# Spring 的依賴註入 @[toc] ## 每博一文案 ```tex "在千千萬萬個選擇里",我永遠選擇去做哪些我認為值得的事,我可能幹得很漂亮,也可能搞得一塌糊塗。 但沒關係,重要的是我為之努力過。”我們很難做好每件事,讓人生不留下任何遺憾,儘力而為就好“享受 生活的過程,接受結果。”人生是 ...
Spring 的依賴註入
@
目錄- Spring 的依賴註入
每博一文案
"在千千萬萬個選擇里",我永遠選擇去做哪些我認為值得的事,我可能幹得很漂亮,也可能搞得一塌糊塗。
但沒關係,重要的是我為之努力過。”我們很難做好每件事,讓人生不留下任何遺憾,儘力而為就好“享受
生活的過程,接受結果。”人生是用來體驗的,不是用來演繹完美的,我慢慢能接受自己身上哪些灰暗的部分,原諒自己
的遲鈍和平庸,允許自己出錯,允許自己偶爾斷電,帶著缺憾拼命綻放,這是與自己達成和解的唯一方式。”
儘力就好,允許所有的事與願違。和不適合你的過去說再見,哪些傷痛的不堪的,霉爛的過去絕口不提。
太陽的起落在告訴我們,永遠會有嶄新的一天。
“真正有價值的事情,都不是輕鬆舒服就能完成的”。那些晨間的寂靜,不眠的星光,清醒的剋制,
孤軍奮戰的堅持,暗暗許下的承諾,才是我熱愛自己的時刻。"人生就是一步一步地打怪升級,堅持
下去,你所執著的努力一定會有所收穫",
——————《網友的評論》
1. 依賴註入
依賴註入實現了控制反轉的思想:
- Spring通過依賴註入的方式來完成Bean(類/對象)的管理。
- Bean的管理:Bean對象的創建,以及Bean對象中屬性的賦值(或者叫做Bean對象之間的關聯的維護)。
依賴註入:
- 依賴指的是對象和對象 之間的關聯關係。
- 註入指的是一種數據傳遞行為,通過註入行為來讓對象和對象產生關係。
依賴註入常見的實現方式包括兩種:
- 第一種:set註入
- 第二種: 構造註入
**準備工作:通過 maven 導入對應 spring6 的相關jar **
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-003-dependency-injection-blog</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- 將項目的打包方式為 jar Java項目的方式-->
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!-- 導入相關的依賴倉庫-->
<dependencies>
<!-- spring6 框架-->
<!--spring contest 倉庫-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit4 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
1.1 構造註入
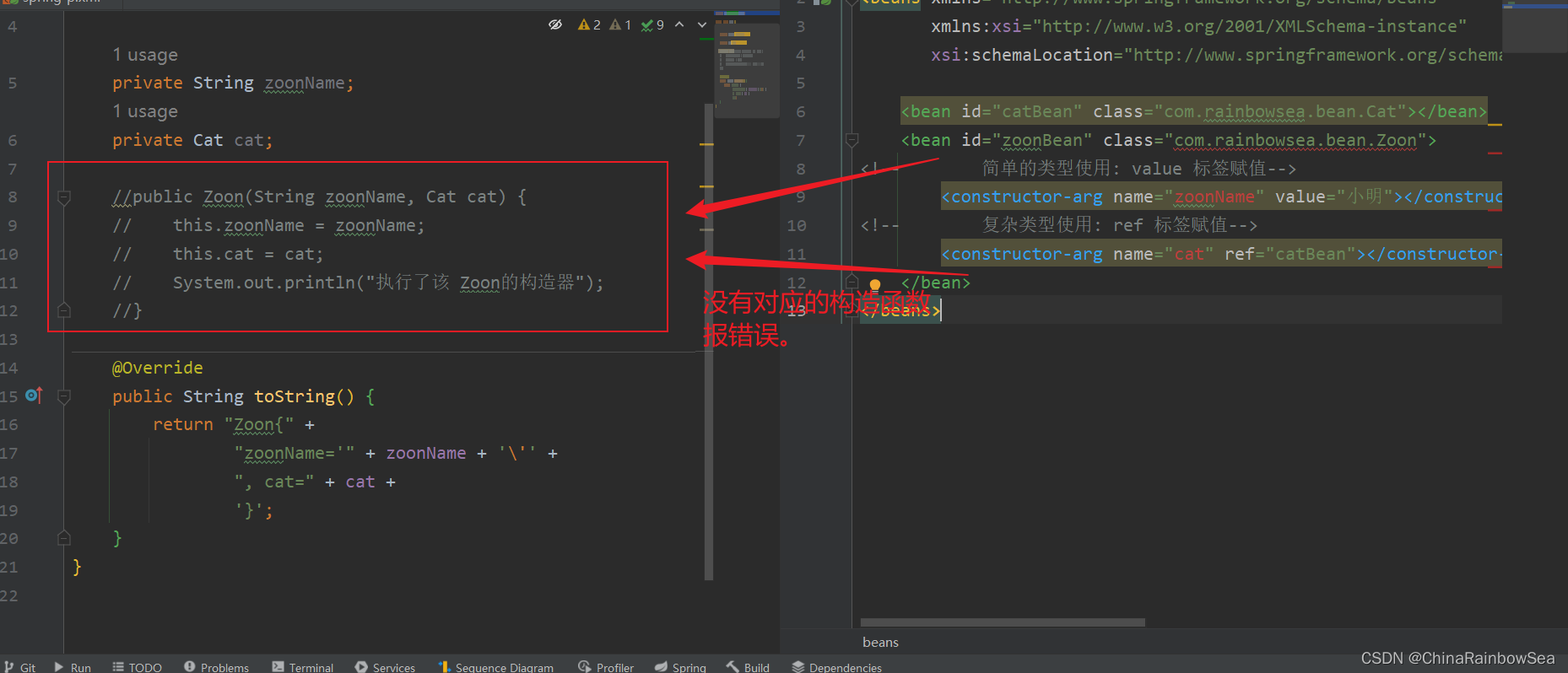
所謂的構造註入:核心就是:調用了對應的構造方法,進行一個類/對象的屬性賦值。
既然要調用構造方法,進行一個屬性的賦值的話,那麼我們的對應屬性的賦值的,構造方法必須存在才行。
構造註入:是在對象創建的時刻進行註入的。
重點:構造註入的使用的標簽是:
<constructor-arg></constructor-arg>
1.1.1 通過參數名進行構造註入
格式:
<bean id="" class="">
<!-- 簡單的類型使用: value 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg name="" value=""></constructor-arg>
<!-- 複雜類型使用: ref 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg name="" ref=""></constructor-arg>
</bean>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Cat {
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Zoon {
private String zoonName;
private Cat cat;
public Zoon(String zoonName, Cat cat) {
this.zoonName = zoonName;
