PV 與 PVC PVC (PersistentVolumeClaim),命名空間(namespace)級別的資源,由 用戶 or StatefulSet 控制器(根據VolumeClaimTemplate) 創建。PVC 類似於 Pod,Pod 消耗 Node 資源,PVC 消耗 PV 資源。Po ...
PV 與 PVC
PVC (PersistentVolumeClaim),命名空間(namespace)級別的資源,由 用戶 or StatefulSet 控制器(根據VolumeClaimTemplate) 創建。PVC 類似於 Pod,Pod 消耗 Node 資源,PVC 消耗 PV 資源。Pod 可以請求特定級別的資源(CPU 和記憶體),而 PVC 可以請求特定存儲捲的大小及訪問模式(Access Mode
PV(PersistentVolume)是集群中的一塊存儲資源,可以是 NFS、iSCSI、Ceph、GlusterFS 等存儲捲,PV 由集群管理員創建,然後由開發者使用 PVC 來申請 PV,PVC 是對 PV 的申請,類似於 Pod 對 Node 的申請。
靜態創建存儲捲
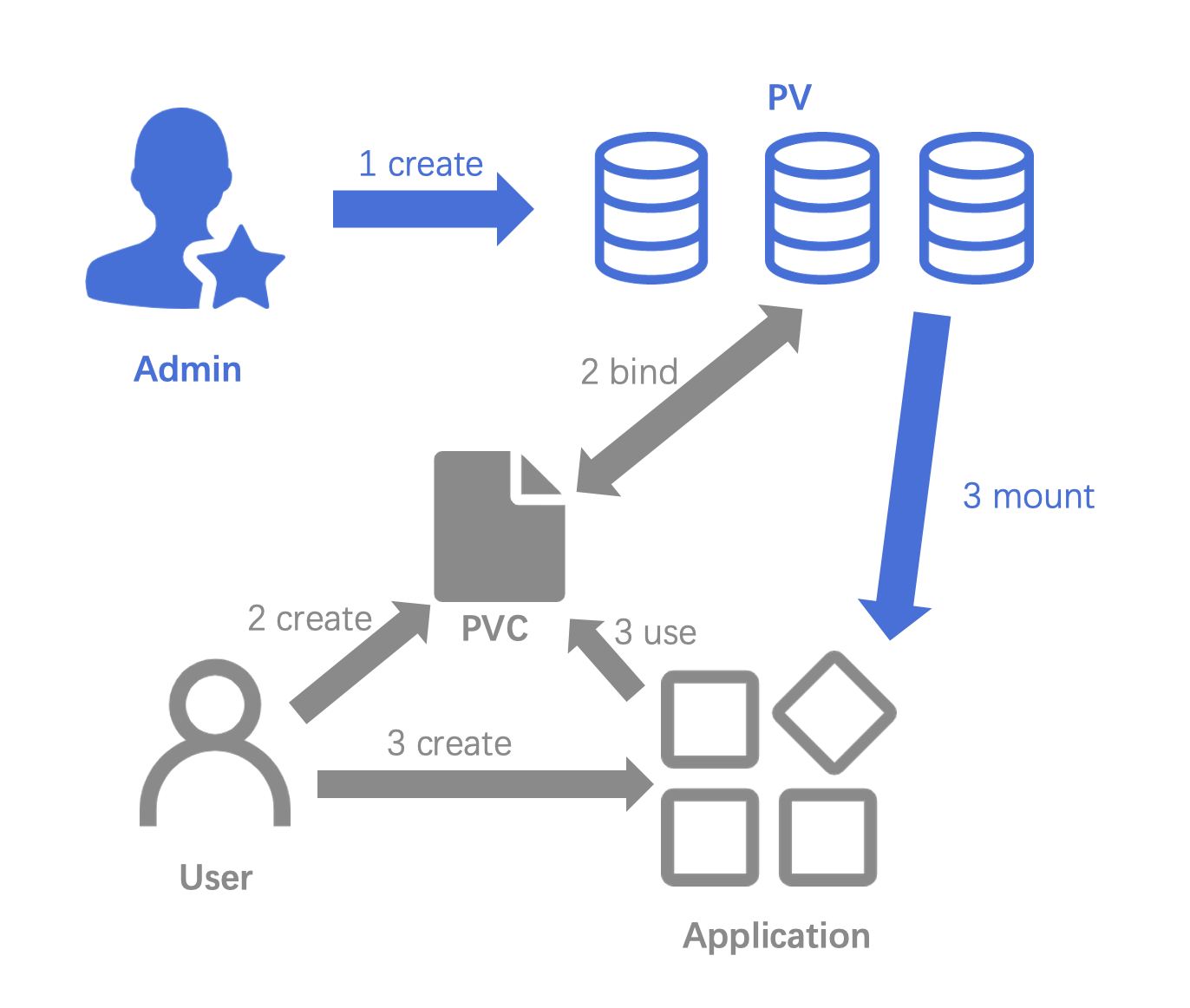
也就是我們手動創建一個pv和pvc,然後將pv和pvc綁定,然後pod使用pvc,這樣就可以使用pv了。
創建一個 nfs 的 pv 以及 對應的 pvc
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: nfs-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 10Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Delete
nfs:
server: 192.168.203.110
path: /data/nfs
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: nfs-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
查看 pvc
$ kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
nfs-pvc Bound nfs-pv 10Gi RWO 101s
創建一個 pod 使用 pvc
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-nfs
spec:
containers:
- image: ubuntu:22.04
name: ubuntu
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- sleep 10000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: nfs-volume
volumes:
- name: nfs-volume
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nfs-pvc
❯ kubectl exec -it test-nfs -- cat /data/nfs
192.168.203.110:/data/nfs
pvc pv 綁定流程
func (ctrl *PersistentVolumeController) syncUnboundClaim(ctx context.Context, claim *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim) error {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
if claim.Spec.VolumeName == "" {
// 是不是延遲綁定 也就是 VolumeBindingMode 為 WaitForFirstConsumer
delayBinding, err := storagehelpers.IsDelayBindingMode(claim, ctrl.classLister)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 通過 pvc 找到最合適的 pv
