原創:扣釘日記(微信公眾號ID:codelogs),歡迎分享,非公眾號轉載保留此聲明。 簡介 日常編程工作中,Java集合會經常被使用到,且經常需要對集合做一些類似過濾、排序、對象轉換之類的操作。 為了簡化這類操作,Java8添加了一套新的Stream API,使用方式就像寫SQL一樣,大大簡化了這 ...
原創:扣釘日記(微信公眾號ID:codelogs),歡迎分享,非公眾號轉載保留此聲明。
簡介
日常編程工作中,Java集合會經常被使用到,且經常需要對集合做一些類似過濾、排序、對象轉換之類的操作。
為了簡化這類操作,Java8添加了一套新的Stream API,使用方式就像寫SQL一樣,大大簡化了這類處理的實現代碼量與可讀性。
基礎Stream函數
比如,我們要查詢雙11期間交易額最大的10筆訂單的用戶信息,用SQL實現的話,大致如下:
select user_id, user_name
from order
where pay_time >= '2022-11-01' and pay_time < '2022-12-01'
order by goods_amount desc
limit 10;
這種處理邏輯,不用Stream API,實現代碼大致如下:
public static List<User> getTop10Users() throws ParseException {
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
// 過濾出雙11訂單
List<Order> filteredOrders = new ArrayList<>();
long begin = DateUtils.parseDate("2022-11-01", "yyyy-MM-dd").getTime();
long end = DateUtils.parseDate("2022-12-01", "yyyy-MM-dd").getTime();
for (Order order : orders) {
if(order.getPayTime().getTime() >= begin && order.getPayTime().getTime() < end) {
filteredOrders.add(order);
}
}
// 按訂單金額倒序排序
filteredOrders.sort(Comparator.comparing(Order::getGoodsAmount).reversed());
// 取前10名訂單,組裝出用戶信息
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
Iterator<Order> it = filteredOrders.iterator();
for (int i = 0; i < 10 && it.hasNext(); i++) {
Order order = it.next();
users.add(new User(order.getUserId(), order.getUserName()));
}
return users;
}
上面代碼與SQL的邏輯是一樣的,但可以發現,上面代碼的可理解性比SQL差很多,原因是SQL使用的是含義更加接近意圖的聲明式語法,而上述代碼如果沒有很好的註釋的話,則需要你的大腦像CPU一樣,將各種指令執行一遍才明白大概意圖。
那我們再用Stream API實現一下這個函數看看,如下:
public static List<User> getTop10Users() throws ParseException {
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
long begin = DateUtils.parseDate("2022-11-01", "yyyy-MM-dd").getTime();
long end = DateUtils.parseDate("2022-12-01", "yyyy-MM-dd").getTime();
List<User> users = orders.stream()
.filter(order -> order.getPayTime().getTime() >= begin && order.getPayTime().getTime() < end)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Order::getGoodsAmount).reversed())
.limit(10)
.map(order -> new User(order.getUserId(), order.getUserName()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return users;
}
這段代碼我沒有加註釋,但只要有過一點經驗的程式員,都能很快明白它是在做啥,這是因為Stream API和SQL設計類似,使用的是更加接近意圖的聲明式函數,看到函數名就大概明白含義了。
大概解釋一下,如下:
stream()函數用於將集合轉換為Stream流對象。filter()函數過濾Stream流中的元素,傳入的邏輯表達式則為過濾規則。sorted()函數排序Stream流中的元素,使用傳入的Comparator比較元素大小。limit()函數取前x個元素,傳入參數指定取的元素個數。map()函數用於轉換Stream中的元素為另一類型元素,可以類比於SQL從表中查詢指定欄位時,就好像是創建了一個包含這些欄位的臨時表一樣。
Stream裡面的函數大多很簡單,就不逐一介紹了,如下:
| 函數 | 用途 | 類比SQL |
|---|---|---|
| map | 轉換Stream中的元素為另一類型元素 | select x,y,z |
| filter | 過濾Stream中元素 | where |
| sorted | 排序Stream中元素 | order by |
| limit | 取前x個元素 | limit |
| distinct | 去重Stream中元素 | distinct |
| count | 計數 | count(*) |
| min | 計算最小值 | min(x) |
| max | 計算最大值 | max(x) |
| forEach | 消費Stream中的每個元素 | - |
| toArray | 轉換為數組 | - |
| findFirst | 獲取第1個元素 | - |
| findAny | 獲取任一個元素,與findFirst區別是findAny可能是數據拆分後多線程處理的,返回值可能不穩定 | - |
| allMatch | Stream中元素全部匹配判定表達式 | - |
| anyMatch | Stream中元素任一匹配判定表達式 | - |
| noneMatch | Stream中元素全部不匹配判定表達式 | - |
| peek | 檢查經過Stream的每個元素,但並不消費元素,一般用於調試目的 | - |
這些是Stream比較基礎的用法,下麵看看一些更高級的用法吧!
reduce函數
可以看到Stream提供了min、max操作,但並沒有提供sum、avg這樣的操作,如果要實現sum、avg操作,就可以使用reduce(迭代)函數來實現,reduce函數有3個,如下:
下麵以訂單金額的sum彙總操作為示例,如下:
帶初始值與累加器的reduce函數
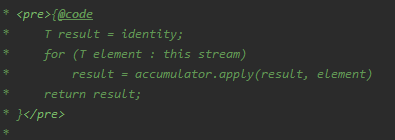
T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
彙總示例:
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
BigDecimal sum = orders.stream()
.map(Order::getGoodsAmount)
.reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);
其中,reduce函數的identity參數BigDecimal.ZERO相當於是初始值,而accumulator參數BigDecimal::add是一個累加器,將Stream中的金額一個個累加起來。
reduce函數的執行邏輯大致如下:
無初始值的reduce函數
Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
彙總示例:
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
BigDecimal sum = orders.stream()
.map(Order::getGoodsAmount)
.reduce(BigDecimal::add)
.orElse(BigDecimal.ZERO);
第2個reduce函數不傳入初始值,只有累加器函數,返回Optional,因此當Stream中沒有元素時,它返回的Optional沒有值,這種情況我使用Optional.orElse函數給了一個預設值BigDecimal.ZERO。
帶初始值、累加器、合併器的reduce函數
<U> U reduce(U identity,
BiFunction<U, ? super T, U> accumulator,
BinaryOperator<U> combiner);
彙總示例:
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
BigDecimal sum = orders.stream()
.reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, (s, o) -> s.add(o.getGoodsAmount()), BigDecimal::add);
這個reduce函數的累加器和前面的不一樣,前面的累加器的迭代元素與彙總結果都是BigDecimal,而這個累加器的迭代元素是Order類型,彙總結果是BigDecimal類型,它們可以不一樣。
另外,這個reduce函數還提供了一個合併器,它是做什麼用的?
其實合併器用於並行流場景,當使用多個線程處理數據時,數據拆分給多個線程後,每個線程使用累加器計算出自己的彙總值,然後使用合併器將各個線程的彙總值再次彙總,從而計算出最後結果,執行過程如下圖:
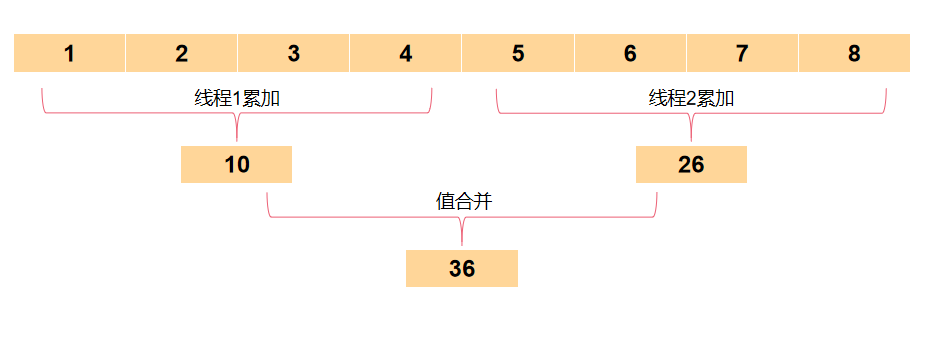
使用reduce實現avg
reduce可以實現avg,但稍微有點繁瑣,如下:
@Data
private static class SumCount {
private BigDecimal sum = BigDecimal.ZERO;
private Integer count = 0;
/**
* 累加函數
* @param val
* @return
*/
public SumCount accumulate(BigDecimal val) {
this.sum = this.sum.add(val);
this.count++;
return this;
}
/**
* 合併函數
* @param sumCount
* @return
*/
public SumCount merge(SumCount sumCount) {
SumCount sumCountNew = new SumCount();
sumCountNew.setSum(this.sum.add(sumCount.sum));
sumCountNew.setCount(this.count + sumCount.count);
return sumCountNew;
}
public Optional<BigDecimal> calAvg(int scale, int roundingMode) {
if (count == 0) {
return Optional.empty();
}
return Optional.of(this.sum.divide(BigDecimal.valueOf(count), scale, roundingMode));
}
}
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
Optional<BigDecimal> avg = orders.stream()
.map(Order::getGoodsAmount)
.reduce(new SumCount(), SumCount::accumulate, SumCount::merge)
.calAvg(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
如上,由於avg是由彙總值除以數量計算出來的,所以需要定義一個SumCount類來記錄彙總值與數量,並實現它的累加器與合併器函數即可。
可以發現,使用reduce函數實現avg功能,還是有點麻煩的,而且代碼可讀性不強,大腦需要繞一下才知道是在求平均數,而collect函數就可以很方便的解決這個問題。
collect函數
Stream API提供了一個collect(收集)函數,用來處理一些比較複雜的使用場景,它傳入一個收集器Collector用來收集流中的元素,並做特定的處理(如彙總),Collector定義如下:
public interface Collector<T, A, R> {
Supplier<A> supplier();
BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator();
BinaryOperator<A> combiner();
Function<A, R> finisher();
Set<Characteristics> characteristics();
}
其實,收集器與reduce是比較類似的,只是比reduce更加靈活了,如下:
- supplier: 初始彙總值提供器,類似reduce中的identity,只是這個初始值是函數提供的。
- accumulator:累加器,將值累加到收集器中,類似reduce中的accumulator。
- combiner:合併器,用於並行流場景,類似reduce中的combiner。
- finisher:結果轉換器,將彙總對象轉換為最終的指定類型對象。
- characteristics:收集器特征標識,如是否支持併發等。
那用收集器實現類似上面的avg試試!
@Data
public class AvgCollector implements Collector<BigDecimal, SumCount, Optional<BigDecimal>> {
private int scale;
private int roundingMode;
public AvgCollector(int scale, int roundingMode) {
