八、迴圈(一) 1、for迴圈 1)for迴圈語法 //for迴圈語法 for(初始化表達式;運行條件表達式;變動表達式) { 迴圈內容; } //示例 for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { std::cout<<i<<std::endl; } std::cout<<"迴圈結束"; ①列印 ...
八、迴圈(一)
1、for迴圈
1)for迴圈語法
//for迴圈語法
for(初始化表達式;運行條件表達式;變動表達式)
{
迴圈內容;
}
//示例
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
std::cout<<i<<std::endl;
}
std::cout<<"迴圈結束";
①列印9-1
//列印9-1
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
for (int i = 9; i > 0; i--)
{
std::cout << i << std::endl;
}
}
②列印所有大寫字母
//列印所有大寫字母
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
for (char i = 65; i <=90; i++) //A的ascii碼為65
{
std::cout << i << std::endl;
}
}
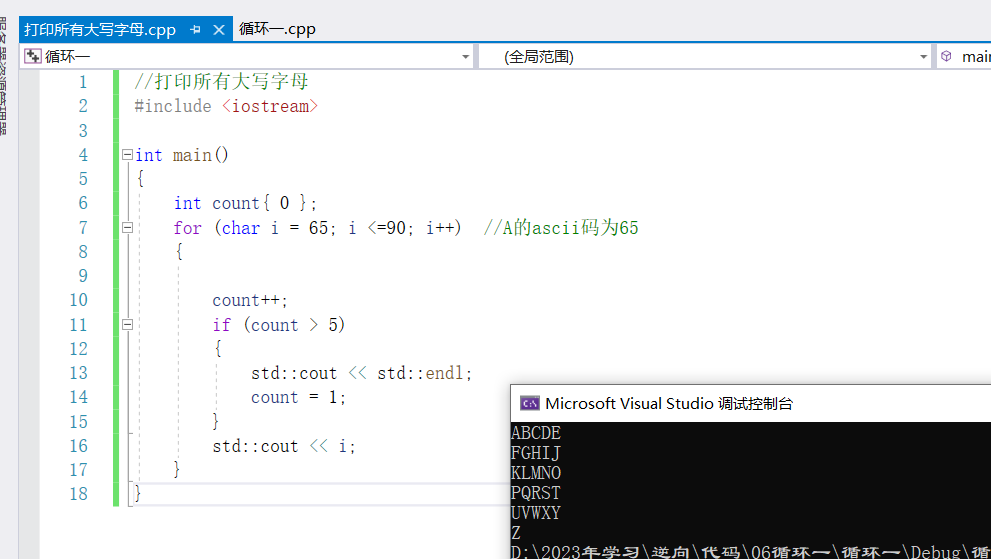
③列印所有大寫字母,但是每行只有五個字母
//列印所有大寫字母
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int count{ 0 };
for (char i = 65; i <=90; i++) //A的ascii碼為65
{
count++;
if (count > 5)
{
std::cout << std::endl;
