本文簡單介紹單例模式,並舉出餓漢式、懶漢式、雙重檢測鎖、靜態內部類(常用)、枚舉等方式實現單例方式,補充防止反射、反序列化破解單例的方法。 ...
1 單例模式(Singleton Pattern)介紹
1.1 單例模式介紹
定義:確保某一類只有一個實例,而且自行實例化並向整個系統提供這個實例。
實現:通過使用private的構造函數確保了在一個應用中只產生一個實例,並且是自行實例化。
示例代碼:
例1-1
-
1 public class Singleton01 { 2 //2、創建一個對象,在類載入的時候初始 3 private static final Singleton01 singleton01 = new Singleton01(); 4 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 5 private Singleton01(){ 6 7 } 8 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 9 public static Singleton01 getSingleton(){ 10 return singleton01; 11 } 12 //類中的其他方法 13 public void doSomething(){ 14 } 15 }
1.2 單例模式的應用
1.2.1 優點
- 單例模式在記憶體中只有一個實例,減少了記憶體開支,特別是一個對象需要頻繁創建、銷毀時,而且創建或銷毀時性能無法優化,單例模式的優勢就非常明顯。
- 單例模式可以避免對資源的多重占用,例如一個寫文件動作,由於只有一個實例存在記憶體中,避免對同一個資源文件的同時寫操作。
- 單例模式可以在系統設置全局的訪問點,優化和共用資源訪問,例如可以設計一個單例類,負責所有數據表的映射處理。
1.2.2 缺點
- 單例模式一般沒有介面,擴展困難。
- 對測試不利,如果單例模式沒有完成,是不能進行測試的。
1.2.3 使用場景
- 要求生成唯一序列號的環境。
- 在整個項目中需要一個共用訪問點或共用數據,例如一個web頁面上的計數器,可以不用把每次刷新都記錄到資料庫中,使用單例模式保存計數器的值,並確保是線程安全的。
- 創建一個對象需要消耗的資源過多,如要訪問IO和資料庫等資源。
- 需要定義大量的靜態常量和靜態方法(如工具類)的環境,可以採用單例模式(當然,也可以直接聲明為static的方式)。
- windows的任務管理器,工廠模式中的工廠....
2 單例模式的實現方式
2.1 餓漢式(線程安全,調用效率高[因為不用加鎖],但是不能延時載入),如例1-1 。
2.2 懶漢式
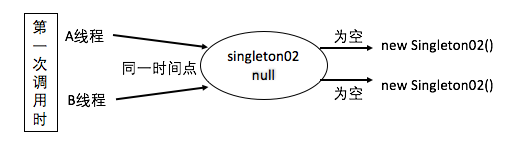
當使用懶載入時(如例2-2-1),在高併發環境下,存線上程安全問題(圖2-2-1),可能出現同時創建多個對象,需要對線程進行加鎖(例2-2-2),此稱為懶漢式,資源利用效率高,實現了懶載入,但是併發調用效率低,由於每次都要載入所有浪費系統資源。
例2-2-1:
-
1 public class Singleton02 { 2 //2、聲明一個私有的靜態變數 3 private static Singleton02 singleton02 ; 4 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 5 private Singleton02(){ 6 } 7 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 8 public static Singleton02 getSingleton(){ 9 //判斷singleton02是否為空,為空賦值 10 if (singleton02 == null){ 11 singleton02 = new Singleton02(); 12 } 13 return singleton02; 14 } 15 }
圖2-2-1
例2-2-2:
-
1 public class Singleton02 { 2 //2、聲明一個私有的靜態變數 3 private static Singleton02 singleton02 ; 4 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 5 private Singleton02(){ 6 } 7 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 8 public static synchronized Singleton02 getSingleton(){ 9 //判斷singleton02是否為空,為空賦值 10 if (singleton02 == null){ 11 singleton02 = new Singleton02(); 12 } 13 return singleton02; 14 } 15 }
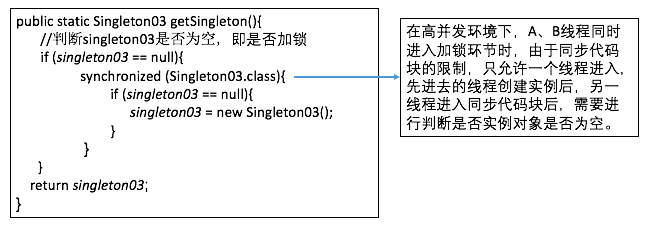
2.3 雙重檢測鎖(由於編譯器優化原因,和jvm底層模型問題,偶爾會出現問題,不建議使用)
例2-3-1
-
1 public class Singleton03 { 2 //2、聲明一個私有的靜態成員變數 3 private static Singleton03 singleton03; 4 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 5 private Singleton03(){ 6 } 7 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 8 public static Singleton03 getSingleton(){ 9 //判斷singleton03是否需要加鎖 10 if (singleton03 == null){ 11 synchronized (Singleton03.class){ 12 if (singleton03 == null){ 13 singleton03 = new Singleton03(); 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 return singleton03; 18 }
圖2-3-1
2.4 靜態內部類(常用)
外部類沒有static,所以靜態內部類不會再外部類載入的時候被初始化,所以實現了懶載入
線程安全,因為實例對象是在靜態內部類載入的時候創建,所以天然是單例的。
例2-4-1
-
1 public class Singleton04 { 2 3 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 4 private Singleton04(){ 5 } 6 //2、創建一個靜態內部類 7 private static class SingletonInstance{ 8 //靜態內部類載入的時候生成單例對象 9 public static Singleton04 singleton04 = new Singleton04(); 10 } 11 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 12 public static Singleton04 getSingleton(){ 13 //當調用該方法是,靜態內部類才會被載入,對象才會new出來 14 return SingletonInstance.singleton04; 15 } 16 }
2.5 枚舉(線程安全,天然就單例的,能避免反射和反序列化帶來的問題,但是不能懶載入)
例2-5-1
-
1 public enum Singleton05 { 2 SINGLETON_05; 3 public void doSomething(){ 4 } 5 }
1 public class Client { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Singleton05 singleton05_01 = Singleton05.SINGLETON_05; 4 Singleton05 singleton05_02 = Singleton05.SINGLETON_05; 5 Singleton05 singleton05_03 = Singleton05.SINGLETON_05; 6 System.out.println(singleton05_01);//SINGLETON_05 7 System.out.println(singleton05_02);//SINGLETON_05 8 System.out.println(singleton05_03);//SINGLETON_05 9 singleton05_01.doSomething(); 10 } 11 }
