來源:https://juejin.cn/post/6844904024332828685 寫在前面 通過閱讀本篇文章你將瞭解到: CompletableFuture的使用 CompletableFure非同步和同步的性能測試 已經有了Future為什麼仍需要在JDK1.8中引入Completable ...
來源:https://juejin.cn/post/6844904024332828685
寫在前面
通過閱讀本篇文章你將瞭解到:
- CompletableFuture的使用
- CompletableFure非同步和同步的性能測試
- 已經有了Future為什麼仍需要在JDK1.8中引入CompletableFuture
- CompletableFuture的應用場景
- 對CompletableFuture的使用優化
場景說明
查詢所有商店某個商品的價格並返回,並且查詢商店某個商品的價格的API為同步 一個Shop類,提供一個名為getPrice的同步方法
- 店鋪類:Shop.java
public class Shop {
private Random random = new Random();
/**
* 根據產品名查找價格
* */
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
}
/**
* 計算價格
*
* @param product
* @return
* */
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
//random.nextDouble()隨機返回折扣
return random.nextDouble() * product.charAt(0) + product.charAt(1);
}
/**
* 通過睡眠模擬其他耗時操作
* */
private void delay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
查詢商品的價格為同步方法,並通過sleep方法模擬其他操作。這個場景模擬了當需要調用第三方API,但第三方提供的是同步API,在無法修改第三方API時如何設計代碼調用提高應用的性能和吞吐量,這時候可以使用CompletableFuture類。
推薦一個開源免費的 Spring Boot 實戰項目:
CompletableFuture使用
Completable是Future介面的實現類,在JDK1.8中引入
-
CompletableFuture的創建:
說明:
-
兩個重載方法之間的區別 => 後者可以傳入自定義Executor,前者是預設的,使用的ForkJoinPool
-
supplyAsync和runAsync方法之間的區別 => 前者有返回值,後者無返回值
-
Supplier是函數式介面,因此該方法需要傳入該介面的實現類,追蹤源碼會發現在run方法中會調用該介面的方法。因此使用該方法創建CompletableFuture對象只需重寫Supplier中的get方法,在get方法中定義任務即可。又因為函數式介面可以使用Lambda表達式,和new創建CompletableFuture對象相比代碼會簡潔不少
-
使用new方法
CompletableFuture<Double> futurePrice = new CompletableFuture<>(); -
使用CompletableFuture#completedFuture靜態方法創建
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> completedFuture(U value) { return new CompletableFuture<U>((value == null) ? NIL : value); }參數的值為任務執行完的結果,一般該方法在實際應用中較少應用
-
使用 CompletableFuture#supplyAsync靜態方法創建 supplyAsync有兩個重載方法:
//方法一 public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) { return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier); } //方法二 public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor) { return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier); } -
使用CompletableFuture#runAsync靜態方法創建 runAsync有兩個重載方法
//方法一 public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) { return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable); } //方法二 public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) { return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable); }
-
-
結果的獲取: 對於結果的獲取CompltableFuture類提供了四種方式
//方式一 public T get() //方式二 public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) //方式三 public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent) //方式四 public T join()說明:
示例:
- get()和get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) => 在Future中就已經提供了,後者提供超時處理,如果在指定時間內未獲取結果將拋出超時異常
- getNow => 立即獲取結果不阻塞,結果計算已完成將返回結果或計算過程中的異常,如果未計算完成將返回設定的valueIfAbsent值
- join => 方法里不會拋出異常
public class AcquireResultTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//getNow方法測試
CompletableFuture<String> cp1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(60 * 1000 * 60 );
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello world";
});
System.out.println(cp1.getNow("hello h2t"));
//join方法測試
CompletableFuture<Integer> cp2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((()-> 1 / 0));
System.out.println(cp2.join());
//get方法測試
CompletableFuture<Integer> cp3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((()-> 1 / 0));
System.out.println(cp3.get());
}
}
說明:
- 第一個執行結果為hello h2t,因為要先睡上1分鐘結果不能立即獲取
- join方法獲取結果方法里不會拋異常,但是執行結果會拋異常,拋出的異常為CompletionException
- get方法獲取結果方法里將拋出異常,執行結果拋出的異常為ExecutionException
- 異常處理: 使用靜態方法創建的CompletableFuture對象無需顯示處理異常,使用new創建的對象需要調用completeExceptionally方法設置捕獲到的異常,舉例說明:
CompletableFuture completableFuture = new CompletableFuture();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
//doSomething,調用complete方法將其他方法的執行結果記錄在completableFuture對象中
completableFuture.complete(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
//異常處理
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(e);
}
}).start();
同步方法Pick非同步方法查詢所有店鋪某個商品價格
店鋪為一個列表:
private static List<Shop> shopList = Arrays.asList(
new Shop("BestPrice"),
new Shop("LetsSaveBig"),
new Shop("MyFavoriteShop"),
new Shop("BuyItAll")
);
同步方法:
private static List<String> findPriceSync(String product) {
return shopList.stream()
.map(shop -> String.format("%s price is %.2f",
shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product))) //格式轉換