this.scale = scale;
this.roundingMode = roundingMode;
}
@Override
public Supplier<SumCount> supplier() {
return SumCount::new;
}
@Override
public BiConsumer<SumCount, BigDecimal> accumulator() {
return (sumCount, bigDecimal) -> {
sumCount.setSum(sumCount.getSum().add(bigDecimal));
sumCount.setCount(sumCount.getCount() + 1);
};
}
@Override
public BinaryOperator<SumCount> combiner() {
return (sumCount, otherSumCount) -> {
SumCount sumCountNew = new SumCount();
sumCountNew.setSum(sumCount.getSum().add(otherSumCount.getSum()));
sumCountNew.setCount(sumCount.getCount() + otherSumCount.getCount());
return sumCountNew;
};
}
@Override
public Function<SumCount, Optional<BigDecimal>> finisher() {
return sumCount -> {
if (sumCount.getCount() == 0) {
return Optional.empty();
}
return Optional.of(sumCount.getSum().divide(
BigDecimal.valueOf(sumCount.getCount()), this.scale, this.roundingMode));
};
}
@Override
public Set<Characteristics> characteristics() {
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(EnumSet.of(Collector.Characteristics.UNORDERED));
}
}
如上,實現一個AvgCollector收集器,然後將這個收集器傳給collect函數即可。
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
Optional<BigDecimal>> avg = orders.stream()
.map(Order::getGoodsAmount)
.collect(new AvgCollector(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
整體執行過程如下:
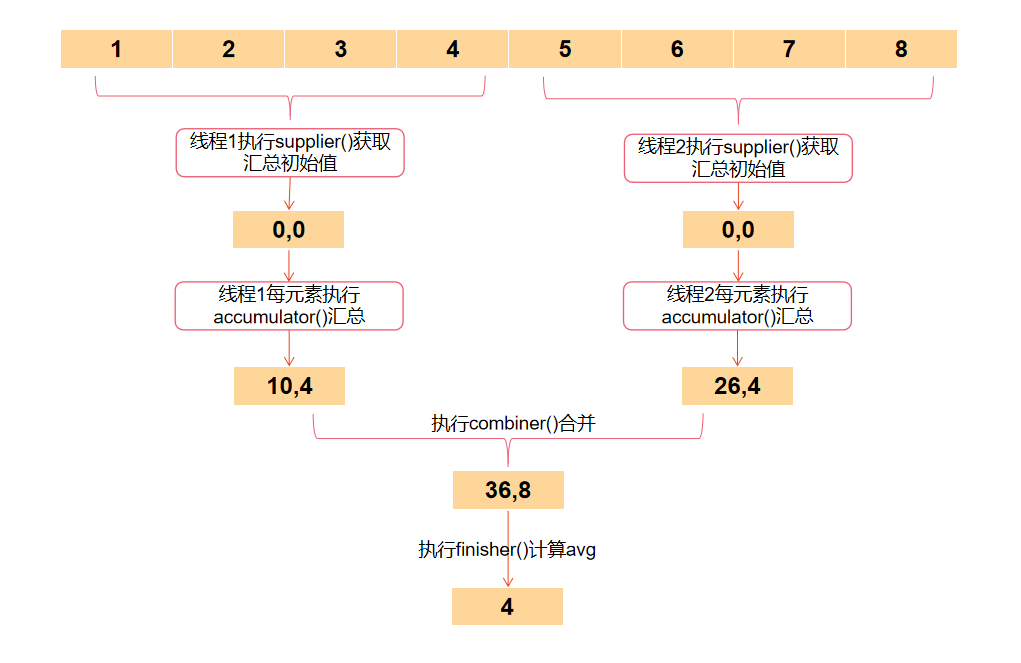
可以發現,其實Collector相比reduce,就是把相關操作都封裝到一個收集器裡面去了,這樣做的好處是,可以事先定義好一些Collector,然後使用方就可以直接拿來用了。
所以,Java也為我們提供了一系列常用場景的Collector,它們放在Collectors中,如下:
| 收集器 | 用途 |
|---|---|
Collectors.toList() |
將流中元素收集為List |
Collectors.toSet() |
將流中元素收集為Set |
Collectors.toMap() |
將流中元素收集為Map |
Collectors.toCollection() |
將流中元素收集為任意集合 |
Collectors.mapping() |
元素類型轉換 |
Collectors.counting() |
計數 |
Collectors.minBy() |
計算最小值 |
Collectors.maxBy() |
計算最大值 |
Collectors.summingXXX() |
求和 |
Collectors.averagingXXX() |
求平均數 |
Collectors.reducing() |
迭代操作 |
Collectors.groupingBy() |
分組彙總 |
Collectors.joining() |
拼接字元串 |
Collectors.collectingAndThen() |
收集結果後,對結果再執行一次類型轉換 |
可以發現,Java已經為我們提供了大量的收集器實現,對於絕大多數場景,我們並不需要自己去實現收集器啦!
