1. 三大組件簡介 Channel 與 Buffer Java NIO 系統的核心在於:通道 (Channel) 和緩衝區 (Buffer)。通道表示打開到 IO 設備 (例如:文件、套接字) 的連接。若需要使用 NIO 系統,需要獲取用於連接 IO 設備的通道 以及用於容納數據的緩衝區。然後操作緩 ...
1. 三大組件簡介
Channel 與 Buffer
Java NIO 系統的核心在於:通道 (Channel) 和緩衝區 (Buffer)。通道表示打開到 IO 設備 (例如:文件、套接字) 的連接。若需要使用 NIO 系統,需要獲取用於連接 IO 設備的通道 以及用於容納數據的緩衝區。然後操作緩衝區,對數據進行處理
簡而言之,通道負責傳輸,緩衝區負責存儲
常見的 Channel 有以下四種,其中 FileChannel 主要用於文件傳輸,其餘三種用於網路通信
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
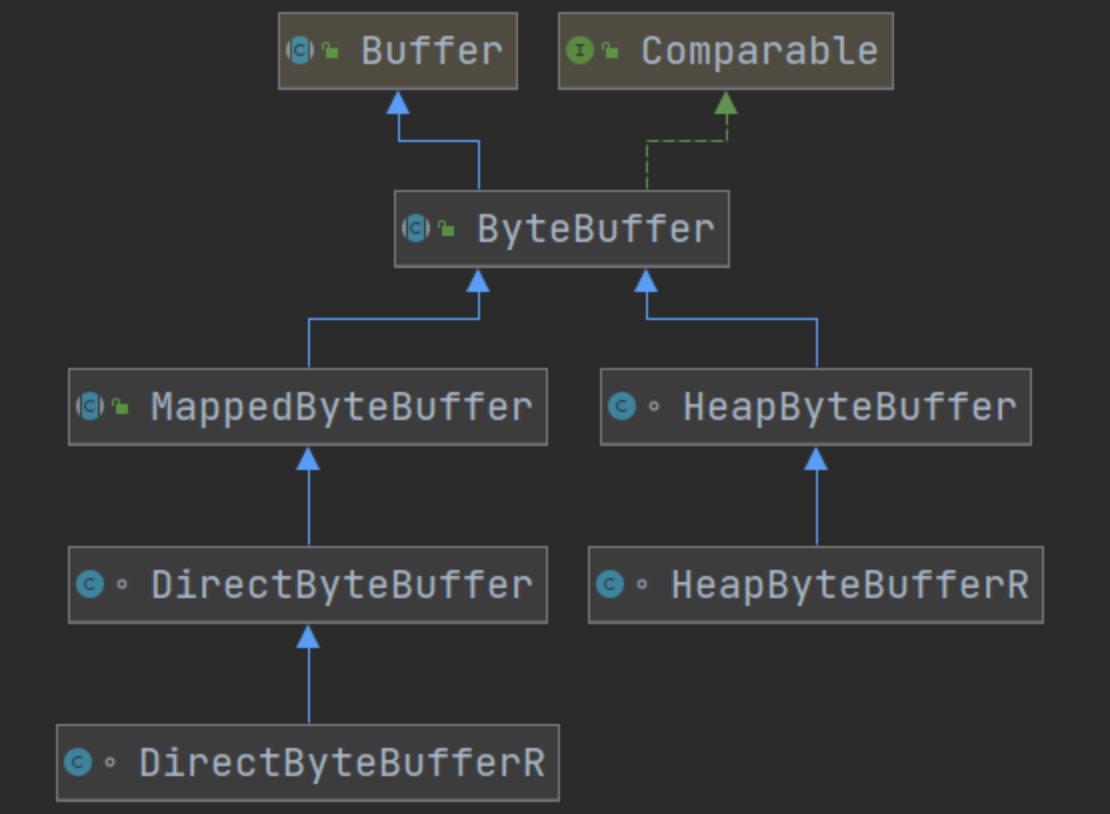
Buffer 有以下幾種,其中使用較多的是 ByteBuffer
-
ByteBuffer
- MappedByteBuffer
- DirectByteBuffer
- HeapByteBuffer
-
ShortBuffer
-
IntBuffer
-
LongBuffer
-
FloatBuffer
-
DoubleBuffer
-
CharBuffer
1、Selector
在使用 Selector 之前,處理 socket 連接還有以下兩種方法
使用多線程技術
為每個連接分別開闢一個線程,分別去處理對應的 socket 連接
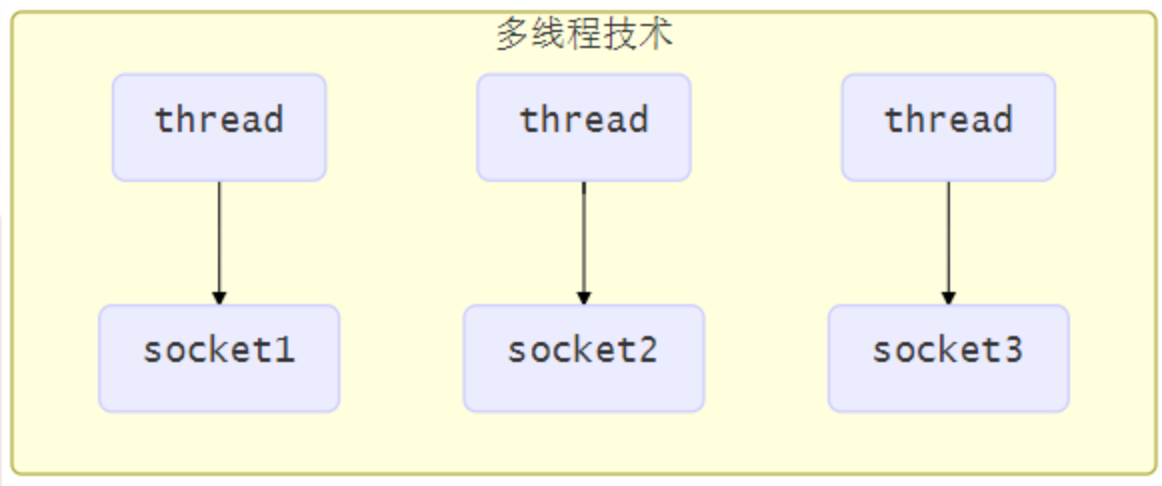
這種方法存在以下幾個問題
- 記憶體占用高
- 每個線程都需要占用一定的記憶體,當連接較多時,會開闢大量線程,導致占用大量記憶體
- 線程上下文切換成本高
- 只適合連接數少的場景
- 連接數過多,會導致創建很多線程,從而出現問題
使用線程池技術
使用線程池,讓線程池中的線程去處理連接
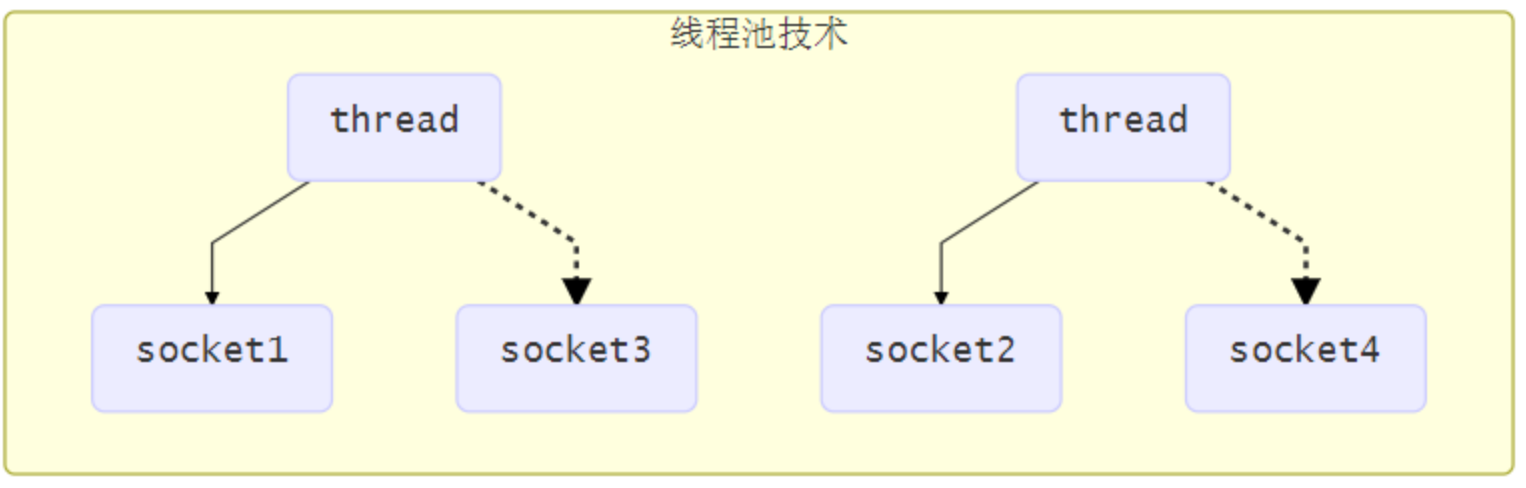
這種方法存在以下幾個問題
- 阻塞模式下,線程僅能處理一個連接
- 線程池中的線程獲取任務(task)後,只有當其執行完任務之後(斷開連接後),才會去獲取並執行下一個任務
- 若 socke 連接一直未斷開,則其對應的線程無法處理其他 socke 連接
- 僅適合短連接場景
- 短連接即建立連接發送請求並響應後就立即斷開,使得線程池中的線程可以快速處理其他連接
使用選擇器
selector 的作用就是配合一個線程來管理多個 channel(fileChannel 因為是阻塞式的,所以無法使用 selector),,獲取這些 channel 上發生的事件,這些 channel 工作在非阻塞模式下,當一個 channel 中沒有執行任務時,可以去執行其他channel 中的任務。適合連接數多,但流量較少的場景
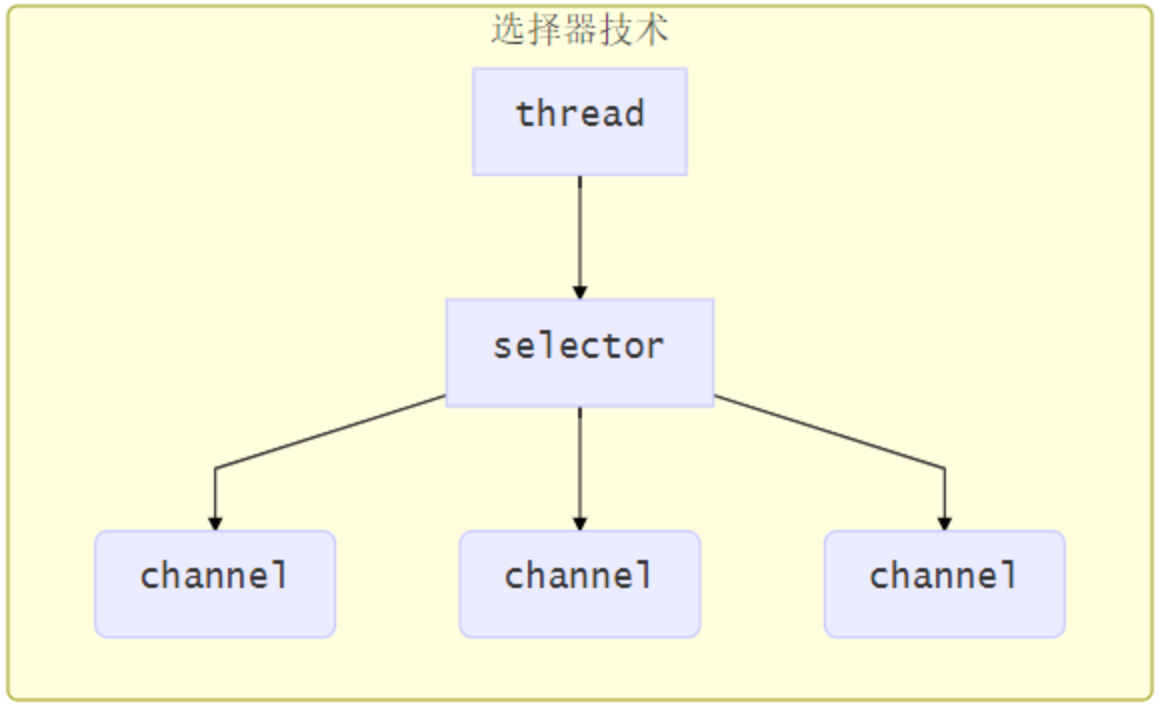
若事件未就緒,調用 selector 的 select () 方法會阻塞線程,直到 channel 發生了就緒事件。這些事件就緒後,select 方法就會返回這些事件交給 thread 來處理
2、ByteBuffer
使用案例
使用方式
-
向 buffer 寫入數據,例如調用 channel.read (buffer)
-
調用 flip () 切換至
讀模式
- flip 會使得 buffer 中的 limit 變為 position,position 變為 0
-
從 buffer 讀取數據,例如調用 buffer.get ()
-
調用 clear () 或者 compact () 切換至
寫模式
- 調用 clear () 方法時 position=0,limit 變為 capacity
- 調用 compact () 方法時,會將緩衝區中的未讀數據壓縮到緩衝區前面
-
重覆以上步驟
使用 ByteBuffer 讀取文件中的內容
public class TestByteBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("stu.txt").getChannel()){
//給緩衝區 分配空間
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
int read = 0 ;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
while ((read =channel.read(buffer))>0){
//切換成 讀模式 limit = position; position=0
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()){
builder.append((char)buffer.get());
}
//清空位元組數組 切換成 寫模式 position=0 ;limit = capacity