this.cat = cat;
System.out.println("執行了該 Zoon的構造器");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Zoon{" +
"zoonName='" + zoonName + '\'' +
", cat=" + cat +
'}';
}
}
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!-- 簡單的類型使用: value 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg name="zoonName" value="小明"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 複雜類型使用: ref 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg name="cat" ref="catBean"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-structure.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
Zoon zoonBean = applicationContext.getBean("zoonBean", Zoon.class);
System.out.println(zoonBean);
}
}
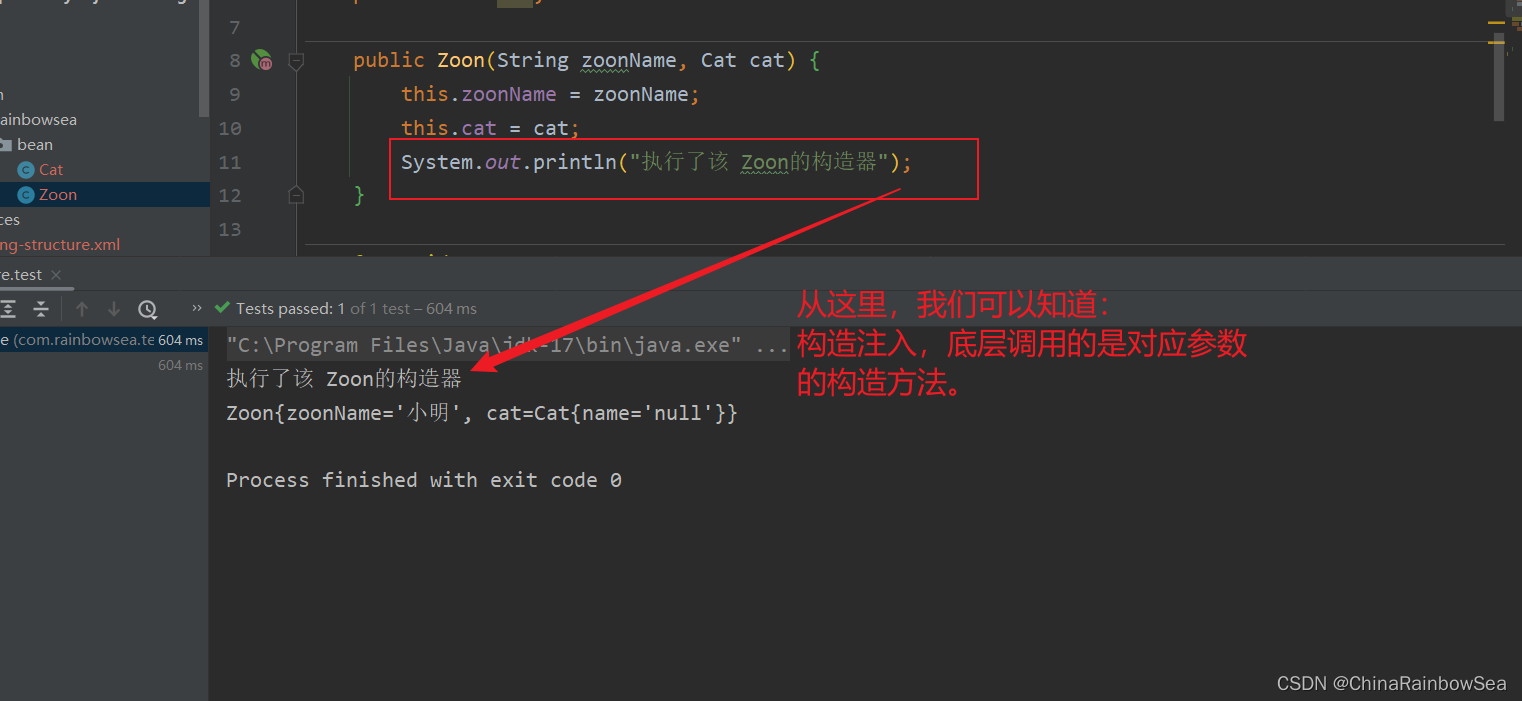
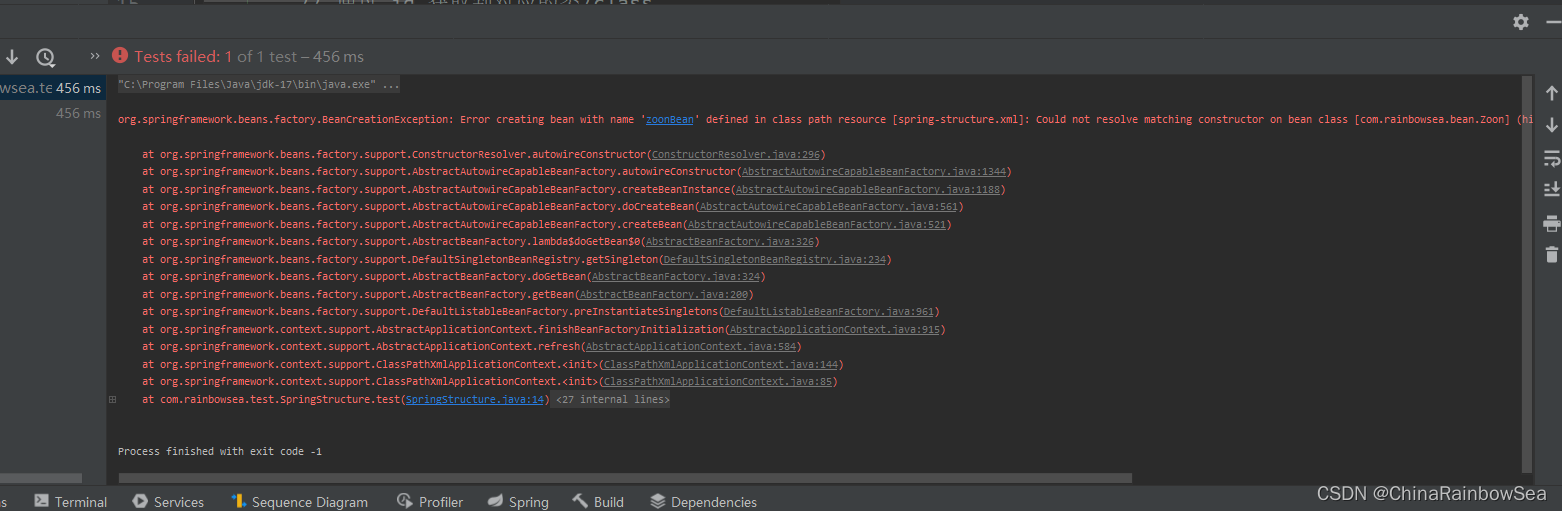
測試如果,我們將構造方法刪除了,就不行了,報如下錯誤:
1.1.2 通過參數的下標,進行構造註入
格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- index 下標註入: 註意:第一個參數是從 0 開始的,簡單的類型使用: value 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg index="0" value=""></constructor-arg>
<!-- 複雜類型使用: ref 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg index="1" ref=""></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!-- index 下標註入: 註意:第一個參數是從 0 開始的,簡單的類型使用: value 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg index="0" value="小明"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 複雜類型使用: ref 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="catBean"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
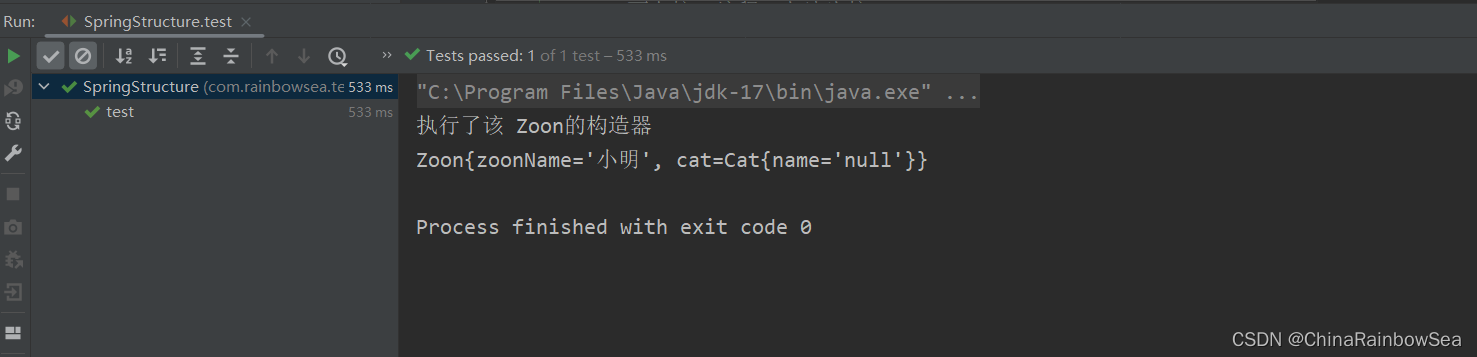
1.1.3 不指定參數下標,不指定參數名字,通過自動裝配的方式
格式:但是這種方式不建議:因為可讀性十分的差。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!-- 簡單的類型使用: value 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg value="xxx"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 複雜類型使用: ref 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg ref="xxx"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!-- 簡單的類型使用: value 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg value="小明"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 複雜類型使用: ref 標簽賦值-->