以上函數就不一一介紹了,介紹幾個典型例子,如下:
元素收集到TreeSet中
TreeSet<Order> orderSet = orders.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));
元素收集到Map中
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
Map<Long, Order> orderMap = orders.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Order::getOrderId, Function.identity()));
如上,Order::getOrderId函數為Map提供Key值,Function.identity()函數定義如下:
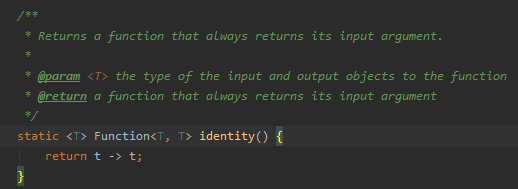
它的作用是直接返回傳給它的參數,你寫成o -> o也是可以的,如果你想得到Map<order_id, goods_amount>這樣的Map,那應該如下寫:
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
Map<Long, BigDecimal> amountMap = orders.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Order::getOrderId, Order::getGoodsAmount));
在知道了怎麼獲取Key與Value後,Collectors.toMap()收集器就知道怎麼去生成Map了。
但toMap有一個容易忽略的坑,就是預設情況下,如果List生成的Key值有重覆,則會拋出異常,如果你不想拋異常,可以再傳入一個衝突處理函數,如下:
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
Map<Long, Order> orderMap = orders.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Order::getOrderId, Function.identity(), (ov, v)->v));
(ov, v)->v函數含義是,當新元素Key值衝突時,ov是map中的舊值,v是新值,返回v則代表使用新值,即後面元素覆蓋前面元素的值。
實現分組彙總操作
比如我們經常需要將List分組為Map<K, List<V>>的形式,可以使用groupingBy收集器,看groupingBy收集器的定義,如下:
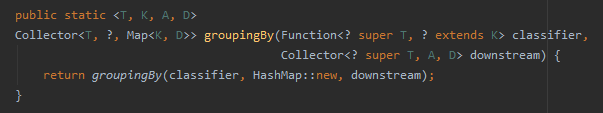
它需要提供兩個參數,第一個參數classifier指定分類的Key回調函數,第二個參數downstream指定下游收集器,即提供每個Key對應Value的聚合收集器。
看幾個例子:
按省份分組彙總訂單
Map<Integer, List<Order>> groupedOrderMap = orders.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Order::getProvince, Collectors.toList()));
其中Order::getProvince函數提供分類的Key值,Collectors.toList()提供分類後的Value聚合操作,將值聚合成List。
按省份分組彙總單量
類似如下SQL:
select province, count(*) from order group by province;
java實現如下:
Map<Integer, Long> groupedCountMap = orders.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Order::getProvince,
Collectors.counting()));
按省份分組彙總金額
類似如下SQL:
select province, sum(goods_amount) from order group by province;
java實現如下:
Map<Integer, Optional<BigDecimal>> groupedAmountMap = orders.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Order::getProvince,
Collectors.mapping(Order::getGoodsAmount,
Collectors.reducing(BigDecimal::add))));
按省份分組彙總單號
類似如下SQL:
select province, group_concat(order_id) from order group by province;
java實現如下:
Map<Integer, String> groupedOrderIdMap = orders.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Order::getProvince,
Collectors.mapping(order -> order.getOrderId().toString(),
Collectors.joining(","))));
按省、市彙總並計算單量、金額等
類似如下SQL:
select province, city, count(*), group_concat(order_id), group_concat(goods_amount),
sum(goods_amount), min(goods_amount), max(goods_amount), avg(goods_amount)
from order
group by province, city;
java實現如下:
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
class ProvinceCityStatistics {
private Integer province;
private Integer city;
private Long count;
private String orderIds;
private List<BigDecimal> amounts;
private BigDecimal sum;
private BigDecimal min;
private BigDecimal max;
private BigDecimal avg;
public ProvinceCityStatistics(Order order){
this.province = order.getProvince();
this.city = order.getCity();
this.count = 1L;
this.orderIds = String.valueOf(order.getOrderId());
this.amounts = new ArrayList<>(Collections.singletonList(order.getGoodsAmount()));
this.sum = order.getGoodsAmount();
this.min = order.getGoodsAmount();
this.max = order.getGoodsAmount();
this.avg = order.getGoodsAmount();
}
public ProvinceCityStatistics accumulate(ProvinceCityStatistics other) {
this.count = this.count + other.count;
this.orderIds = this.orderIds + "," + other.orderIds;
this.amounts.addAll(other.amounts);
this.sum = this.sum.add(other.sum);
this.min = this.min.compareTo(other.min) <= 0 ? this.min : other.min;