buffer.clear();
}
System.out.println(builder.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
}
}
列印結果:
0123456789abcdef
核心屬性
位元組緩衝區的父類 Buffer 中有幾個核心屬性,如下
// Invariants: mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity;
- capacity:緩衝區的容量。通過構造函數賦予,一旦設置,無法更改
- limit:緩衝區的界限。位於 limit 後的數據不可讀寫。緩衝區的限制不能為負,並且 不能大於其容量
- position: 下一個讀寫位置的索引(類似 PC)。緩衝區的位置不能為負,並且不能大於 limit
- mark:記錄當前 position 的值。position 被改變後,可以通過調用 reset () 方法恢復到 mark 的位置。
以上四個屬性必須滿足以下要求
mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
核心方法
put () 方法
- put () 方法可以將一個數據放入到緩衝區中。
- 進行該操作後,postition 的值會 +1,指向下一個可以放入的位置。capacity = limit ,為緩衝區容量的值。
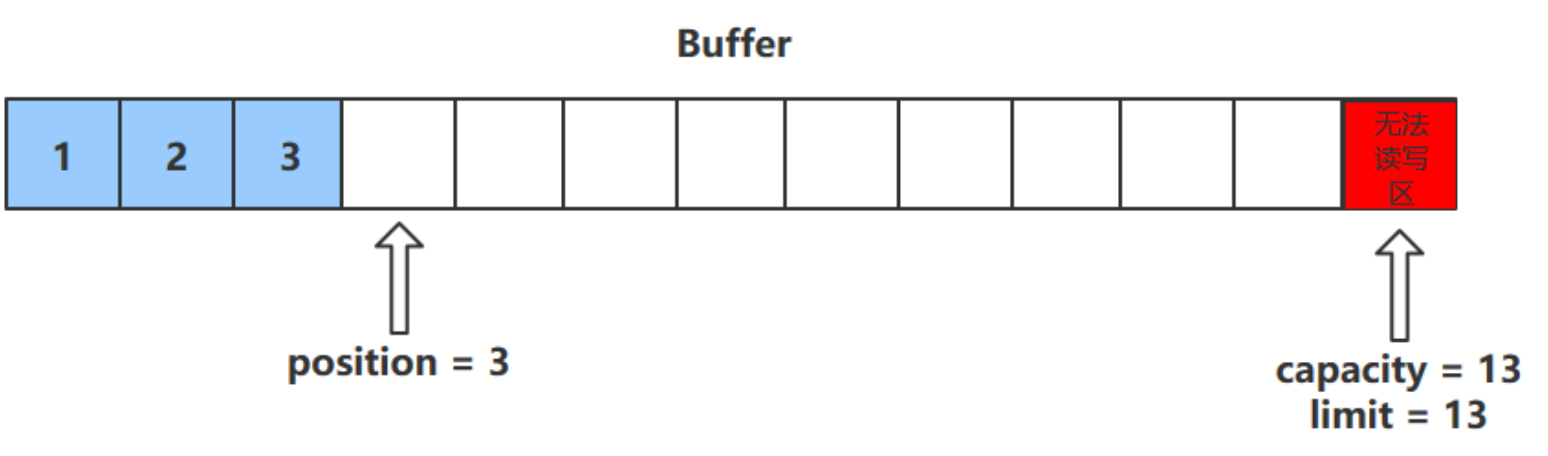
flip () 方法
- flip () 方法會 切換對緩衝區的操作模式 ,由 寫 -> 讀 / 讀 -> 寫
- 進行該操作後
- 如果是 寫模式 -> 讀模式,position = 0 , limit 指向最後一個元素的下一個位置,capacity 不變
- 如果是讀 -> 寫 ,則恢復為 put () 方法中的值
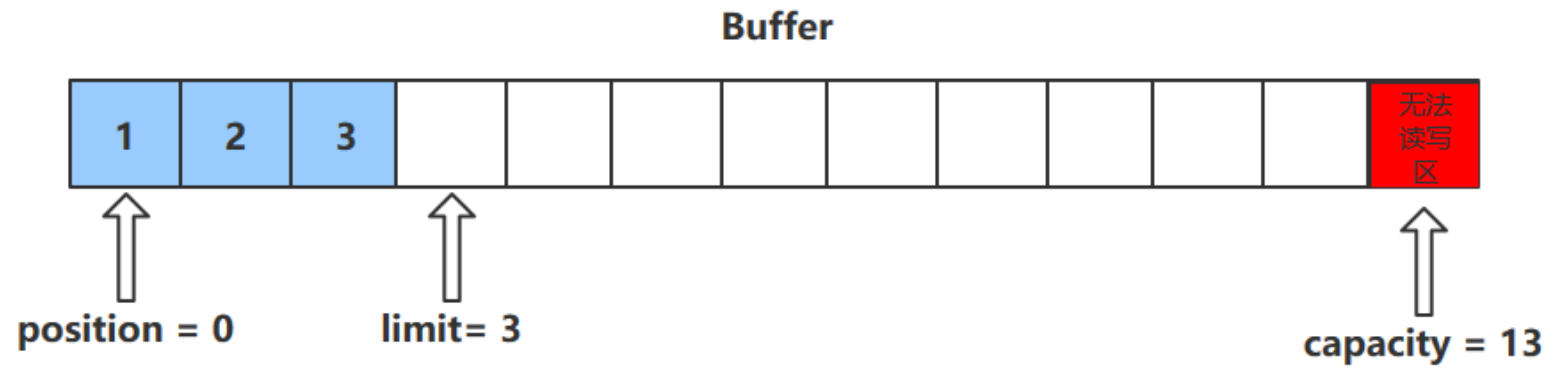
get () 方法
- get () 方法會讀取緩衝區中的一個值
- 進行該操作後,position 會 +1 ,如果超過了 limit 則會拋出異常
- 註意:get (i) 方法不會改變 position 的值
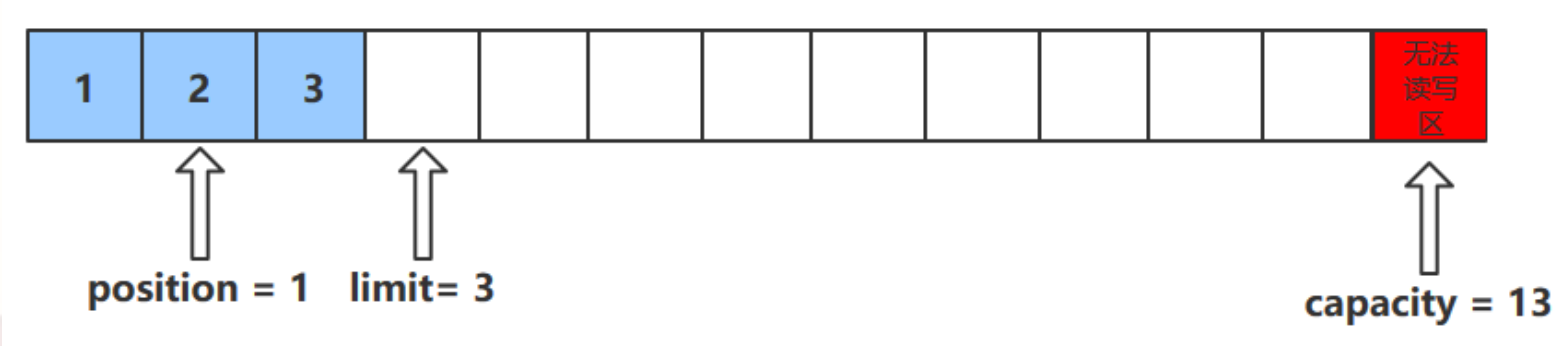
rewind () 方法
- 該方法 只能在讀模式下使用
- rewind () 方法後,會恢復 position、limit 和 capacity 的值,變為進行 get () 前的值
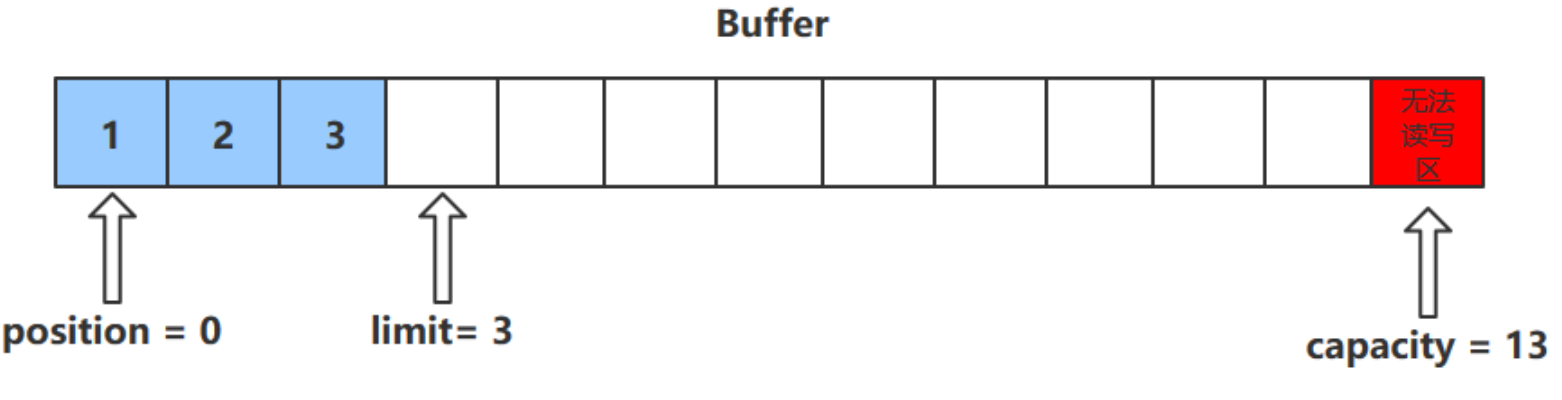
clear () 方法
- clear () 方法會將緩衝區中的各個屬性恢復為最初的狀態,position = 0, capacity = limit
- 此時緩衝區的數據依然存在,處於 “被遺忘” 狀態,下次進行寫操作時會覆蓋這些數據
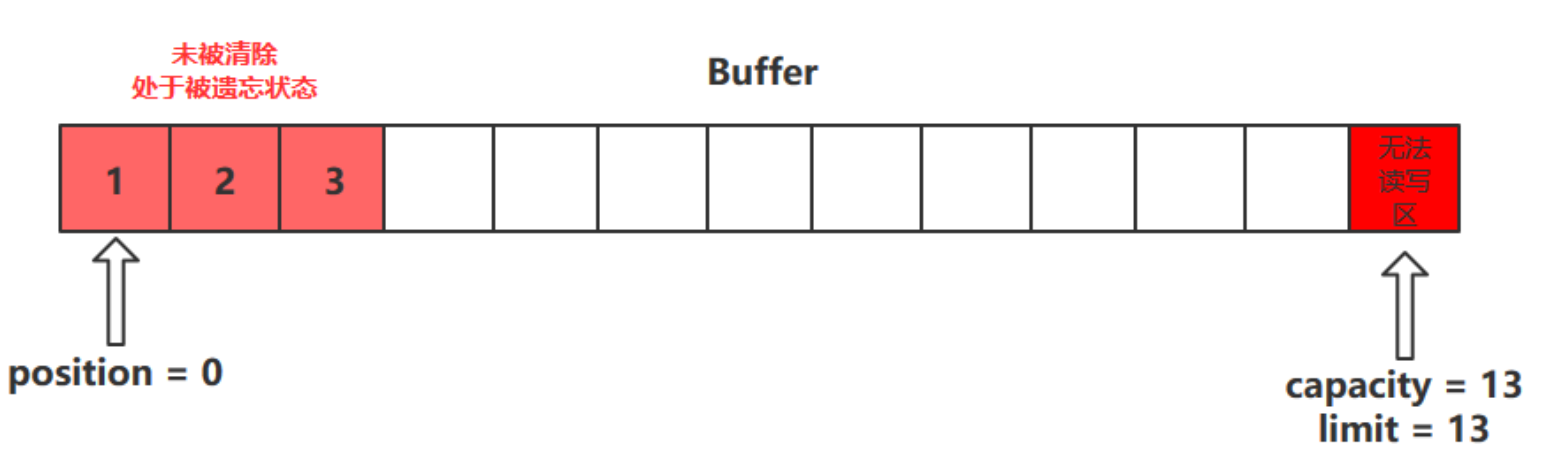
mark () 和 reset () 方法
- mark () 方法會將 postion 的值保存到 mark 屬性中
- reset () 方法會將 position 的值改為 mark 中保存的值
compact () 方法
此方法為 ByteBuffer 的方法,而不是 Buffer 的方法
- compact 會把未讀完的數據向前壓縮,然後切換到寫模式
- 數據前移後,原位置的值並未清零,寫時會覆蓋之前的值
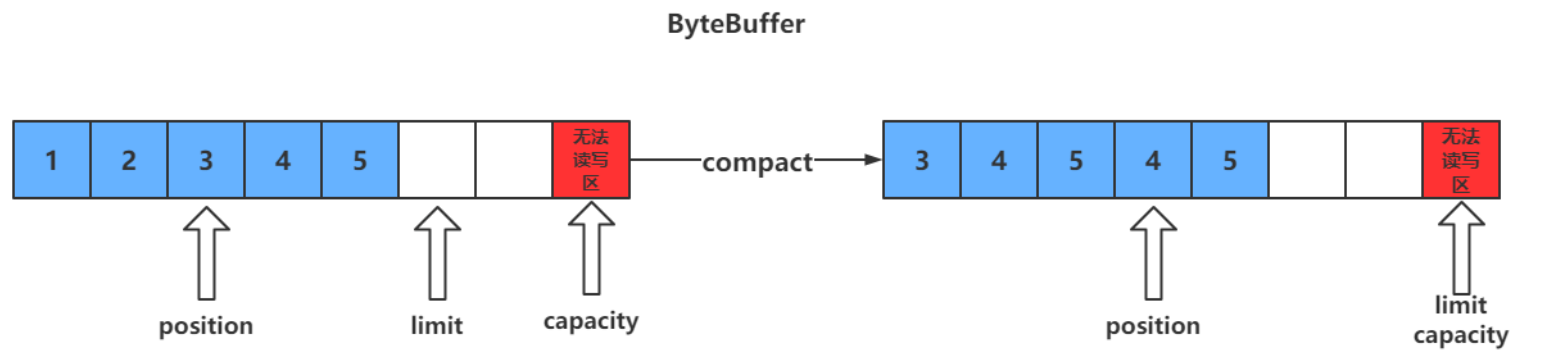
clear() VS compact()
clear 只是對 position、limit、mark 進行重置,而 compact 在對 position 進行設置,以及 limit、mark 進行重置的同時,還涉及到數據在記憶體中拷貝(會調用 array)。所以 compact 比 clear 更耗性能。但 compact 能保存你未讀取的數據,將新數據追加到為讀取的數據之後;而 clear 則不行,若你調用了 clear,則未讀取的數據就無法再讀取到了
所以需要根據情況來判斷使用哪種方法進行模式切換
方法調用及演示
ByteBuffer 調試工具類
需要先導入 netty 依賴
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.51.Final</version>
</dependency>
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import io.netty.util.internal.MathUtil;
import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil;
import io.netty.util.internal.MathUtil.*;
public class ByteBufferUtil {
private static final char[] BYTE2CHAR = new char[256];