volume, err := ctrl.volumes.findBestMatchForClaim(claim, delayBinding)
if err != nil {
logger.V(2).Info("Synchronizing unbound PersistentVolumeClaim, Error finding PV for claim", "PVC", klog.KObj(claim), "err", err)
return fmt.Errorf("error finding PV for claim %q: %w", claimToClaimKey(claim), err)
}
if volume == nil {
//// No PV found for this claim
} else /* pv != nil */ {
claimKey := claimToClaimKey(claim)
logger.V(4).Info("Synchronizing unbound PersistentVolumeClaim, volume found", "PVC", klog.KObj(claim), "volumeName", volume.Name, "volumeStatus", getVolumeStatusForLogging(volume))
// 綁定 pv 和 pvc
// 這裡會處理 pvc 的 spec.volumeName status 和 pv 的 status
if err = ctrl.bind(ctx, volume, claim); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
} else /* pvc.Spec.VolumeName != nil */ {
/*
......
*/
}
}
// 選擇
func FindMatchingVolume(
claim *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
volumes []*v1.PersistentVolume,
node *v1.Node,
excludedVolumes map[string]*v1.PersistentVolume,
delayBinding bool) (*v1.PersistentVolume, error) {
var smallestVolume *v1.PersistentVolume
var smallestVolumeQty resource.Quantity
requestedQty := claim.Spec.Resources.Requests[v1.ResourceName(v1.ResourceStorage)]
requestedClass := GetPersistentVolumeClaimClass(claim)
var selector labels.Selector
if claim.Spec.Selector != nil {
internalSelector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(claim.Spec.Selector)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error creating internal label selector for claim: %v: %v", claimToClaimKey(claim), err)
}
selector = internalSelector
}
// Go through all available volumes with two goals:
// - find a volume that is either pre-bound by user or dynamically
// provisioned for this claim. Because of this we need to loop through
// all volumes.