this.max = this.max.compareTo(other.max) >= 0 ? this.max : other.max;
this.avg = this.sum.divide(BigDecimal.valueOf(this.count), 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
return this;
}
}
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
Map<String, Optional<ProvinceCityStatistics>> groupedMap = orders.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(order -> order.getProvince() + "," + order.getCity(),
Collectors.mapping(order -> new ProvinceCityStatistics(order),
Collectors.reducing(ProvinceCityStatistics::accumulate)))
);
groupedMap.values().stream().map(Optional::get).forEach(provinceCityStatistics -> {
Integer province = provinceCityStatistics.getProvince();
Integer city = provinceCityStatistics.getCity();
long count = provinceCityStatistics.getCount();
String orderIds = provinceCityStatistics.getOrderIds();
List<BigDecimal> amounts = provinceCityStatistics.getAmounts();
BigDecimal sum = provinceCityStatistics.getSum();
BigDecimal min = provinceCityStatistics.getMin();
BigDecimal max = provinceCityStatistics.getMax();
BigDecimal avg = provinceCityStatistics.getAvg();
System.out.printf("province:%d, city: %d -> count: %d, orderIds: %s, amounts: %s," +
" sum: %s, min: %s, max: %s, avg : %s %n",
province, city, count, orderIds, amounts, sum, min, max, avg);
});
執行結果如下:

可以發現,使用Collectors.reducing可以實現功能,但有點繁瑣,且代碼含義不明顯,因此我封裝了一個MultiCollector收集器,用來將多種收集器組合起來,實現這種複雜場景,如下:
/**
* 將多個收集器,組合成一個收集器
* 彙總結果保存在Map<String, Object>中,最終結果轉換成R類型返回
*
* @param <T>
*/
public class MultiCollector<T, R> implements Collector<T, Map<String, Object>, R> {
private Class<R> clazz;
private Map<String, Collector<T, ?, ?>> collectorMap;
public MultiCollector(Class<R> clazz, Map<String, Collector<T, ?, ?>> collectorMap) {
this.clazz = clazz;
this.collectorMap = collectorMap;
}
@Override
public Supplier<Map<String, Object>> supplier() {
Map<String, Supplier<?>> supplierMap = new HashMap<>();
collectorMap.forEach((fieldName, collector) -> supplierMap.put(fieldName, collector.supplier()));
return () -> {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
supplierMap.forEach((fieldName, supplier) -> {
map.put(fieldName, supplier.get());
});
return map;
};
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public BiConsumer<Map<String, Object>, T> accumulator() {
Map<String, BiConsumer<?, T>> accumulatorMap = new HashMap<>();
collectorMap.forEach((fieldName, collector) -> accumulatorMap.put(fieldName, collector.accumulator()));
return (map, order) -> {
accumulatorMap.forEach((fieldName, accumulator) -> {
((BiConsumer)accumulator).accept(map.get(fieldName), order);
});
};
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public BinaryOperator<Map<String, Object>> combiner() {
Map<String, BinaryOperator<?>> combinerMap = new HashMap<>();
collectorMap.forEach((fieldName, collector) -> combinerMap.put(fieldName, collector.combiner()));
return (map, otherMap) -> {
combinerMap.forEach((fieldName, combiner) -> {
map.put(fieldName, ((BinaryOperator)combiner).apply(map.get(fieldName), otherMap.get(fieldName)));
});
return map;
};
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public Function<Map<String, Object>, R> finisher() {
Map<String, Function<?, ?>> finisherMap = new HashMap<>();
collectorMap.forEach((fieldName, collector) -> finisherMap.put(fieldName, collector.finisher()));
// 將Map<String, Object>反射轉換成指定類對象,這裡用json反序列化也可以
return map -> {
R result = newInstance(clazz);
finisherMap.forEach((fieldName, finisher) -> {
Object value = ((Function)finisher).apply(map.get(fieldName));
setFieldValue(result, fieldName, value);
});
return result;
};
}
@Override