private static final char[] HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4];
private static final String[] HEXPADDING = new String[16];
private static final String[] HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4];
private static final String[] BYTE2HEX = new String[256];
private static final String[] BYTEPADDING = new String[16];
static {
final char[] DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F];
HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F];
}
int i;
// Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(" ");
}
HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB).
for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12);
buf.append(StringUtil.NEWLINE);
buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
buf.setCharAt(buf.length() - 9, '|');
buf.append('|');
HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) {
BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i);
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(' ');
}
BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) {
if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.';
} else {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i;
}
}
}
/**
* 列印所有內容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugAll(ByteBuffer buffer) {
int oldlimit = buffer.limit();
buffer.limit(buffer.capacity());
StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), oldlimit);
System.out.println(origin);
buffer.limit(oldlimit);
}
/**
* 列印可讀取內容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugRead(ByteBuffer buffer) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.limit() - buffer.position());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), buffer.limit());
System.out.println(builder);
}
private static void appendPrettyHexDump(StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) {
if (MathUtil.isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity())) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length
+ ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity() + ')');
}
if (length == 0) {
return;
}
dump.append(
" +-------------------------------------------------+" +
StringUtil.NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" +
StringUtil.NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
final int startIndex = offset;
final int fullRows = length >>> 4;
final int remainder = length & 0xF;
// Dump the rows which have 16 bytes.
for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) {
int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex;
// Per-row prefix.
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(" |");
// ASCII dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append('|');
}
// Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes.
if (remainder != 0) {
int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex;
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append(" |");
// Ascii dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append('|');
}
dump.append(StringUtil.NEWLINE +
"+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
}
private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix(StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) {
if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) {
dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]);
} else {
dump.append(StringUtil.NEWLINE);
dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
dump.setCharAt(dump.length() - 9, '|');
dump.append('|');
}
}
public static short getUnsignedByte(ByteBuffer buffer, int index) {
return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF);
}
}
調用 ByteBuffer 的方法
public class TestByteBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
// 向buffer中寫入1個位元組的數據
buffer.put((byte)97);
// 使用工具類,查看buffer狀態
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
// 向buffer中寫入4個位元組的數據
buffer.put(new byte[]{98, 99, 100, 101});
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
// 獲取數據
buffer.flip();
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
System.out.println(buffer.get());
System.out.println(buffer.get());
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
// 使用compact切換模式
buffer.compact();
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
// 再次寫入
buffer.put((byte)102);
buffer.put((byte)103);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
}
}
運行結果
// 向緩衝區寫入了一個位元組的數據,此時postition為1
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [1], limit: [10]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |a......... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
// 向緩衝區寫入四個位元組的數據,此時position為5
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [10]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 62 63 64 65 00 00 00 00 00 |abcde..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
// 調用flip切換模式,此時position為0,表示從第0個數據開始讀取
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 62 63 64 65 00 00 00 00 00 |abcde..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
// 讀取兩個位元組的數據
97
98
// position變為2
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [2], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 62 63 64 65 00 00 00 00 00 |abcde..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
// 調用compact切換模式,此時position及其後面的數據被壓縮到ByteBuffer前面去了
// 此時position為3,會覆蓋之前的數據
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [3], limit: [10]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 63 64 65 64 65 00 00 00 00 00 |cdede..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
// 再次寫入兩個位元組的數據,之前的 0x64 0x65 被覆蓋
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [10]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 63 64 65 66 67 00 00 00 00 00 |cdefg..... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
字元串與 ByteBuffer 的相互轉換
方法一
編碼:字元串調用 getByte 方法獲得 byte 數組,將 byte 數組放入 ByteBuffer 中
解碼:先調用 ByteBuffer 的 flip 方法,然後通過 StandardCharsets 的 decoder 方法解碼
public class Translate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 準備兩個字元串
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "";
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
// 通過字元串的getByte方法獲得位元組數組,放入緩衝區中
buffer1.put(str1.getBytes());
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);
// 將緩衝區中的數據轉化為字元串
// 切換模式
buffer1.flip();
// 通過StandardCharsets解碼,獲得CharBuffer,再通過toString獲得字元串
str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString();
System.out.println(str2);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);
}
}
運行結果
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [16]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |hello...........|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
hello
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |hello...........|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
方法二
編碼:通過 StandardCharsets 的 encode 方法獲得 ByteBuffer,此時獲得的 ByteBuffer 為讀模式,無需通過 flip 切換模式
