1. Graylog2 簡介 Graylog 是一個簡單易用、功能較全面的日誌管理工具,相比 ELK 組合, 優點: 部署維護簡單,一體化解決方案,不像ELK三個獨立系統集成。 查相比ES json語法,搜索語法更加簡單,如 source:mongo AND reponse_time_ms:>500 ...
1. Graylog2 簡介
Graylog 是一個簡單易用、功能較全面的日誌管理工具,相比 ELK 組合, 優點:
-
- 部署維護簡單,一體化解決方案,不像ELK三個獨立系統集成。
- 查相比ES json語法,搜索語法更加簡單,如 source:mongo AND reponse_time_ms:>5000。
- 內置簡單的告警。
- 可以將搜索條件導出為 json格式文本,方便開發調用ES rest api搜索腳本。
- 自己開發採集日誌的腳本,並用curl/nc發送到Graylog Server,發送格式是自定義的GELF,Flunted和Logstash都有相應的輸出GELF消息的插件。自己開髮帶來很大的自由度。實際上只需要用inotifywait監控日誌的modify事件,並把日誌的新增行用curl/netcat發送到Graylog Server就可。
- UI 比較友好,搜索結果高亮顯示。
當然,在拓展性上,graylog還是不如ELK。
Graylog整體組成:
-
- Graylog提供 graylog 對外介面, CPU 密集
- Elasticsearch 日誌文件的持久化存儲和檢索, IO 密集
- MongoDB 存儲一些 Graylog 的配置
2. Graylog架構
單server架構 :
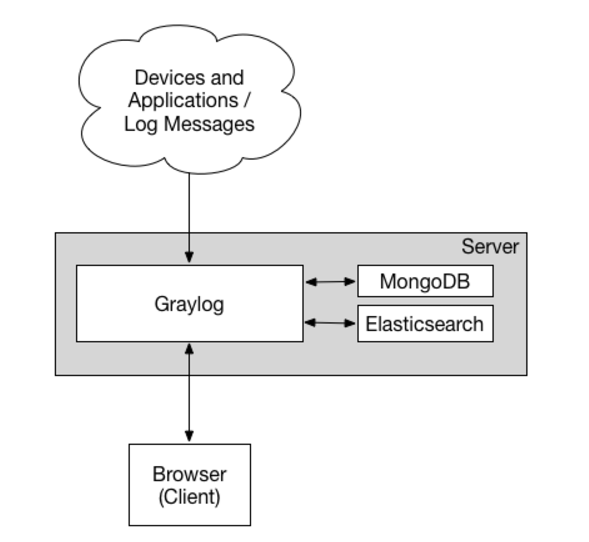
Graylog集群架構 :
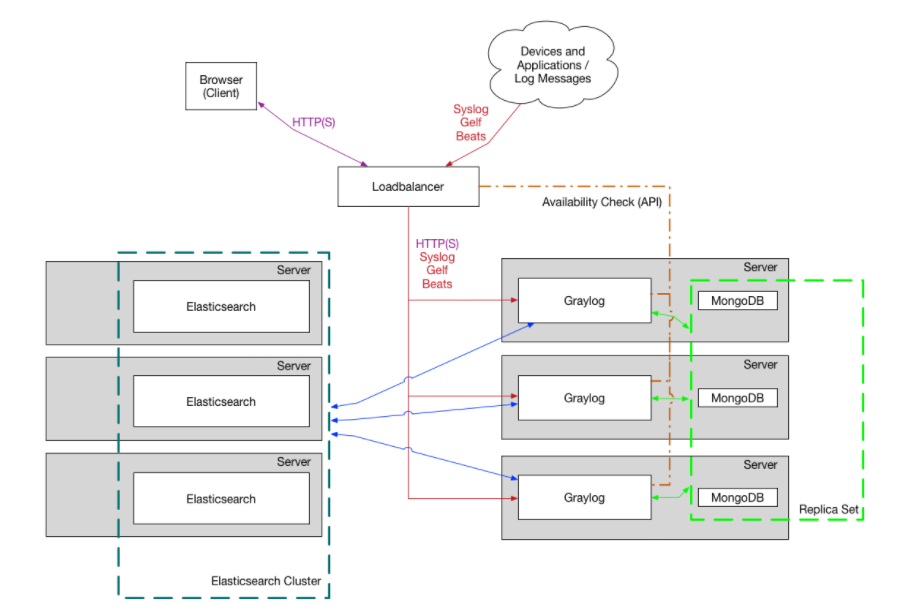
3. Graylog安裝
這裡我搭建的是集群方案,但是將ES與Graylog和MongoDB部署在同一臺server上。
① 前提條件:
$ sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-headless.x86_64
$ sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
$ setenforce 0
#安裝pwgen
$ sudo yum install epel-release
$ sudo yum install pwgen
② MongoDB安裝:
創建/etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-3.2.repo文件,添加如下內容:
[mongodb-org-3.2] name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/3.2/x86_64/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-3.2.asc
安裝MongoDB:
sudo yum install mongodb-org
啟動服務:
$ sudo chkconfig --add mongod $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable mongod.service $ sudo systemctl start mongod.service
③Elasticsearch安裝:
Graylog 2.3.x 支持 Elasticsearch 5.x版本。
首先安裝Elastic GPG key以及repository文件,然後yum安裝:
$ rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
$ cat /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo [elasticsearch-5.x] name=Elasticsearch repository for 5.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/5.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md
$ sudo yum install elasticsearch
編輯Elasticsearch配置文件/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml,添加cluster信息:

# cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: graylog # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: shop-log-02 # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # path.data: /data/elasticsearch/db # # Path to log files: # path.logs: /data/elasticsearch/logs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 10.2.2.42 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: # http.port: 9200 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # # 這裡給其他兩個節點的地址 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["10.2.2.41", "10.2.2.43"] # # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): # discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 # # For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Gateway ----------------------------------- # # Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started: # #gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3 # # For more information, consult the gateway module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"elasticsearch.yml
啟動Elasticsearch服務:
$ sudo chkconfig --add elasticsearch $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch.service $ sudo systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
④Graylog安裝
$ sudo rpm -Uvh https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-2.3-repository_latest.rpm $ sudo yum install graylog-server
編輯graylog配置文件 /etc/graylog/server/server.conf,添加 password_secret和 password_secret_sha2(必須)
可以使用 echo -n yourpassword | sha256sum 命令來生成 password_secret_sha2。
設置rest_listen_uri以及web_listen_uri為公共ip或公共hostname,以便連接graylog。

1 # cat /etc/graylog/server/server.conf 2 ############################ 3 # GRAYLOG CONFIGURATION FILE 4 ############################ 5 # 6 # This is the Graylog configuration file. The file has to use ISO 8859-1/Latin-1 character encoding. 7 # Characters that cannot be directly represented in this encoding can be written using Unicode escapes 8 # as defined in https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se8/html/jls-3.html#jls-3.3, using the \u prefix. 9 # For example, \u002c. 10 # 11 # * Entries are generally expected to be a single line of the form, one of the following: 12 # 13 # propertyName=propertyValue 14 # propertyName:propertyValue 15 # 16 # * White space that appears between the property name and property value is ignored, 17 # so the following are equivalent: 18 # 19 # name=Stephen 20 # name = Stephen 21 # 22 # * White space at the beginning of the line is also ignored. 23 # 24 # * Lines that start with the comment characters ! or # are ignored. Blank lines are also ignored. 25 # 26 # * The property value is generally terminated by the end of the line. White space following the 27 # property value is not ignored, and is treated as part of the property value. 28 # 29 # * A property value can span several lines if each line is terminated by a backslash (鈥榎鈥 character. 30 # For example: 31 # 32 # targetCities=\ 33 # Detroit,\ 34 # Chicago,\ 35 # Los Angeles 36 # 37 # This is equivalent to targetCities=Detroit,Chicago,Los Angeles (white space at the beginning of lines is ignored). 38 # 39 # * The characters newline, carriage return, and tab can be inserted with characters \n, \r, and \t, respectively. 40 # 41 # * The backslash character must be escaped as a double backslash. For example: 42 # 43 # path=c:\\docs\\doc1 44 # 45 46 # If you are running more than one instances of Graylog server you have to select one of these 47 # instances as master. The master will perform some periodical tasks that non-masters won't perform. 48 is_master = false 49 50 # The auto-generated node ID will be stored in this file and read after restarts. It is a good idea 51 # to use an absolute file path here if you are starting Graylog server from init scripts or similar. 52 node_id_file = /etc/graylog/server/node-id 53 54 # You MUST set a secret to secure/pepper the stored user passwords here. Use at least 64 characters. 55 # Generate one by using for example: pwgen -N 1 -s 96 56 password_secret = BjwAAuTEWDQNtAKhUL5lQ3TvW41saWseKpRdTSrecBFifsCJDXak4fudnACBcaMyl0I4yzJDF801Kyasdfsdfasdfasdfasd 57 58 # The default root user is named 'admin' 59 root_username = admin 60 61 # You MUST specify a hash password for the root user (which you only need to initially set up the 62 # system and in case you lose connectivity to your authentication backend) 63 # This password cannot be changed using the API or via the web interface. If you need to change it, 64 # modify it in this file. 65 # Create one by using for example: echo -n yourpassword | shasum -a 256 66 # and put the resulting hash value into the following line 67 root_password_sha2 = 926c00b3f65df24b65a9a7b58a989add920c81441dccd2 68 dsfasdfasdf 69 # The email address of the root user. 70 # Default is empty 71 #root_email = "" 72 73 # The time zone setting of the root user. See http://www.joda.org/joda-time/timezones.html for a list of valid time zones. 74 # Default is UTC 75 root_timezone = Asia/Shanghai 76 77 # Set plugin directory here (relative or absolute) 78 plugin_dir = /usr/share/graylog-server/plugin 79 80 # REST API listen URI. Must be reachable by other Graylog server nodes if you run a cluster. 81 # When using Graylog Collectors, this URI will be used to receive heartbeat messages and must be accessible for all collectors. 82 rest_listen_uri = http://10.2.2.42:9000/api/ 83 84 # REST API transport address. Defaults to the value of rest_listen_uri. Exception: If rest_listen_uri 85 # is set to a wildcard IP address (0.0.0.0) the first non-loopback IPv4 system address is used. 86 # If set, this will be promoted in the cluster discovery APIs, so other nodes may try to connect on 87 # this address and it is used to generate URLs addressing entities in the REST API. (see rest_listen_uri) 88 # You will need to define this, if your Graylog server is running behind a HTTP proxy that is rewriting 89 # the scheme, host name or URI. 90 # This must not contain a wildcard address (0.0.0.0). 91 rest_transport_uri = http://10.2.2.42:9000/api/ 92 93 # Enable CORS headers for REST API. This is necessary for JS-clients accessing the server directly. 94 # If these are disabled, modern browsers will not be able to retrieve resources from the server. 95 # This is enabled by default. Uncomment the next line to disable it. 96 #rest_enable_cors = false 97 98 # Enable GZIP support for REST API. This compresses API responses and therefore helps to reduce 99 # overall round trip times. This is enabled by default. Uncomment the next line to disable it. 100 #rest_enable_gzip = false 101 102 # Enable HTTPS support for the REST API. This secures the communication with the REST API with 103 # TLS to prevent request forgery and eavesdropping. This is disabled by default. Uncomment the 104 # next line to enable it. 105 #rest_enable_tls = true 106 107 # The X.509 certificate chain file in PEM format to use for securing the REST API. 108 #rest_tls_cert_file = /path/to/graylog.crt 109 110 # The PKCS#8 private key file in PEM format to use for securing the REST API. 111 #rest_tls_key_file = /path/to/graylog.key 112 113 # The password to unlock the private key used for securing the REST API. 114 #rest_tls_key_password = secret 115 116 # The maximum size of the HTTP request headers in bytes. 117 #rest_max_header_size = 8192 118 119 # The maximal length of the initial HTTP/1.1 line in bytes. 120 #rest_max_initial_line_length = 4096 121 122 # The size of the thread pool used exclusively for serving the REST API. 123 #rest_thread_pool_size = 16 124 125 # Comma separated list of trusted proxies that are allowed to set the client address with X-Forwarded-For 126 # header. May be subnets, or hosts. 127 #trusted_proxies = 127.0.0.1/32, 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1/128 128 129 # Enable the embedded Graylog web interface. 130 # Default: true 131 web_enable = true 132 133 # Web interface listen URI. 134 # Configuring a path for the URI here effectively prefixes all URIs in the web interface. This is a replacement 135 # for the application.context configuration parameter in pre-2.0 versions of the Graylog web interface. 136 web_listen_uri = http://10.2.2.42:9000/ 137 138 # Web interface endpoint URI. This setting can be overriden on a per-request basis with the X-Graylog-Server-URL header. 139 # Default: $rest_transport_uri 140 web_endpoint_uri = http://42.111.111.111:9000/api 141 142 # Enable CORS headers for the web interface. This is necessary for JS-clients accessing the server directly. 143 # If these are disabled, modern browsers will not be able to retrieve resources from the server. 144 web_enable_cors = true 145 146 # Enable/disable GZIP support for the web interface. This compresses HTTP responses and therefore helps to reduce 147 # overall round trip times. This is enabled by default. Uncomment the next line to disable it. 148 #web_enable_gzip = false 149 150 # Enable HTTPS support for the web interface. This secures the communication of the web browser with the web interface 151 # using TLS to prevent request forgery and eavesdropping. 152 # This is disabled by default. Uncomment the next line to enable it and see the other related configuration settings. 153 #web_enable_tls = true 154 155 # The X.509 certificate chain file in PEM format to use for securing the web interface. 156 #web_tls_cert_file = /path/to/graylog-web.crt 157 158 # The PKCS#8 private key file in PEM format to use for securing the web interface. 159 #web_tls_key_file = /path/to/graylog-web.key 160 161 # The password to unlock the private key used for securing the web interface. 162 #web_tls_key_password = secret 163 164 # The maximum size of the HTTP request headers in bytes. 165 #web_max_header_size = 8192 166 167 # The maximal length of the initial HTTP/1.1 line in bytes. 168 #web_max_initial_line_length = 4096 169 170 # The size of the thread pool used exclusively for serving the web interface. 171 #web_thread_pool_size = 16 172 173 # List of Elasticsearch hosts Graylog should connect to. 174 # Need to be specified as a comma-separated list of valid URIs for the http ports of your elasticsearch nodes. 175 # If one or more of your elasticsearch hosts require authentication, include the credentials in each node URI that 176 # requires authentication. 177 # 178 # Default: http://127.0.0.1:9200 179 elasticsearch_hosts = http://grayloguser:[email protected]:9200,http://grayloguser:[email protected]:9200,http://grayloguser:[email protected]:9200 180 181 # Maximum amount of time to wait for successfull connection to Elasticsearch HTTP port. 182 # 183 # Default: 10 Seconds 184 #elasticsearch_connect_timeout = 10s 185 186 # Maximum amount of time to wait for reading back a response from an Elasticsearch server. 187 # 188 # Default: 60 seconds 189 #elasticsearch_socket_timeout = 60s 190 191 # Maximum idle time for an Elasticsearch connection. If this is exceeded, this connection will 192 # be tore down. 193 # 194 # Default: inf 195 #elasticsearch_idle_timeout = -1s 196 197 # Maximum number of total connections to Elasticsearch. 198 # 199 # Default: 20 200 #elasticsearch_max_total_connections = 20 201 202 # Maximum number of total connections per Elasticsearch route (normally this means per 203 # elasticsearch server). 204 # 205 # Default: 2 206 #elasticsearch_max_total_connections_per_route = 2 207 208 # Maximum number of times Graylog will retry failed requests to Elasticsearch. 209 # 210 # Default: 2 211 #elasticsearch_max_retries = 2 212 213 # Enable automatic Elasticsearch node discovery through Nodes Info, 214 # see https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.4/cluster-nodes-info.html 215 # 216 # WARNING: Automatic node discovery does not work if Elasticsearch requires authentication, e. g. with Shield. 217 # 218 # Default: false 219 #elasticsearch_discovery_enabled = true 220 221 # Filter for including/excluding Elasticsearch nodes in discovery according to their custom attributes, 222 # see https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.4/cluster.html#cluster-nodes 223 # 224 # Default: empty 225 #elasticsearch_discovery_filter = rack:42 226 227 # Frequency of the Elasticsearch node discovery. 228 # 229 # Default: 30s 230 # elasticsearch_discovery_frequency = 30s 231 232 # Enable payload compression for Elasticsearch requests. 233 # 234 # Default: false 235 #elasticsearch_compression_enabled = true 236 237 # Graylog will use multiple indices to store documents in. You can configured the strategy it uses to determine 238 # when to rotate the currently active write index. 239 # It supports multiple rotation strategies: 240 # - "count" of messages per index, use elasticsearch_max_docs_per_index below to configure 241 # - "size" per index, use elasticsearch_max_size_per_index below to configure 242 # valid values are "count", "size" and "time", default is "count" 243 # 244 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 245 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 246 rotation_strategy = count 247 248 # (Approximate) maximum number of documents in an Elasticsearch index before a new index 249 # is being created, also see no_retention and elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices. 250 # Configure this if you used 'rotation_strategy = count' above. 251 # 252 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 253 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 254 elasticsearch_max_docs_per_index = 20000000 255 256 # (Approximate) maximum size in bytes per Elasticsearch index on disk before a new index is being created, also see 257 # no_retention and elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices. Default is 1GB. 258 # Configure this if you used 'rotation_strategy = size' above. 259 # 260 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 261 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 262 #elasticsearch_max_size_per_index = 1073741824 263 264 # (Approximate) maximum time before a new Elasticsearch index is being created, also see 265 # no_retention and elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices. Default is 1 day. 266 # Configure this if you used 'rotation_strategy = time' above. 267 # Please note that this rotation period does not look at the time specified in the received messages, but is 268 # using the real clock value to decide when to rotate the index! 269 # Specify the time using a duration and a suffix indicating which unit you want: 270 # 1w = 1 week 271 # 1d = 1 day 272 # 12h = 12 hours 273 # Permitted suffixes are: d for day, h for hour, m for minute, s for second. 274 # 275 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 276 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 277 #elasticsearch_max_time_per_index = 1d 278 279 # Disable checking the version of Elasticsearch for being compatible with this Graylog release. 280 # WARNING: Using Graylog with unsupported and untested versions of Elasticsearch may lead to data loss! 281 #elasticsearch_disable_version_check = true 282 283 # Disable message retention on this node, i. e. disable Elasticsearch index rotation. 284 #no_retention = false 285 286 # How many indices do you want to keep? 287 # 288 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 289 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 290 elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices = 20 291 292 # Decide what happens with the oldest indices when the maximum number of indices is reached. 