atexit 處理器中再次調用 exit 為什麼能正常運行?atexit 處理器中再次調用 atexit 註冊的函數為什麼能正常被調用?帶著這些疑問來看看 glibc 是用什麼數據結構存儲終止處理器的,另外看看列印這些結構時遇到了哪些問題 ...
前言
之前在寫 apue 系列的時候,曾經對系統介面的很多行為產生過好奇,當時就想研究下對應的源碼,但是苦於 linux 源碼過於龐雜,千頭萬緒不知從何開啟,就一直拖了下來。
最近在查一個問題時無意間接觸到了 code browser 這個線上源碼查看器,它同時解決了源碼包下載和環境搭建的問題,版本也幫你選好了,直接原地起飛進入源碼查看:
下麵是查找 glibc exit 的過程:

語法高亮、風格切換、跳轉 (定義/引用) 等功能做的還是很全面的,看代碼綽綽有餘,簡直是我等 coder 之福音。
這裡感謝 Bing 同學的介紹,感興趣讀者可以在文末參考它寫的關於 glibc exit 的另一篇文章,也很不錯的。
glibc exit
之前寫過一篇介紹 linux 進程環境的文章(《 [apue] 進程環境那些事兒》),其中提到了 glibc exit 會主動調用 atexit 註冊的處理器,且有以下特性:
- LIFO,先進後出的順序
- 註冊幾次調用幾次
- atexit 處理器中再次調用 exit 能完成剩餘處理器的調用
- atexit 處理器中再次註冊的 atexit 處理器能被調用
下麵帶著這些問題,來看 glibc exit 的源碼,以及它是如何實現上面這些特性的。
atexit 處理器結構
開門見山:
void
exit (int status)
{
__run_exit_handlers (status, &__exit_funcs, true, true);
}
static struct exit_function_list initial;
struct exit_function_list *__exit_funcs = &initial;
uint64_t __new_exitfn_called;exit 只調用了一個 __run_exit_handlers 介面,它需要的 atexit 處理器列表存儲在 __exit_funcs 參數中,是從這裡傳入的。
未曾開言先轉腚,來看下 __exit_funcs 的結構:
enum
{
ef_free, /* `ef_free' MUST be zero! */
ef_us,
ef_on,
ef_at,
ef_cxa
};
struct exit_function
{
/* `flavour' should be of type of the `enum' above but since we need
this element in an atomic operation we have to use `long int'. */
long int flavor;
union
{
void (*at) (void);
struct
{
void (*fn) (int status, void *arg);
void *arg;
} on;
struct
{
void (*fn) (void *arg, int status);
void *arg;
void *dso_handle;
} cxa;
} func;
};
struct exit_function_list
{
struct exit_function_list *next;
size_t idx;
struct exit_function fns[32];
};exit_function_list 作為容器有點類似 stl 中的 deque,是由 exit_function 塊組成的鏈表,兼顧了可擴展性與遍歷效率兩個方面:
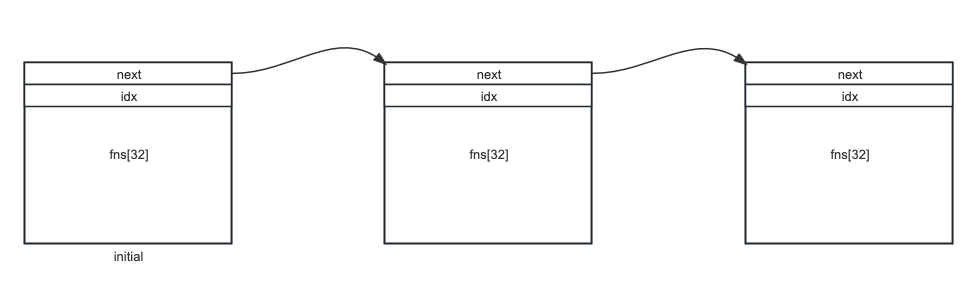
其中 idx 記錄了實際的元素個數,塊之間通過 next 指針鏈接。
註意第一個塊是在棧上分配的 initial 對象,之後的塊才是在堆上分配的。
fns 數組存儲的 exit_function 記錄可以包含三種不同類型的函數原型:
- void (*at) (void) : atexit 註冊的函數
- void (*on) (int status, void* arg) :__on_exit 註冊的函數,與 atexit 的不同之處僅在於回調時多了一個 status 參數
- void (*cxa) (void *arg, int status) :__internal_atexit 註冊的函數,它又被以下介面調用:
- __cxa_atexit,在程式退出或 so 卸載時調用,主要是為編譯器開放的內部介面
- __cxa_at_quick_exit,它又被 __new_quick_exit 所調用,後者和 exit 幾乎一致
其中 quick_exit 調用 __run_exit_handlers 的後兩個參數為 false,少清理了一些內容,以達到"快速退出"的目的。
void
__new_quick_exit (int status)
{
/* The new quick_exit, following C++11 18.5.12, does not run object
destructors. While C11 says nothing about object destructors,
since it has none, the intent is to run the registered
at_quick_exit handlers and then run _Exit immediately without
disturbing the state of the process and threads. */
__run_exit_handlers (status, &__quick_exit_funcs, false, false);
}另外 atexit 也是通過調用 __cxa_atexit 實現的:
int
atexit (void (*func) (void))
{
return __cxa_atexit ((void (*) (void *)) func, NULL, __dso_handle);
}arg 參數為 NULL;so 模塊句柄預設為當前模塊。 所以實際上並沒有類型為 ef_at 的處理器,基本全是 ef_cxa,另外
- 將 ef_free 置為整個 enum 第一個元素也是有用意的,通過 calloc 分配的記憶體,自動將內容清零,而對應的 flavor 恰好就是 ef_free
- ef_us (use) 表示槽位被占用,但是具體的類型有待後面設置 (ef_at/ef_on/ef_cxa),具有一些臨時性,但不可或缺
處理器的註冊
直接上源碼:
int
__internal_atexit (void (*func) (void *), void *arg, void *d,
struct exit_function_list **listp)
{
struct exit_function *new;
/* As a QoI issue we detect NULL early with an assertion instead
of a SIGSEGV at program exit when the handler is run (bug 20544). */
assert (func != NULL);
__libc_lock_lock (__exit_funcs_lock);
new = __new_exitfn (listp);
if (new == NULL)
{
__libc_lock_unlock (__exit_funcs_lock);
return -1;
}
new->func.cxa.fn = (void (*) (void *, int)) func;
new->func.cxa.arg = arg;
new->func.cxa.dso_handle = d;
new->flavor = ef_cxa;
__libc_lock_unlock (__exit_funcs_lock);
return 0;
}參數賦值到變數 new 的成員後,沒看到插入列表的動作,懷疑是在 __new_exitfn 時直接分配的:
/* Must be called with __exit_funcs_lock held. */
struct exit_function *
__new_exitfn (struct exit_function_list **listp)
{
struct exit_function_list *p = NULL;
struct exit_function_list *l;
struct exit_function *r = NULL;
size_t i = 0;
if (__exit_funcs_done)
/* Exit code is finished processing all registered exit functions,
therefore we fail this registration. */
return NULL;
for (l = *listp; l != NULL; p = l, l = l->next)
{
for (i = l->idx; i > 0; --i)
if (l->fns[i - 1].flavor != ef_free)
break;
if (i > 0)
break;
/* This block is completely unused. */
l->idx = 0;
}
if (l == NULL || i == sizeof (l->fns) / sizeof (l->fns[0]))
{
/* The last entry in a block is used. Use the first entry in
the previous block if it exists. Otherwise create a new one. */
if (p == NULL)
{
assert (l != NULL);
p = (struct exit_function_list *) calloc (1, sizeof (struct exit_function_list));
if (p != NULL)
{
p->next = *listp;
*listp = p;
}
}
if (p != NULL)
{
r = &p->fns[0];
p->idx = 1;
}
}
else
{
/* There is more room in the block. */
r = &l->fns[i];
l->idx = i + 1;
}
/* Mark entry as used, but we don't know the flavor now. */
if (r != NULL)
{
r->flavor = ef_us;
++__new_exitfn_called;
}
return r;
}確實如此,另外這個內部介面是沒有鎖的,所以調用它的介面必需持有鎖 (__exit_funcs_lock)。
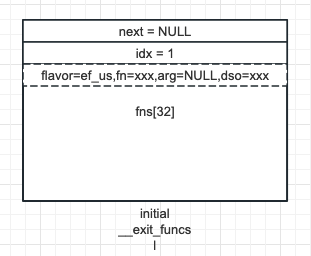
代碼不太好看,直接上圖,當第一次分配時,僅有 initial 一個塊,內部 32 個槽位,第一次命中最後的 else 條件,直接分配處理器 (場景 1):
前 32 個都不用額外分配記憶體 (場景 2):
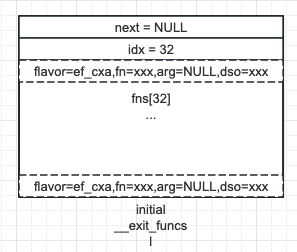
第 33 個開始分配新的 exit_function_list,並移動 __exit_funcs 指針指向新分配的塊作為列表的頭 (場景 3):
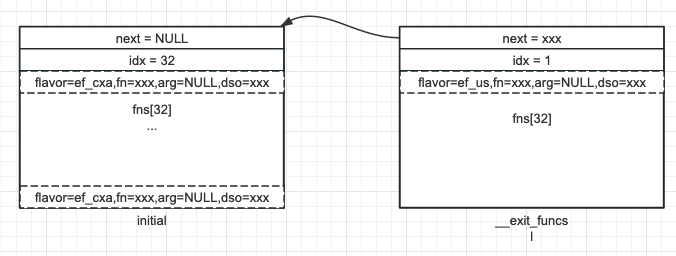
結合上面的場景來理解下代碼:
- 插入記錄時,第一個 for 迴圈基本不進入,因為當前塊一般有有效的記錄 (for 迴圈的作用是尋找第一個不空閑的塊,這隻在 atexit 處理器被調用且在其中註冊新的處理器時才有用,所以暫時放一放)
- l 一般指向當前分配的塊,中間這個 if 大段落,如果記錄不滿,則直接分配新的元素 (else),並遞增 idx,此時對應場景 1 & 2
- 如果 l 為空或記錄已滿,則分配新的塊。此時對應場景 3,__exit_funcs 作為鏈表頭會指向新分配的塊,將 idx 設置為 1,並將第一個記錄返回
- 最後設置新分配記錄的 flavor 為 ef_us 表示占用
因為 atexit 沒提供對應的撤銷方法,所以這個 deque 在程式運行期間只會單向增長。
另外有幾個小的點也需要註意,後面會用到:
- 初始時判斷了 __exit_funcs_done 標誌位,如果已經設立,就不允許分配新的記錄了
- 設置 flavor 的同時也遞增了變數 __new_exitfn_called 的值,它記錄了總的處理器註冊總量,因為在清理函數被調用時可能會註冊新的處理器 (此時總量將超過 deque 的尺寸)
處理器的調用
直接上代碼:
/* Call all functions registered with `atexit' and `on_exit',
in the reverse of the order in which they were registered
perform stdio cleanup, and terminate program execution with STATUS. */
void
__run_exit_handlers (int status, struct exit_function_list **listp,
bool run_list_atexit, bool run_dtors)
{
/* First, call the TLS destructors. */
if (run_dtors)
__call_tls_dtors ();
__libc_lock_lock (__exit_funcs_lock);
/* We do it this way to handle recursive calls to exit () made by
the functions registered with `atexit' and `on_exit'. We call
everyone on the list and use the status value in the last
exit (). */
while (true)
{
struct exit_function_list *cur;
restart:
cur = *listp;
if (cur == NULL)
{
/* Exit processing complete. We will not allow any more
atexit/on_exit registrations. */
__exit_funcs_done = true;
break;
}
while (cur->idx > 0)
{
struct exit_function *const f = &cur->fns[--cur->idx];
const uint64_t new_exitfn_called = __new_exitfn_called;
switch (f->flavor)
{
void (*cxafct) (void *arg, int status);
void *arg;
case ef_free:
case ef_us:
break;
case ef_on:
...
case ef_at:
...
case ef_cxa:
/* To avoid dlclose/exit race calling cxafct twice (BZ 22180),
we must mark this function as ef_free. */
f->flavor = ef_free;
cxafct = f->func.cxa.fn;
arg = f->func.cxa.arg;
/* Unlock the list while we call a foreign function. */
__libc_lock_unlock (__exit_funcs_lock);
cxafct (arg, status);
__libc_lock_lock (__exit_funcs_lock);
break;
}
if (__glibc_unlikely (new_exitfn_called != __new_exitfn_called))
/* The last exit function, or another thread, has registered
more exit functions. Start the loop over. */
goto restart;
}
*listp = cur->next;
if (*listp != NULL)
/* Don't free the last element in the chain, this is the statically
allocate element. */
free (cur);
}
__libc_lock_unlock (__exit_funcs_lock);
if (run_list_atexit)
RUN_HOOK (__libc_atexit, ());
_exit (status);
}先整理下主脈絡:
- __call_tls_dctors 處理線程局部存儲的釋放,這裡不涉及主題,略過
- 主迴圈加鎖遍歷處理器 deque
- 處理 libc 的 atexit 列表,略過
- 調用 _exit 退出進程
重點就落在中間的兩個 while 迴圈上,外層用於遍歷塊,內層遍歷塊上的記錄。為突出重點,switch 內只保留了 ef_cxa 的內容,其它的類似。
- 回顧之前列表建立的過程,cur 指向的是最新分配的處理器,所以調用順序 FILO 的問題得到瞭解答,特別是在遍歷塊內部時,也是倒序遍歷的
- 在回調前解鎖,回調後加鎖,這樣避免用戶在回調中再次調用 atexit 註冊處理器時發生死鎖
- 每次回調之前記錄當前處理器的總量 (new_exitfn_called),回調結束後將它與當前值對比,從而可以得知是否設置了新的 atexit 處理器
- 如果相同,表示沒有註冊新處理器,對當前結構沒影響,繼續遍歷當前塊和整個 deque
- 如果不相同,說明插入了新記錄,當前指針已經失效,需要重新遍歷,這裡直接 goto restart 重新開始遍歷
- 註意在回調前,先將處理器信息複製到棧上,同時將 flavor 設置為 ef_free,避免重啟遍歷時,重覆遍歷此記錄造成死迴圈
- 整個塊遍歷結束後,移動 __exit_funcs 到下個塊,同時釋放當前塊,如果下個塊不為空的話 (當移動到 initial 時,next 為空,不釋放 initial 指向的記憶體,因為它不是在堆上分配的)
- 當 cur 遍歷到最後一個塊 (initial) 的 next (NULL) 後,表明整個 deque 遍歷完畢,設置 __exit_funcs_done 標誌,這可以阻止 atexit 再次註冊處理器
特性分析
有了上面的鋪墊,再來分析其它的特性就清楚了:
- 註冊幾次回調幾次,這是因為插入了多個記錄,雖然它們的 func 欄位都指向同一個地址
- 處理器中調用 exit 能完成剩餘處理器的調用,原因分為兩個方面:
- 處理器回調前已經解鎖,因此再次調用 exit 時可以正常進入這裡
- 處理器回調前已經把標誌設為了 ef_free,所以再次遍歷時,不會再處理當前記錄,而是接著之前遍歷位置繼續遍歷
- 最終呈現的效果是剩餘的處理器被接著調用了,但是這裡一定要清楚,調用 exit 的回調其實沒有返回,_exit 會保證它終結在最深層的處理器那裡
最後一個特性:處理器中再次註冊的 atexit 處理器能被調用,這個稍微複雜一點,需要結合之前註冊部分的邏輯來看,再複習一下 __new_exitfn:
/* Must be called with __exit_funcs_lock held. */
struct exit_function *
__new_exitfn (struct exit_function_list **listp)
{
struct exit_function_list *p = NULL;
struct exit_function_list *l;
struct exit_function *r = NULL;
size_t i = 0;
if (__exit_funcs_done)
/* Exit code is finished processing all registered exit functions,
therefore we fail this registration. */
return NULL;
for (l = *listp; l != NULL; p = l, l = l->next)
{
for (i = l->idx; i > 0; --i)
if (l->fns[i - 1].flavor != ef_free)
break;
if (i > 0)
break;
/* This block is completely unused. */
l->idx = 0;
}
if (l == NULL || i == sizeof (l->fns) / sizeof (l->fns[0]))
{
/* The last entry in a block is used. Use the first entry in
the previous block if it exists. Otherwise create a new one. */
if (p == NULL)
{
assert (l != NULL);
p = (struct exit_function_list *) calloc (1, sizeof (struct exit_function_list));
if (p != NULL)
{
p->next = *listp;
*listp = p;
}
}
if (p != NULL)
{
r = &p->fns[0];
p->idx = 1;
}
}
else
{
/* There is more room in the block. */
r = &l->fns[i];
l->idx = i + 1;
}
/* Mark entry as used, but we don't know the flavor now. */
if (r != NULL)
{
r->flavor = ef_us;
++__new_exitfn_called;
}
return r;
}假設當前調用的處理器是 handler_p,新註冊的處理器是 handle_c,從上到下看:
- 因未遍歷完所有記錄,__exit_funcs_done 未設置,所以仍可以註冊新的處理器
- 第一個 for 迴圈掃描當前塊,將剛纔回調 handler_p 而設立的 ef_free 記錄回退掉
- 如果當前不是第一個記錄,則表明並非整個塊空閑,直接使用剛設置為 ef_free 的記錄,來存儲 handler_c 的信息,圖 1 展示了這種場景下的狀態
- 如果當前是第一個記錄,則整個塊已空閑,將 idx 設置為 0,並繼續向下個塊遍歷
- 如果下個塊為 NULL,表示當前已經是最後一個塊,狀態見圖 2
- 否則繼續檢查下個塊,此時一般不空閑 (一般是滿的),見圖 3
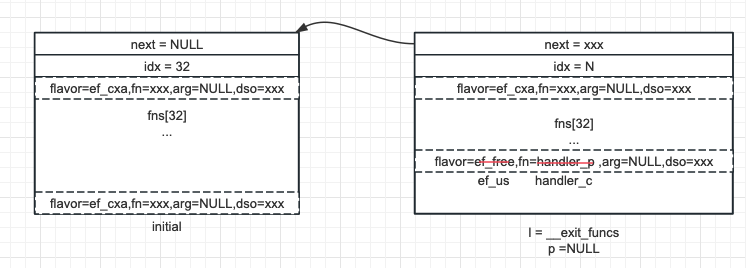
圖 1

圖 2
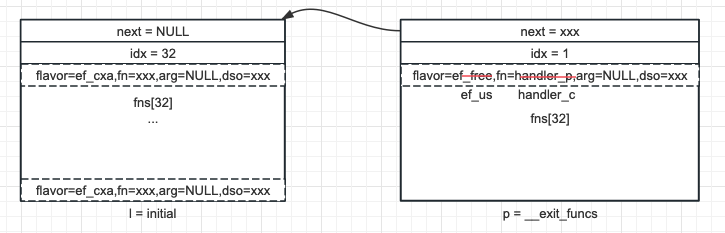
圖 3
以上 3 個場景中,每次僅回退一個記錄,這是由於我們假設 handler_p 是第一個被調用的處理器,如果它不是第一個被調用的,是否就能出現回退多個記錄的場景?