count = 1;
}
std::cout << i;
}
}
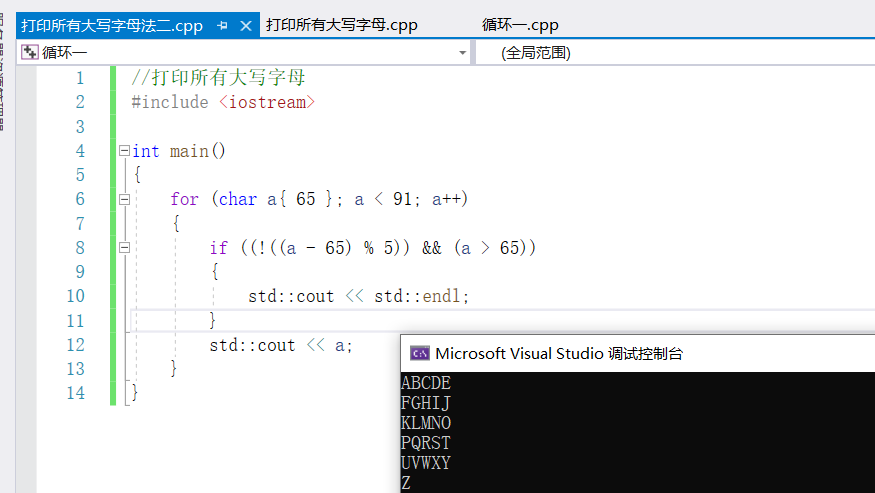
法二:
//列印所有大寫字母
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
for (char a{ 65 }; a < 91; a++)
{
if ((!((a - 65) % 5)) && (a > 65)) //取餘數,如果餘數=0,則進行換行
{
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << a;
}
}
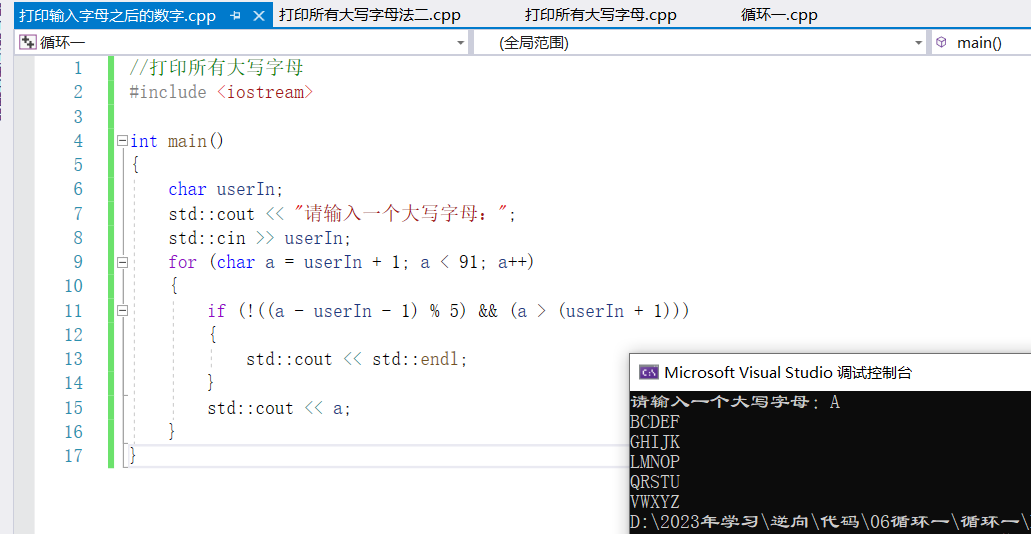
④要求用戶輸入一個大寫字母,列印從這個字母後的所有大寫字母,比如用戶輸入C,那麼屏蔽上列印DEFG..Z
//輸入一個大寫字母,列印從這個字母後的所有大寫字母
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
char userIn;
std::cout << "請輸入一個大寫字母:";
std::cin >> userIn;
for (char a = userIn + 1; a < 91; a++)
{
if (!((a - userIn - 1) % 5) && (a > (userIn + 1)))
{
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << a;
}
}
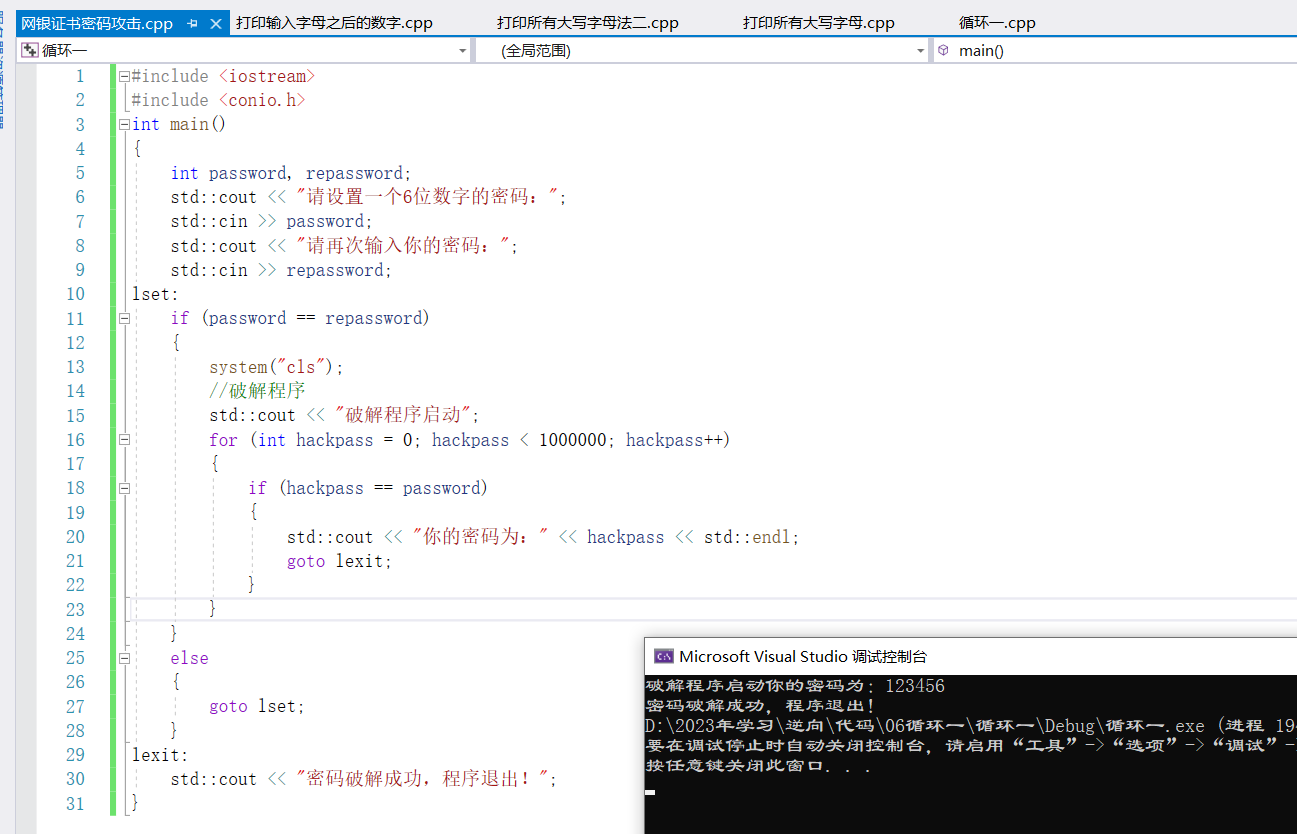
2、for迴圈之網銀證書密碼攻擊
需求:設計一個系統來模擬網銀密碼被攻擊的場景,用戶輸入一個6位數字密碼,然後我們破解它的密碼並顯示出來
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
int password, repassword;