<constructor-arg ref="catBean"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
1.2 set 註入
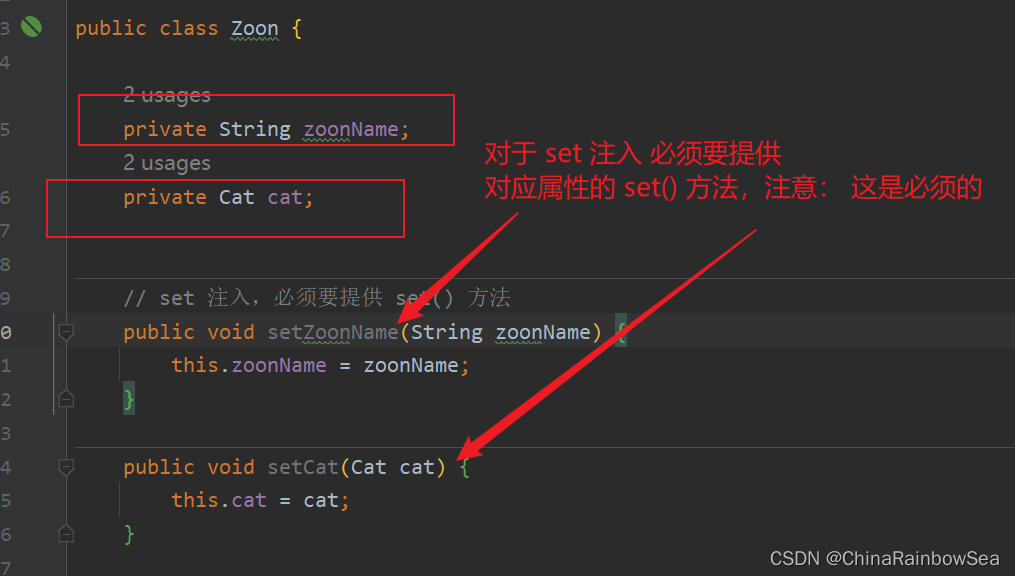
set 註入顧名思義:是基於 set () 方法實現的,底層通過反射機制調用屬性對應的 set() 方法然後給屬性賦值。這種方式 要求屬性必須對外提供 set() 方法。
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Cat {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Zoon {
private String zoonName;
private Cat cat;
// set 註入,必須要提供 set() 方法
public void setZoonName(String zoonName) {
this.zoonName = zoonName;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Zoon{" +
"zoonName='" + zoonName + '\'' +
", cat=" + cat +
'}';
}
}
set註入的格式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="xxx" class="xxx">
<!-- set 註入使用: <property></property> 標簽:
同樣的: value 為簡單類型的賦值-->
<property name="xxx" value=""></property>
<!--
同樣的: ref 為複雜類型的賦值-->
<!-- name 屬性怎麼指定值,set 方法的方法名: ,然後把剩下的單詞字母變小寫,寫到這裡-->
<!-- ref 翻譯為引用,英語單詞: references ,ref 後面指定的是 bean 的id-->
<!-- id 是唯一的不可以重覆的出現的 ref 和 value 是一樣的。-->
<property name="xxx" ref="xxx"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
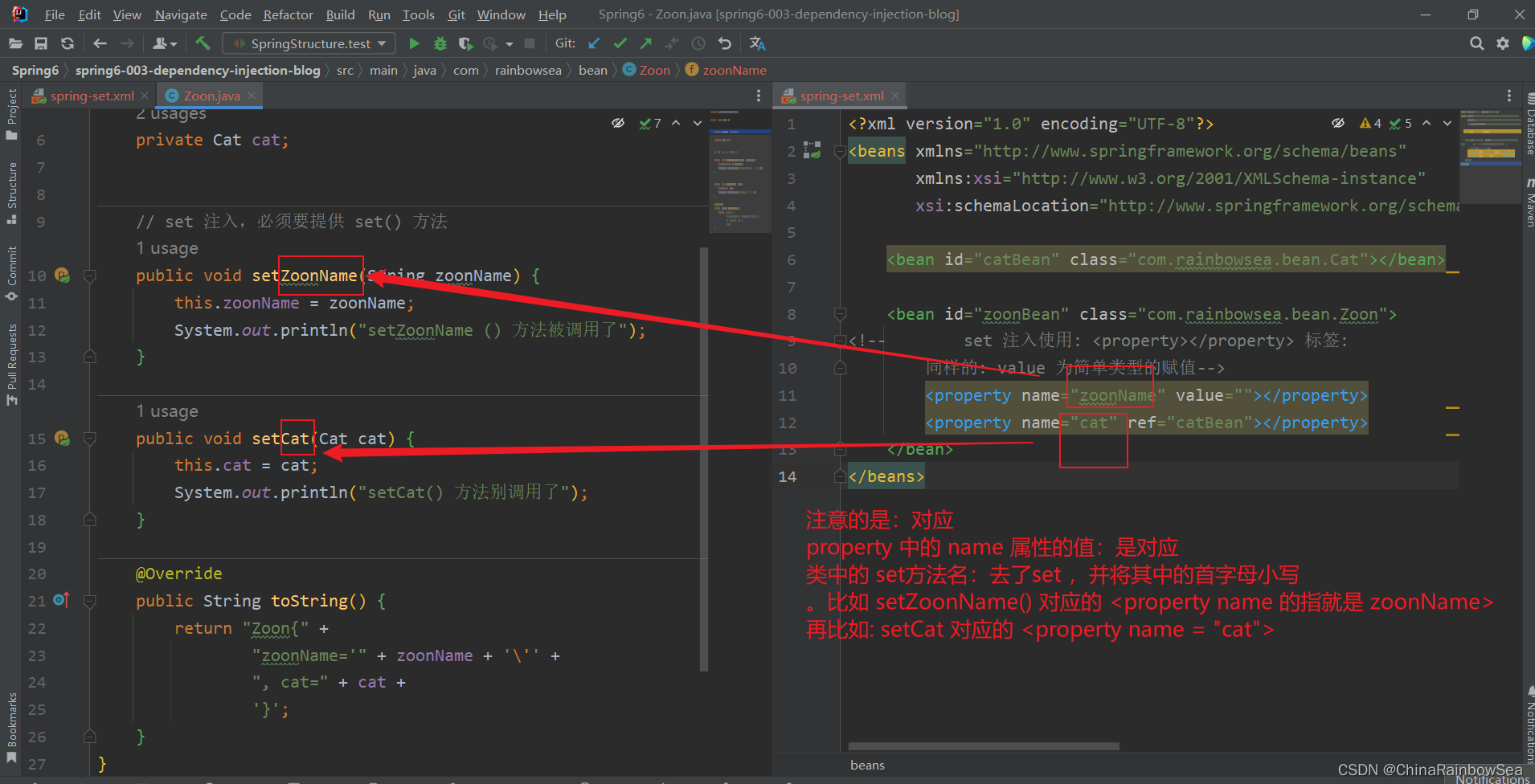
需要註意的是:
- 其中的
<property name="xxx"></property>中的 name 必須是 對應類當中的 set() 方法。去了,set,其次是 首字母小寫 。這是不可以亂寫的。 - Eg:
說明property標簽的name是:setUserDao()方法名演變得到的。演變的規律是:
● setUsername() 演變為 username
● setPassword() 演變為 password
● setUserDao() 演變為 userDao
● setUserService() 演變為 userService
- 具體的如下圖所示:
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-set.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
Zoon zoonBean = applicationContext.getBean("zoonBean", Zoon.class);
System.out.println(zoonBean);
}
}
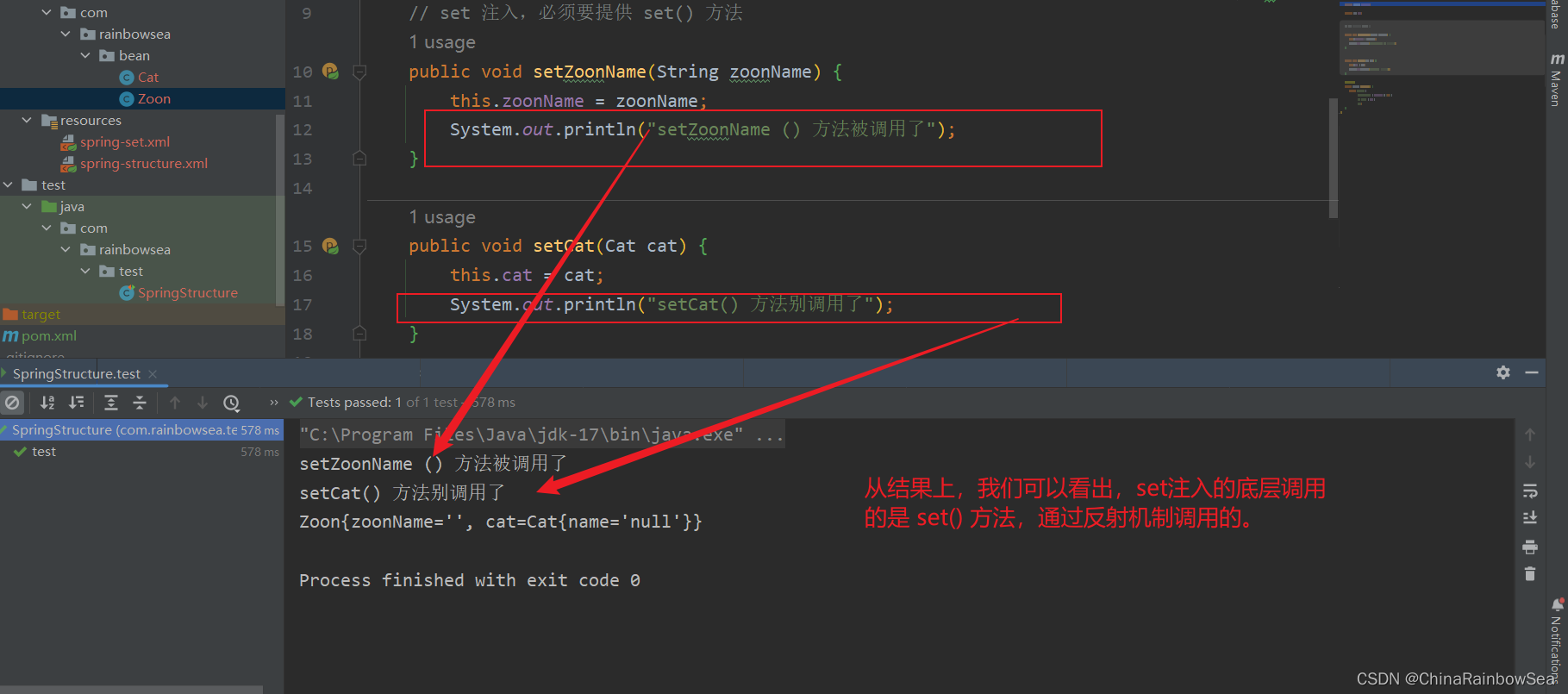
測試:我們如果把: 對應的 set 方法註釋掉了,運行測試一下。
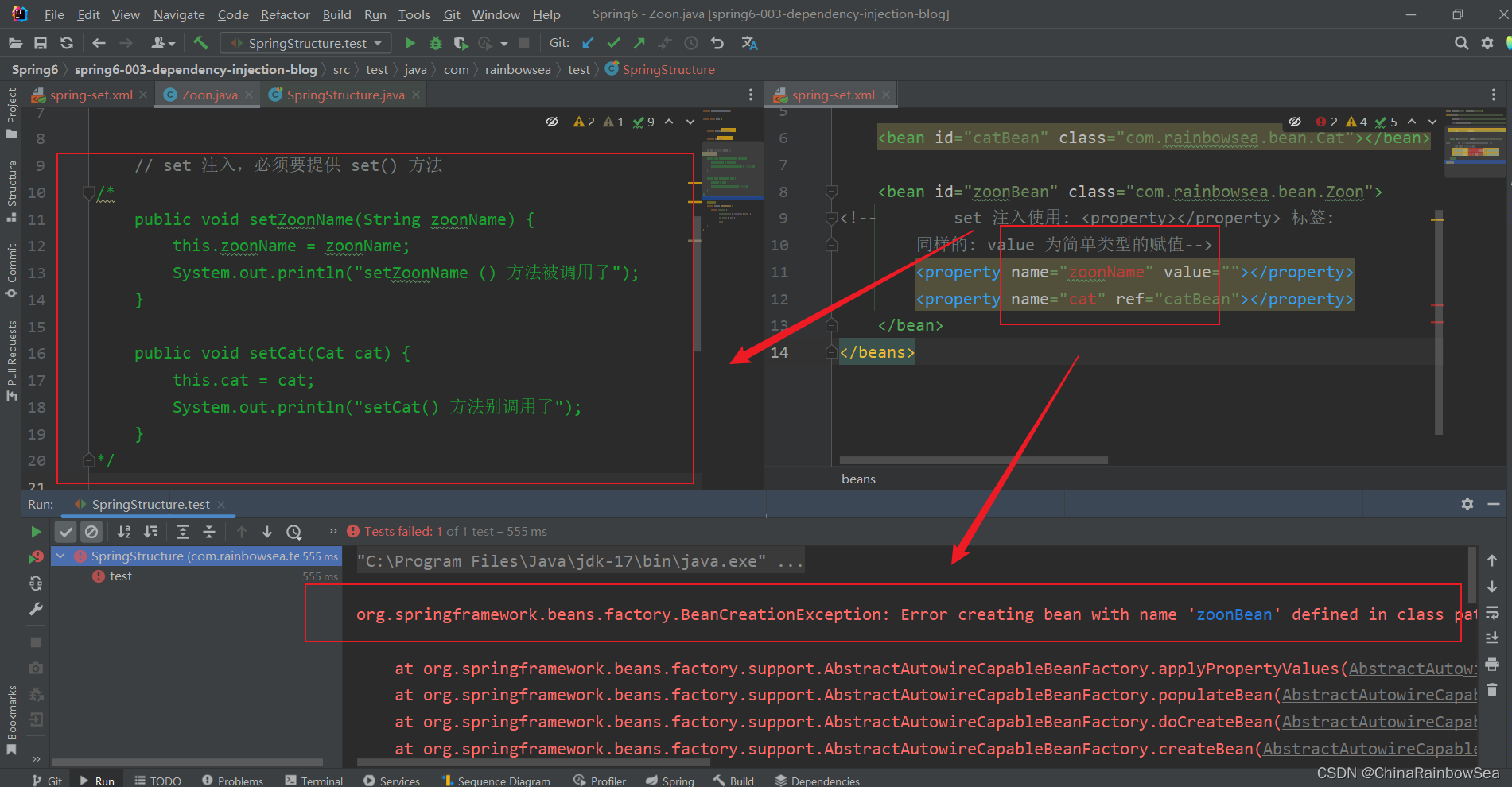
從結果上,我們可以看出:set 方法是必須 存在的。
set 註入的簡單總結:
- 實現原理:
通過property標簽獲取到屬性名:userDao:
通過性名推斷出set方法名:setUserDao
通過反射機制調用setUserDao()方法給屬性賦值