public Set<Characteristics> characteristics() {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
private static <R> R newInstance(Class<R> clazz){
try {
return clazz.newInstance();
} catch (ReflectiveOperationException e) {
return ExceptionUtils.rethrow(e);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("all")
private static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value){
if (obj instanceof Map){
((Map)obj).put(fieldName, value);
} else {
try {
new PropertyDescriptor(fieldName, obj.getClass()).getWriteMethod().invoke(obj, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
ExceptionUtils.rethrow(e);
}
}
}
}
然後封裝一些語義更加明確的通用Collector方法,如下:
public class CollectorUtils {
/**
* 取第一個元素,類似Stream.findFirst,返回Optional<U>
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T,U> Collector<T, ?, Optional<U>> findFirst(Function<T, U> mapper){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper, Collectors.reducing((u1, u2) -> u1));
}
/**
* 取第一個元素,類似Stream.findFirst,返回U,可能是null
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T,U> Collector<T, ?, U> findFirstNullable(Function<T, U> mapper){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper,
Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.reducing((u1, u2) -> u1), opt -> opt.orElse(null)));
}
/**
* 收集指定欄位值為List
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T,U> Collector<T, ?, List<U>> toList(Function<T, U> mapper){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper, Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 收集指定欄位為逗號分隔的字元串
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T, U> Collector<T, ?, String> joining(Function<T, U> mapper, CharSequence delimiter){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper.andThen(o -> Objects.toString(o, "")), Collectors.joining(delimiter));
}
/**
* 對BigDecimal求和,返回Optional<BigDecimal>類型彙總值
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T> Collector<T, ?, Optional<BigDecimal>> summingBigDecimal(Function<T, BigDecimal> mapper){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper, Collectors.reducing(BigDecimal::add));
}
/**
* 對BigDecimal求和,返回BigDecimal類型彙總值,可能是null
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T> Collector<T, ?, BigDecimal> summingBigDecimalNullable(Function<T, BigDecimal> mapper){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper,
Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.reducing(BigDecimal::add), opt -> opt.orElse(null)));
}
/**
* 對BigDecimal求平均值,返回Optional<BigDecimal>類型平均值
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T> Collector<T, ?, Optional<BigDecimal>> averagingBigDecimal(Function<T, BigDecimal> mapper, int scale, int roundingMode){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper, new AvgCollector(scale, roundingMode));
}
/**
* 對BigDecimal求平均值,返回BigDecimal類型平均值,可能是null
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T> Collector<T, ?, BigDecimal> averagingBigDecimalNullable(Function<T, BigDecimal> mapper, int scale, int roundingMode){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper,
Collectors.collectingAndThen(
new AvgCollector(scale, roundingMode), opt -> opt.orElse(null)));
}
/**
* 求最小值,返回最小值Optional<U>
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T,U extends Comparable<? super U>> Collector<T, ?, Optional<U>> minBy(Function<T, U> mapper){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper, Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(Function.identity())));
}
/**
* 求最小值,返回最小值U,可能是null
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T,U extends Comparable<? super U>> Collector<T, ?, U> minByNullable(Function<T, U> mapper){
return Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.mapping(mapper,
Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(Function.identity()))), opt -> opt.orElse(null));
}
/**
* 求最大值,返回最大值Optional<U>
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T,U extends Comparable<? super U>> Collector<T, ?, Optional<U>> maxBy(Function<T, U> mapper){
return Collectors.mapping(mapper, Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Function.identity())));
}
/**
* 求最大值,返回最大值U,可能是null
* @param mapper 獲取欄位值的函數
* @return
*/
public static <T,U extends Comparable<? super U>> Collector<T, ?, U> maxByNullable(Function<T, U> mapper){
return Collectors.collectingAndThen(
Collectors.mapping(mapper,
Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Function.identity()))), opt -> opt.orElse(null));
}
}
CollectorUtils中封裝的各Collector用途如下:
| 方法 | 用途 |
|---|---|
findFirst(mapper) |
獲取第一個值,類似Stream.findFirst,返回Optional |
findFirstlNullable(mapper) |
獲取第一個值,類似Stream.findFirst,返回值可能是null |
toList(mapper) |
用於實現對指定欄位收集為List |
joining(mapper) |
實現類似group_concat(order_id)的功能 |
summingBigDecimal(mapper) |
用於對BigDecimal做彙總處理,返回Optional<BigDecimal> |
summingBigDecimalNullable(mapper) |
用於對BigDecimal做彙總處理,返回BigDecimal |
averagingBigDecimal(mapper) |
實現對BigDecimal求平均數,返回Optional<BigDecimal> |
averagingBigDecimal(mapper) |
實現對BigDecimal求平均數,返回BigDecimal |
minBy(mapper) |
實現求最小值,返回Optional<BigDecimal> |
minByNullable(mapper) |
實現求最小值,返回BigDecimal |
maxBy(mapper) |
實現求最大值,返回Optional<BigDecimal> |
maxByNullable(mapper) |
實現求最大值,返回BigDecimal |
然後結合MultiCollector收集器與CollectorUtils中的各種Collector,就可以實現各種複雜的分組彙總邏輯了,如下:
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
class ProvinceCityStatistics {
private Integer province;
private Integer city;
private Long count;
private String orderIds;
private List<BigDecimal> amounts;
private BigDecimal sum;
private BigDecimal min;
private BigDecimal max;
private BigDecimal avg;
}
List<Order> orders = getOrders();
Map<String, ProvinceCityStatistics> groupedMap = orders.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(order -> order.getProvince() + "," + order.getCity(),
new MultiCollector<>(
ProvinceCityStatistics.class,
//指定ProvinceCityStatistics各欄位對應的收集器
MapBuilder.<String, Collector<Order, ?, ?>>create()
.put("province", CollectorUtils.findFirstNullable(Order::getProvince))
.put("city", CollectorUtils.findFirstNullable(Order::getCity))
.put("count", Collectors.counting())
.put("orderIds", CollectorUtils.joining(Order::getOrderId, ","))
.put("amounts", CollectorUtils.toList(Order::getGoodsAmount))
.put("sum", CollectorUtils.summingBigDecimalNullable(Order::getGoodsAmount))
.put("min", CollectorUtils.minByNullable(Order::getGoodsAmount))
.put("max", CollectorUtils.maxByNullable(Order::getGoodsAmount))
.put("avg", CollectorUtils.averagingBigDecimalNullable(Order::getGoodsAmount, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP))
.build()
)
)
);
groupedMap.forEach((key, provinceCityStatistics) -> {
Integer province = provinceCityStatistics.getProvince();
Integer city = provinceCityStatistics.getCity();
long count = provinceCityStatistics.getCount();
String orderIds = provinceCityStatistics.getOrderIds();
List<BigDecimal> amounts = provinceCityStatistics.getAmounts();
BigDecimal sum = provinceCityStatistics.getSum();
BigDecimal min = provinceCityStatistics.getMin();
BigDecimal max = provinceCityStatistics.getMax();
BigDecimal avg = provinceCityStatistics.getAvg();
System.out.printf("province:%d, city: %d -> count: %d, orderIds: %s, amounts: %s," +
" sum: %s, min: %s, max: %s, avg : %s %n",
province, city, count, orderIds, amounts, sum, min, max, avg);
});
執行結果如下:

我想如果搞懂了這個,Collector API幾乎就全玩明白了