std::cout << "請設置一個6位數字的密碼:";
std::cin >> password;
std::cout << "請再次輸入你的密碼:";
std::cin >> repassword;
lset:
if (password == repassword)
{
system("cls");
//破解程式
std::cout << "破解程式啟動";
for (int hackpass = 0; hackpass < 1000000; hackpass++)
{
if (hackpass == password)
{
std::cout << "你的密碼為:" << hackpass << std::endl;
goto lexit;
}
}
}
else
{
goto lset;
}
lexit:
std::cout << "密碼破解成功,程式退出!";
}
3、for迴圈補充知識
1)迴圈的嵌套
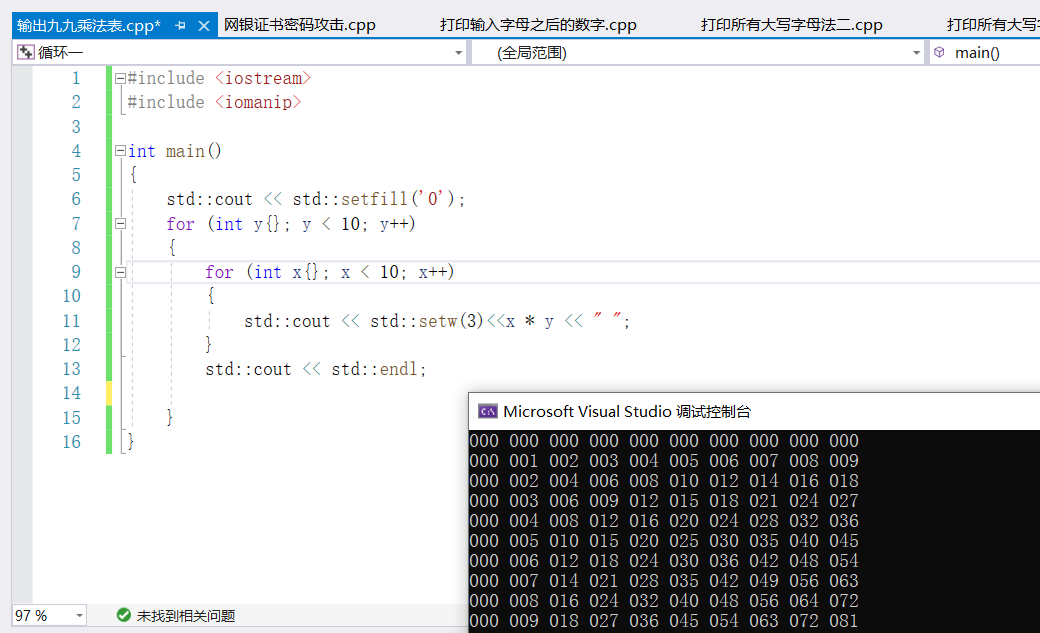
①列印九九乘法表,輸出結果如下
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main()
{
std::cout << std::setfill('0');
for (int y{}; y < 10; y++)
{
for (int x{}; x < 10; x++)
{
std::cout << std::setw(3)<<x * y << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
2)跳出for迴圈的三種方式
| 能力 | 語句 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | continue | 跳出本次迴圈,進入下一次迴圈 |
| 2 | break | 跳出迴圈 |
| 3 | goto | 跳出嵌套迴圈,即跳出所有迴圈 |