property標簽的 name是屬性名。
property標簽的ref是要註入的bean對象的id。(通過ref屬性來完成bean的裝配,這是bean最簡單的一種裝配方式。裝配指的是:創建系統組件之間關聯的動作)
set註入的核心實現原理:通過反射機制調用set方法來給屬性賦值,讓兩個對象之間產生關係。
2. set註入的各種方式詳解
實際上在實際的開發過程中,我們使用的更多的是 set()方法的註入 。
2.1 set 註入外部Bean
外部Bean的特點: bean定義到外面,在property標簽中使用ref 屬性或是 value 屬性進行註入。通常這種方式是常用。
格式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!--如下:方式是 外部 bean 的註入的方式-->
<property name="zoonName" value=""></property>
<property name="cat" ref="catBean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
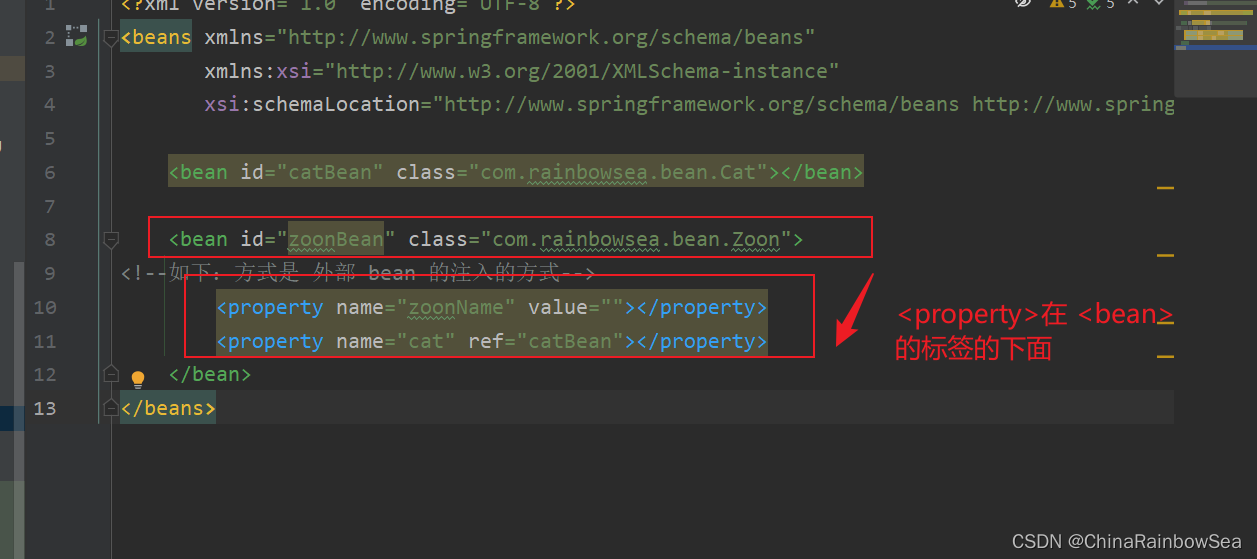
上面:我們測試用的 set 註入的方式:用的都是這種外部 Bean 的方式。
2.2 set 註入內部Bean
內部Bean的方式:在bean標簽中嵌套bean標簽:
具體格式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="zoonBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon">
<!--如下:方式是 內部 bean 的註入的方式-->
<property name="cat" >
<!-- <property> 標簽當中嵌入了 <bean>進行一個賦值-->
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat">
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
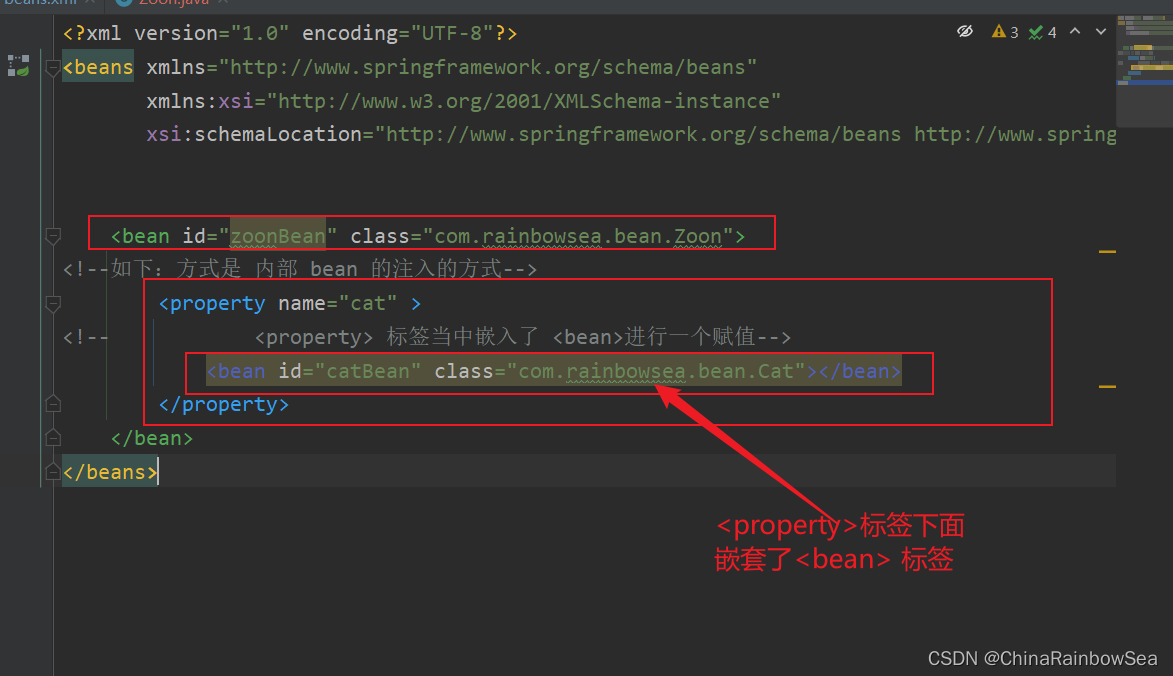
運行測試:
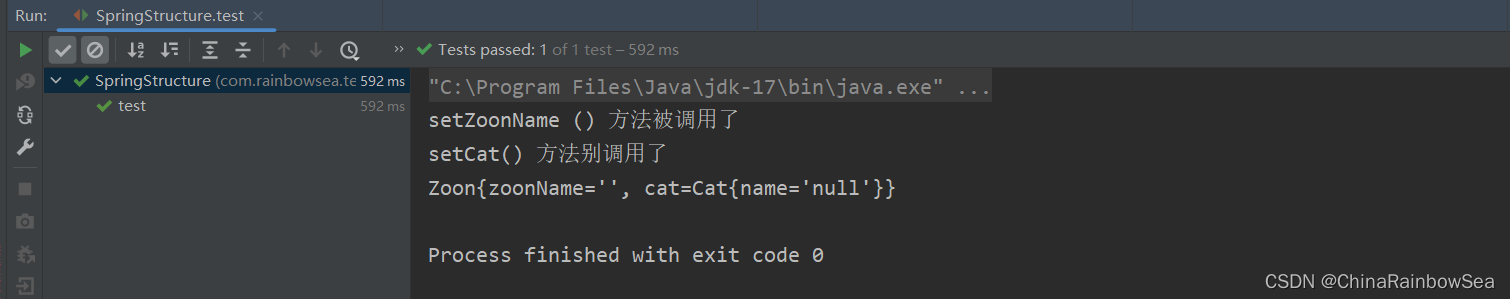
2.3 set 註入類型
2.3.1 set 註入簡單類型
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class Cat {
private int age;
private String name;
// set註入:底層反射調用 set 方法
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
格式:
在set 註入當中:簡單類型的註使用 value 標簽屬性,進行一個屬性的賦值操作
需要特別註意:如果給簡單類型賦值,使用value屬性或value標簽。而不是ref。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
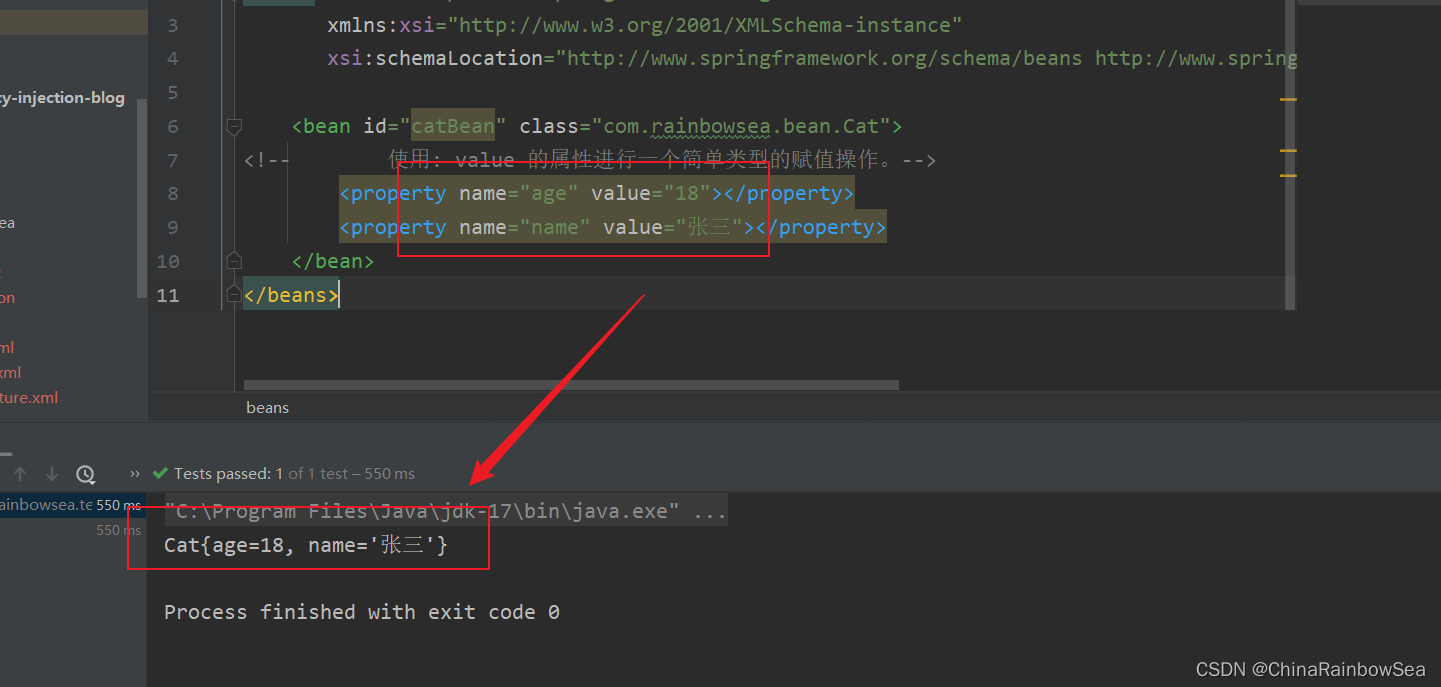
<bean id="catBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat">
<!-- 使用: value 的屬性進行一個簡單類型的賦值操作。-->
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<property name="name" value="張三"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.Cat;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.Zoon;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
Cat catBean = applicationContext.getBean("catBean", Cat.class);
System.out.println(catBean);
}
}
既然我們知道了:簡單類型如何使用 set 註入了,那麼我們就需要知道哪些是 簡單類型了 ?