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
非同步方法:
private static List<String> findPriceAsync(String product) {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> completableFutureList = shopList.stream()
//轉非同步執行
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> String.format("%s price is %.2f",
shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)))) //格式轉換
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return completableFutureList.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join) //獲取結果不會拋出異常
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
性能測試結果:
Find Price Sync Done in 4141
Find Price Async Done in 1033
非同步執行效率提高四倍
為什麼仍需要CompletableFuture
在JDK1.8以前,通過調用線程池的submit方法可以讓任務以非同步的方式運行,該方法會返回一個Future對象,通過調用get方法獲取非同步執行的結果:
private static List<String> findPriceFutureAsync(String product) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
List<Future<String>> futureList = shopList.stream().map(shop -> es.submit(() -> String.format("%s price is %.2f",
shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)))).collect(Collectors.toList());
return futureList.stream()
.map(f -> {
String result = null;
try {
result = f.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
既生瑜何生亮,為什麼仍需要引入CompletableFuture?對於簡單的業務場景使用Future完全沒有,但是想將多個非同步任務的計算結果組合起來,後一個非同步任務的計算結果需要前一個非同步任務的值等等,使用Future提供的那點API就囊中羞澀,處理起來不夠優雅,這時候還是讓CompletableFuture以聲明式的方式優雅的處理這些需求。而且在Future編程中想要拿到Future的值然後拿這個值去做後續的計算任務,只能通過輪詢的方式去判斷任務是否完成這樣非常占CPU並且代碼也不優雅,用偽代碼表示如下:
while(future.isDone()) {
result = future.get();
doSomrthingWithResult(result);
}
但CompletableFuture提供了API幫助我們實現這樣的需求
其他API介紹
whenComplete計算結果的處理:
對前面計算結果進行處理,無法返回新值 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
//方法二
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
//方法三
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
說明:
- BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn參數 => 定義對結果的處理
- Executor executor參數 => 自定義線程池
- 以async結尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執行組合操作
示例:
public class WhenCompleteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello");
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = cf1.whenComplete((v, e) ->
System.out.println(String.format("value:%s, exception:%s", v, e)));
System.out.println(cf2.join());
}
}
thenApply轉換:
將前面計算結果的的CompletableFuture傳遞給thenApply,返回thenApply處理後的結果。可以認為通過thenApply方法實現CompletableFuture<T>至CompletableFuture<U>的轉換。白話一點就是將CompletableFuture的計算結果作為thenApply方法的參數,返回thenApply方法處理後的結果 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}
//方法二
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(asyncPool, fn);
}
//方法三
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {
return uniApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}
說明:
- Function<? super T,? extends U> fn參數 => 對前一個CompletableFuture 計算結果的轉化操作
- Executor executor參數 => 自定義線程池
- 以async結尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執行組合操作 示例:
public class ThenApplyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenApplyTest::randomInteger).thenApply((i) -> i * 8);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
public static Integer randomInteger() {
return 10;
}
}
這裡將前一個CompletableFuture計算出來的結果擴大八倍
thenAccept結果處理:
thenApply也可以歸類為對結果的處理,thenAccept和thenApply的區別就是沒有返回值 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) {
return uniAcceptStage(null, action);
}
//方法二
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) {
return uniAcceptStage(asyncPool, action);
}
//方法三
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,
Executor executor) {
return uniAcceptStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}
說明:
- Consumer<? super T> action參數 => 對前一個CompletableFuture計算結果的操作
- Executor executor參數 => 自定義線程池
- 同理以async結尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執行組合操作 示例:
public class ThenAcceptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenAcceptTest::getList).thenAccept(strList -> strList.stream()
.forEach(m -> System.out.println(m)));
}
public static List<String> getList() {
return Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
}
}
將前一個CompletableFuture計算出來的結果列印出來
thenCompose非同步結果流水化:
thenCompose方法可以將兩個非同步操作進行流水操作 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) {
return uniComposeStage(null, fn);
}
//方法二
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) {
return uniComposeStage(asyncPool, fn);
}
//方法三
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn,