考慮下麵這個用例:假設有 handler_3 / handler_2 / handler_1 三個處理器依次被調用,前兩個處理器都沒有註冊新的處理器,handler_1 註冊了兩個新的 handler,分別為 handler_i / handler_ii。
首先假設 3 個 handler 都在一個塊中,註冊完兩個新 handler 後狀態如下圖:

圖 4
在註冊 handler_i 時回退了三次、handler_ii 時回退了兩次,因此是可以回退多個記錄的,畢竟 __run_exit_handlers 僅僅將遍歷過記錄的 flavor 設置為 ef_free 而沒有修改任何 idx。
下麵來看看是否存在跨塊回退多個記錄的場景,假設 handler_1 與 handler_2 跨塊,則調用 handler_1 註冊 handler_i 後的狀態已變為下圖:
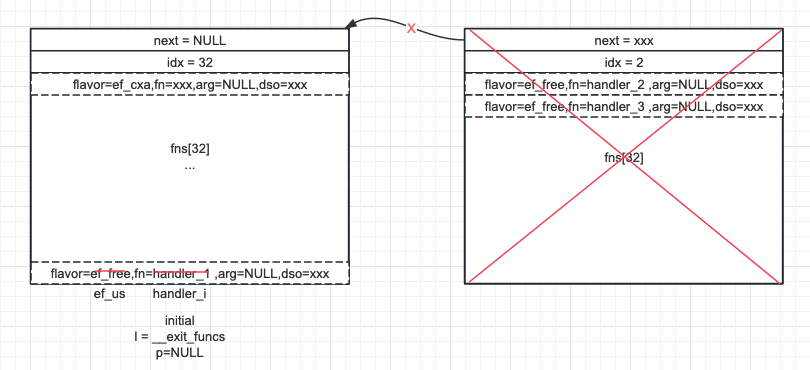
圖 5
這是因為處理完 handler_2 前一個塊已經被釋放不可訪問了,好在目前 l 指向的塊已滿且 p == NULL,回退到了當初擴展塊時的狀態 (註冊處理器的場景 3),從而重新分配塊和記錄,最終效果如圖 6:
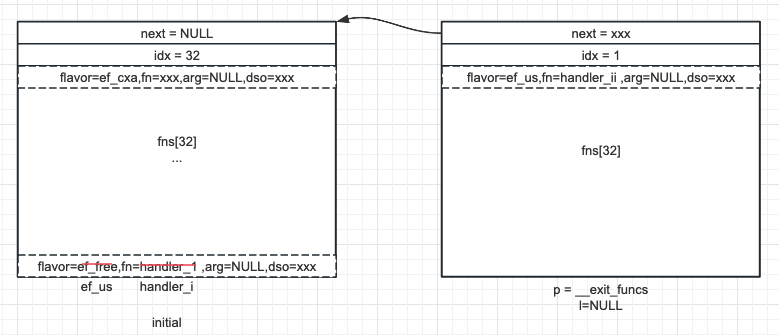
因為是新分配的塊,就不存在覆蓋的問題了。
總結一下:
- 可以回退多個記錄,但是只限制在一個塊內
- p == NULL 時一般是需要分配新的塊了
在這個基礎上繼續執行 __run_exit_handlers,來看新註冊的處理器是如何被調用的:
- 首先回顧 __new_exitfn,當它註冊新處理器後,會遞增 __new_exitfn_called 的值
- 回到 __run_exit_handlers,因檢測到 __new_exitfn_called 發生了變化,會 goto restart 重新執行整個 while 迴圈
- 重新遍歷時,會首先處理新加入的處理器,且也是按 FILO 的順序處理
至此最後一個特性分析完畢。
結語
從這裡也可以看到一個標準的 atexit 需要考慮的問題:
- 程式運行期間單向增長
- 程式退出時反向減少
- 有可能在執行回調時註冊新的處理器從而導致再次增長,所以並不是單向減少
代碼優化
glibc 主要花費了大量的精力處理第三個場景,不過經過本文一番分析,似乎不需要做的如此複雜。
...
for (l = *listp; l != NULL; p = l, l = l->next)
{
for (i = l->idx; i > 0; --i)
if (l->fns[i - 1].flavor != ef_free)
break;
if (i > 0)
break;
/* This block is completely unused. */
l->idx = 0;
}
if (l == NULL || i == sizeof (l->fns) / sizeof (l->fns[0]))
{
/* The last entry in a block is used. Use the first entry in
the previous block if it exists. Otherwise create a new one. */
if (p == NULL)
{
assert (l != NULL);
p = (struct exit_function_list *) calloc (1, sizeof (struct exit_function_list));
if (p != NULL)
{
p->next = *listp;
*listp = p;
}
}
if (p != NULL)
{
r = &p->fns[0];
p->idx = 1;
}
}
else
{
/* There is more room in the block. */
r = &l->fns[i];
l->idx = i + 1;
}
...例如回退記錄實際不存在跨塊的可能,那麼回退時就可以只考慮當前塊了,__new_exitfn 中第一個兩層的 for 迴圈就可以簡化為單層:
...
l = *listp;
for (i = l->idx; i > 0; --i)
if (l->fns[i - 1].flavor != ef_free)
break;
if (i == 0)
/* This block is completely unused. */
l->idx = 0;
if (i == sizeof (l->fns) / sizeof (l->fns[0]))
{
/* The last entry in a block is used. Use the first entry in
the previous block if it exists. Otherwise create a new one. */
assert (p == NULL);
assert (l != NULL);
p = (struct exit_function_list *) calloc (1, sizeof (struct exit_function_list));
if (p != NULL)
{
p->next = *listp;
*listp = p;
}
}
else
{
/* There is more room in the block. */
r = &l->fns[i];
l->idx = i + 1;
}
...經過簡化後,l 永遠不為 NULL,p 永遠為 NULL,第二個 if 段中對 l 和 p 是否為 NULL 的判斷就可以去掉了。看起來是不是簡潔了一些?
當然了,上面的代碼是沒有經過驗證的,保不齊哪裡還有邏輯漏洞,歡迎大家來找茬~
dump exit_function_list
本來是打算把 __exit_funcs 中的內容列印出來看看,然而 glibc 設置了完備的符號隱藏,無法獲取這個變數的地址:
extern struct exit_function_list *__exit_funcs attribute_hidden;
extern struct exit_function_list *__quick_exit_funcs attribute_hidden;
extern uint64_t __new_exitfn_called attribute_hidden;
/* True once all registered atexit/at_quick_exit/onexit handlers have been
called */
extern bool __exit_funcs_done attribute_hidden;其中 attribute_hidden 就是設置符號的 visibility 屬性:
# define attribute_hidden __attribute__ ((visibility ("hidden")))例如在示例代碼中插入下麵的聲明:
enum
{
ef_free,
ef_us,
ef_on,
ef_at,
ef_cxa
};
struct exit_function
{
long int flavor;
union
{
void (*at) (void);
struct
{
void (*fn) (int status, void *arg);
void *arg;
} on;
struct
{
void (*fn) (void *arg, int status);
void *arg;
void *dso_handle;
} cxa;
} func;
};
struct exit_function_list
{
struct exit_function_list *next;
size_t idx;
struct exit_function fns[32];
};
extern struct exit_function_list *__exit_funcs;併在 main 中列印 __exit_funcs 的地址:
printf ("__exit_funcs: %p\n", __exit_funcs);編譯時會報錯:
$ make
gcc -Wall -g dumpexit.o apue.o -o dumpexit
dumpexit.o: In function `dump_exit':
/home/users/yunhai01/code/apue/07.chapter/dumpexit.c:70: undefined reference to `__exit_funcs'
dumpexit.o: In function `main':
/home/users/yunhai01/code/apue/07.chapter/dumpexit.c:103: undefined reference to `__exit_funcs'
collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status
make: *** [dumpexit] Error 1正打算放棄,無意間看到這樣一段巨集:
#if defined SHARED || defined LIBC_NONSHARED \
|| (BUILD_PIE_DEFAULT && IS_IN (libc))
# define attribute_hidden __attribute__ ((visibility ("hidden")))
#else
# define attribute_hidden
#endif看起來符號隱藏只針對共用庫,改為靜態鏈接試試:
dumpexit: dumpexit.o apue.o
gcc -Wall -g $^ -o $@ -static
dumpexit.o: dumpexit.c ../apue.h
gcc -Wall -g -c $< -o $@ -std=c99居然通過了。運行程式,可以正常列印 __exit_funcs 地址:
$ ./dumpexit
__exit_funcs: 0x6c74a0註意這一步需要安裝 glibc 靜態庫:
sudo yum install glibc-static否則報下麵的鏈接錯誤:
$ make dumpexit
gcc -Wall -g dumpexit.o apue.o -o dumpexit -static
/usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lc
collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status
