Linux常用命令 1、 關機/重啟/註銷 | 常用命令 | 作用 | | | | | shutdown -h now | 即刻關機 | | shutdown -h 10 | 10分鐘後關機 | | shutdown -h 11:00 | 11:00關機 | | shutdown -h +10 | ...
Linux常用命令
1、 關機/重啟/註銷
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| shutdown -h now | 即刻關機 |
| shutdown -h 10 | 10分鐘後關機 |
| shutdown -h 11:00 | 11:00關機 |
| shutdown -h +10 | 預定時間關機(10分鐘後) |
| shutdown -c | 取消指定時間關機 |
| shutdown -r now | 重啟 |
| shutdown -r 10 | 10分鐘之後重啟 |
| shutdown -r 11:00 | 定時重啟 |
| reboot | 重啟 |
| init 6 | 重啟 |
| init 0 | 即刻關機 |
| telinit 0 | 關機 |
| poweroff | 即刻關機 |
| halt | 關機 |
| sync | buff數據同步到磁碟 (建議關機之前都執行) |
| logout | 退出登錄Shell |
2、 系統信息和性能查看
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| uname -a | 查看內核/OS/CPU信息 |
| uname -r | 查看內核版本 |
| uname -m | 查看處理器架構 |
| arch | 查看處理器架構 |
| hostname | 查看電腦名 |
| who | 顯示當前登錄系統的⽤戶 |
| who am i | 顯示登錄時的⽤戶名 |
| whoami | 顯示當前⽤戶名 |
| cat /proc/version | 查看linux版本信息 |
| cat /proc/cpuinfo | 查看CPU信息 |
| cat /proc/interrupts | 查看中斷 |
| cat /proc/loadavg | 查看系統負載 |
| uptime | 查看系統運⾏時間、⽤戶數、負載 |
| env | 查看系統的環境變數 |
| lspci -tv | 查看系統PCI設備信息 |
| lsmod | 查看已載入的系統模塊 |
| lsusb -tv | 查看系統USB設備信息 ( yum install usbutils -y) |
| grep MemTotal /proc/meminfo | 查看記憶體總量 |
| grep MemFree /proc/meminfo | 查看空閑記憶體量 |
| free -m | 查看記憶體⽤量和交換區⽤量 |
| date | 顯示系統⽇期時間 |
| cal 2023 | 顯示2023⽇歷表 |
| top | 動態顯示cpu/記憶體/進程等情況 |
| vmstat 1 20 | 每1秒採⼀次系統狀態,採20次 |
| iostat | 查看io讀寫/cpu使⽤情況 |
| sar -u 1 10 | 查詢cpu使⽤情況(1秒⼀次,共10次) |
| sar -d 1 10 | 查詢磁碟性能 (1秒⼀次,共10次) |
3、 磁碟和分區
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| fdisk -l | 查看所有磁碟分區 |
| swapon -s | 查看所有交換分區 |
| df -h / df -hl | 查看磁碟使⽤情況及掛載點 |
| du -sh logs | 查看指定某個⽬錄(logs)的⼤⼩ |
| du -sk * | sort -rn | 從⾼到低依次顯示⽂件和⽬錄⼤⼩ |
| mount /dev/hda2 /mnt/hda2 | 掛載hda2盤 |
| mount -t ntfs /dev/sdc1 /mnt/usbhd1 | 指定⽂件系統類型掛載(如ntfs) |
| mount -o loop xxx.iso /mnt/cdrom | 掛載iso⽂件 |
| mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/usbdisk | 掛載usb盤/快閃記憶體設備 |
| umount -v /dev/sda1 | 通過掛載點卸載 |
| fuser -km /mnt/hda1 | 強制卸載(慎⽤) |
4、 ⽤戶和⽤戶組
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| useradd wq | 創建⽤戶 |
| userdel -r wq | 刪除⽤戶 |
| usermod -g group_name user_name | 修改⽤戶的組 |
| usermod -aG group_name user_name | 將⽤戶添加到組 |
| usermod -d /root/logs wq | 更改登錄目錄 |
| groups root | 查看root⽤戶所在的組 |
| groupadd group_name | 創建⽤戶組 |