Executor executor) {
return uniComposeStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}
說明:
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn參數 => 當前CompletableFuture計算結果的執行- Executor executor參數 => 自定義線程池
- 同理以async結尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執行組合操作 示例:
public class ThenComposeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenComposeTest::getInteger)
.thenCompose(i -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> i * 10));
System.out.println(result.get());
}
private static int getInteger() {
return 666;
}
private static int expandValue(int num) {
return num * 10;
}
}
執行流程圖:
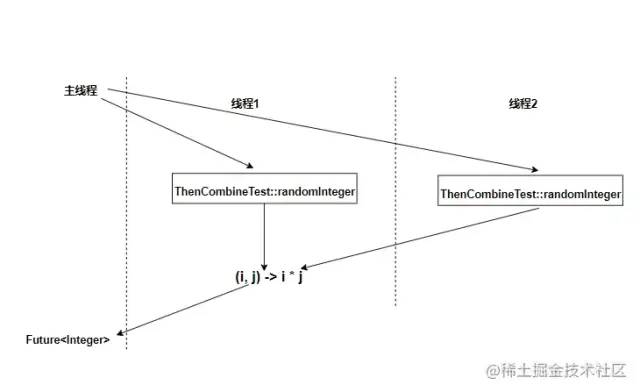
thenCombine組合結果:
thenCombine方法將兩個無關的CompletableFuture組合起來,第二個Completable並不依賴第一個Completable的結果 提供了三個方法:
//方法一
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(
CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) {
return biApplyStage(null, other, fn);
}
//方法二
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(
CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) {
return biApplyStage(asyncPool, other, fn);
}
//方法三
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(
CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor) {
return biApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), other, fn);
}
說明:
- CompletionStage<? extends U> other參數 => 新的CompletableFuture的計算結果
- BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn參數 => 定義了兩個CompletableFuture對象完成計算後如何合併結果,該參數是一個函數式介面,因此可以使用Lambda表達式
- Executor executor參數 => 自定義線程池
- 同理以async結尾的方法將會在一個新的線程中執行組合操作
示例:
public class ThenCombineTest {
private static Random random = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenCombineTest::randomInteger).thenCombine(
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(ThenCombineTest::randomInteger), (i, j) -> i * j
);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
public static Integer randomInteger() {
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}
將兩個線程計算出來的值做一個乘法在返回 執行流程圖:
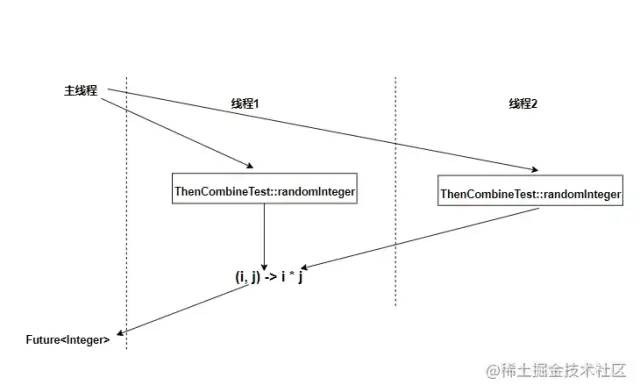
allOf&anyOf組合多個CompletableFuture:
方法介紹:
//allOf
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {
return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}
//anyOf
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {
return orTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}
說明:
- allOf => 所有的CompletableFuture都執行完後執行計算。
- anyOf => 任意一個CompletableFuture執行完後就會執行計算
示例:
- allOf方法測試
public class AllOfTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("hello");
return null;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("world"); return null;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> result = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
}
allOf方法沒有返回值,適合沒有返回值並且需要前面所有任務執行完畢才能執行後續任務的應用場景
- anyOf方法測試
public class AnyOfTest {
private static Random random = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
randomSleep();
System.out.println("hello");
return "hello";});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
randomSleep();
System.out.println("world");
return "world";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> result = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
System.out.println(result.get());
}
private static void randomSleep() {
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
兩個線程都會將結果列印出來,但是get方法只會返回最先完成任務的結果。該方法比較適合只要有一個返回值就可以繼續執行其他任務的應用場景
註意點
很多方法都提供了非同步實現【帶async尾碼】,但是需小心謹慎使用這些非同步方法,因為非同步意味著存在上下文切換,可能性能不一定比同步好。如果需要使用非同步的方法,先做測試,用測試數據說話!!!
CompletableFuture的應用場景
存在IO密集型的任務可以選擇CompletableFuture,IO部分交由另外一個線程去執行。Logback、Log4j2非同步日誌記錄的實現原理就是新起了一個線程去執行IO操作,這部分可以以CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{ioOperation();})的方式去調用。如果是CPU密集型就不推薦使用了推薦使用並行流
優化空間
supplyAsync執行任務底層實現:
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> asyncSupplyStage(Executor e, Supplier<U> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<U> d = new CompletableFuture<U>();
e.execute(new AsyncSupply<U>(d, f));
return d;
}
底層調用的是線程池去執行任務,而CompletableFuture中預設線程池為ForkJoinPool
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
ForkJoinPool線程池的大小取決於CPU的核數。CPU密集型任務線程池大小配置為CPU核心數就可以了,但是IO密集型,線程池的大小由CPU數量 * CPU利用率 * (1 + 線程等待時間/線程CPU時間)確定。而CompletableFuture的應用場景就是IO密集型任務,因此預設的ForkJoinPool一般無法達到最佳性能,我們需自己根據業務創建線程池。
近期熱文推薦:
1.1,000+ 道 Java面試題及答案整理(2022最新版)
4.別再寫滿屏的爆爆爆炸類了,試試裝飾器模式,這才是優雅的方式!!
覺得不錯,別忘了隨手點贊+轉發哦!



