# lab util ## sleep 1. 介紹:主要用來熟悉下環境以及代碼結構。 > - See `kernel/sysproc.c` for the xv6 kernel code that implements the `sleep` system call (look for `sys_s ...
lab util
sleep
-
介紹:主要用來熟悉下環境以及代碼結構。
- See
kernel/sysproc.cfor the xv6 kernel code that implements thesleepsystem call (look forsys_sleep),user/user.hfor the C definition ofsleepcallable from a user program, anduser/usys.Sfor the assembler code that jumps from user code into the kernel forsleep.
- See
-
代碼:
#include "kernel/types.h" #include "user/user.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc <= 1) { fprintf(2, "usage: sleep `time`...\n"); } int tick_num = atoi(argv[1]); sleep(tick_num); exit(0); }
pingpong
-
單個管道一般用於單向通信,父子進程可通過兩個管道進行雙向通信。(管道詳細行為參考
primes實驗部分) -
代碼:
#include "kernel/types.h" #include "user/user.h" #define BUFFSIZE 128 void perror_exit(char* err_msg) { fprintf(2, "%s\n", err_msg); exit(-1); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int toson_fd[2]; int toparent_fd[2]; int ret1 = pipe(toson_fd); int ret2 = pipe(toparent_fd); if (ret1 == -1 || ret2 == -1) { perror_exit("pipe error"); } int pid = fork(); if (pid == -1) { // perror_exit("fork error"); } else if (pid == 0) { // child process close(toson_fd[1]); close(toparent_fd[0]); // read from the pipe1 char buf[BUFFSIZE]; int rbytes = read(toson_fd[0], buf, sizeof(buf)); if (rbytes == -1) { perror_exit("read error"); } buf[rbytes] = '\0'; // print the msg from parent fprintf(1, "%d: received %s\n", getpid(), buf); // write response to parent (to pipe2) char resp[4] = "pong"; int ret = write(toparent_fd[1], resp, sizeof(resp)); if (ret == -1) { perror_exit("write error"); } } else { // parent process close(toson_fd[0]); close(toparent_fd[1]); // write to son char msg[4] = "ping"; int ret = write(toson_fd[1], msg, sizeof(msg)); if (ret == -1) { perror_exit("write error"); } // read from son char buf[BUFFSIZE]; int rbytes = read(toparent_fd[0], buf, sizeof(buf)); if (rbytes == -1) { perror_exit("read"); } buf[rbytes] = '\0'; // print the resp from son fprintf(1, "%d: received %s\n", getpid(), buf); } exit(0); }
primes
介紹
實驗要求通過 fork 和 pipe 系統調用建立起如下素數篩的 pipeline.
p = get a number from left neighbor
print p
loop:
n = get a number from left neighbor
if (p does not divide n)
send n to right neighbor

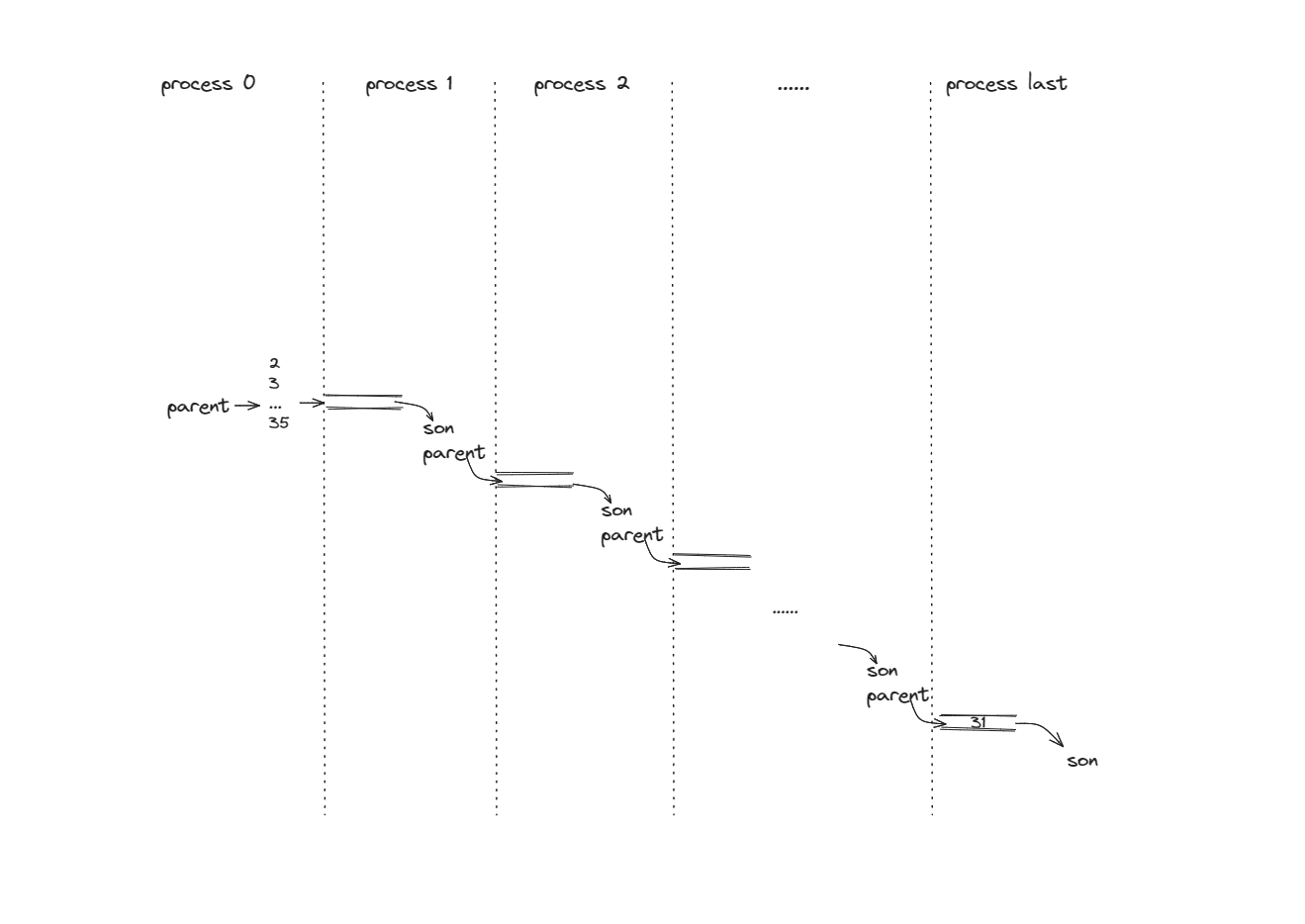
思路
CSP 的關鍵點在於:單個步驟內部操作是串列的,所有步驟之間是併發的。步驟之間的通信通過特定的 channel 完成,這裡通過 pipe 完成。
如上圖,除去第一個進程和最後一個進程,每個進程有兩種身份(父/子)。
分析上述 pipeline, 每個進程需做如下事情:
-
從 left-side-pipe 中讀取數據,嘗試列印素數 prime。
- 如果 left-side-pipe 的寫端關閉且沒讀到數據,代表沒有數據到達。本進程任務結束,正常 exit.
-
建立一個新的 right-side-pipe, fork 出一個子進程, 自身即作為“父身份”根據第一步得出的 prime 進行 filter, 將過濾後的數據傳入 right-side-pipe. wait 子進程,等待子進程列印結束。
- 進程 p0 由 shell fork 創建,如果 p0 不 wait 子進程,父進程 p0 可能在所有子進程列印完成前結束,此時 shell 會向終端輸出提示符
$,造成$穿插在列印結果中的現象。 - 不 wait:
- 子進程還在運行,父進程結束 -> 孤兒進程 -> 由 init 收養。缺點:原父進程得不到子進程的狀態。
- 父進程還在運行,子進程結束 -> 僵屍進程。缺點:占用資源得不到釋放 (
task_struct)。
- 進程 p0 由 shell fork 創建,如果 p0 不 wait 子進程,父進程 p0 可能在所有子進程列印完成前結束,此時 shell 會向終端輸出提示符
notes: fork 出來的子進程重覆上述操作。
註意點
- 註意 close(pipe) 的時機,最保險的做法是儘可能早關閉不需要的讀寫端。
- wait 操作。
- 錯誤處理。
代碼
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "user/user.h"
#define NULL 0
void perror_exit(char* err_msg) {
fprintf(2, "%s\n", err_msg);
exit(-1);
}
void child_processing(int left_pipe[2]) {
// every process do things below:
// 0. read from left-side pipe, and try to print a prime.
// 1. create a new right-side pipe, do fork, pass the filtered data to right-side pipe.
// notes: The new child processes forked will recursively do the above tasks.