| groupdel group_name | 刪除⽤戶組 |
| groupmod -n new_name old_name | 重命名⽤戶組 |
| su - user_name | 完整切換到⼀個⽤戶環境 |
| passwd | 修改⼝令 |
| passwd wq | 修改某⽤戶的⼝令 |
| w | 查看活動⽤戶 |
| id wq | 查看指定⽤戶wq信息 |
| last | 查看⽤戶登錄⽇志 |
| crontab -l | 查看當前⽤戶的計劃任務 |
| cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd | 查看系統所有⽤戶 |
| cut -d: -f1 /etc/group | 查看系統所有組 |
5、 ⽹絡和進程管理
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ifconfig | 查看⽹絡接⼝屬性 |
| ifconfig eth0 | 查看某⽹卡的配置 |
| route -n | 查看路由表 |
| netstat -lntp | 查看所有監聽端⼝ |
| netstat -antp | 查看已經建⽴的TCP連接 |
| netstat -lutp | 查看TCP/UDP的狀態信息 |
| ifup eth0 | 啟⽤eth0⽹絡設備 |
| ifdown eth0 | 禁⽤eth0⽹絡設備 |
| iptables -L | 查看iptables規則 |
| ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 | 配置ip地址 |
| dhclient eth0 | 以dhcp模式啟⽤eth0 |
| route add -net 0/0 gw Gateway_IP | 配置預設⽹關 |
| route add -net 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.0.0 gw 192.168.1.1 | 配置靜態路由到達⽹ 絡'192.168.0.0/16' |
| route del 0/0 gw Gateway_IP | 刪除靜態路由 |
| host qq.com | 解析主機名 (yum install bind-utils -y) |
| nslookup qq.com | 查詢DNS記錄,查看功能變數名稱解 析是否正常 |
| ps -ef | 查看所有進程 |
| ps -ef | grep java | 過濾出你需要的進程 |
| kill -s name | kill指定名稱的進程 |
| kill -s pid | kill指定pid的進程 |
| kill -9 pid (等於kill -s 9 pid) | 表示強制,儘快終止一個進程 |
6、 常⻅系統服務命令
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| chkconfig --list | 列出系統服務 |
| service <服務名> status | 查看某個服務 |
| service <服務名> start | 啟動某個服務 |
| service <服務名> stop | 終⽌某個服務 |
| service <服務名> restart | 重啟某個服務 |
| systemctl status <服務名> | 查看某個服務 |
| systemctl start <服務名> | 啟動某個服務 |
| systemctl stop <服務名> | 終⽌某個服務 |
| systemctl restart <服務名> | 重啟某個服務 |
| systemctl enable <服務名> | 開啟⾃啟動 |
| systemctl disable <服務名> | 關閉⾃啟動 |
7、 ⽂件和⽬錄操作
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| cd <⽬錄名> | 進⼊某個⽬錄 |
| cd .. | 回上級⽬錄 |
| cd ../.. | 回上兩級⽬錄 |
| cd | 進個⼈主⽬錄 |
| cd - | 回上⼀步所在⽬錄 |
| pwd | 顯示當前路徑 |
| ls | 查看⽂件⽬錄列表 |
| ls -F | 查看⽬錄中內容(顯示是⽂件還是⽬錄) |
| ls -l | 查看⽂件和⽬錄的詳情列表 |
| ls -a | 查看隱藏⽂件 |
| ls -lh | 查看⽂件和⽬錄的詳情列表(增強⽂件⼤⼩易讀性) |
| ls -lSr | 查看⽂件和⽬錄列表(以⽂件⼤⼩升序查看) |
| tree | 查看⽂件和⽬錄的樹形結構 (yum install tree -y) |
| mkdir <⽬錄名> | 創建⽬錄 |
| mkdir dir1 dir2 | 同時創建兩個⽬錄 |
| mkdir -p /tmp/dir1/dir2 | 創建⽬錄樹 |
| rm -f file1 | 刪除'file1'⽂件 |
| rmdir dir1 | 刪除'dir1'⽬錄 |
| rm -rf dir1 | 刪除'dir1'⽬錄和其內容 |
| rm -rf dir1 dir2 | 同時刪除兩個⽬錄及其內容 |
