本文分享自華為雲社區《如何為物聯網設備註入“華為雲+鴻蒙DNA”?看華為雲IoT怎麼答【華為雲IoT +鴻蒙】》,作者: 華為IoT雲服務。 根據市場咨詢機構預測,2025年全球物聯網設備將達到252億個。但各種智能設備大多都有一套自己的系統,而且互相“孤立”,無法交流。鴻蒙的到來,就是要用同一套語 ...
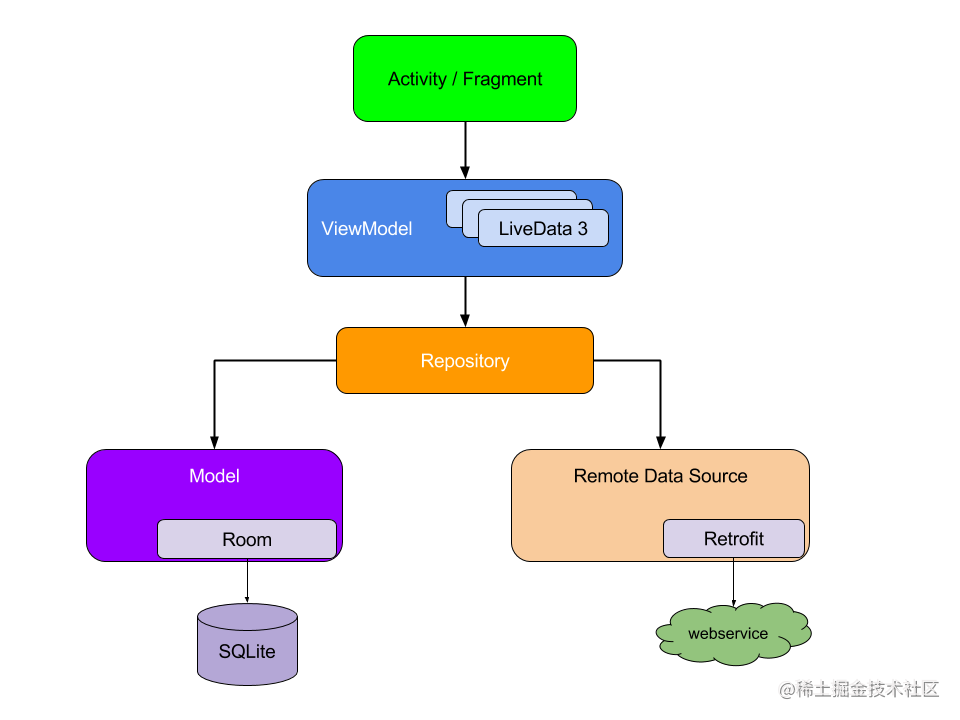 MVVM架構,將整個應用分為三層,View層,VM層,Model層。其中View層單向引用VM層,VM層單向引用Model層。如上圖。
單向引用,而非雙向引用,這是MVVM與MVP最大的區別。View層,只是單向引用VM層,VM層不需要引用View層,但是卻可以
更新View層。這是通過VM層的觀察者模式實現的,在這裡使用架構組件LiveData,觀察者註冊LiveData,當LiveData數據發生變更
的時候,就會通知註冊的觀察者。
VM層,執行業務邏輯,獲取Model層的數據,Model層的數據由repository來提供。
舉例子:
ChooseAreaFragment是View層,它持有ViewModel,它可以監聽相關數據,相關數據發生變化的時候,對應的UI就會被更新。
比如:dataChanged數據發生變化,就會執行定義的觀察者操作。
viewModel.dataChanged.observe(this, Observer {
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()
listView.setSelection(0)
closeProgressDialog()
})
MVVM架構,將整個應用分為三層,View層,VM層,Model層。其中View層單向引用VM層,VM層單向引用Model層。如上圖。
單向引用,而非雙向引用,這是MVVM與MVP最大的區別。View層,只是單向引用VM層,VM層不需要引用View層,但是卻可以
更新View層。這是通過VM層的觀察者模式實現的,在這裡使用架構組件LiveData,觀察者註冊LiveData,當LiveData數據發生變更
的時候,就會通知註冊的觀察者。
VM層,執行業務邏輯,獲取Model層的數據,Model層的數據由repository來提供。
舉例子:
ChooseAreaFragment是View層,它持有ViewModel,它可以監聽相關數據,相關數據發生變化的時候,對應的UI就會被更新。
比如:dataChanged數據發生變化,就會執行定義的觀察者操作。
viewModel.dataChanged.observe(this, Observer {
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()
listView.setSelection(0)
closeProgressDialog()
})
class ChooseAreaFragment : Fragment() {
private val viewModel by lazy { ViewModelProviders.of(this, InjectorUtil.getChooseAreaModelFactory()).get(ChooseAreaViewModel::class.java) }
private var progressDialog: ProgressDialog? = null
private lateinit var adapter: ArrayAdapter<String>
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? {
val view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.choose_area, container, false)
val binding = DataBindingUtil.bind<ChooseAreaBindingImpl>(view)
binding?.viewModel = viewModel