簡單類型包括哪些呢?可以通過Spring的源碼來分析一下:BeanUtils類
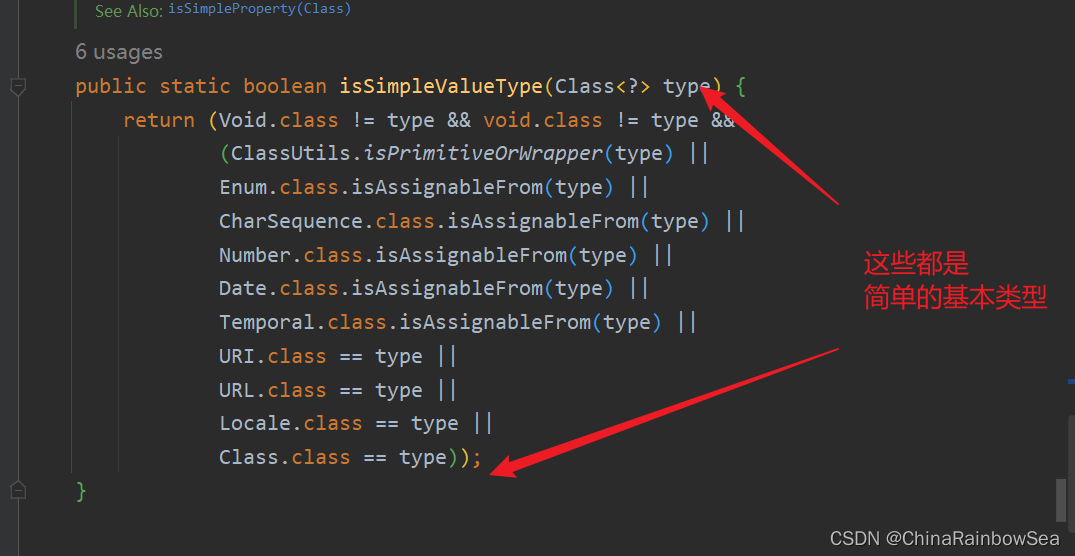
/**
* Check if the given type represents a "simple" value type: a primitive or
* primitive wrapper, an enum, a String or other CharSequence, a Number, a
* Date, a Temporal, a URI, a URL, a Locale, or a Class.
* <p>{@code Void} and {@code void} are not considered simple value types.
* @param type the type to check
* @return whether the given type represents a "simple" value type
* @see #isSimpleProperty(Class)
*/
public static boolean isSimpleValueType(Class<?> type) {
return (Void.class != type && void.class != type &&
(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(type) ||
Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
CharSequence.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Number.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Date.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Temporal.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
URI.class == type ||
URL.class == type ||
Locale.class == type ||
Class.class == type));
}
通過源碼分析得知,簡單類型包括:
- 基本數據類型
- 基本數據類型對應的包裝類
- String或其他的CharSequence子類
- Number子類
- Date子類
- Enum子類
- URI
- URL
- Temporal子類
- Locale
- Class
- 另外還包括以上簡單值類型對應的數組類型。
測試驗證:
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
/**
* 枚舉類
*/
public enum Season {
SPRING,SUMMER,AUTUMN,WINTER
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class SimpleValueType {
// 下麵的都是簡單的類型
private int age;
private Integer age2;
private boolean flag;
private Boolean flag2;
private char c;
private Character c2;
private Season season; // 枚舉
private String username;
private Class clazz;
// set 註入必須要:設置 set() 方法
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setAge2(Integer age2) {
this.age2 = age2;
}
public void setFlag(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
public void setFlag2(Boolean flag2) {
this.flag2 = flag2;
}
public void setC(char c) {
this.c = c;
}
public void setC2(Character c2) {
this.c2 = c2;
}
public void setSeason(Season season) {
this.season = season;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
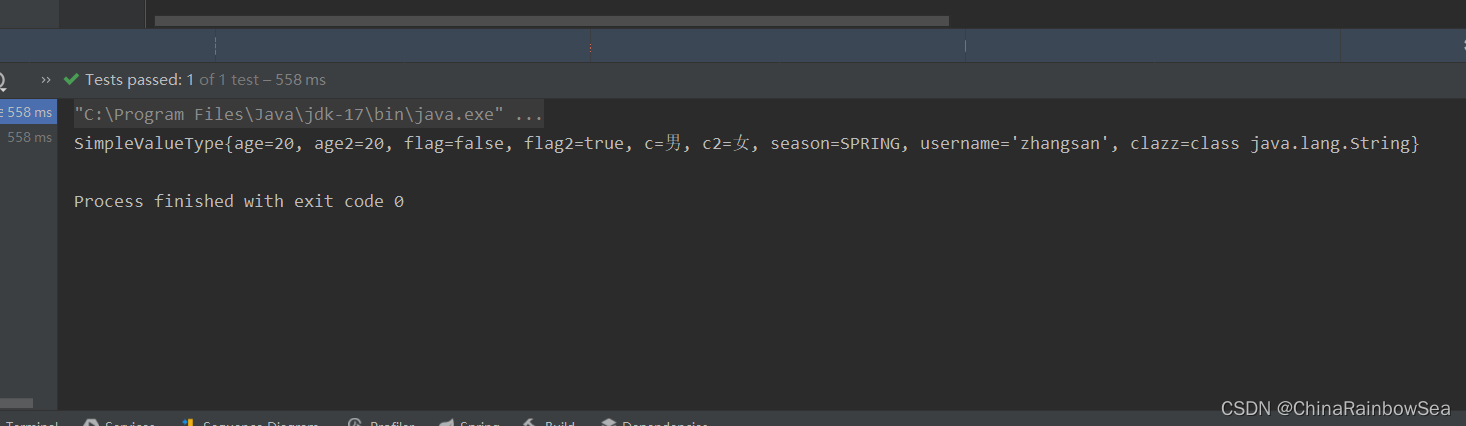
return "SimpleValueType{" +
"age=" + age +
", age2=" + age2 +
", flag=" + flag +
", flag2=" + flag2 +
", c=" + c +
", c2=" + c2 +
", season=" + season +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", clazz=" + clazz +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="svt" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType">
<!-- 下麵這種方式是外部的註入-->
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
<property name="age2" value="20"></property>
<property name="username" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="season" value="SPRING"></property>
<property name="flag" value="false"></property>
<property name="flag2" value="true"></property>
<property name="c" value="男"></property>
<!-- 如果簡單類型使用的是 ref 是會報錯的, ref 註入的是 bean 類的信息-->
<property name="c2" value="女"></property>