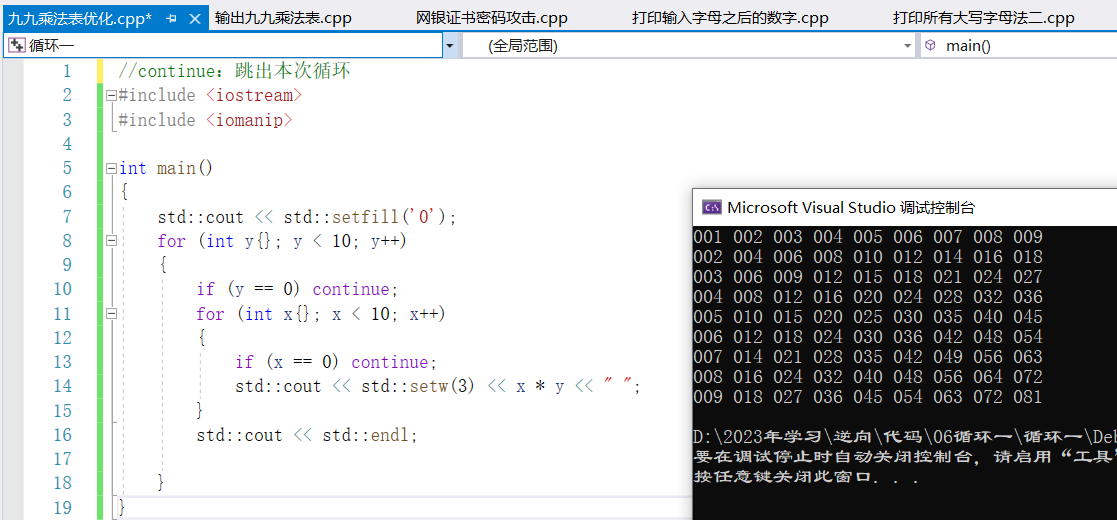
①continue:跳出本次迴圈
//continue:跳出本次迴圈
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main()
{
std::cout << std::setfill('0');
for (int y{}; y < 10; y++)
{
if (y == 0) continue;
for (int x{}; x < 10; x++)
{
if (x == 0) continue;
std::cout << std::setw(3) << x * y << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
②break:跳出迴圈
//break:跳出迴圈
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main()
{
std::cout << std::setfill('0');
for (int y{}; y < 10; y++)
{
for (int x{}; x < 10; x++)
{
if (x == 5) break;
std::cout << std::setw(3) << x * y << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
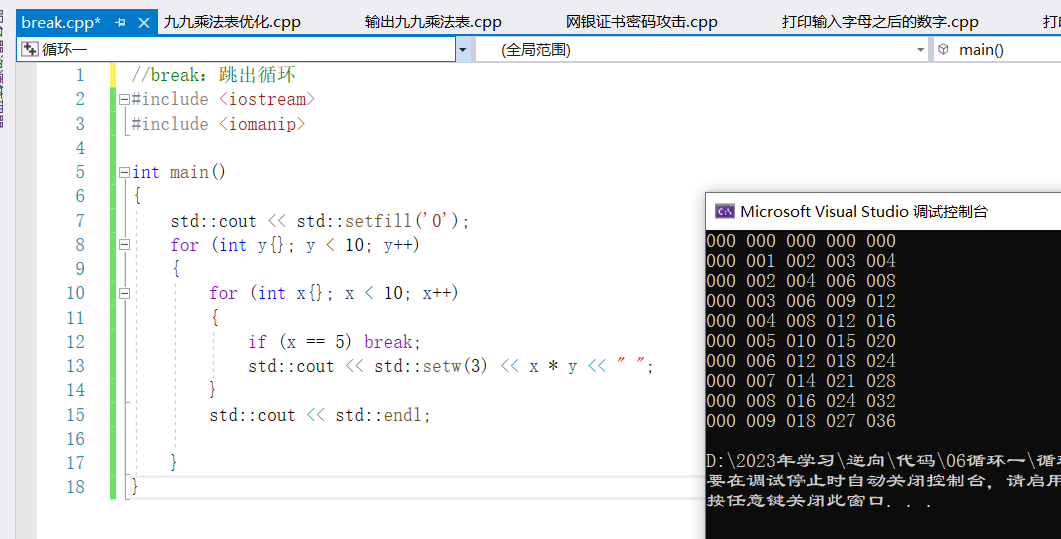
註:break只能跳出本層迴圈,但是無法跳出上層迴圈
③goto:可以跳出所有迴圈
3)for迴圈的變體
//正常for迴圈
for(初始化;條件;變動表達式)
{
}
//變體一:無初始化,只要前面聲明過,for中就不需要初始化
for(;條件;變動表達式)
{
}
//變體二:無變動表達式
for(;條件;) //死迴圈
{
}
//變體三:
for(;;) //無條件執行,中間是一個條件表達式,即bool值
{
}