| mv old_dir new_dir | 重命名/移動⽬錄 |
| cp file1 file2 | 複製⽂件 |
| cp dir/* . | 複製某⽬錄下的所有⽂件⾄當前⽬錄 |
| cp -a dir1 dir2 | 複製⽬錄 |
| cp -a /tmp/dir1 . | 複製⼀個⽬錄⾄當前⽬錄 |
| ln -s file1 link1 | 創建指向⽂件/⽬錄的軟鏈接 |
| ln file1 lnk1 | 創建指向⽂件/⽬錄的物理鏈接 |
| find / -name file1 | 從跟⽬錄開始搜索⽂件/⽬錄 |
| find / -user user1 | 搜索⽤戶user1的⽂件/⽬錄 |
| find /dir -name *.bin | 在⽬錄/dir中搜帶有.bin尾碼的⽂件 |
| locate <關鍵詞> | 快速定位⽂件 ( yum install mlocate -y |
| updatedb) | |
| locate *.mp4 | 尋找.mp4結尾的⽂件 |
| whereis <關鍵詞> | 顯示某⼆進位⽂件/可執⾏⽂件的路徑 |
| which <關鍵詞> | 查找系統⽬錄下某的⼆進位⽂件 |
| chmod ugo+rwx dir1 | 設置⽬錄所有者(u)、群組(g)及其他⼈(o)的讀(r)寫 (w)執⾏(x)許可權 |
| chmod go-rwx dir1 | 移除群組(g)與其他⼈(o)對⽬錄的讀寫執⾏許可權 |
| chown user1 file1 | 改變⽂件的所有者屬性 |
| chown -R user1 dir1 | 改變⽬錄的所有者屬性 |
| chgrp group1 file1 | 改變⽂件群組 |
| chown user1:group1 file1 | 改變⽂件的所有⼈和群組 |
8、 ⽂件查看和處理
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| cat file1 | 查看⽂件內容 |
| cat -n file1 | 查看內容並標示⾏數 |
| tac file1 | 從最後⼀⾏開始反看⽂件內容 |
| more file1 | 查看⼀個⻓⽂件的內容 |
| less file1 | 類似more命令,但允許反向操作 |
| head -2 file1 | 查看⽂件前兩⾏ |
| tail -2 file1 | 查看⽂件後兩⾏ |
| tail -f /log/msg | 實時查看添加到⽂件中的內容 |
| tail -f -n 20 debug.log | 20行一批滾動查看文件內容 |
| grep haha hello.txt | 在⽂件hello.txt中查找關鍵詞haha |
| grep ^sheep hello.txt | 在⽂件hello.txt中查找以sheep開頭的內容 |
| grep [0-9] hello.txt | 選擇hello.txt⽂件中所有包含數字的⾏ |
| sed 's/s1/s2/g' hello.txt | 將hello.txt⽂件中的s1替換成s2 |
| sed '/^$/d' hello.txt | 從hello.txt⽂件中刪除所有空⽩⾏ |
| sed '/ *#/d; /^$/d' hello.txt | 從hello.txt⽂件中刪除所有註釋和空⽩⾏ |
| sed -e '1d' hello.txt | 從⽂件hello.txt 中排除第⼀⾏ |
| sed -n '/s1/p' hello.txt | 查看只包含關鍵詞"s1"的⾏ |
| sed -e 's/ *$//' hello.txt | 刪除每⼀⾏最後的空⽩字元 |
| sed -e 's/s1//g' hello.txt | 從⽂檔中只刪除辭彙s1並保留剩餘全部 |
| sed -n '1,5p;5q' hello.txt | 查看從第1⾏到第5⾏內容 |
| sed -n '5p;5q' hello.txt | 查看第5⾏ |
| paste file1 file2 | 合併兩個⽂件或兩欄的內容 |
| paste -d '+' file1 file2 | 合併兩個⽂件或兩欄的內容,中間⽤"+"區分 |
| sort file1 file2 | 排序兩個⽂件的內容 |
| comm -1 file1 file2 | ⽐較兩個⽂件的內容(去除'file1'所含內容) |
| comm -2 file1 file2 | ⽐較兩個⽂件的內容(去除'file2'所含內容) |
| comm -3 file1 file2 | ⽐較兩個⽂件的內容(去除兩⽂件共有部分) |
9、 打包和解壓
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| zip xxx.zip file | 壓縮⾄zip包 |
| zip -r xxx.zip file1 file2 dir1 | 將多個⽂件+⽬錄壓成zip包 |
| unzip xxx.zip | 解壓zip包 |
| tar -cvf xxx.tar file | 創建⾮壓縮tar包 |
| tar -cvf xxx.tar file1 file2 dir1 | 將多個⽂件+⽬錄打tar包 |
| tar -tf xxx.tar | 查看tar包的內容 |