<property name="clazz" value="java.lang.String"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
SimpleValueType svt = applicationContext.getBean("svt", SimpleValueType.class);
System.out.println(svt);
}
}
註意了: 特殊的日期時間進行一個特殊的賦值:
從上面的 BeanUtils 我們可以知道的的是 Date ,它是被Spring定義為了一個簡單類型,來進行處理的。
但是,我們進行一個如下的測試:
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestDate {
private Date date;
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TestDate{" +
"date=" + date +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="testDateBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate">
<property name="date" value="2023 -05-6"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
TestDate testDate = applicationContext.getBean("date", TestDate.class);
System.out.println(testDate);
}
}
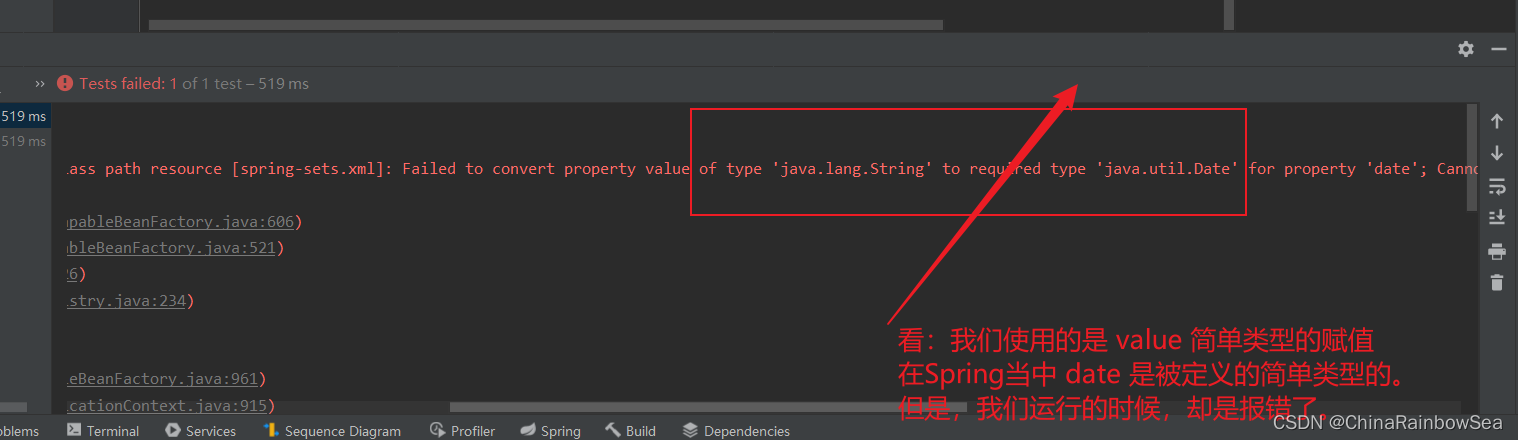
報錯的原因是:
從報錯的信息上,我們可以看到:
[
說:
'java.lang.String' to required type 'java.util.Date'說 這個 2023 -05-6 這個字元串,無法轉換成 java.util.Date 類型。<property name="date" value="2023 -05-6"></property>如果你硬要把Date 當作簡單類型的話,使用 value 賦值的話,這個日期字元串格式有要求的。所有的要求就是: new Date toString 列印顯示的格式形式:Fri Jun 30 11:27:41 CST 2023。但是,我們在實際開發中,我們一般不會把 Date 當做簡單類型,雖然是簡單類型,但是我們一般採用的是ref 的Date 類型的屬性賦值。
- 如果把Date當做簡單類型的話,日期字元串格式不能隨便寫。格式必須符合Date的toString()方法格式。顯然這就比較雞肋了。如果我們提供一個這樣的日期字元串:2010-10-11,在這裡是無法賦值給Date類型的屬性的。
- spring6之後,當註入的是URL,那麼這個url字元串是會進行有效性檢測的。如果是一個存在的url,那就沒問題。如果不存在則報錯。
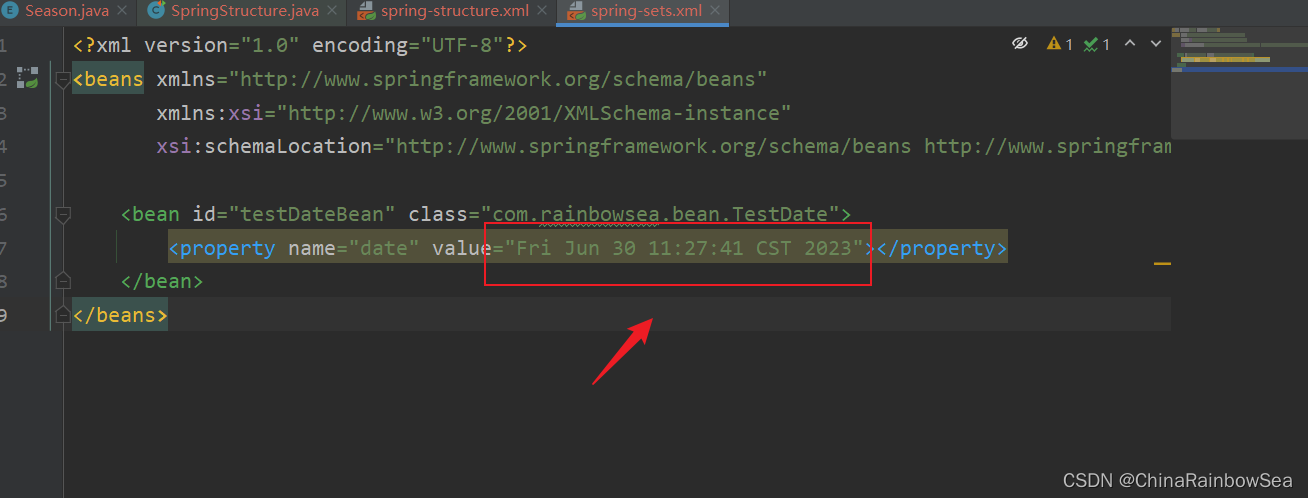
測試使用: 我們要求的格式: Fri Jun 30 11:27:41 CST 2023 進行一個 Date 的測試
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="testDateBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate">
<property name="date" value="Fri Jun 30 11:27:41 CST 2023"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
TestDate testDate = applicationContext.getBean("testDateBean", TestDate.class);
System.out.println(testDate);
}
}
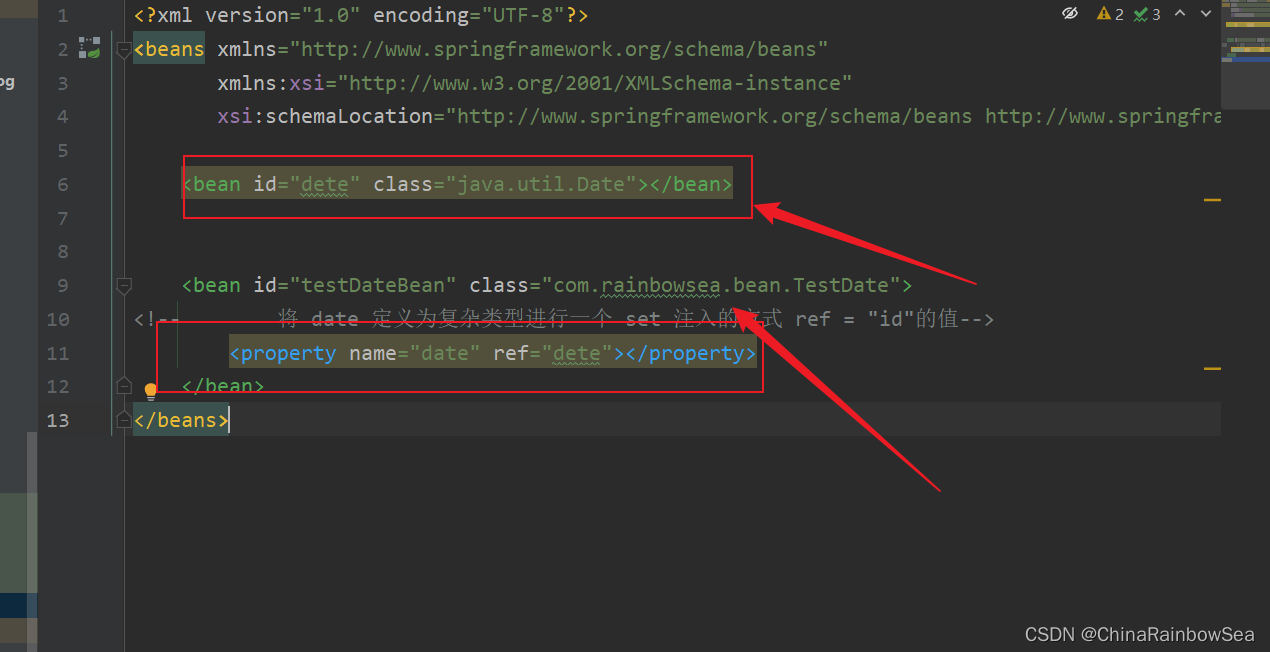
測試將 Date 當作為複雜類型進行一個set 註入的方式:測試
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dete" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<bean id="testDateBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate">
<!-- 將 date 定義為複雜類型進行一個 set 註入的方式 ref = "id"的值-->
<property name="date" ref="dete"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.SimpleValueType;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.TestDate;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
TestDate testDate = applicationContext.getBean("testDateBean", TestDate.class);
System.out.println(testDate);
}
}
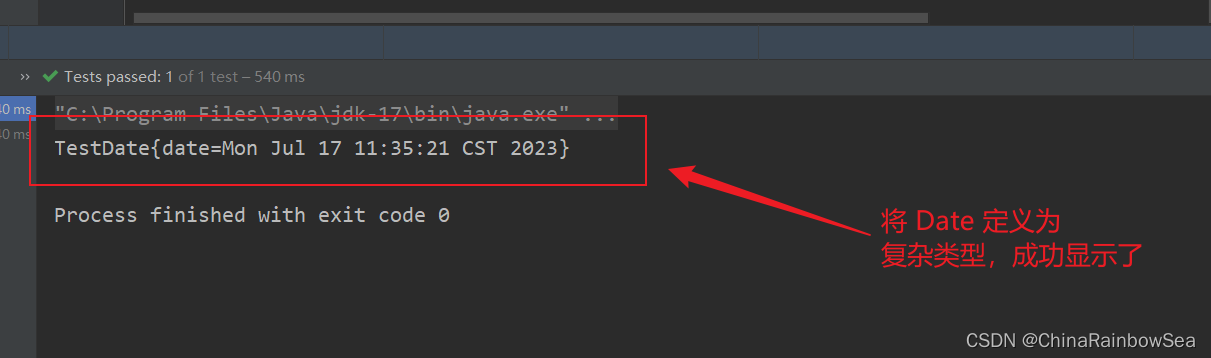
經典案例:給數據源的屬性註入值:
假設我們現在要自己手寫一個數據源,我們都知道所有的數據源都要實現javax.sql.DataSource介面,並且數據源中應該有連接資料庫的信息,例如:driver、url、username、password等。
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
// set 註入必須提供 set () 方法
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="data" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"></property>
<property name="username" value="name"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
MyDataSource data = applicationContext.getBean("data", MyDataSource.class);
System.out.println(data);