// - find the smallest matching one if there is no volume pre-bound to
// the claim.
for _, volume := range volumes {
if _, ok := excludedVolumes[volume.Name]; ok {
// Skip volumes in the excluded list
continue
}
if volume.Spec.ClaimRef != nil && !IsVolumeBoundToClaim(volume, claim) {
continue
}
volumeQty := volume.Spec.Capacity[v1.ResourceStorage]
if volumeQty.Cmp(requestedQty) < 0 {
continue
}
// filter out mismatching volumeModes
if CheckVolumeModeMismatches(&claim.Spec, &volume.Spec) {
continue
}
// check if PV's DeletionTimeStamp is set, if so, skip this volume.
if volume.ObjectMeta.DeletionTimestamp != nil {
continue
}
nodeAffinityValid := true
if node != nil {
// Scheduler path, check that the PV NodeAffinity
// is satisfied by the node
// CheckNodeAffinity is the most expensive call in this loop.
// We should check cheaper conditions first or consider optimizing this function.
err := CheckNodeAffinity(volume, node.Labels)
if err != nil {
nodeAffinityValid = false
}
}
if IsVolumeBoundToClaim(volume, claim) {
// If PV node affinity is invalid, return no match.
// This means the prebound PV (and therefore PVC)
// is not suitable for this node.
if !nodeAffinityValid {
return nil, nil
}
return volume, nil
}
if node == nil && delayBinding {
// PV controller does not bind this claim.
// Scheduler will handle binding unbound volumes
// Scheduler path will have node != nil
continue
}
// filter out:
// - volumes in non-available phase
// - volumes whose labels don't match the claim's selector, if specified
// - volumes in Class that is not requested
// - volumes whose NodeAffinity does not match the node
if volume.Status.Phase != v1.VolumeAvailable {
// We ignore volumes in non-available phase, because volumes that
// satisfies matching criteria will be updated to available, binding
// them now has high chance of encountering unnecessary failures
// due to API conflicts.
continue
} else if selector != nil && !selector.Matches(labels.Set(volume.Labels)) {
continue
}
if GetPersistentVolumeClass(volume) != requestedClass {
continue
}
if !nodeAffinityValid {
continue
}
if node != nil {
// Scheduler path
// Check that the access modes match
if !CheckAccessModes(claim, volume) {
continue
}
}
if smallestVolume == nil || smallestVolumeQty.Cmp(volumeQty) > 0 {
smallestVolume = volume
smallestVolumeQty = volumeQty
}
}
if smallestVolume != nil {
// Found a matching volume
return smallestVolume, nil
}
return nil, nil
}
kubelet 綁定
if err := os.MkdirAll(dir, 0750); err != nil {
return err
}
source := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s", nfsMounter.server, nfsMounter.exportPath)
options := []string{}
if nfsMounter.readOnly {
options = append(options, "ro")
}
mountOptions := util.JoinMountOptions(nfsMounter.mountOptions, options)
err = nfsMounter.mounter.MountSensitiveWithoutSystemd(source, dir, "nfs", mountOptions, nil)
kubelet 就會在調用 sudo mount -t nfs ... 命令把 nfs 綁定到主機上 綁定的目錄大概為 /var/lib/kubelet/pods/[POD-ID]/volumes/
StorageClass
StorageClass 是 Kubernetes 中用來定義存儲捲的類型的資源對象,StorageClass 用來定義存儲捲的類型,比如 NFS、iSCSI、Ceph、GlusterFS 等存儲捲。StorageClass 是集群級別的資源,由集群管理員創建,用戶可以使用 StorageClass 來動態創建 PV。
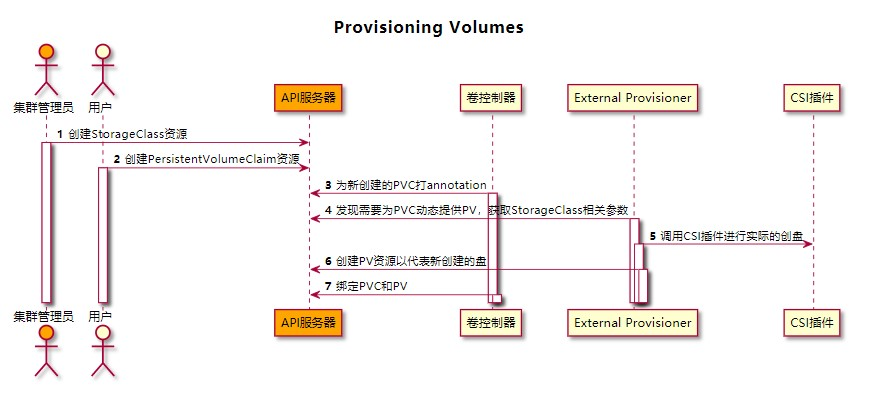
動態創建存儲捲
動態創建存儲捲相比靜態創建存儲捲,少了集群管理員的干預,流程如下圖所示:

創建一個 StorageClass pvc pod
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: local-storage
provisioner: rancher.io/local-path
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: my-local-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 128Mi
storageClassName: local-storage
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test
spec:
containers:
- image: ubuntu:22.04
name: ubuntu
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- sleep 10000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: my-local-pvc
volumes:
- name: my-local-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: my-local-pvc
查看 pv
❯ kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pvc-9d257d8a-29a8-4abf-a1e2-c7e4953fc0ca 128Mi RWO Delete Bound default/my-local-pvc local-storage 85s
StorageClass 創建 pv 流程
// 還是 syncUnboundClaim 中
// volume 為空,說明沒有找到合適的 pv 那麼去檢查 如果 pvc 的 storageClassName 不為空,那麼就會去找到對應的 storageClass
if volume == nil {
switch {
case delayBinding && !storagehelpers.IsDelayBindingProvisioning(claim):
// ......
case storagehelpers.GetPersistentVolumeClaimClass(claim) != "":
// 如果 pvc 的 storageClassName 不為空,那麼就會去找到對應的 storageClass
if err = ctrl.provisionClaim(ctx, claim); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
default:
}
return nil
}
func (ctrl *PersistentVolumeController) provisionClaim(ctx context.Context, claim *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim) error {
plugin, storageClass, err := ctrl.findProvisionablePlugin(claim)
ctrl.scheduleOperation(logger, opName, func() error {
var err error
if plugin == nil {
// 如果是外部的 provisioner 這裡我們就安裝了 rancher.io/local-path 這個插件
// 所以這裡會調用 provisionClaimOperationExternal
_, err = ctrl.provisionClaimOperationExternal(ctx, claim, storageClass)
} else {
// 內部的 provisioner 直接處理
_, err = ctrl.provisionClaimOperation(ctx, claim, plugin, storageClass)
}
return err
})
return nil
}
// 如果是外部的 provisioner 會在 pvc 的 annotations 加入 volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-provisioner: rancher.io/local-path 和 volume.kubernetes.io/storage-provisioner: rancher.io/local-path
func (ctrl *PersistentVolumeController) setClaimProvisioner(ctx context.Context, claim *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim, provisionerName string) (*v1.PersistentVolumeClaim, error) {
if val, ok := claim.Annotations[storagehelpers.AnnStorageProvisioner]; ok && val == provisionerName {
// annotation is already set, nothing to do
return claim, nil
}
// The volume from method args can be pointing to watcher cache. We must not
// modify these, therefore create a copy.
claimClone := claim.DeepCopy()
// TODO: remove the beta storage provisioner anno after the deprecation period
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
metav1.SetMetaDataAnnotation(&claimClone.ObjectMeta, storagehelpers.AnnBetaStorageProvisioner, provisionerName)
metav1.SetMetaDataAnnotation(&claimClone.ObjectMeta, storagehelpers.AnnStorageProvisioner, provisionerName)
updateMigrationAnnotations(logger, ctrl.csiMigratedPluginManager, ctrl.translator, claimClone.Annotations, true)
newClaim, err := ctrl.kubeClient.CoreV1().PersistentVolumeClaims(claim.Namespace).Update(ctx, claimClone, metav1.UpdateOptions{})
if err != nil {
return newClaim, err
}
_, err = ctrl.storeClaimUpdate(logger, newClaim)
if err != nil {
return newClaim, err
}
return newClaim, nil
}
kubernetes external provisioner
kubernetes external provisioner 是一個獨立的進程,用來動態創建 PV,它通過監聽 StorageClass 的事件,當 StorageClass 的 ReclaimPolicy 為 Retain 時,會創建 PV。
在這裡我新建一個 關於 nfs 的 external provisioner
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"path/filepath"
"github.com/golang/glog"
v1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
"k8s.io/client-go/util/homedir"
"sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/log"
"sigs.k8s.io/sig-storage-lib-external-provisioner/v10/controller"
)
const provisionerName = "provisioner.test.com/nfs"
var _ controller.Provisioner = &nfsProvisioner{}
type nfsProvisioner struct {
client kubernetes.Interface
}
func (p *nfsProvisioner) Provision(ctx context.Context, options controller.ProvisionOptions) (*v1.PersistentVolume, controller.ProvisioningState, error) {
if options.PVC.Spec.Selector != nil {
return nil, controller.ProvisioningFinished, fmt.Errorf("claim Selector is not supported")
}
glog.V(4).Infof("nfs provisioner: VolumeOptions %v", options)
pv := &v1.PersistentVolume{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: options.PVName,
},
Spec: v1.PersistentVolumeSpec{
PersistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: *options.StorageClass.ReclaimPolicy,
AccessModes: options.PVC.Spec.AccessModes,
MountOptions: options.StorageClass.MountOptions,
Capacity: v1.ResourceList{
v1.ResourceName(v1.ResourceStorage): options.PVC.Spec.Resources.Requests[v1.ResourceName(v1.ResourceStorage)],
},
PersistentVolumeSource: v1.PersistentVolumeSource{
NFS: &v1.NFSVolumeSource{
Server: options.StorageClass.Parameters["server"],
Path: options.StorageClass.Parameters["path"],
ReadOnly: options.StorageClass.Parameters["readOnly"] == "true",
},
},
},
}
return pv, controller.ProvisioningFinished, nil
}
func (p *nfsProvisioner) Delete(ctx context.Context, volume *v1.PersistentVolume) error {
// 因為是 nfs 沒有產生實際的資源,所以這裡不需要刪除
// 如果在 provisioner 中創建了資源,那麼這裡需要刪除
// 一般是調用 csi 創建/刪除資源
return nil
}
func main() {
l := log.FromContext(context.Background())
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", filepath.Join(homedir.HomeDir(), ".kube", "config"))
if err != nil {
glog.Fatalf("Failed to create kubeconfig: %v", err)
}
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
if err != nil {
glog.Fatalf("Failed to create client: %v", err)
}
clientNFSProvisioner := &nfsProvisioner{
client: clientset,
}
pc := controller.NewProvisionController(l,
clientset,
provisionerName,
clientNFSProvisioner,
controller.LeaderElection(true),
)
glog.Info("Starting provision controller")
pc.Run(context.Background())
}
創建一個 nfs 的 storageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: my-nfs
provisioner: provisioner.test.com/nfs
reclaimPolicy: Delete
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
parameters:
server: "192.168.203.110"
path: /data/nfs
readOnly: "false"
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: my-nfs-pvc
spec:
storageClassName: my-nfs
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-nfs
spec:
containers:
- image: ubuntu:22.04
name: ubuntu
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- sleep 10000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: my-nfs-pvc
volumes:
- name: my-nfs-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: my-nfs-pvc
❯ kubectl exec -it test-nfs -- cat /data/nfs