解碼:通過 StandardCharsets 的 decoder 方法解碼
public class Translate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 準備兩個字元串
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "";
// 通過StandardCharsets的encode方法獲得ByteBuffer
// 此時獲得的ByteBuffer為讀模式,無需通過flip切換模式
ByteBuffer buffer1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode(str1);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);
// 將緩衝區中的數據轉化為字元串
// 通過StandardCharsets解碼,獲得CharBuffer,再通過toString獲得字元串
str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString();
System.out.println(str2);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);
}
}
運行結果
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
hello
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
方法三
編碼:字元串調用 getByte () 方法獲得位元組數組,將位元組數組傳給 ByteBuffer 的 wrap () 方法,通過該方法獲得 ByteBuffer。同樣無需調用 flip 方法切換為讀模式
解碼:通過 StandardCharsets 的 decoder 方法解碼
public class Translate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 準備兩個字元串
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "";
// 通過StandardCharsets的encode方法獲得ByteBuffer
// 此時獲得的ByteBuffer為讀模式,無需通過flip切換模式
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.wrap(str1.getBytes());
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);
// 將緩衝區中的數據轉化為字元串
// 通過StandardCharsets解碼,獲得CharBuffer,再通過toString獲得字元串
str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString();
System.out.println(str2);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer1);
}
}
運行結果
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
hello
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
粘包與半包
現象
網路上有多條數據發送給服務端,數據之間使用 \n 進行分隔
但由於某種原因這些數據在接收時,被進行了重新組合,例如原始數據有 3 條為
- Hello,world\n
- I’m Nyima\n
- How are you?\n
變成了下麵的兩個 byteBuffer (粘包,半包)
- Hello,world\nI’m Nyima\nHo
- w are you?\n
出現原因
粘包
發送方 在發送數據時,並不是一條一條地發送數據,而是將數據整合在一起,當數據達到一定的數量後再一起發送。這就會導致多條信息被放在一個緩衝區中被一起發送出去
半包
接收方 的緩衝區的大小是有限的,當接收方的緩衝區滿了以後,就需要將信息截斷,等緩衝區空了以後再繼續放入數據。這就會發生一段完整的數據最後被截斷的現象
解決辦法
-
通過 get (index) 方法遍歷 ByteBuffer,遇到分隔符時進行處理。
註意
:get (index) 不會改變 position 的值
- 記錄該段數據長度,以便於申請對應大小的緩衝區
- 將緩衝區的數據通過 get () 方法寫入到 target 中
-
調用 compact 方法切換模式,因為緩衝區中可能還有未讀的數據
public class ByteBufferDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
// 模擬粘包+半包
buffer.put("Hello,world\nI'm Nyima\nHo".getBytes());