}
}
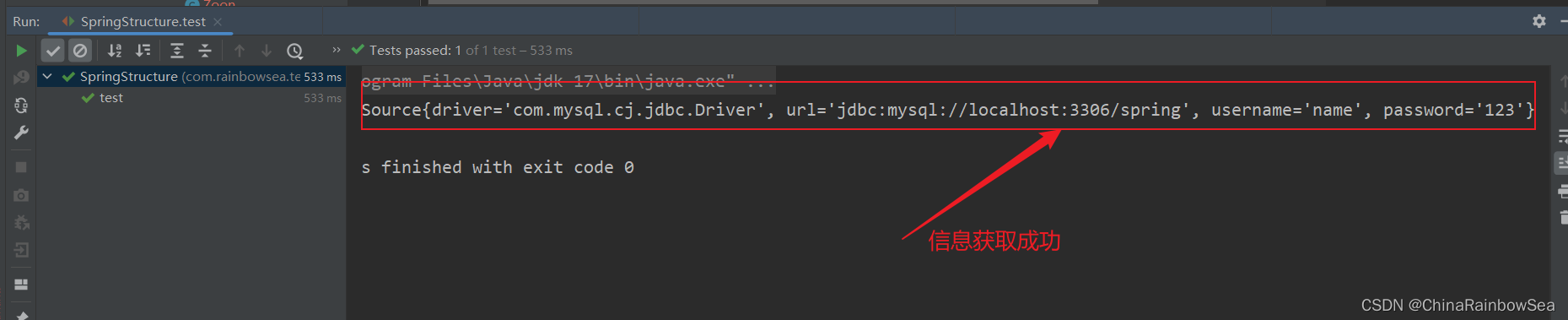
2.3.2 set 複雜類型註入的方式
格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="張三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- ref 表示的是複雜類型,其中的值表示的是: 對應的複雜類型的id 值。-->
<property name="user" ref="userBean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class People {
private User user;
private String name;
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"user=" + user +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="張三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- ref 表示的是複雜類型,其中的值表示的是: 對應的複雜類型的id 值。-->
<property name="user" ref="userBean"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
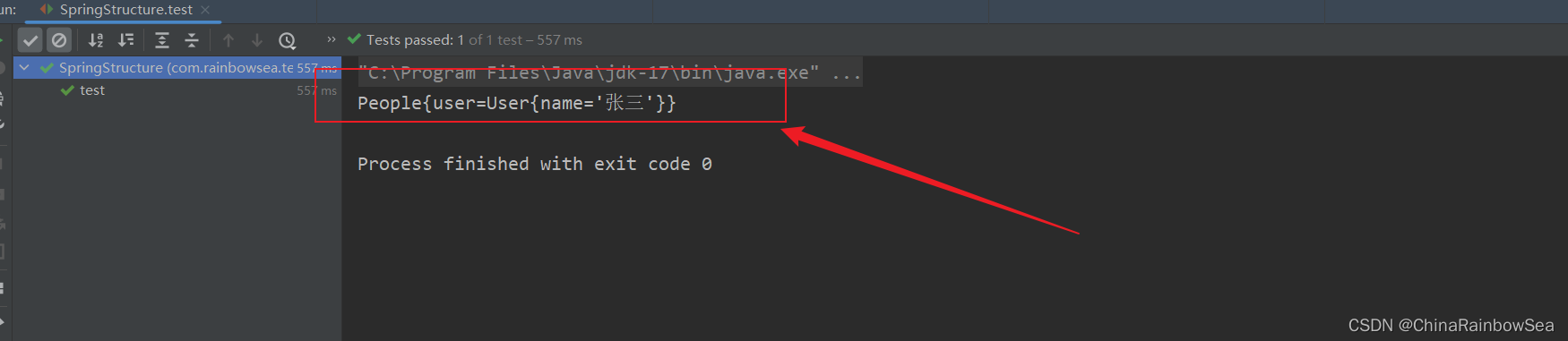
2.4 級聯屬性賦值
級聯的要求:
- 對應級聯的類下的屬性的賦值,必須提供 get() 方法,因為級聯的底層調用的就是 get() 方法。不然無法級聯到。
- 註意:級聯的上下放置的順序,級聯當中的使用的 id ,必須在級聯之前先定義處理出來,不然同樣無法級聯到。
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class People {
private User user;
private String name;
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 使用級聯的話,必須提供其中的 get() 方法進行一個獲取
// 級聯的底層調用的就是 get()方法。
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"user=" + user +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User"></bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<!-- ref 表示的是複雜類型,其中的值表示的是: 對應的複雜類型的id 值。-->
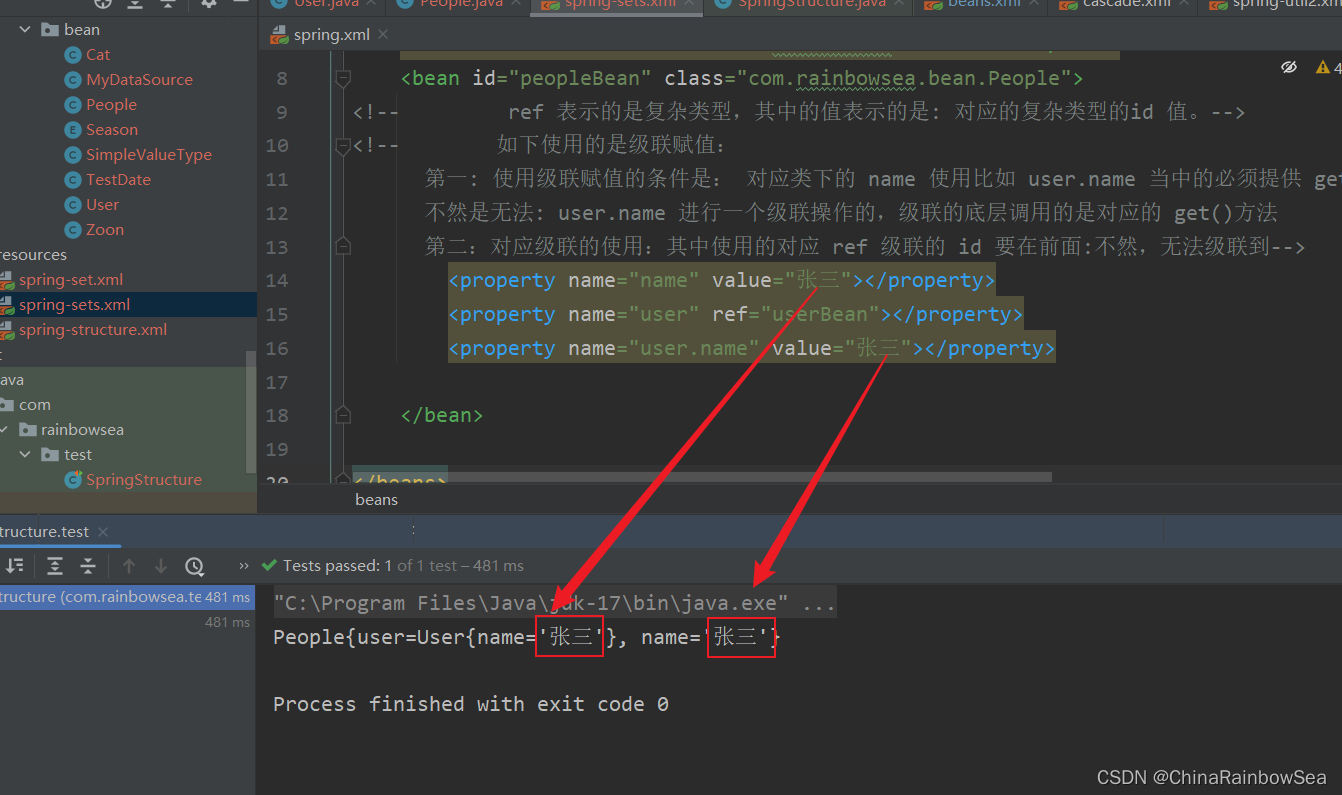
<!-- 如下使用的是級聯賦值:
第一: 使用級聯賦值的條件是: 對應類下的 name 使用比如 user.name 當中的必須提供 get() 方法。
不然是無法: user.name 進行一個級聯操作的,級聯的底層調用的是對應的 get()方法
第二:對應級聯的使用:其中使用的對應 ref 級聯的 id 要在前面:不然,無法級聯到-->
<property name="name" value="張三"></property>
<property name="user" ref="userBean"></property>
<property name="user.name" value="張三"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
級聯用的比較少,所以大家瞭解一下就好了。
2.5 set 註入數組類型
關於set 數組類型的註入的方式:
格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User"></bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name">
<!-- 數組的賦值使用: array 標簽-->
<array>
<value></value>
<value></value>
<value></value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
2.5.1 當數組中的元素是簡單類型
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class People {
private String[] name;
public void setName(String[] name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name=" + Arrays.toString(name) +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User"></bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name">
<!-- 數組的賦值使用: array 標簽-->
<array>
<!-- 簡單類型使用: value-->
<value>張三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name">
<!-- 數組的賦值使用: array 標簽-->
<array>
<!-- 簡單類型使用: value-->
<value>張三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
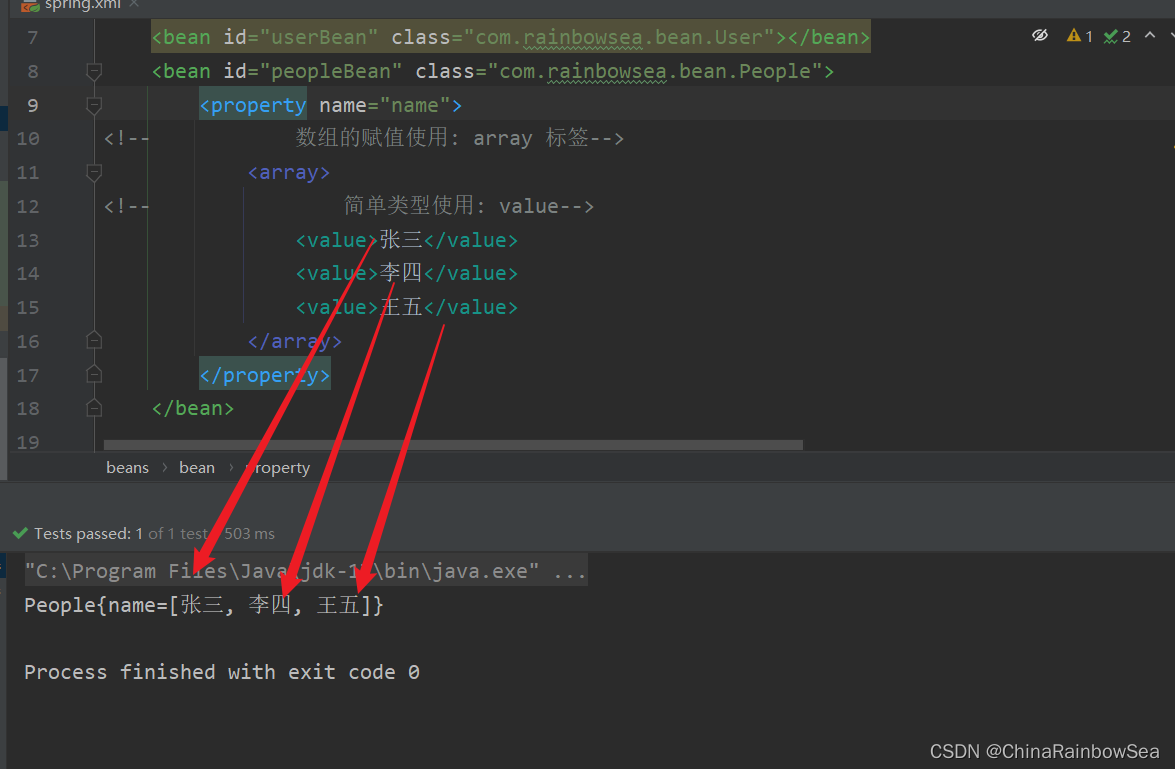
2.5.2 當數組中的元素是複雜類型
格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="xxx1" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="張三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="xxx2" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="users">
<!-- 數組的賦值使用: array 標簽-->
<array>
<!-- 複雜型使用: ref bean 是對應的id-->
<ref bean="xxx1"></ref>