192.168.203.110:/data/nfs
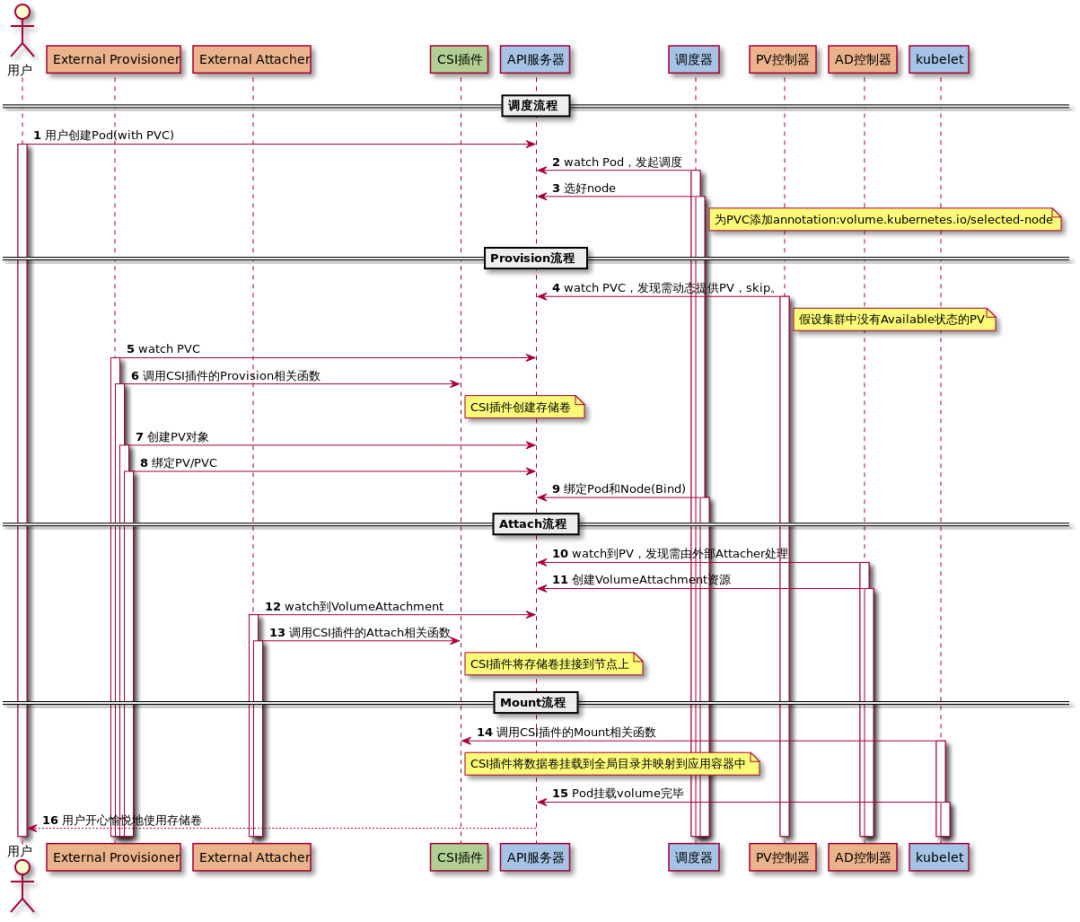
CSI 流程
持久化存儲流程圖如下:
Provisioner
當部署 csi-controller 時 ,會啟動一個伴生容器,項目地址為 https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/external-provisioner 這個項目是一個 csi 的 provisioner
它會監控屬於自己的pvc,當有新的pvc創建時,會調用 csi 的 createVolume 方法,創建一個 volume,然後創建一個 pv。當 pvc 刪除時,會調用 csi 的 deleteVolume 方法,然後刪除 volume 和 pv。
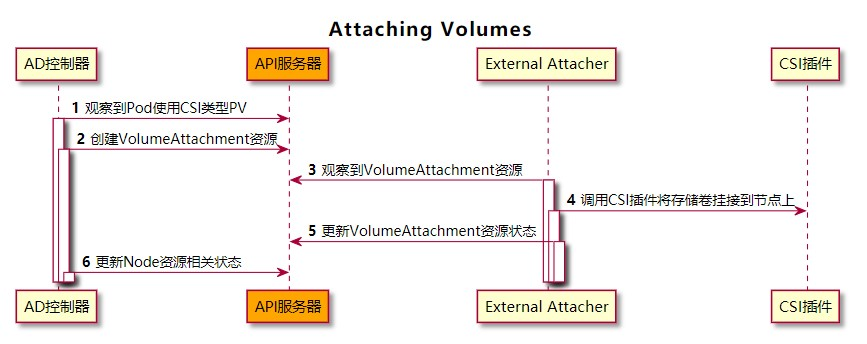
Attacher
external-attacher 也是 csi-controller 的伴生容器,項目地址為 https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/external-attacher 這個項目是一個 csi 的 attacher, 它會監控 AttachDetachController 資源,當有新的資源創建時,會調用 csi 的 controllerPublishVolume 方法,掛載 volume 到 node 上。當資源刪除時,會調用 csi 的 controllerUnpublishVolume 方法,卸載 volume。

Snapshotter
external-snapshotter 也是 csi-controller 的伴生容器,項目地址為 https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/external-snapshotter 這個項目是一個 csi 的 snapshotter, 它會監控 VolumeSnapshot 資源,當有新的資源創建時,會調用 csi 的 createSnapshot 方法,創建一個快照。當資源刪除時,會調用 csi 的 deleteSnapshot 方法,刪除快照。
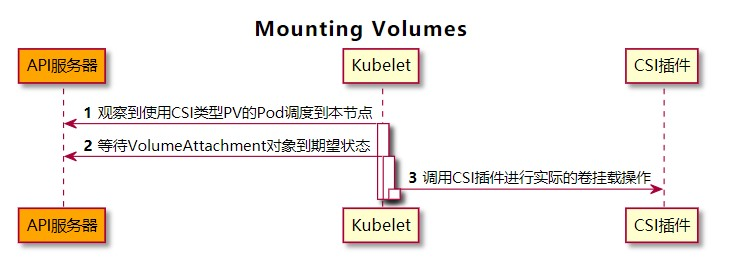
csi-node
csi-node 是一個 kubelet 的插件,所以它需要每個節點上都運行,當 pod 創建時,並且 VolumeAttachment 的 .spec.Attached 時,kubelet 會調用 csi 的 NodeStageVolume 函數,之後插件(csiAttacher)調用內部 in-tree CSI 插件(csiMountMgr)的 SetUp 函數,該函數內部會調用 csi 的 NodePublishVolume 函數,掛載 volume 到 pod 上。當 pod 刪除時,kubelet 觀察到包含 CSI 存儲捲的 Pod 被刪除,於是調用內部 in-tree CSI 插件(csiMountMgr)的 TearDown 函數,該函數內部會通過 unix domain socket 調用外部 CSI 插件的 NodeUnpublishVolume 函數。kubelet 調用內部 in-tree CSI 插件(csiAttacher)的 UnmountDevice 函數,該函數內部會通過 unix domain socket 調用外部 CSI 插件的 NodeUnstageVolume 函數。

csi-node-driver-registrar
這個是 csi-node 的伴生容器,項目地址為 https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/node-driver-registrar,
它的主要作用是向 kubelet 註冊 csi 插件,kubelet 會調用 csi 插件的 Probe 方法,如果返回成功,kubelet 會調用 csi 插件的 NodeGetInfo 方法,獲取節點信息。
csi-livenessprobe
這個是 csi-node 的伴生容器,項目地址為 https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/livenessprobe, 它的主要作用是給 kubernetes 的 livenessprobe 提供一個介面,用來檢查 csi 插件是否正常運行。它在 /healthz 時,會調用 csi 的 Probe 方法,如果返回成功,返回 200,否則返回 500。