return view
}
override fun onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState)
adapter = ChooseAreaAdapter(context!!, R.layout.simple_item, viewModel.dataList)
listView.adapter = adapter
observe()
}
private fun observe() {
viewModel.currentLevel.observe(this, Observer { level ->
when (level) {
LEVEL_PROVINCE -> {
titleText.text = "中國"
backButton.visibility = View.GONE
}
LEVEL_CITY -> {
titleText.text = viewModel.selectedProvince?.provinceName
backButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
LEVEL_COUNTY -> {
titleText.text = viewModel.selectedCity?.cityName
backButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
}
})
viewModel.dataChanged.observe(this, Observer {
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()
listView.setSelection(0)
closeProgressDialog()
})
viewModel.isLoading.observe(this, Observer { isLoading ->
if (isLoading) showProgressDialog()
else closeProgressDialog()
})
viewModel.areaSelected.observe(this, Observer { selected ->
if (selected && viewModel.selectedCounty != null) {
if (activity is MainActivity) {
val intent = Intent(activity, WeatherActivity::class.java)
intent.putExtra("weather_id", viewModel.selectedCounty!!.weatherId)
startActivity(intent)
activity?.finish()
} else if (activity is WeatherActivity) {
val weatherActivity = activity as WeatherActivity
weatherActivity.drawerLayout.closeDrawers()
weatherActivity.viewModel.weatherId = viewModel.selectedCounty!!.weatherId
weatherActivity.viewModel.refreshWeather()
}
viewModel.areaSelected.value = false
}
})
if (viewModel.dataList.isEmpty()) {
viewModel.getProvinces()
}
}
/**
* 顯示進度對話框
*/
private fun showProgressDialog() {
if (progressDialog == null) {
progressDialog = ProgressDialog(activity)
progressDialog?.setMessage("正在載入...")
