來源:blog.csdn.net/weixin_42653522/article/details/117151913 1、前言 ApplicationContext 中的事件處理是通過 ApplicationEvent 類和 ApplicationListener 介面提供的。如果將實現了 Appl ...
來源:blog.csdn.net/weixin_42653522/article/details/117151913
1、前言
ApplicationContext 中的事件處理是通過 ApplicationEvent 類和 ApplicationListener 介面提供的。如果將實現了 ApplicationListener 介面的 bean 部署到容器中,則每次將 ApplicationEvent 發佈到ApplicationContext 時,都會通知到該 bean,這簡直是典型的觀察者模式。設計的初衷就是為了系統業務邏輯之間的解耦,提高可擴展性以及可維護性。
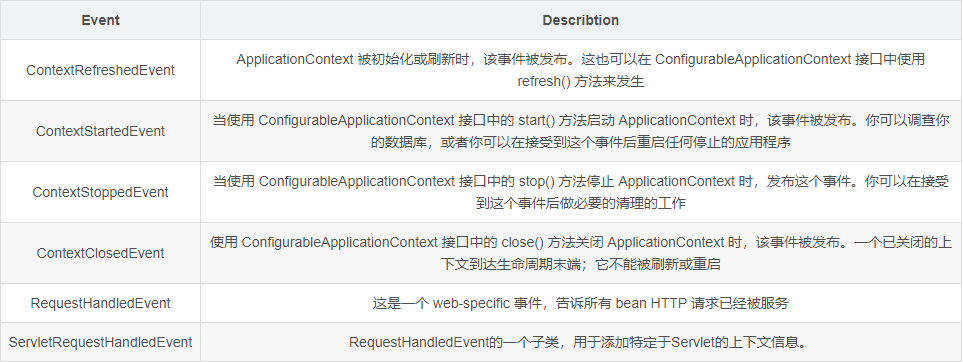
Spring 中提供了以下的事件
2、ApplicationEvent 與 ApplicationListener 應用
推薦一個開源免費的 Spring Boot 實戰項目:
實現
1、自定義事件類,基於 ApplicationEvent 實現擴展
public class DemoEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2753705718295396328L;
private String msg;
public DemoEvent(Object source, String msg) {
super(source);
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
2、定義 Listener 類,實現 ApplicationListener介面,並且註入到 IOC 中。等發佈者發佈事件時,都會通知到這個bean,從而達到監聽的效果。
@Component
public class DemoListener implements ApplicationListener<DemoEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(DemoEvent demoEvent) {
String msg = demoEvent.getMsg();
System.out.println("bean-listener 收到了 publisher 發佈的消息: " + msg);
}
}
3、要發佈上述自定義的 event,需要調用 ApplicationEventPublisher 的 publishEvent 方法,我們可以定義一個實現 ApplicationEventPublisherAware 的類,並註入 IOC來進行調用。
@Component
public class DemoPublisher implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware {
private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;
}
public void sendMsg(String msg) {
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new DemoEvent(this, msg));
}
}
4、客戶端調用 publisher
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/event")
public class DemoClient implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@GetMapping("/publish")
public void publish(){
DemoPublisher bean = applicationContext.getBean(DemoPublisher.class);
bean.sendMsg("發佈者發送消息......");
}
}
輸出結果:
bean-listener 收到了 publisher 發佈的消息: 發佈者發送消息......
基於註解
我們可以不用實現 AppplicationListener 介面 ,在方法上使用 @EventListener 註冊事件。如果你的方法應該偵聽多個事件,並不使用任何參數來定義,可以在 @EventListener 註解上指定多個事件。
重寫 DemoListener 類如下:
public class DemoListener {
@EventListener(value = {DemoEvent.class, TestEvent.class})
public void processApplicationEvent(DemoEvent event) {
String msg = event.getMsg();
System.out.println("bean-listener 收到了 publisher 發佈的消息: " + msg);
}
}
事件過濾
如果希望通過一定的條件對事件進行過濾,可以使用 @EventListener 的 condition 屬性。以下實例中只有 event 的 msg 屬性是 my-event 時才會進行調用。
@EventListener(value = {DemoEvent.class, TestEvent.class}, condition = "#event.msg == 'my-event'")
public void processApplicationEvent(DemoEvent event) {
String msg = event.getMsg();
System.out.println("bean-listener 收到了 publisher 發佈的消息: " + msg);
}
此時,發送符合條件的消息,listener 才會偵聽到 publisher 發佈的消息。
bean-listener 收到了 publisher 發佈的消息: my-event
非同步事件監聽
前面提到的都是同步處理事件,那如果我們希望某個特定的偵聽器非同步去處理事件,如何做?
使用 @Async 註解可以實現類內方法的非同步調用,這樣方法在執行的時候,將會在獨立的線程中被執行,調用者無需等待它的完成,即可繼續其他的操作。
@EventListener
@Async
public void processApplicationEvent(DemoEvent event) {
String msg = event.getMsg();
System.out.println("bean-listener 收到了 publisher 發佈的消息: " + msg);
}
使用非同步監聽時,有兩點需要註意:
- 如果非同步事件拋出異常,則不會將其傳播到調用方。
- 非同步事件監聽方法無法通過返回值來發佈後續事件,如果需要作為處理結果發佈另一個事件,請插入
ApplicationEventPublisher以手動發佈事件
3、好處及應用場景
ApplicationContext 在運行期會自動檢測到所有實現了 ApplicationListener 的 bean,並將其作為事件接收對象。當我們與 spring 上下文交互觸發 publishEvent 方法時,每個實現了 ApplicationListener 的 bean 都會收到 ApplicationEvent 對象,每個 ApplicationListener 可以根據需要只接收自己感興趣的事件。
這樣做有什麼好處呢?
