前言 隨著spring boot2.0的發佈。項目組的API介面已經考慮向spring boot轉型。底層介面我們一直用的mybatis,所以這篇文章我特意練習了下在spring boot種集成mybatis。 一、準備工作 1、pom.xml 2、項目結構 配置文件依然放在resources目錄下 ...
前言
隨著spring boot2.0的發佈。項目組的API介面已經考慮向spring boot轉型。底層介面我們一直用的mybatis,所以這篇文章我特意練習了下在spring boot種集成mybatis。
一、準備工作
1、pom.xml
1 <dependencies> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId> 5 <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> 6 </dependency> 7 <dependency> 8 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 9 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 10 <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> 11 </dependency> 12 <dependency> 13 <groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId> 14 <artifactId>sqljdbc4</artifactId> 15 <version>4.0</version> 16 </dependency> 17 <dependency> 18 <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> 19 <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> 20 <version>1.3.2</version> 21 </dependency> 22 <dependency> 23 <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> 24 <artifactId>druid</artifactId> 25 <version>1.1.9</version> 26 </dependency> 27 <dependency> 28 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 29 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> 30 <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> 31 <scope>test</scope> 32 </dependency> 33 </dependencies>
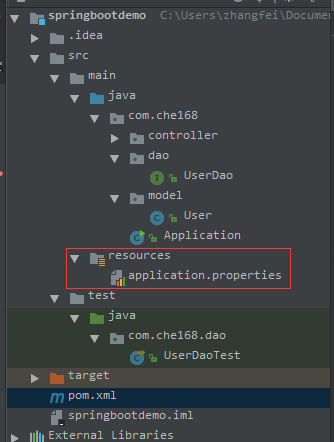
2、項目結構
配置文件依然放在resources目錄下,spring boot中支持properties、也支持yml的方式。
3、使用註解的方式編寫UserMapper
public interface UserDao {
@Select("select * from tb_user")
List<User> getAllUsers();
@Select("select * from tb_user where id=#{id}")
User getById(int id);
@Insert("insert into tb_user(name,address) values(#{name},#{address})")
void insert(User user);
@Update("update tb_user set name=#{name},address=#{address} where id=#{id}")
void update(User user);
@Delete("delete from tb_user where id=#{id}")
void delete(int id);
}
啟動類 Application.java。 主要是MapperScan註解,配置映射包目錄com.che168.dao
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.che168.dao")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
單元測試
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserDaoTest {
@Autowired
UserDao userDao;
@Test
public void getAllUsers(){
List<User> allUsers=userDao.getAllUsers();
System.out.println(allUsers.size());
}
@Test
public void getById(){
int id=1;
User model=userDao.getById(id);
System.out.println("name:"+model.getName()+",address:"+model.getAddress());
}
@Test
public void insert(){
User user=new User();
user.setName("雲龍");
user.setAddress("山西太原");
userDao.insert(user);
}
@Test
public void update(){
User user=new User();
user.setId(4);
user.setName("雲龍");
user.setAddress("山西運城");
userDao.update(user);
}
@Test
public void delete(){
userDao.delete(4);
}
}
二、使用配置文件的方式
配置文件的方式和我們之前在SpringMVC中集成的方式大致相同,把xml文件單獨放在mapper目錄下,把sql相關操作全部放在xml中, 介面用來編寫方法簽名,然後配置映射,在spring boot中不同的地方就是把mapper-config.xml和實體類映射文件需要配置在application.properties中,如下配置,在此就不再贅述了。
mybatis.config-locations=classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml



