工具方法。對函數的統一管理。 jquery2.0.3版本$.Callback()部分的源碼如下: // String to Object options format cache var optionsCache = {}; // Convert String-formatted options i ...
工具方法。對函數的統一管理。
jquery2.0.3版本$.Callback()部分的源碼如下:

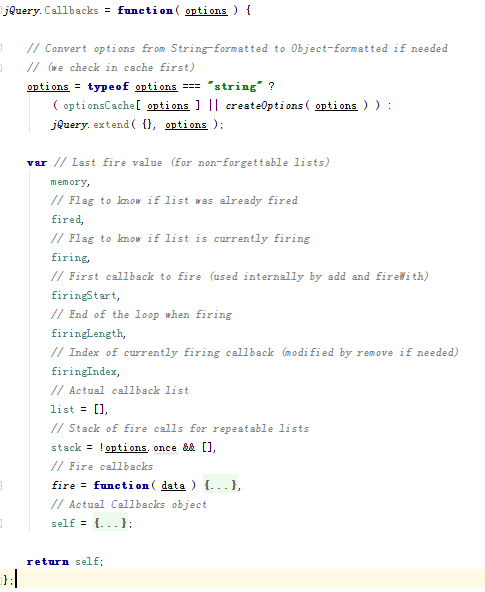
// String to Object options format cache var optionsCache = {}; // Convert String-formatted options into Object-formatted ones and store in cache function createOptions( options ) { var object = optionsCache[ options ] = {}; jQuery.each( options.match( core_rnotwhite ) || [], function( _, flag ) { object[ flag ] = true; }); return object; } /* * Create a callback list using the following parameters: * * options: an optional list of space-separated options that will change how * the callback list behaves or a more traditional option object * * By default a callback list will act like an event callback list and can be * "fired" multiple times. * * Possible options: * * once: will ensure the callback list can only be fired once (like a Deferred) * * memory: will keep track of previous values and will call any callback added * after the list has been fired right away with the latest "memorized" * values (like a Deferred) * * unique: will ensure a callback can only be added once (no duplicate in the list) * * stopOnFalse: interrupt callings when a callback returns false * */ jQuery.Callbacks = function( options ) { // Convert options from String-formatted to Object-formatted if needed // (we check in cache first) options = typeof options === "string" ? ( optionsCache[ options ] || createOptions( options ) ) : jQuery.extend( {}, options ); var // Last fire value (for non-forgettable lists) memory, // Flag to know if list was already fired fired, // Flag to know if list is currently firing firing, // First callback to fire (used internally by add and fireWith) firingStart, // End of the loop when firing firingLength, // Index of currently firing callback (modified by remove if needed) firingIndex, // Actual callback list list = [], // Stack of fire calls for repeatable lists stack = !options.once && [], // Fire callbacks fire = function( data ) { memory = options.memory && data; fired = true; firingIndex = firingStart || 0; firingStart = 0; firingLength = list.length; firing = true; for ( ; list && firingIndex < firingLength; firingIndex++ ) { if ( list[ firingIndex ].apply( data[ 0 ], data[ 1 ] ) === false && options.stopOnFalse ) { memory = false; // To prevent further calls using add break; } } firing = false; if ( list ) { if ( stack ) { if ( stack.length ) { fire( stack.shift() ); } } else if ( memory ) { list = []; } else { self.disable(); } } }, // Actual Callbacks object self = { // Add a callback or a collection of callbacks to the list add: function() { if ( list ) { // First, we save the current length var start = list.length; (function add( args ) { jQuery.each( args, function( _, arg ) { var type = jQuery.type( arg ); if ( type === "function" ) { if ( !options.unique || !self.has( arg ) ) { list.push( arg ); } } else if ( arg && arg.length && type !== "string" ) { // Inspect recursively add( arg ); } }); })( arguments ); // Do we need to add the callbacks to the // current firing batch? if ( firing ) { firingLength = list.length; // With memory, if we're not firing then // we should call right away } else if ( memory ) { firingStart = start; fire( memory ); } } return this; }, // Remove a callback from the list remove: function() { if ( list ) { jQuery.each( arguments, function( _, arg ) { var index; while( ( index = jQuery.inArray( arg, list, index ) ) > -1 ) { list.splice( index, 1 ); // Handle firing indexes if ( firing ) { if ( index <= firingLength ) { firingLength--; } if ( index <= firingIndex ) { firingIndex--; } } } }); } return this; }, // Check if a given callback is in the list. // If no argument is given, return whether or not list has callbacks attached. has: function( fn ) { return fn ? jQuery.inArray( fn, list ) > -1 : !!( list && list.length ); }, // Remove all callbacks from the list empty: function() { list = []; firingLength = 0; return this; }, // Have the list do nothing anymore disable: function() { list = stack = memory = undefined; return this; }, // Is it disabled? disabled: function() { return !list; }, // Lock the list in its current state lock: function() { stack = undefined; if ( !memory ) { self.disable(); } return this; }, // Is it locked? locked: function() { return !stack; }, // Call all callbacks with the given context and arguments fireWith: function( context, args ) { if ( list && ( !fired || stack ) ) { args = args || []; args = [ context, args.slice ? args.slice() : args ]; if ( firing ) { stack.push( args ); } else { fire( args ); } } return this; }, // Call all the callbacks with the given arguments fire: function() { self.fireWith( this, arguments ); return this; }, // To know if the callbacks have already been called at least once fired: function() { return !!fired; } }; return self; };View Code
一、$.Callback()的簡單使用及應用場景
1、$.Callback()的用法。
觀察者模式,添加完後統一觸發。
function aaa(){ alert(1); } function bbb(){ alert(2); } var cb= $.Callbacks(); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(bbb); cb.fire();
2、好處,應用場景。
要統一的管理aaa和bbb。有時候如下,很難對不同作用域下的函數進行統一管理。
function aaa(){ alert(1); } (function(){ function bbb(){ alert(2); } })(); aaa(); bbb();
只能彈出1,因為bbb是局部作用域中的。
$callback可以做到。如下,只要cb是全局的。
var cb= $.Callbacks(); function aaa(){ alert(1); } cb.add(aaa); (function(){ function bbb(){ alert(2); } cb.add(bbb); })(); cb.fire();
對應複雜情況很有用。統一管理,通過fire統一觸發。
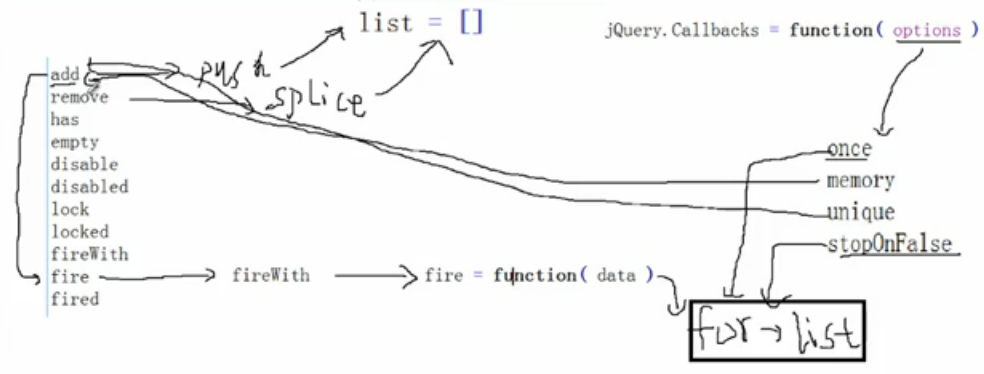
二、原理圖
Callback接收一個參數,可以有4個選項,once,memory,unique,stopOnFalse。
self單體有這些方法:add,remove,has,empty,disable,disabled,lock,locked, fireWith,fire,fired。
list=[]數組變數,用來收集回調函數。fire的時候對其迴圈調用。
add:push數組
fire:調用fireWith,fireWith允許傳參,fire可傳可不傳。
fireWith:調用私有函數fire,在私有函數fire中for迴圈list。
remove:splice數組。
4個參數:
- once針對fire()只迴圈一次
- memory 針對add,作用到add上,add時判斷有memory就去執行fire。
- unique 針對add,添加的時候就可以去重
- stopOnFalse 針對fire,在for迴圈時遇到false,立即跳出迴圈
三、更多用法
1、callback4個參數的作用
- once: 只能夠觸發一次。
- memory: 當隊列已經觸發之後,再添加進來的函數就會直接被調用,不需要再觸發一次。
- unique: 保證函數的唯一
- stopOnFalse: 只要有一個回調返回 false,就中斷後續的調用。
舉例:
不傳參數,fire幾次就觸發幾次。

function aaa() { alert(1); } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks(); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(bbb); cb.fire(); //1 2 cb.fire();//1 2View Code
- once:fire只能觸發一次,源碼中fire後如果有once就把list幹掉了,list=undefined了。
function aaa() { alert(1); } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks('once'); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(bbb); cb.fire(); //1 2 cb.fire();
不傳參數,在fire之後add的回調不能被fire。

//不寫參數,只彈出1,2不會彈出 function aaa() { alert(1); } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks(); cb.add(aaa); cb.fire(); //1 cb.add(bbb);View Code
- memory記憶,在fire前面後面add的方法都能得到執行。
function aaa() { alert(1); } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks('memory'); cb.add(aaa); cb.fire(); //1 2 cb.add(bbb);
- unique:去重

//不加參數,add2次aaa,就會觸發2次aaa function aaa() { alert(1); } var cb = $.Callbacks(); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(aaa); cb.fire(); //1 1View Code
function aaa() { alert(1); } var cb = $.Callbacks('unique'); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(aaa); cb.fire(); //1 加了unique參數,同樣的函數不能多次add
- stopOnFalse:函數返回false跳出迴圈
function aaa() { alert(1); return false; } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks(); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(bbb); cb.fire(); //1 2 不傳參,第一個函數返回false時後面的函數也能正常執行
function aaa() { alert(1); return false; } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks('stopOnFalse'); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(bbb); cb.fire(); //1 //傳參stopOnFalse,第一個函數返回false時後面的函數不再執行
2、callback也可以接收組合的形式
function aaa() { alert(1); } function bbb() { alert(2); } //組合使用,只執行一次,並且彈出1 2 var cb = $.Callbacks('once memory'); cb.add(aaa); cb.fire(); //1 cb.add(bbb); cb.fire();
源碼中:
傳入了 once和memory後,
options={once:true,memory:true}
optionCache={
"once memory":{once:true,memory:true}
}
6、fire()可以傳參
參數作為每個回調函數的實參
function aaa(n) { alert("aaa "+n); } function bbb(n) { alert("bbb "+n); } var cb = $.Callbacks(); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(bbb); //fire傳參 cb.fire("hello"); //彈出aaa hello 和bbb hello
四、源碼
Callbacks就是一個工具函數,內部定義了一個self ,add和remove還有has等掛在self上。
1、參數處理
$.Callbacks有4個可選的參數,可以組合傳入,用空格分隔。比如 $.Callbacks("once memory unique");
這樣傳入的構造函數字元串實際上是一個字元串,源碼中做了處理會把這個字元串轉成對象。
// String to Object options format cache var optionsCache = {}; // Convert String-formatted options into Object-formatted ones and store in cache function createOptions( options ) { var object = optionsCache[ options ] = {}; jQuery.each( options.match( core_rnotwhite ) || [], function( _, flag ) { object[ flag ] = true; }); return object; }
在構造函數中傳入一個options後,先進行如下處理調用。把一個字元串處理成一個對象。
傳入的options="once memory unique"處理後options={once:true,memory:true,unique:true}。
// Convert options from String-formatted to Object-formatted if needed // (we check in cache first) options = typeof options === "string" ? ( optionsCache[ options ] || createOptions( options ) ) : jQuery.extend( {}, options );
