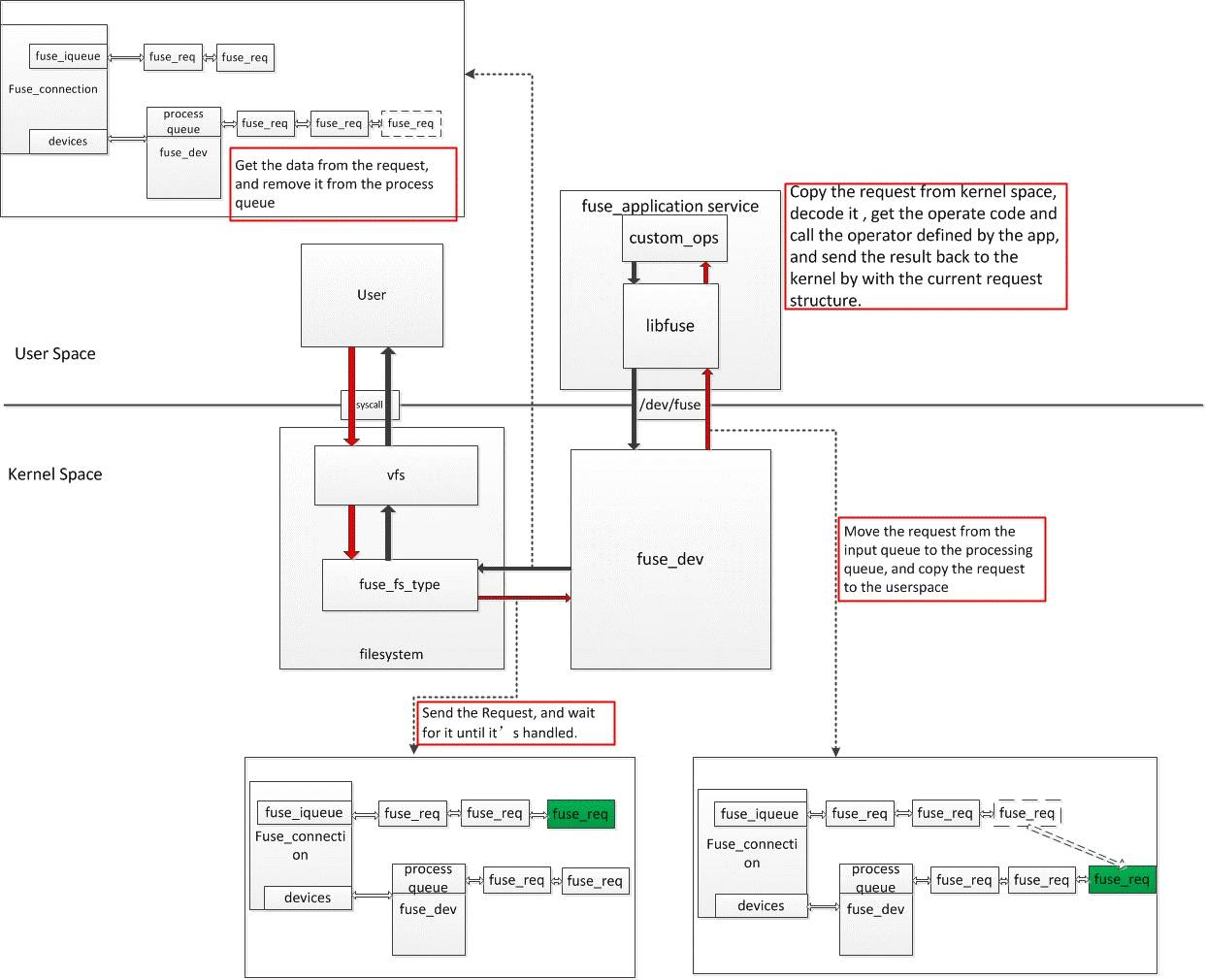
以open為例,整個調用的過程如下:
1- 用戶態app調用glibc open介面,觸發sys_open系統調用。
2- sys_open 調用fuse中inode節點定義的open方法。
3- inode中open生成一個request消息,並通過/dev/fuse發送request消息到用戶態libfuse。
4- Libfuse調用fuse_application用戶自定義的open的方法,並將返回值通過/dev/fuse通知給內核。
5- 內核收到request消息的處理完成的喚醒,並將結果放回給VFS系統調用結果。
6- 用戶態app收到open的返回結果。
FUSE 包含兩個大的發行版本:fuse2 和 fuse3 ,那麼fuse2 和 fuse3之間有什麼區別呢?(What exactly is the difference between fuse2 and fuse3?)