293 # The following strategies are availble: 294 # - delete # Deletes the index completely (Default) 295 # - close # Closes the index and hides it from the system. Can be re-opened later. 296 # 297 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 298 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 299 retention_strategy = delete 300 301 # How many Elasticsearch shards and replicas should be used per index? Note that this only applies to newly created indices. 302 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 303 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 304 elasticsearch_shards = 3 305 elasticsearch_replicas = 1 306 307 # Prefix for all Elasticsearch indices and index aliases managed by Graylog. 308 # 309 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 310 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 311 elasticsearch_index_prefix = graylog 312 313 # Name of the Elasticsearch index template used by Graylog to apply the mandatory index mapping. 314 # Default: graylog-internal 315 # 316 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 317 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 318 #elasticsearch_template_name = graylog-internal 319 320 # Do you want to allow searches with leading wildcards? This can be extremely resource hungry and should only 321 # be enabled with care. See also: http://docs.graylog.org/en/2.1/pages/queries.html 322 allow_leading_wildcard_searches = false 323 324 # Do you want to allow searches to be highlighted? Depending on the size of your messages this can be memory hungry and 325 # should only be enabled after making sure your Elasticsearch cluster has enough memory. 326 allow_highlighting = true 327 328 # Analyzer (tokenizer) to use for message and full_message field. The "standard" filter usually is a good idea. 329 # All supported analyzers are: standard, simple, whitespace, stop, keyword, pattern, language, snowball, custom 330 # Elasticsearch documentation: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/2.3/analysis.html 331 # Note that this setting only takes effect on newly created indices. 332 # 333 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 334 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 335 elasticsearch_analyzer = standard 336 337 # Global request timeout for Elasticsearch requests (e. g. during search, index creation, or index time-range 338 # calculations) based on a best-effort to restrict the runtime of Elasticsearch operations. 339 # Default: 1m 340 #elasticsearch_request_timeout = 1m 341 342 # Global timeout for index optimization (force merge) requests. 343 # Default: 1h 344 #elasticsearch_index_optimization_timeout = 1h 345 346 # Maximum number of concurrently running index optimization (force merge) jobs. 347 # If you are using lots of different index sets, you might want to increase that number. 348 # Default: 20 349 #elasticsearch_index_optimization_jobs = 20 350 351 # Time interval for index range information cleanups. This setting defines how often stale index range information 352 # is being purged from the database. 353 # Default: 1h 354 #index_ranges_cleanup_interval = 1h 355 356 # Batch size for the Elasticsearch output. This is the maximum (!) number of messages the Elasticsearch output 357 # module will get at once and write to Elasticsearch in a batch call. If the configured batch size has not been 358 # reached within output_flush_interval seconds, everything that is available will be flushed at once. Remember 359 # that every outputbuffer processor manages its own batch and performs its own batch write calls. 360 # ("outputbuffer_processors" variable) 361 output_batch_size = 500 362 363 # Flush interval (in seconds) for the Elasticsearch output. This is the maximum amount of time between two 364 # batches of messages written to Elasticsearch. It is only effective at all if your minimum number of messages 365 # for this time period is less than output_batch_size * outputbuffer_processors. 366 output_flush_interval = 1 367 368 # As stream outputs are loaded only on demand, an output which is failing to initialize will be tried over and 369 # over again.