過程如下:options="once memory unique"是string類型,所以先從optionsCache中獲取,現在optionsCache為{}所以optionsCache[ options ]是undefined走後面的createOptions( options ) 。create操作中先新建一個以options為鍵的空對象,再迴圈給對象中填充。迴圈操作完
optionCache為
optionCache={ "once memory unique":{once:true,memory:true,unique:true} }
options為
options={once:true,memory:true,unique:true}
2、add源碼
主要是把回調函數Push到數組list中。
add: function() { if ( list ) { //list初始化為[],if判斷會返回true // First, we save the current length var start = list.length; (function add( args ) { jQuery.each( args, function( _, arg ) { ////處理cb.add(aaa,bbb)這種調用 var type = jQuery.type( arg );//arg就是每一個函數 if ( type === "function" ) {//arg是函數就push到list中,此時有個判斷有沒有unique if ( !options.unique || !self.has( arg ) ) {//有unique走後面,判斷list中有沒有這個函數,有就不添加了 list.push( arg ); } } else if ( arg && arg.length && type !== "string" ) { //處理cb.add([aaa,bbb])這種調用 // Inspect recursively add( arg );//遞歸分解,最終還是push到list } }); })( arguments ); // Do we need to add the callbacks to the // current firing batch? if ( firing ) { firingLength = list.length; // With memory, if we're not firing then // we should call right away } else if ( memory ) { firingStart = start; fire( memory ); } } return this; },
3、remove源碼
// Remove a callback from the list remove: function() { if ( list ) { jQuery.each( arguments, function( _, arg ) { var index; while( ( index = jQuery.inArray( arg, list, index ) ) > -1 ) { list.splice( index, 1 );//主要就是splice刪除操作 // Handle firing indexes if ( firing ) { if ( index <= firingLength ) { firingLength--; } if ( index <= firingIndex ) { firingIndex--; } } } }); } return this; },
4、fire源碼
1、整體調用邏輯
self的fire調用self的fireWith,fireWith把參數傳遞到fire()函數。
// Call all callbacks with the given context and arguments fireWith: function( context, args ) { if ( list && ( !fired || stack ) ) { args = args || []; args = [ context, args.slice ? args.slice() : args ]; if ( firing ) { stack.push( args ); } else { fire( args ); } } return this; }, // Call all the callbacks with the given arguments fire: function() { self.fireWith( this, arguments ); return this; },
fire()時主要是for迴圈
// Fire callbacks fire = function( data ) { memory = options.memory && data; fired = true;//fired變為true說明已經調用過一次了, firingIndex = firingStart || 0; firingStart = 0; firingLength = list.length; firing = true;//觸發進行時 for ( ; list && firingIndex < firingLength; firingIndex++ ) { if ( list[ firingIndex ].apply( data[ 0 ], data[ 1 ] ) === false && options.stopOnFalse ) {//每次函數調用同時處理stopOnFalse的情況 memory = false; // To prevent further calls using add //stopOnFalse後有memory也不好使了 break; } } firing = false;//觸髮結束 if ( list ) { if ( stack ) { if ( stack.length ) { fire( stack.shift() ); } } else if ( memory ) { list = []; } else { self.disable(); } } },
2、firing特殊情況
比如在 fire 處理隊列中,某個函數又在隊列中添加了一個回調函數,或者,在隊列中又刪除了某個回調函數。 fire 處理過程中,某個函數又調用了 fire 來觸發事件呢?
先通過例子來看一下效果
function aaa() { alert(1); cb.fire(); //在這裡調用fire()會出現什麼問題 死迴圈 } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks(); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(bbb); cb.fire();
在執行函數的過程中再次調用fire()的執行順序是怎樣的?
