目的:handle的出現主要是為瞭解決線程間通訊。 舉個例子,android是不允許在主線程中訪問網路,因為這樣會阻塞主線程,影響性能,所以訪問網路都是放在子線程中執行,對於網路返回的結果則需要顯示在主線程中,handler就是連接主線程和子線程的橋梁。 1.handler基本使用方法 看一下使用方 ...
目的:handle的出現主要是為瞭解決線程間通訊。
舉個例子,android是不允許在主線程中訪問網路,因為這樣會阻塞主線程,影響性能,所以訪問網路都是放在子線程中執行,對於網路返回的結果則需要顯示在主線程中,handler就是連接主線程和子線程的橋梁。
1.handler基本使用方法
看一下使用方法:
public static final int EMPTY_MSG = 0; @SuppressLint("HandlerLeak") Handler handler = new Handler(){ @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what){ case 0: Toast.makeText(MainActivitys.this, "接受到消息", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; } } }; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { handler.sendEmptyMessage(0); } }).start(); }
通過上邊代碼就完成了子線程向主線程發送消息的功能。
2. handler,Looper,MessageQueue 解釋
handler:負責發送和處理消息
Looper:消息迴圈器,也可以理解為消息泵,主動地獲取消息,並交給handler來處理
MessageQueue:消息隊列,用來存儲消息
3.源碼分析
程式的啟動是在ActivityThread的main方法中
public static void main(){ Looper.prepare(); //1 Handler handler = new Handler();//2 Looper.loop(); //3 }
Looper.prepare()會初始化當前線程的looper
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); } sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); }
會調用到sThreadLocal.set()方法,ThreadLocal是線程安全的,不同的線程獲取到的值是不一樣的,下麵先分析一下ThreadLocal是如何做到線程安全。
public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); }
不同的線程會設置不同的looper,下麵看一下ThreadLocalMap是如何存儲數據的
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal firstKey, Object firstValue) { table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue); }
ThreadLocalMap會創建一個數組,key是通過特殊的演算法來創建出來,一個線程中會有一個ThreadLocalMap,這個map中會存多個ThreadLocal和values。
下麵看下ThreadLocalMap是如何set一個值的
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) { // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at // least as common to use set() to create new entries as // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast // path would fail more often than not. Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { ThreadLocal k = e.get(); if (k == key) { e.value = value; return; } if (k == null) { replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return; } } tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); int sz = ++size; if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) rehash(); }
其實是遍歷threadLocalMap中的table,如果當前table中存在threadLocal這個key就更新,不存在就新建。ThreadLocal的set方法到此結束。
下麵看下Handler handler = new Handler()中執行了哪些操作:
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) { mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); mQueue = mLooper.mQueue; }
重要的就是構造函數中這兩個方法,在handler中初始化looper和messageQueue。這個就不展開講了。
下麵看一下Looper.loop()這個步驟,我做了一些精簡,把無關的代碼去掉了。
public static void loop() { final Looper me = myLooper(); final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; for (;;) { Message msg = queue.next(); // might block if (msg == null) { // No message indicates that the message queue is quitting. return; } msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); msg.recycleUnchecked(); } }
queue.next()是個無限for迴圈,其實也是個阻塞方法,其中比較重要的是下麵這個方法,其作用是不會一直迴圈。底層採用的是pipe/epoll機制。
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
Message next() { // Return here if the message loop has already quit and been disposed. // This can happen if the application tries to restart a looper after quit // which is not supported. final long ptr = mPtr; if (ptr == 0) { return null; } int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; for (;;) { if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) { Binder.flushPendingCommands(); } nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis); synchronized (this) { // Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found. final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); Message prevMsg = null; Message msg = mMessages; if (msg != null && msg.target == null) { // Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue. do { prevMsg = msg; msg = msg.next; } while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous()); } if (msg != null) { if (now < msg.when) { // Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready. nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } else { // Got a message. mBlocked = false; if (prevMsg != null) { prevMsg.next = msg.next; } else { mMessages = msg.next; } msg.next = null; if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg); msg.markInUse(); return msg; } } else { // No more messages. nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1; } // Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled. if (mQuitting) { dispose(); return null; } // If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run. // Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message // in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future. if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0 && (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) { pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size(); } if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) { // No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more. mBlocked = true; continue; } if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) { mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)]; } mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers); } // Run the idle handlers. // We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration. for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) { final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i]; mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler boolean keep = false; try { keep = idler.queueIdle(); } catch (Throwable t) { Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t); } if (!keep) { synchronized (this) { mIdleHandlers.remove(idler); } } } // Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again. pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0; // While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered // so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting. nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; } }
message.next()返回消息之後會接著調用 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);在這個方法裡邊會進行判斷,來決定執行哪一種回調。
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) { if (msg.callback != null) { handleCallback(msg); } else { if (mCallback != null) { if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) { return; } } handleMessage(msg); } }
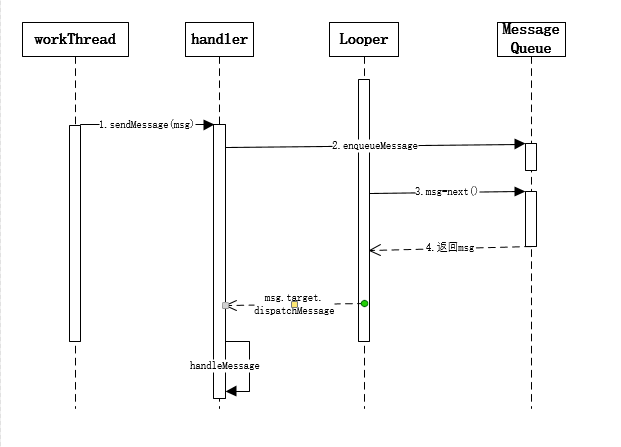
到此整個handler的流程就結束了。最後附上一張handler的時序圖。