FUSE 安裝
FUSE 安裝分為兩種方式,一種是 編譯安裝,另外一張是通過包管理軟體(YUM)進行安裝。編譯安裝按照官方教程安裝即可。
我使用的操作系統是 Fedora 29, 所以嘗試使用yum進行安裝:
首先使用rpm 命令查一下當前系統是否已經安裝了fuse:
[root@docker 4.19.13-300.fc29.x86_64]# rpm -aq | grep fuse fuse-common-3.2.3-14.fc29.x86_64 fuse-2.9.7-14.fc29.x86_64 fuse-libs-2.9.7-14.fc29.x86_64 glusterfs-fuse-5.2-1.fc29.x86_64 gvfs-fuse-1.38.1-1.fc29.x86_64 zfs-fuse-0.7.2.2-6.fc27.x86_64
可見已經安裝好了,當前系統中使用的是fuse的2.9.7版本,並且是有相應的庫。所以算是已經安裝好了。如果系統中沒有上述安裝包,可以使用yum進行安裝。
[root@docker 4.19.13-300.fc29.x86_64]# yum search fuse Last metadata expiration check: 1:10:16 ago on Sat 12 Jan 2019 10:13:49 PM CST. ============================================================================ Summary & Name Matched: fuse ============================================================================ fuse.x86_64 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 utilities fuse.x86_64 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 utilities fuse-libs.x86_64 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 libraries fuse-libs.i686 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 libraries fuse-libs.x86_64 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 libraries fuse3-libs.i686 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v3 libraries fuse3-libs.x86_64 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v3 libraries fuse-devel.i686 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 devel files fuse-devel.x86_64 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 devel files fuse3-devel.i686 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v3 devel files fuse3-devel.x86_64 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v3 devel files fuse-common.x86_64 : Common files for File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 and v3 fuse-common.x86_64 : Common files for File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 and v3
通過自己的需求,安裝對應版本的安裝包:fuse-common.x86_64 這個軟體包在v2和v3兩個版本中都能進行使用。當然你也可以查看包里的內容,進一步瞭解fuse的組成。
fuse 的內核模塊也已經內置到操作系統內核之中了:
[root@docker fuse]# pwd /lib/modules/4.19.10-300.fc29.x86_64/kernel/fs/fuse [root@docker fuse]# ls fuse.ko.xz
為了能夠開發屬於自己的文件系統,還要安裝fuse開發包:
fuse-devel.x86_64 : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 devel files
Name : fuse-devel Version : 2.9.7 Release : 14.fc29 Arch : x86_64 Size : 36 k Source : fuse-2.9.7-14.fc29.src.rpm Repo : fedora Summary : File System in Userspace (FUSE) v2 devel files URL : http://fuse.sf.net License : LGPLv2+ Description : With FUSE it is possible to implement a fully functional filesystem in a : userspace program. This package contains development files (headers, : pgk-config) to develop FUSE v2 based applications/filesystems.
我們從包描述可以看到,包中包括了一些開發所需要一些頭文件, 動態鏈接庫(.so),pgk-config 文件等。
FUSE 簡單使用(DEMO)
high-level API:
/* FUSE: Filesystem in Userspace Copyright (C) 2001-2007 Miklos Szeredi <[email protected]> This program can be distributed under the terms of the GNU GPL. See the file COPYING. gcc -Wall hello.c `pkg-config fuse --cflags --libs` -o hello */ #define FUSE_USE_VERSION 26 //先定義, fuse.h中有判斷 #include <fuse.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <fcntl.h> static const char *hello_str = "Hello World!