"Android項目刮刮獎詳解(二)" 前言 上一期我們已經實現了一個簡易的刮刮卡功能,這一期我們來將其完善一下 目標 + 將刮刮獎的寬高改為合適高度 + 將刮刮獎位置居中 + 將信息層的圖片換成文字(重點) 實現 1. 將刮刮獎的寬高改為合適高度和將刮刮獎位置居中 這裡其實很簡單,我們直接到lay ...
前言
上一期我們已經實現了一個簡易的刮刮卡功能,這一期我們來將其完善一下
目標
- 將刮刮獎的寬高改為合適高度
- 將刮刮獎位置居中
將信息層的圖片換成文字(重點)
實現
將刮刮獎的寬高改為合適高度和將刮刮獎位置居中
這裡其實很簡單,我們直接到layout佈局之中將大小修改一下即可,同時,在佈局中利用
gravity修改位置<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center" tools:context="com.wan.guajiang.MainActivity"> <com.wan.guajiang.GuaGuaKa android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="100dp"/> </LinearLayout>將信息層的圖片換成文字
之前我們信息層繪製的是中獎圖片,如果沒有圖片怎麼辦?當然是直接拿文字來代替啦,canvas不僅可以畫圖片,還可以畫文字,寫文字
首先,我們來瞭解一下canvas的drawText方法參數
drawText(String text, float x, floaty, Paint paint);
text即使要寫的文字內容,x,y是寫的位置,需要註意的是,這裡的x,y坐標並不是文字的左上角,而是一個與左下角比較接近的位置。大概在這裡:如圖

最後一個參數就是畫筆了,這個畫筆設置與之前相似,待會再補充一下
我們想要把文字寫在信息層的正中間,x,y的坐標該怎麼寫呢?由上圖可以知道,canvas使用drawText方法,xy的坐標其實是位於文字的左下角的,下圖便是圖解
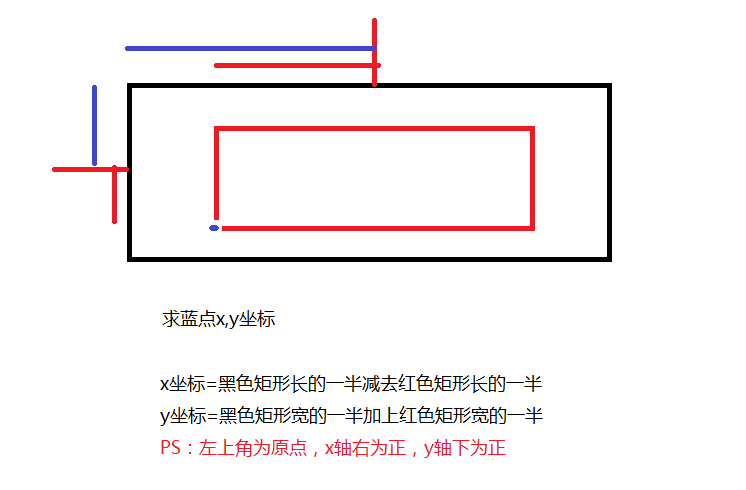
相信這張圖還是很好理解的,我們繼續,開始寫代碼
首先,我們需要個文字內容
String message = "恭喜中獎,3萬元!";定義我們的畫筆Paint,對其進行相關設置
這裡得提一下,我們需要一個Rect矩形來得到文字內容的背景大小,也就是上圖中的紅色矩形,Paint畫筆中提供了一個方法
getTextBounds,我們可以通過此方法來獲得文字內容的背景大小
messagePaint.getTextBounds(String text,float start,float end,Rect rect);上述代碼的意思是,截取text文字中的從start到end的長度,將截取的長度和文字的高度形成一個矩形,rect矩形接收這個矩形
Rect mBackground = new Rect();//用來接收getTextBounds返回的矩形 Paint messagePaint = new Paint(); messagePaint.setColor(Color.RED); messagePaint.setAntiAlias(true); messagePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); messagePaint.getTextBounds(message,0,message.length(),mBackground); messagePaint.setTextSize(30);計算x,y坐標,canvas使用drawText寫出文字
我們有兩種方法來獲得之前黑色矩形的長和寬,一種是使用getMeasured,另一種使用mBitmap.get方法來獲得長和寬canvas.drawText(message,getMeasuredWidth()/2-mBackground.width()/2,getMeasuredHeight()/2+mBackground.height()/2,messagePaint);或者:
canvas.drawText(message,mBitmap.getWidth()/2-mBackground.width()/2,mBitmap.getHeight()/2+mBackground.height()/2,messagePaint);測試圖
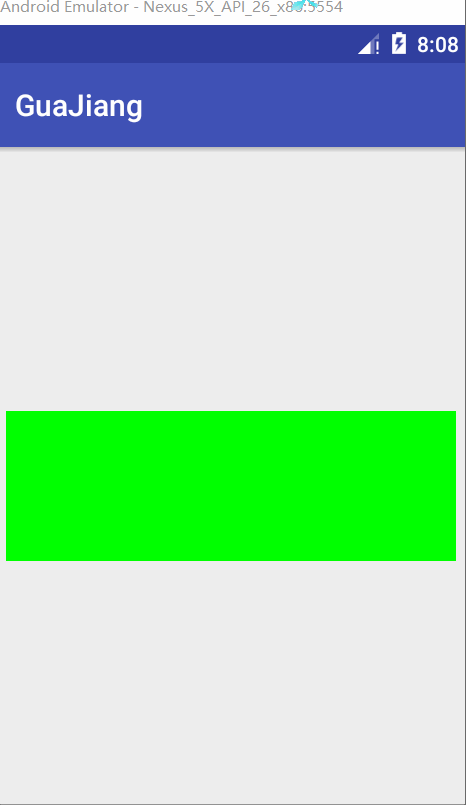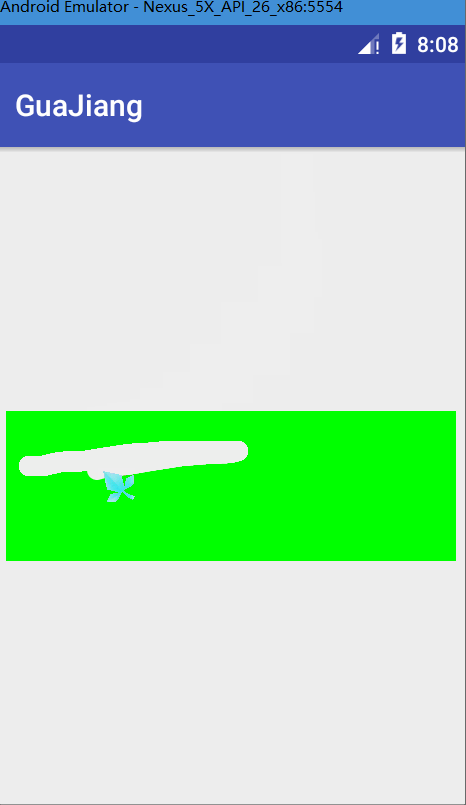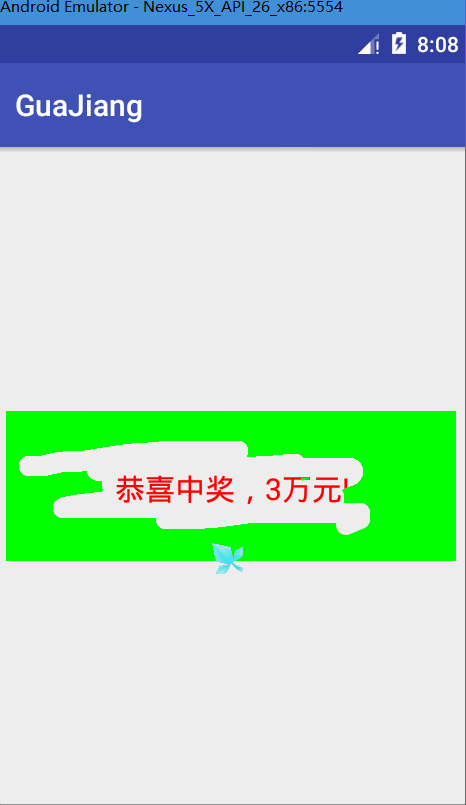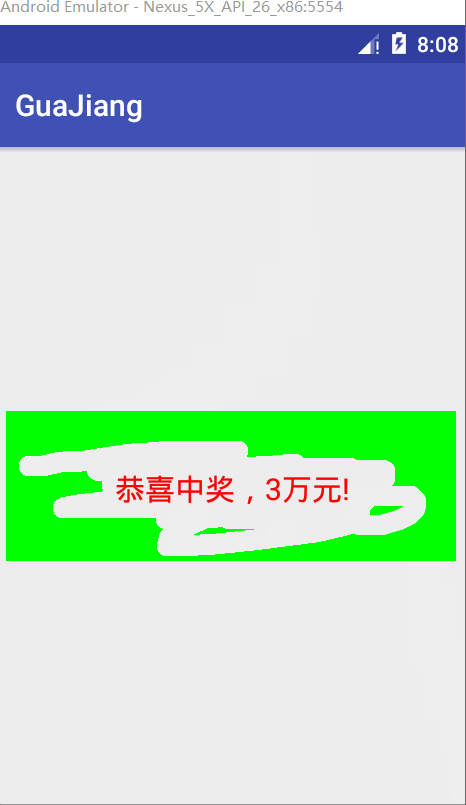
完整代碼
public class GuajiangView extends View {
/**
* 繪製線條的Paint,即用戶手指繪製Path
*/
private Paint mOutterPaint = new Paint();
/**
* 記錄用戶繪製的Path
*/
private Path mPath = new Path();
/**
* 記憶體中創建的Canvas
*/
private Canvas mCanvas;
/**
* mCanvas繪製內容在其上
*/
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private int mLastX;
private int mLastY;
private String message;//中獎信息
private Rect mBackground;//文字背景矩形大小
private Paint messagePaint = new Paint();//文字畫筆
private boolean isClear = false;
public GuajiangView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public GuajiangView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public GuajiangView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public GuajiangView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
Log.d(TAG, "onMeasure: 測量");
int width = getMeasuredWidth();
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
// 初始化bitmap
mBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);//以獲得的寬高創建一個32位的bitmap
mCanvas = new Canvas(mBitmap);//以bitmap創建了一個畫布
mCanvas.drawColor(Color.GREEN);//設置畫布的顏色為綠色
mBackground = new Rect();
message = "恭喜中獎,3萬元!";
messagePaint.setColor(Color.RED);
messagePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
messagePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
messagePaint.getTextBounds(message,0,message.length(),mBackground);
messagePaint.setTextSize(30);
// 設置畫筆
mOutterPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
mOutterPaint.setAntiAlias(true);//使用抗鋸齒功能,會消耗較大資源,繪製圖形速度會變慢
mOutterPaint.setDither(true);//圖像抖動處理,會使繪製出來的圖片顏色更加平滑和飽滿,圖像更加清晰
mOutterPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mOutterPaint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND);//圓角,平滑
mOutterPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND); //圓角
mOutterPaint.setStrokeWidth(20); // 設置畫筆寬度
messagePaint.setColor(Color.RED);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
Log.d(TAG, "onDraw: 畫");
canvas.drawText(message,mBitmap.getWidth()/2-mBackground.width()/2,getMeasuredHeight()/2+mBackground.height()/2,messagePaint);
drawPath();
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, 0,0, null);
}
private void drawPath() {
Log.d(TAG, "drawPath: ");
mOutterPaint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.DST_OUT));
mCanvas.drawPath(mPath, mOutterPaint);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//當手指按到屏幕上的時候,Path路徑之中就使用moveto方法,移動到手指當前位置,invalidate刷新View,回調onDraw方法,(還沒有畫出來)
//之後,手指移動,action是處於ACTION_MOVE的狀態,Path路徑使用lineto方法(畫直線),
// 同時,將x,y坐標進行了更新,invalidate刷新View,回調onDraw方法,canvas通過drawpath使用畫筆將path畫了出來,之後如果用戶沒有抬起手指,則繼續迴圈ACTION_MOVE中的步驟
int action = event.getAction();
int x = (int) event.getX();//獲得x坐標
int y = (int) event.getY();//獲得y坐標
switch (action){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
mPath.moveTo(mLastX, mLastY);//之後回調onDraw方法canvas將path
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
mPath.lineTo(x, y);//之後回調onDraw方法時canvas畫直線到(x,y)該點
mLastX = x;//更新x坐標
mLastY = y;//更新y坐標
break;
default:break;
}
invalidate();//刷新View,回調onDraw方法
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent: invalidate");
return true;
}
}