close(left_pipe[1]);
int prime;
int rbytes = read(left_pipe[0], &prime, sizeof(prime));
if (rbytes == -1) {
close(left_pipe[0]);
perror_exit("read error");
} else if (rbytes == 0) {
// No more data reaches here
close(left_pipe[0]);
exit(0);
} else {
fprintf(1, "prime %d\n", prime);
}
int right_pipe[2];
int ret = pipe(right_pipe);
if (ret == -1) {
perror_exit("pipe error");
}
ret = fork();
if (ret == -1) {
perror_exit("fork error");
} else if (ret > 0) { // parent/current process
close(right_pipe[0]);
// do filtering, write data into the right-side pipe
int num;
while ((rbytes = read(left_pipe[0], &num, sizeof(num))) != 0) {
if (rbytes == -1) {
perror_exit("read error");
}
if (num % prime != 0) {
write(right_pipe[1], &num, sizeof(num));
}
}
// if rbytes == 0, no more data reaches. the job of this process is done
close(left_pipe[0]);
close(right_pipe[1]);
wait(NULL);
exit(0);
} else if (ret == 0) { // child process
child_processing(right_pipe);
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int pipe_fds[2];
int ret = pipe(pipe_fds);
if (ret == -1) {
perror_exit("pipe error");
}
// create child process
int pid = fork();
if (pid == -1) {
perror_exit("fork error");
} else if (pid == 0) { // child process
// read from pipe, do filtering and pass the data to next stage
child_processing(pipe_fds);
} else { // parent process
close(pipe_fds[0]);
const int MAX = 35;
for (uint32 i = 2; i <= MAX; ++ i) {
write(pipe_fds[1], &i, sizeof(i));
}
close(pipe_fds[1]);
wait(NULL);
}
exit(0);
}
知識點
- 多個寫者向同一管道寫數據時,可以確保寫入不超過 PIPE_BUF 位元組的操作是原子的。
- 即假設 A 寫入數據 aa; B 寫入數據 bb. 可以保證管道內數據必是 aabb 或者 bbaa,不會出現 abab 此類交叉的情況。
- 如果寫入數據量超過限制,內核會將其切分成若幹個片段進行傳輸,
write()調用會阻塞直到所有數據都被寫入管道位置(此時便可能出現數據交叉的情況)。
- 如果管道的寫端被關閉,從讀端讀數據的進程讀完所有剩餘數據後,將會看到文件結束,
read()返回 0. - 管道容量是有限的,非特權進程可以通過
fctnl(fd, F_SETPIPE_SIZE, size)進行修改,修改範圍為 pagesize 和 /proc/sys/fs/pipe-max-size 之間。- 更大的管道容量意味著更少的上下文切換。
- 管道用於單向通信,即某進程在一端讀,另一進程在一端寫。
- 如果允許父子進程都能夠讀/寫同一管道,那麼會發生競爭,需要額外的同步機制。
- 如果需要雙向通信,分別在兩個方向上各設立一個管道即可。
- 關閉未使用管道 fd.
- 如果讀進程沒有關閉管道的寫端,那麼在其他進程關閉了寫入文件描述符後,讀者也不會看到文件結束,因為內核知道至少還存在一個管道的寫入描述符打開著,即讀取進程自己。
- 如果寫進程沒有關閉管道的讀端,那麼即使其他進程已經關閉了讀端文件描述符,寫進程仍然能夠向管道中寫入數據,最後管道被寫滿,後續的寫入請求會被永遠阻塞。
- 當進程嘗試向一個管道寫入數據,但是沒有進程占用該管道讀端時,內核會向進程發送
SIGPIPE信號,預設處理會殺死進程。
find
-
思路:查找待查找目錄下所有條目:
- 如果是目錄,遞歸查找
- 如果是普通文件,比對文件名,輸出
-
實現:參考
ls.c實現。目錄文件本質也是一個文件,不過文件內容是一個個 directory entry. 因此對於目錄,讀取其文件內容至 dir_entry 中,判斷其類型,進行相應處理。 -
代碼:
#include "kernel/types.h"
#include "kernel/stat.h"
#include "kernel/fs.h"
#include "user/user.h"
char* fmtname(char *path) {
static char buf[DIRSIZ+1];
char *p;
// Find first character after last slash.
for (p = path + strlen(path); p >= path && *p != '/'; p--)
;
p++;
// Return blank-padded name.
if (strlen(p) >= DIRSIZ)
return p;
memmove(buf, p, strlen(p));
memset(buf+strlen(p), ' ', DIRSIZ-strlen(p));
return buf;
}
void find(char* path, char* file_name) {
int fd = open(path, 0);
if (fd < 0) {
fprintf(2, "find: cannot open %s\n", path);
goto clean;
}
int ret;
struct stat st;
ret = fstat(fd, &st);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(2, "find: cannot stat %s\n", path);
goto clean;
}
if (st.type != T_DIR) {
fprintf(2, "find: the first param should be directory\n");
goto clean;
}
char buf[512];
if (strlen(path) + 1 + DIRSIZ + 1 > sizeof buf) {
fprintf(2, "find: path too long\n");
goto clean;
}
strcpy(buf, path);
char* p = buf + strlen(buf);
*p++ = '/';
struct dirent de;
while (read(fd, &de, sizeof(de)) == sizeof(de)){
if (de.inum == 0)
continue;
memmove(p, de.name, DIRSIZ);
p[DIRSIZ] = '\0';
if (stat(buf, &st) < 0) {
printf("find: cannot stat %s\n", buf);
continue;
}
switch (st.type) {
case T_FILE:
if (strcmp(file_name, de.name) == 0) {
fprintf(1, "%s\n", buf);
}
break;
case T_DIR:
if (strcmp(".", de.name) != 0 && strcmp("..", de.name) != 0) {
find(buf, file_name);
}
break;
case T_DEVICE:
break;
}
}
clean:
close(fd);
return;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(2, "Usage: %s <directory> <filename>\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
find(argv[1], argv[2]);
exit(0);
}