\n"; static const char *hello_path = "/hello"; // 與函數stat()類似,用於得到文件屬性,並將其存入到結構體struct stat當中 struct stat *stbuf static int hello_getattr(const char *path, struct stat *stbuf) { int res = 0; memset(stbuf, 0, sizeof(struct stat)); // 使用memset進行初始化結構體 if (strcmp(path, "/") == 0) { stbuf->st_mode = S_IFDIR | 0755; // S_IFDIR 用於說明 / 為目錄 stbuf->st_nlink = 2; } else if (strcmp(path, hello_path) == 0) { stbuf->st_mode = S_IFREG | 0444; // S_IFREG 用於說明/hello 為常規文件 stbuf->st_nlink = 1; stbuf->st_size = strlen(hello_str); // 設置文件長度為hello_str的長度 } else res = -ENOENT; // 返回錯誤信息,沒有該文件或者目錄 return res; // 成功執行的時候,此函數返回值為 0 } // 該函數用於讀取目錄中的內容,併在/目錄下增加了. .. hello 三個目錄項 static int hello_readdir(const char *path, void *buf, fuse_fill_dir_t filler, off_t offset, struct fuse_file_info *fi) { (void) offset; (void) fi; if (strcmp(path, "/") != 0) return -ENOENT; /* fill, 其作用是在readdir函數中增加一個目錄項 typedef int (*fuse_fill_dir_t) (void *buf, const char *name, const struct stat *stbuf, off_t off); */ filler(buf, ".", NULL, 0); filler(buf, "..", NULL, 0); filler(buf, hello_path + 1, NULL, 0); //指針+1(/hello), 即增加 hello 目錄項,去掉前面的'/' return 0; } // 打開文件函數 static int hello_open(const char *path, struct fuse_file_info *fi) { if (strcmp(path, hello_path) != 0) return -ENOENT; if ((fi->flags & 3) != O_RDONLY) return -EACCES; return 0; } // 讀文件函數 static int hello_read(const char *path, char *buf, size_t size, off_t offset, struct fuse_file_info *fi) { size_t len; (void) fi; if(strcmp(path, hello_path) != 0) return -ENOENT; len = strlen(hello_str); if (offset < len) { if (offset + size > len) size = len - offset; memcpy(buf, hello_str + offset, size); } else size = 0; return size; } // 註冊自定義函數 static struct fuse_operations hello_oper = { .getattr = hello_getattr, .readdir = hello_readdir, .open = hello_open, .read = hello_read, // 讀文件函數 }; // 調用 fuse_main , 把控制權交給了fuse int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { return fuse_main(argc, argv, &hello_oper, NULL); }
執行:
掛載:
[root@docker example]# mkdir /tmp/fuse
[root@docker fuse-example]# ./hello /tmp/fuse/ [root@docker fuse-example]# cd /tmp/fuse/
讀取文件屬性: [root@docker fuse]# ll total 0 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 13 Jan 1 1970 hello 讀取目錄屬性: [root@docker tmp]# ll /tmp/ total 4 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 0 Jan 1 1970 fuse
卸載:
[root@docker tmp]# fusermount -u /tmp/fuse
[root@docker tmp]# ls /tmp/fuse/
當然你也可以修改代碼,對fuse的特性進一步嘗試。
low-level API: low-level api 相對於 high-level api 來說,有更好的自由度;high-level相對於 low-level api 則有更簡單的api使用,如果閱讀過fuse源碼過後,使用low-level api將使得可控性更強。下麵是hello.c 的low-level api 版本
/* FUSE: Filesystem in Userspace Copyright (C) 2001-2007 Miklos Szeredi <[email protected]> This program can be distributed under the terms of the GNU GPL. See the file COPYING. gcc -Wall hello_ll.c `pkg-config fuse --cflags --libs` -o hello_ll */ #define FUSE_USE_VERSION 26 #include <fuse_lowlevel.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <assert.h> static const char *hello_str = "Hello World!\n"; static const char *hello_name = "hello"; static int hello_stat(fuse_ino_t ino, struct stat *stbuf) { stbuf->st_ino = ino; switch (ino) { case 1: stbuf->st_mode = S_IFDIR | 0755; stbuf->st_nlink = 2; break; case 2: stbuf->st_mode = S_IFREG | 0444; stbuf->st_nlink = 1; stbuf->st_size = strlen(hello_str); break; default: return -1; } return 0; } static void hello_ll_getattr(fuse_req_t req, fuse_ino_t ino, struct fuse_file_info *fi) { struct stat stbuf; (void) fi; memset(&stbuf, 0, sizeof(stbuf)); if (hello_stat(ino, &stbuf) == -1) fuse_reply_err(req, ENOENT); else fuse_reply_attr(req, &stbuf, 1.0); } static void