var bBtn=true;//用bBtn避免死迴圈 function aaa() { alert(1); if(bBtn){ cb.fire();//註意這裡fire調用後執行順序是1 2 1 2,而不是1 1 2 2 bBtn=false; } } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks(); cb.add(aaa); cb.add(bbb); cb.fire();
結論:把函數運行過程中觸發的fire()放到了運行過程的隊列當中。
fire 處理過程中,某個函數又調用了 fire 來觸發事件時,jQuery的處理方式如下:
將這個嵌套的事件先保存起來,等到當前的回調序列處理完成之後,再檢查被保存的事件,繼續完成處理。顯然,使用隊列是處理這種情況的理想數據結構,如果遇到這種狀況,我們就將事件數據入隊,待處理的時候,依次出隊數據進行處理。什麼時候需要這種處理呢?顯然不是once的情況。在JavaScript中,堆隊列也是通過數組來實現的,push用來將數據追加到數組的最後,而shift用來出隊,從數據的最前面獲取數據。
不過,jQuery沒有稱之為隊列,而是取名stack。
// Stack of fire calls for repeatable lists stack = !options.once && [],
入隊
源碼中,在fireWith的時候判斷for迴圈有沒有執行完
fireWith: function( context, args ) { ...if ( firing ) {//firing在for迴圈沒有走完時一直是true stack.push( args );//所以這句話意思就是函數執行時再去fire()調用就會push到stack數組中 } else { fire( args ); } } return this; },
出隊
再去調用fire()的時候
// Fire callbacks fire = function( data ) { memory = options.memory && data; fired = true;//fired變為true說明已經調用過一次了, firingIndex = firingStart || 0; firingStart = 0; firingLength = list.length; firing = true;//觸發進行時 for ( ; list && firingIndex < firingLength; firingIndex++ ) { if ( list[ firingIndex ].apply( data[ 0 ], data[ 1 ] ) === false && options.stopOnFalse ) {//每次函數調用同時處理stopOnFalse的情況 memory = false; // To prevent further calls using add //stopOnFalse後有memory也不好使了 break; } } firing = false;//觸髮結束 if ( list ) { if ( stack ) { //這就是出現在函數執行過程中再次fire()的時候,等迴圈執行完,再去按順序執行 if ( stack.length ) { fire( stack.shift() ); } } else if ( memory ) {//只執行一次的時候,有once,memory就清空list,此時fire()就相當於一個執行一個空數組 list = []; } else { self.disable();//disable阻止後續任何的fire()操作 } } },
針對下麵這段源碼的一個例子:
once和memory同時存在的時候,fire()無效因為list為[]了,但是add仍然有效。
當有memory的時候,把之前添加的清空;允許添加並再次運行fire後清空;當不存在memory的時候既只有once配置,fire之後既不允許做任何操作了。
else if ( memory ) {//只執行一次的時候,有once,memory就清空list,此時fire()就相當於一個執行一個空數組 list = []; } else { self.disable();//disable阻止後續任何的fire()操作 }
disable阻止後續任何的fire()操作。
function aaa() { alert(1); } function bbb() { alert(2); } //組合使用,只執行一次,並且彈出1 2 3 var cb = $.Callbacks('once memory'); cb.add(aaa); cb.fire(); //1 cb.fire();//此時list為[] cb.add(bbb); cb.fire(); function ccc(){ alert(3); } cb.add(ccc);
5、其他源碼
has(fn):判斷list有沒有fn
empty: 清空數組list=[]
disable:全部鎖住,禁止了,如下
// Have the list do nothing anymore disable: function() { list = stack = memory = undefined; return this; },
disabled:判斷是不是禁止了。return !list;
lock:只是把stack鎖住
// Lock the list in its current state lock: function() { stack = undefined; if ( !memory ) { self.disable(); } return this; },
locked:是否locked。 return !stack;
6、 lock和disable的區別
disable禁止所有操作
function aaa() { alert(1); } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks('memory'); cb.add(aaa); cb.fire(); //1 cb.disable();//disable()後只能彈出1 因為禁止所有操作了,雖然有Memory cb.add(bbb);//不起作用了,此時list變為undefined了 cb.fire();//不起作用了
lock只是鎖住數組
function aaa() { alert(1); } function bbb() { alert(2); } var cb = $.Callbacks('memory'); cb.add(aaa); cb.fire(); //1 2 cb.lock();//lock()只是把後續的fire()鎖住,其他操作是鎖不住的 cb.add(bbb); cb.fire();//不起作用了 此時list為[]
參考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/haogj/p/4473477.html
本文作者starof,因知識本身在變化,作者也在不斷學習成長,文章內容也不定時更新,為避免誤導讀者,方便追根溯源,請諸位轉載註明出處:http://www.cnblogs.com/starof/p/6885500.html有問題歡迎與我討論,共同進步。