在傳統的項目中,各個業務邏輯之間耦合性比較強,controller 和 service 間都是關聯關係,然而,使用 ApplicationEvent 監聽 publisher 這種方式,類間關係是什麼樣的?我們不如畫張圖來看看。
DemoPublisher 和 DemoListener 兩個類間並沒有直接關聯,解除了傳統業務邏輯兩個類間的關聯關係,將耦合降到最小。這樣在後期更新、維護時難度大大降低了。
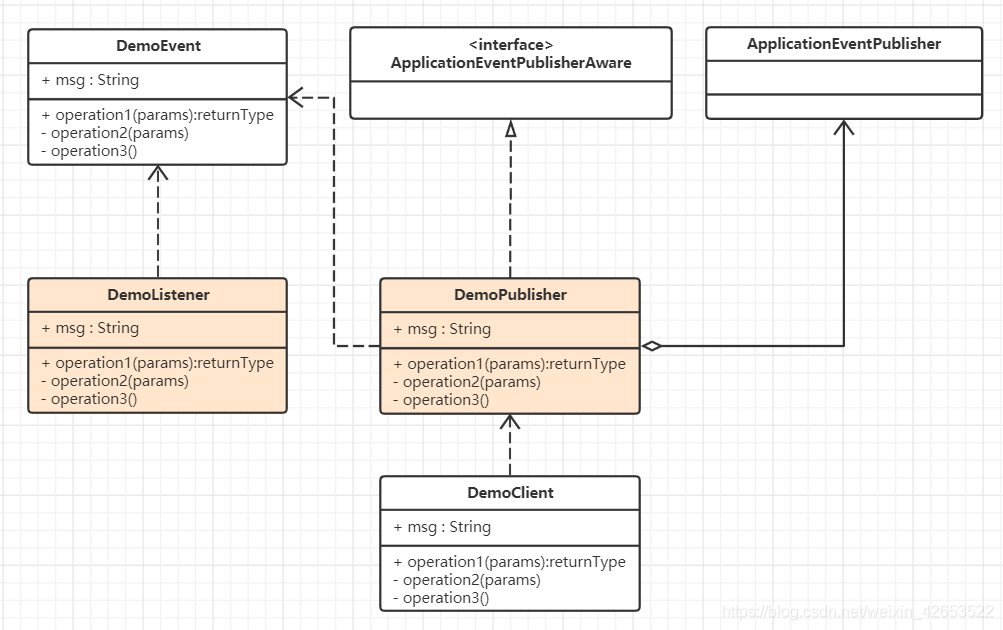
ApplicationEvent 使用觀察者模式實現,那什麼時候適合使用觀察者模式呢?觀察者模式也叫 發佈-訂閱模式,例如,微博的訂閱,我們訂閱了某些微博賬號,當這些賬號發佈消息時,我們都會收到通知。
總結來說,定義對象間的一種一對多的依賴關係,當一個對象的狀態發生改變時,所有依賴於它的對象都得到通知並被自動更新,從而實現廣播的效果。
4、源碼閱讀

Spring中的事件機制流程
1、ApplicationEventPublisher是Spring的事件發佈介面,事件源通過該介面的pulishEvent方法發佈事件
2、ApplicationEventMulticaster就是Spring事件機制中的事件廣播器,它預設提供一個SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster實現,如果用戶沒有自定義廣播器,則使用預設的。它通過父類AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster的getApplicationListeners方法從事件註冊表(事件-監聽器關係保存)中獲取事件監聽器,並且通過invokeListener方法執行監聽器的具體邏輯
3、ApplicationListener就是Spring的事件監聽器介面,所有的監聽器都實現該介面,本圖中列出了典型的幾個子類。其中RestartApplicationListnener在SpringBoot的啟動框架中就有使用
4、在Spring中通常是ApplicationContext本身擔任監聽器註冊表的角色,在其子類AbstractApplicationContext中就聚合了事件廣播器ApplicationEventMulticaster和事件監聽器ApplicationListnener,並且提供註冊監聽器的addApplicationListnener方法
通過上圖就能較清晰的知道當一個事件源產生事件時,它通過事件發佈器ApplicationEventPublisher發佈事件,然後事件廣播器ApplicationEventMulticaster會去事件註冊表ApplicationContext中找到事件監聽器ApplicationListnener,並且逐個執行監聽器的onApplicationEvent方法,從而完成事件監聽器的邏輯。
來到ApplicationEventPublisher 的 publishEvent 方法內部
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
//
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
}
多播事件方法
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 遍歷所有的監聽者
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
// 非同步調用監聽器
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
// 同步調用監聽器
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
invokeListener
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
doInvokeListener
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
// 這裡是事件發生的地方
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
......
}
}
點擊 ApplicationListener 介面 onApplicationEvent 方法的實現,可以看到我們重寫的方法。

5、總結
Spring 使用反射機制,獲取了所有繼承 ApplicationListener 介面的監聽器,在 Spring 初始化時,會把監聽器都自動註冊到註冊表中。
Spring 的事件發佈非常簡單,我們來總結一下:
- 定義一個繼承
ApplicationEvent的事件 - 定義一個實現
ApplicationListener的監聽器或者使用@EventListener監聽事件 - 定義一個發送者,調用
ApplicationContext直接發佈或者使用ApplicationEventPublisher來發佈自定義事件
最後,發佈-訂閱模式可以很好的將業務邏輯進行解耦(上圖驗證過),大大提高了可維護性、可擴展性。
近期熱文推薦:
1.1,000+ 道 Java面試題及答案整理(2022最新版)
4.別再寫滿屏的爆爆爆炸類了,試試裝飾器模式,這才是優雅的方式!!
覺得不錯,別忘了隨手點贊+轉發哦!