hello_ll_lookup(fuse_req_t req, fuse_ino_t parent, const char *name) { struct fuse_entry_param e; if (parent != 1 || strcmp(name, hello_name) != 0) fuse_reply_err(req, ENOENT); else { memset(&e, 0, sizeof(e)); e.ino = 2; e.attr_timeout = 1.0; e.entry_timeout = 1.0; hello_stat(e.ino, &e.attr); fuse_reply_entry(req, &e); } } struct dirbuf { char *p; size_t size; }; static void dirbuf_add(fuse_req_t req, struct dirbuf *b, const char *name, fuse_ino_t ino) { struct stat stbuf; size_t oldsize = b->size; b->size += fuse_add_direntry(req, NULL, 0, name, NULL, 0); b->p = (char *) realloc(b->p, b->size); memset(&stbuf, 0, sizeof(stbuf)); stbuf.st_ino = ino; fuse_add_direntry(req, b->p + oldsize, b->size - oldsize, name, &stbuf, b->size); } #define min(x, y) ((x) < (y) ? (x) : (y)) static int reply_buf_limited(fuse_req_t req, const char *buf, size_t bufsize, off_t off, size_t maxsize) { if (off < bufsize) return fuse_reply_buf(req, buf + off, min(bufsize - off, maxsize)); else return fuse_reply_buf(req, NULL, 0); } // 讀取文件夾目錄 static void hello_ll_readdir(fuse_req_t req, fuse_ino_t ino, size_t size, off_t off, struct fuse_file_info *fi) { (void) fi; if (ino != 1) fuse_reply_err(req, ENOTDIR); else { struct dirbuf b; memset(&b, 0, sizeof(b)); dirbuf_add(req, &b, ".", 1); dirbuf_add(req, &b, "..", 1); dirbuf_add(req, &b, hello_name, 2); reply_buf_limited(req, b.p, b.size, off, size); free(b.p); } } // 處理打開操作函數,檢查許可權 static void hello_ll_open(fuse_req_t req, fuse_ino_t ino, struct fuse_file_info *fi) { if (ino != 2) fuse_reply_err(req, EISDIR); else if ((fi->flags & 3) != O_RDONLY) fuse_reply_err(req, EACCES); else fuse_reply_open(req, fi); } // 讀取函數 返回 hello_str 中的值 static void hello_ll_read(fuse_req_t req, fuse_ino_t ino, size_t size, off_t off, struct fuse_file_info *fi) { (void) fi; assert(ino == 2); reply_buf_limited(req, hello_str, strlen(hello_str), off, size); } // 註冊的自定義函數 static struct fuse_lowlevel_ops hello_ll_oper = { .lookup = hello_ll_lookup, .getattr = hello_ll_getattr, .readdir = hello_ll_readdir, .open = hello_ll_open, .read = hello_ll_read, }; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { // FUSE_ARGS_INIT 本身是一個巨集函數,用於生成 struct fuse_args 結構體, 結構體在源代碼 fuse_opt.h 文件建中定義; struct fuse_args args = FUSE_ARGS_INIT(argc, argv); // A communication channel, providing hooks for sending and receiving* messages struct fuse_chan *ch; // 與 fuse 中 session 相關, 在源代碼 fuse_session.c 中進行定義 一個channel char *mountpoint; // 一個字元串指針 int err = -1; // 錯誤返回值,預設的返回值為 -1 // fuse_parse_cmdline 是解析命令行參數的一種工具類,他可以解析fuse本身自身的選項,第一個出現的非選項參數被認為是掛載點 // 如果出現多個非選項參數,則認為是錯誤! if (fuse_parse_cmdline(&args, &mountpoint, NULL, NULL) != -1 && // 掛載, 調用了底層的 fuse_mount_common 函數 (ch = fuse_mount(mountpoint, &args)) != NULL) { struct fuse_session *se; // 創建一個session se = fuse_lowlevel_new(&args, &hello_ll_oper, sizeof(hello_ll_oper), NULL); if (se != NULL) { if (fuse_set_signal_handlers(se) != -1) { fuse_session_add_chan(se, ch); err = fuse_session_loop(se); // 處理信息 fuse_remove_signal_handlers(se); fuse_session_remove_chan(ch); } fuse_session_destroy(se); } fuse_unmount(mountpoint, ch); } // 釋放參數占用的空間 fuse_opt_free_args(&args); return err ? 1 : 0; }
執行:(同樣執行和High-level API 相同的操作進行驗證)
上面第二個代碼,我只註釋了很少一部分,因為我還有一部分源碼沒有看懂,為此我專門寫了另外一篇文章來記錄我對fuse 示例代碼 的註釋,等看懂後陸續更新對應註釋,希望能幫助你。
FUSE 文件系統 example部分 源碼註釋 (libfuse 2.9.9)
資源來源自網路,保持更新,轉載請註明出處。https://www.cnblogs.com/xuyaowen/p/fuse.html