// 調用split函數處理
split(buffer);
buffer.put("w are you?\n".getBytes());
split(buffer);
}
private static void split(ByteBuffer buffer) {
// 切換為讀模式
buffer.flip();
for(int i = 0; i < buffer.limit(); i++) {
// 遍歷尋找分隔符
// get(i)不會移動position
if (buffer.get(i) == '\n') {
// 緩衝區長度
int length = i+1-buffer.position();
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(length);
// 將前面的內容寫入target緩衝區
for(int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
// 將buffer中的數據寫入target中
target.put(buffer.get());
}
// 列印查看結果
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(target);
}
}
// 切換為寫模式,但是緩衝區可能未讀完,這裡需要使用compact
buffer.compact();
}
}
運行結果
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [12], limit: [12]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 48 65 6c 6c 6f 2c 77 6f 72 6c 64 0a |Hello,world. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [10], limit: [10]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 49 27 6d 20 4e 79 69 6d 61 0a |I'm Nyima. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [13], limit: [13]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 48 6f 77 20 61 72 65 20 79 6f 75 3f 0a |How are you?. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
3、FileChannel
工作模式
FileChannel 只能在阻塞模式下工作,所以無法搭配 Selector
獲取
不能直接打開 FileChannel,必須通過 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 來獲取 FileChannel,它們都有 getChannel 方法
- 通過 FileInputStream 獲取的 channel 只能讀
- 通過 FileOutputStream 獲取的 channel 只能寫
- 通過 RandomAccessFile 是否能讀寫 根據構造 RandomAccessFile 時的讀寫模式決定
讀取
通過 FileInputStream 獲取 channel,通過 read 方法將數據寫入到 ByteBuffer 中
read 方法的返回值表示讀到了多少位元組,若讀到了文件末尾則返回 - 1
int readBytes = channel.read(buffer);
可根據返回值判斷是否讀取完畢
while(channel.read(buffer) > 0) {
// 進行對應操作
...
}
寫入
因為 channel 也是有大小的,所以 write 方法並不能保證一次將 buffer 中的內容全部寫入 channel。必須需要按照以下規則進行寫入
// 通過hasRemaining()方法查看緩衝區中是否還有數據未寫入到通道中
while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buffer);
}
關閉
通道需要 close,一般情況通過 try-with-resource 進行關閉,最好使用以下方法獲取 strea 以及 channel,避免某些原因使得資源未被關閉
public class TestChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("stu.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("student.txt");
FileChannel inputChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel = fos.getChannel()) {
// 執行對應操作
...