3 防止反射破解單例
3.1反射破解單例示例:
例3-1-1
1 //破解類 2 public class Client { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 4 5 Singleton01 singleton1 = Singleton01.getSingleton(); 6 Singleton01 singleton2 = Singleton01.getSingleton(); 7 System.out.println(singleton1 == singleton2); //true 8 9 //暴力反射破解單例 10 Class<Singleton01> clazz = (Class<Singleton01>) Class.forName("com.pri.singleton_a.Singleton01"); 11 Constructor<Singleton01> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(null); 12 constructor.setAccessible(true); 13 Singleton01 singleton3 = constructor.newInstance(null); 14 15 System.out.println(singleton1 == singleton3); //false 16 } 17 } 18 19 //單例類 20 public class Singleton01 { 21 //2、創建一個對象,在類載入的時候初始 22 private static final Singleton01 singleton01 = new Singleton01(); 23 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 24 private Singleton01(){ 25 26 } 27 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 28 public static Singleton01 getSingleton(){ 29 return singleton01; 30 } 31 //類中的其他方法 32 public void doSomething(){ 33 } 34 }
3.2 防止反射破解單例
在單例空參構造中添加判斷,如
例3-2-1:
-
1 public class Singleton01 { 2 //2、創建一個對象,在類載入的時候初始 3 private static final Singleton01 singleton01 = new Singleton01(); 4 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 5 private Singleton01(){ 6 if (singleton01 != null){ 7 throw new RuntimeException("已有實例,不能再調用此方法實例化"); 8 } 9 } 10 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 11 public static Singleton01 getSingleton(){ 12 return singleton01; 13 } 14 //類中的其他方法 15 public void doSomething(){ 16 } 17 } 18 19 //運行結果 :Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: 已有實例,不能再調用此方法實例化
4 防止反序列化破解單例
4.1 反序列化破解單例
例4-1-1
-
1 //破解類 2 public class Client { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 4 5 Singleton01 singleton1 = Singleton01.getSingleton(); 6 Singleton01 singleton2 = Singleton01.getSingleton(); 7 System.out.println(singleton1 == singleton2); //true 8 9 /*//1、將對象序列化到文件 10 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("singleton.txt"); 11 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); 12 oos.writeObject(singleton1); 13 14 oos.close(); 15 out.close();*/ 16 17 //2、從文件中讀取對象(反序列化) 18 FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(new File("singleton.txt")); 19 20 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(input); 21 Singleton01 singleton3 = (Singleton01) ois.readObject(); 22 23 System.out.println(singleton1 == singleton3); //false 24 } 25 } 26 27 //單例類 28 public class Singleton01 implements Serializable { 29 //2、創建一個對象,在類載入的時候初始 30 private static final Singleton01 singleton01 = new Singleton01(); 31 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 32 private Singleton01(){ 33 if (singleton01 != null){ 34 throw new RuntimeException("已有實例,不能再調用此方法實例化"); 35 } 36 } 37 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 38 public static Singleton01 getSingleton(){ 39 return singleton01; 40 } 41 //類中的其他方法 42 public void doSomething(){ 43 } 44 }
4.2 防止反序列化破解單例
在單例類中添加一個readResolve()方法,如例4-2-1.
例4-2-1
-
1 public class Singleton01 implements Serializable { 2 //2、創建一個對象,在類載入的時候初始 3 private static final Singleton01 singleton01 = new Singleton01(); 4 //1、私有化構造方法,現在以new的方式創建多個對象 5 private Singleton01(){ 6 if (singleton01 != null){ 7 throw new RuntimeException("已有實例,不能再調用此方法實例化"); 8 } 9 } 10 //3、對外提供一個靜態方法,以獲取實例對象 11 public static Singleton01 getSingleton(){ 12 return singleton01; 13 } 14 //類中的其他方法 15 public void doSomething(){ 16 } 17 18 //反序列化時,直接return singleton01,不生成對象 19 private Object readResolve() throws ObjectStreamException{ 20 return singleton01; 21 } 22 }