<ref bean="xxx2"></ref>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
**舉例: **
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class People {
private User[] users;
public void setUsers(User[] users) {
this.users = users;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"users=" + Arrays.toString(users) +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="張三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userBean2" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="users">
<!-- 數組的賦值使用: array 標簽-->
<array>
<!-- 複雜類型使用: ref-->
<ref bean="userBean"></ref>
<ref bean="userBean2"></ref>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
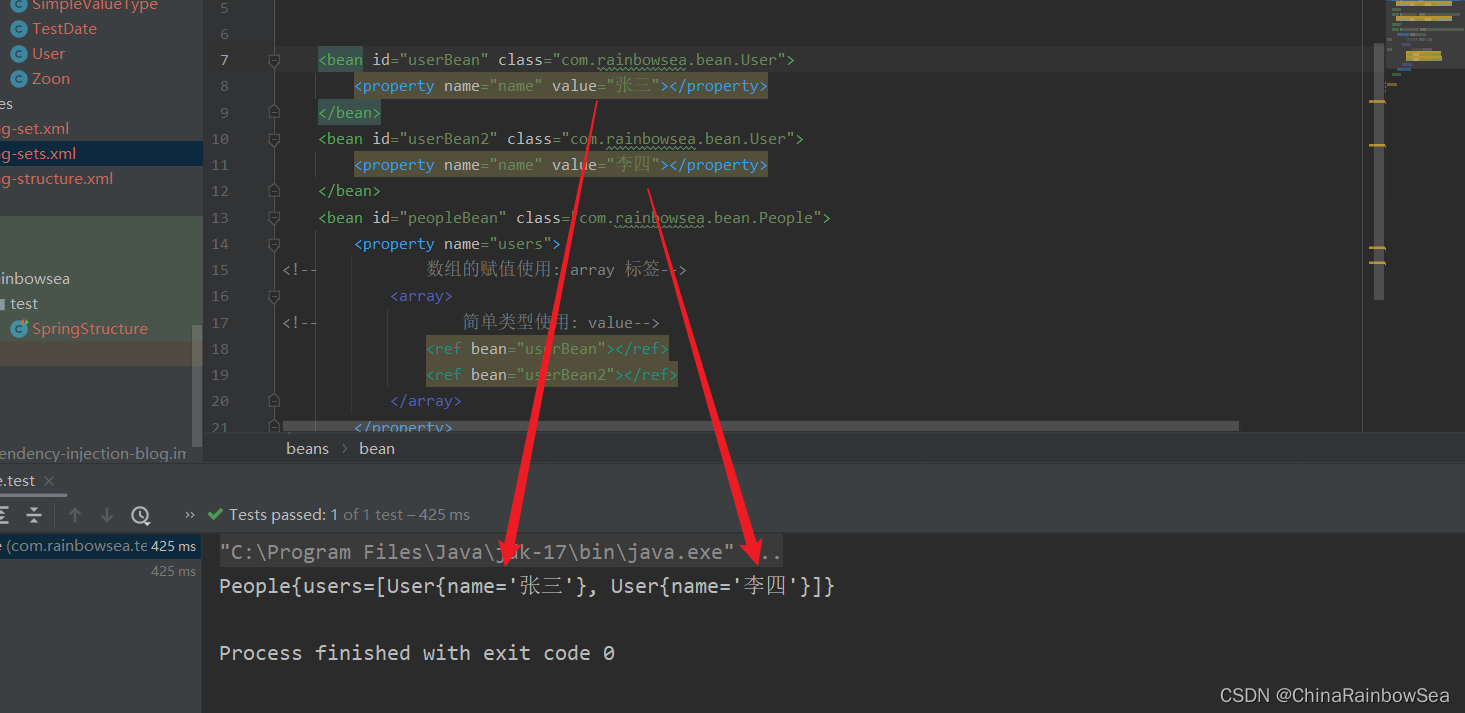
2.6 set註入List集合類型
List集合:有序可重覆
2.6.1 set 註入 List集合簡單類型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="name">
<!-- List 集合使用 <list> 標簽進行註入,簡單類型使用 <value> -->
<list>
<value>張三</value>
<value>李四</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.List;
public class People {
private List<String> name;
public void setName(List<String> name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name=" + name +
'}';
}
}
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
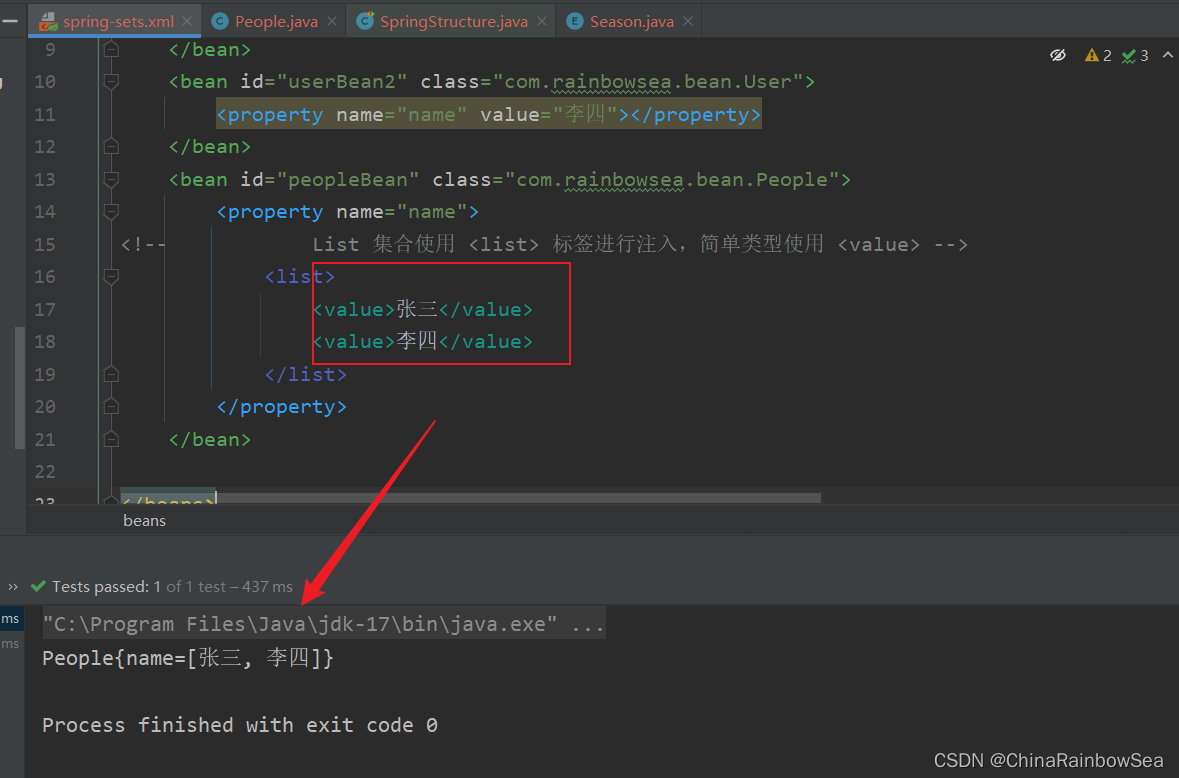
2.6.2 set 註入List集合複雜類型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="張三"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userBean2" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="李四"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="users">
<!-- List 集合使用 <list> 標簽進行註入,簡單類型使用 <ref> bean=對應的Id -->
<list>
<ref bean="userBean"></ref>
<ref bean="userBean2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
public class User {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bean;
import java.util.List;
public class People {
private List<User> users;
public void setUsers(List<User> users) {
this.users = users;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"users=" + users +
'}';
}
}
運行測試:
package com.rainbowsea.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.MyDataSource;
import com.rainbowsea.bean.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringStructure {
@Test
public void test() {
// 獲取到對應的 spring6當中的xml的,容器對象
// 面向介面編程,左邊為介面,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-sets.xml");
// 通過 id 獲取到對應的類/class
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
}
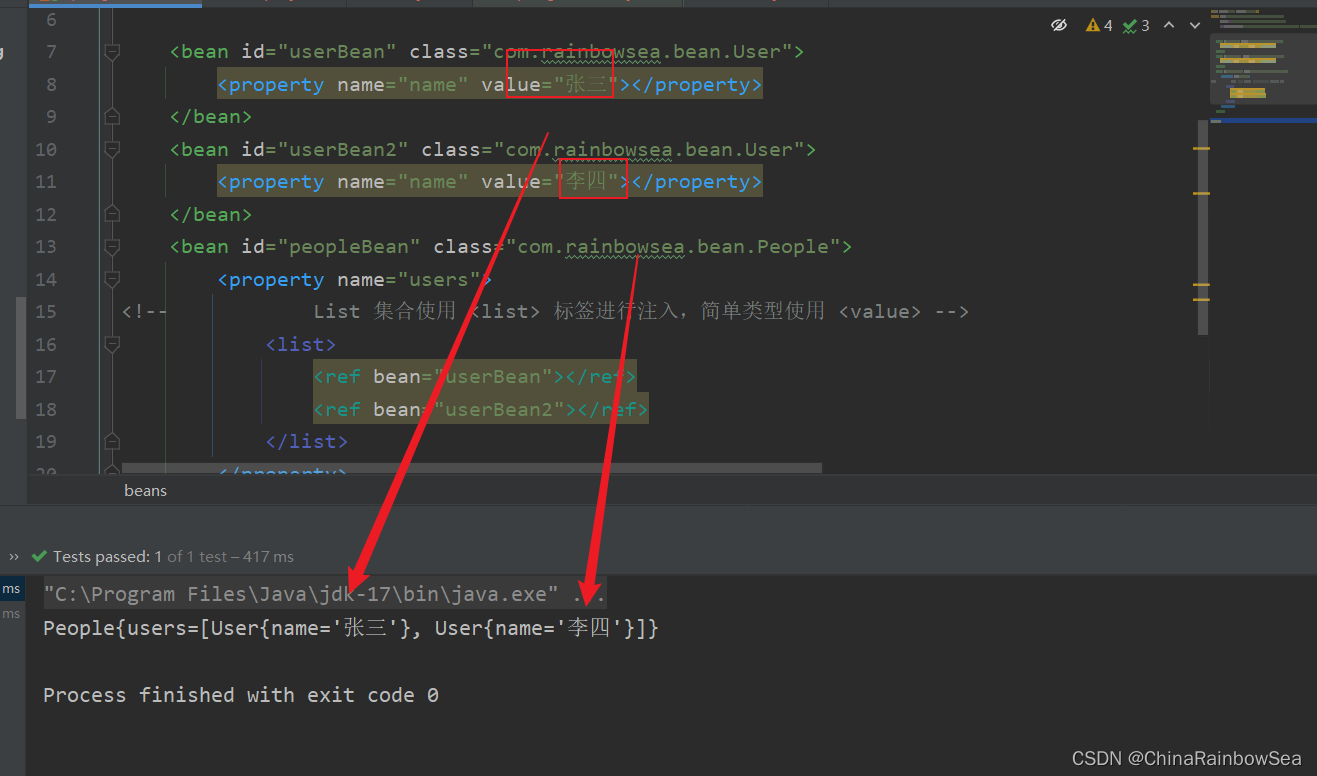
註意:註入List集合的時候使用list標簽,如果List集合中是簡單類型使用value標簽,反之使用ref標簽。
2.7 set註入Set集合類型
Set集合:無序不可重覆
2.7.1 set 註入 Set集合簡單類型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.rainbowsea.bean.People">
<property name="names">
<!-- set 集合使用 <set> 標簽進行註入,複雜類型使用 <value> 進行 -->
<set>
<value>張三</value>
<value>李四</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.rainbowsea.bean; import java.util.Set; public class People { private Set<String> names; public void setNames(Set<String> names) { this.names = names; } @Override public String toString() { return "People{" + "names=" + names + '}'; } }