progressDialog?.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(false)
}
progressDialog?.show()
}
/**
* 關閉進度對話框
*/
private fun closeProgressDialog() {
progressDialog?.dismiss()
}
companion object {
const val LEVEL_PROVINCE = 0
const val LEVEL_CITY = 1
const val LEVEL_COUNTY = 2
}
}
VM層,ViewModel:
使用LiveData包裝被View層監聽的數據,在VM層數據發生的變化,會通知到View層,但卻無需要View層的引用。
因為LiveData應用了觀察者模式,註冊的觀察者,在數據發生變化的時候,會自動通知觀察者。
如下,currentLevel,dataChanged,isLoading等都是使用LiveData包裝的,意味著,它們發生變化的時候View層會監聽得到,從而進行相應的更新操作。
在VM層,持有Model層的引用,Model層的數據獲取,網路請求,都依賴repository實現。
class ChooseAreaViewModel(private val repository: PlaceRepository) : ViewModel() {
var currentLevel = MutableLiveData<Int>()
var dataChanged = MutableLiveData<Int>()
var isLoading = MutableLiveData<Boolean>()
var areaSelected = MutableLiveData<Boolean>()
var selectedProvince: Province? = null
var selectedCity: City? = null
var selectedCounty: County? = null
lateinit var provinces: MutableList<Province>
lateinit var cities: MutableList<City>
lateinit var counties: MutableList<County>
val dataList = ArrayList<String>()
fun getProvinces() {
currentLevel.value = LEVEL_PROVINCE
launch {
provinces = repository.getProvinceList()
dataList.addAll(provinces.map { it.provinceName })
}
}
private fun getCities() = selectedProvince?.let {
currentLevel.value = LEVEL_CITY
launch {
cities = repository.getCityList(it.provinceCode)
dataList.addAll(cities.map { it.cityName })
}
}
private fun getCounties() = selectedCity?.let {
currentLevel.value = LEVEL_COUNTY
launch {
counties = repository.getCountyList(it.provinceId, it.cityCode)
dataList.addAll(counties.map { it.countyName })
}
}
fun onListViewItemClick(parent: AdapterView<*>, view: View, position: Int, id: Long) {
when {
currentLevel.value == LEVEL_PROVINCE -> {
selectedProvince = provinces[position]
getCities()
}
currentLevel.value == LEVEL_CITY -> {
selectedCity = cities[position]
getCounties()
}
currentLevel.value == LEVEL_COUNTY -> {
selectedCounty = counties[position]
areaSelected.value = true
}
}
}
fun onBack() {
if (currentLevel.value == LEVEL_COUNTY) {
getCities()
} else if (currentLevel.value == LEVEL_CITY) {
getProvinces()
}
}
private fun launch(block: suspend () -> Unit) = viewModelScope.launch {
try {
isLoading.value = true
dataList.clear()
block()
dataChanged.value = dataChanged.value?.plus(1)
isLoading.value = false
} catch (t: Throwable) {
t.printStackTrace()
Toast.makeText(CoolWeatherApplication.context, t.message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
dataChanged.value = dataChanged.value?.plus(1)
isLoading.value = false
}
}
}
Model層:
在這個例子中,Model層對外提供的方法是
getProvinceList,getCityList,getCountyList。
它的數據來源,可能是資料庫Dao,或者是網路,各自的實現,再委托到具體的方法去實現。
class PlaceRepository private constructor(private val placeDao: PlaceDao, private val network: CoolWeatherNetwork) {
suspend fun getProvinceList() = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
var list = placeDao.getProvinceList()
if (list.isEmpty()) {
list = network.fetchProvinceList()
placeDao.saveProvinceList(list)
}
list
}
suspend fun getCityList(provinceId: Int) = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
var list = placeDao.getCityList(provinceId)
if (list.isEmpty()) {
list = network.fetchCityList(provinceId)
list.forEach { it.provinceId = provinceId }
placeDao.saveCityList(list)
}
list
}
suspend fun getCountyList(provinceId: Int, cityId: Int) = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
var list = placeDao.getCountyList(cityId)
if (list.isEmpty()) {
list = network.fetchCountyList(provinceId, cityId)
list.forEach { it.cityId = cityId }
placeDao.saveCountyList(list)
}
list
}
companion object {
private var instance: PlaceRepository? = null
fun getInstance(placeDao: PlaceDao, network: CoolWeatherNetwork): PlaceRepository {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized(PlaceRepository::class.java) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = PlaceRepository(placeDao, network)
}
}
}
return instance!!
}
}
}
以上就是MVVM的實例解析。應用MVVM的時候,關鍵是劃分功能屬於哪一個層次,然後,再確定引用關係。劃分功能屬於哪個層次,可以依據單一職責原則,讓功能代碼原子化,再在這一基礎上去區分層次。
版權聲明:
作者:ttylinux
出處:http://www.cnblogs.com/ttylinux/
本文版權歸作者,歡迎轉載,但未經作者同意必須保留此段聲明,且在文章頁面明顯位置給出原文連接,否則保留追究法律責任的權利。