}
}
}
位置
position
channel 也擁有一個保存讀取數據位置的屬性,即 position
long pos = channel.position();
可以通過 position (int pos) 設置 channel 中 position 的值
long newPos = ...;
channel.position(newPos);
設置當前位置時,如果設置為文件的末尾
- 這時讀取會返回 -1
- 這時寫入,會追加內容,但要註意如果 position 超過了文件末尾,再寫入時在新內容和原末尾之間會有空洞(00)
強制寫入
操作系統出於性能的考慮,會將數據緩存,不是立刻寫入磁碟,而是等到緩存滿了以後將所有數據一次性的寫入磁碟。可以調用 force(true) 方法將文件內容和元數據(文件的許可權等信息)立刻寫入磁碟
2、兩個 Channel 傳輸數據
transferTo 方法
使用 transferTo 方法可以快速、高效地將一個 channel 中的數據傳輸到另一個 channel 中,但一次只能傳輸 2G 的內容
transferTo 底層使用了零拷貝技術
public class TestChannel {
public static void main(String[] args){
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("stu.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("student.txt");
FileChannel inputChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel = fos.getChannel()) {
// 參數:inputChannel的起始位置,傳輸數據的大小,目的channel
// 返回值為傳輸的數據的位元組數
// transferTo一次只能傳輸2G的數據
inputChannel.transferTo(0, inputChannel.size(), outputChannel);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
當傳輸的文件大於 2G 時,需要使用以下方法進行多次傳輸
public class TestChannel {
public static void main(String[] args){
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("stu.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("student.txt");
FileChannel inputChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel = fos.getChannel()) {
long size = inputChannel.size();
long capacity = inputChannel.size();
// 分多次傳輸
while (capacity > 0) {
// transferTo返回值為傳輸了的位元組數
capacity -= inputChannel.transferTo(size-capacity, capacity, outputChannel);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3、Path 與 Paths
- Path 用來表示文件路徑
- Paths 是工具類,用來獲取 Path 實例
Path source = Paths.get("1.txt"); // 相對路徑 不帶盤符 使用 user.dir 環境變數來定位 1.txt
Path source = Paths.get("d:\\1.txt"); // 絕對路徑 代表了 d:\1.txt 反斜杠需要轉義
Path source = Paths.get("d:/1.txt"); // 絕對路徑 同樣代表了 d:\1.txt
Path projects = Paths.get("d:\\data", "projects"); // 代表了 d:\data\projects
- . 代表了當前路徑
- .. 代表了上一級路徑
例如目錄結構如下
d:
|- data
|- projects
|- a
|- b
代碼
Path path = Paths.get("d:\\data\\projects\\a\\..\\b");
System.out.println(path);
System.out.println(path.normalize()); // 正常化路徑 會去除 . 以及 ..
輸出結果為
d:\data\projects\a\..\b
d:\data\projects\b
4、Files
查找
檢查文件是否存在
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
System.out.println(Files.exists(path));
創建
創建一級目錄
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.createDirectory(path);
- 如果目錄已存在,會拋異常 FileAlreadyExistsException
- 不能一次創建多級目錄,否則會拋異常 NoSuchFileException
創建多級目錄用
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1/d2");
Files.createDirectories(path);
拷貝及移動
拷貝文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.copy(source, target);
- 如果文件已存在,會拋異常 FileAlreadyExistsException
如果希望用 source 覆蓋 掉 target,需要用 StandardOption 來控制
Files.copy(source, target, StandardOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
移動文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Files.move(source, target, StandardOption.ATOMIC_MOVE);
- StandardOption.ATOMIC_MOVE 保證文件移動的原子性
刪除
刪除文件
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.delete(target);
- 如果文件不存在,會拋異常 NoSuchFileException
刪除目錄
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.delete(target);
- 如果目錄還有內容,會拋異常 DirectoryNotEmptyException
遍歷
可以使用 Files 工具類中的 walkFileTree (Path, FileVisitor) 方法,其中需要傳入兩個參數
-
Path:文件起始路徑
-
FileVisitor:文件訪問器,
使用訪問者模式
-
介面的實現類
SimpleFileVisitor
有四個方法
- preVisitDirectory:訪問目錄前的操作
- visitFile:訪問文件的操作
- visitFileFailed:訪問文件失敗時的操作
- postVisitDirectory:訪問目錄後的操作
-
public class TestFiles {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AtomicInteger ditCount = new AtomicInteger();
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
Files.walkFileTree(Paths.get("D:\\Program Files\\jdk7"),new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(Path dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.err.println("=====>"+dir);
ditCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.preVisitDirectory(dir, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println("=====>"+file);
fileCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println("dir count :"+ditCount);
System.out.println("file count :"+fileCount);
}
}
運行結果如下
...
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\SystemV\EST5EDT
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\SystemV\HST10
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\SystemV\MST7
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\SystemV\MST7MDT
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\SystemV\PST8
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\SystemV\PST8PDT
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\SystemV\YST9
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\SystemV\YST9YDT
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\WET
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\lib\zi\ZoneInfoMappings
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\LICENSE
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\README.txt
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\release
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\THIRDPARTYLICENSEREADME-JAVAFX.txt
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\THIRDPARTYLICENSEREADME.txt
=====>D:\Program Files\jdk7\jre7\Welcome.html
dir count :183
file count :2437
本文由
傳智教育博學谷教研團隊發佈。如果本文對您有幫助,歡迎
關註和點贊;如果您有任何建議也可留言評論或私信,您的支持是我堅持創作的動力。轉載請註明出處!