make: *** [dumpexit] Error 1下麵增加一些列印的代碼:
void dump_exit_func (struct exit_function *ef)
{
switch (ef->flavor)
{
case ef_free:
printf ("free slot\n");
break;
case ef_us:
printf ("occupy slot\n");
break;
case ef_on:
printf ("on_exit function: %p, arg: %p\n", ef->func.on.fn, ef->func.on.arg);
break;
case ef_at:
printf ("atexit function: %p\n", ef->func.at);
break;
case ef_cxa:
printf ("cxa_exit function: %p, arg: %p, dso: %p\n", ef->func.cxa.fn, ef->func.cxa.arg, ef->func.cxa.dso_handle);
break;
default:
printf ("unknown type: %d\n", ef->flavor);
break;
}
}
void dump_exit ()
{
struct exit_function_list *l = __exit_funcs;
while (l != NULL)
{
printf ("total %d record\n", l->idx);
for (int i=0; i<l->idx; ++ i)
{
dump_exit_func (&l->fns[i]);
}
l = l->next;
}
}平平無奇的代碼,為了增加可讀性,事先註冊了幾個處理器:
void do_dirty_work ()
{
printf ("doing dirty works!\n");
}
void bye ()
{
printf ("bye, forks~\n");
}
void times ()
{
static int counter = 32;
printf ("times %d\n", counter--);
}
int main ()
{
int ret = 0;
printf ("__exit_funcs: %p\n", __exit_funcs);
ret = atexit (do_dirty_work);
if (ret != 0)
err_sys ("atexit");
else
printf ("register do_dirty_work %p\n", (void *)do_dirty_work);
ret = atexit (bye);
if (ret != 0)
err_sys ("bye1");
else
printf ("register bye %p\n", (void *)bye);
ret = atexit (times);
if (ret != 0)
err_sys ("times");
else
printf ("register times %p\n", (void *)times);
dump_exit ();
printf ("main is done!\n");
return 0;
}運行後效果如下:
$ ./dumpexit
__exit_funcs: 0x6c74a0
register do_dirty_work 0x40115a
register bye 0x40116a
register times 0x40117a
total 4 record
cxa_exit function: 0x24a492d7cf90f3f0, arg: (nil), dso: (nil)
cxa_exit function: 0x24a492d76ac4f3f0, arg: (nil), dso: (nil)
cxa_exit function: 0x24a492d76aa4f3f0, arg: (nil), dso: (nil)
cxa_exit function: 0x24a492d76a84f3f0, arg: (nil), dso: (nil)
main is done!
times 32
bye, forks~
doing dirty works!看起來有 4 個處理器,然而它們的地址卻都一樣,和我準備的那三個函數地址完全不同。
不清楚是否因為 glibc 版本變遷,導致 __exit_funcs 的內部結構發生了變化,還是什麼其它原因導致成員對齊出了問題,最終沒有列印出來預期的結果,有瞭解的同學不吝賜教。
後記
code browser 已經足夠強大,美中不足的是缺少書簽功能,在追蹤調用棧時回退不是特別方便。
好在 Bing 同學已經貼心的為我們提供了相關的插件:https://github.com/caibingcheng/codebrowser-bookmark
安裝之後瀏覽本文用的到幾個關鍵函數效果如下:
直接點擊書簽就可以跳轉到歷史位置了,比之前多次回退方便多了。
實際操作起來非常簡單,以我古老的 firefox 為例:
- 安裝油猴腳本管理器:https://addons.mozilla.org/zh-CN/firefox/addon/tampermonkey/,這一步基本是安裝了一個瀏覽器 add-on
- 導入書簽插件:https://greasyfork.org/zh-CN/import,這一步需要填入 Bing 同學提供的腳本地址 (https://raw.githubusercontent.com/caibingcheng/codebrowser-bookmark/master/index.js),然後點擊導入:
在新頁面中安裝導入的插件:

從彈出的視窗中選擇直接安裝:

這裡會提示安裝油猴腳本管理器,如果已經安裝可以忽略提示:

點擊安裝後就可以看到腳本版本了:
回到 code browser,刷新下頁面就可以看到書簽小視窗啦~
需要註意的是,書簽是本地存儲的,在一臺設備上創建的書簽,不會自動同步到另一臺設備哦。
參考
[1]. code browser
[2]. glibc-exit源碼閱讀
[3]. codebrowser書簽插件
本文來自博客園,作者:goodcitizen,轉載請註明原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/goodcitizen/p/how_exit_calls_atexit_functions.html