| tar -xvf xxx.tar | 解壓tar包 |
| tar -xvf xxx.tar -C /dir | 將tar包解壓⾄指定⽬錄 |
| tar -cvfj xxx.tar.bz2 dir | 創建bz2壓縮包 |
| tar -jxvf xxx.tar.bz2 | 解壓bz2壓縮包 |
| tar -cvfz xxx.tar.gz dir | 創建gzip壓縮包 |
| tar -zxvf xxx.tar.gz | 解壓gzip壓縮包 |
| bunzip2 xxx.bz2 | 解壓bz2壓縮包 |
| bzip2 filename | 壓縮⽂件 |
| gunzip xxx.gz | 解壓gzip壓縮包 |
| gzip filename | 壓縮⽂件 |
| gzip -9 filename | 最⼤程度壓縮 |
10、 RPM包管理命令
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| rpm -qa | 查看已安裝的rpm包 |
| rpm -q pkg_name | 查詢某個rpm包 |
| rpm -q --whatprovides xxx | 顯示xxx功能是由哪個包提供的 |
| rpm -q --whatrequires xxx | 顯示xxx功能被哪個程式包依賴的 |
| rpm -q --changelog xxx | 顯示xxx包的更改記錄 |
| rpm -qi pkg_name | 查看⼀個包的詳細信息 |
| rpm -qd pkg_name | 查詢⼀個包所提供的⽂檔 |
| rpm -qc pkg_name | 查看已安裝rpm包提供的配置⽂件 |
| rpm -ql pkg_name | 查看⼀個包安裝了哪些⽂件 |
| rpm -qf filename | 查看某個⽂件屬於哪個包 |
| rpm -qR pkg_name | 查詢包的依賴關係 |
| rpm -ivh xxx.rpm | 安裝rpm包 |
| rpm -ivh --test xxx.rpm | 測試安裝rpm包 |
| rpm -ivh --nodeps xxx.rpm | 安裝rpm包時忽略依賴關係 |
| rpm -e xxx | 卸載程式包 |
| rpm -Fvh pkg_name | 升級確定已安裝的rpm包 |
| rpm -Uvh pkg_name | 升級rpm包(若未安裝則會安裝) |
| rpm -V pkg_name | RPM包詳細信息校驗 |
11、 YUM包管理命令
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| yum repolist enabled | 顯示可⽤的源倉庫 |
| yum search pkg_name | 搜索軟體包 |
| yum install pkg_name | 下載並安裝軟體包 |
| yum install --downloadonly pkg_name | 只下載不安裝 |
| yum list | 顯示所有程式包 |
| yum list installed | 查看當前系統已安裝包 |
| yum list updates | 查看可以更新的包列表 |
| yum check-update | 查看可升級的軟體包 |
| yum update | 更新所有軟體包 |
| yum update pkg_name | 升級指定軟體包 |
| yum deplist pkg_name | 列出軟體包依賴關係 |
| yum remove pkg_name | 刪除軟體包 |
| yum clean all | 清除緩存 |
| yum clean packages | 清除緩存的軟體包 |
| yum clean headers | 清除緩存的header |
12、 DPKG包管理命令 ( yum install dpkg -y)
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| dpkg -c xxx.deb | 列出deb包的內容 |
| dpkg -i xxx.deb | 安裝/更新deb包 |
| dpkg -r pkg_name | 移除deb包 |
| dpkg -P pkg_name | 移除deb包(不保留配置) |
| dpkg -l | 查看系統中已安裝deb包 |
| dpkg -l pkg_name | 顯示包的⼤致信息 |
| dpkg -L pkg_name | 查看deb包安裝的⽂件 |
| dpkg -s pkg_name | 查看包的詳細信息 |
| dpkg –unpack xxx.deb | 解開deb包的內容 |
13、 APT軟體⼯具
| 常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| apt-cache search pkg_name | 搜索程式包 |
| apt-cache show pkg_name | 獲取包的概覽信息 |
| apt-get install pkg_name | 安裝/升級軟體包 |
| apt-get purge pkg_name | 卸載軟體(包括配置) |
| apt-get remove pkg_name | 卸載軟體(不包括配置) |
| apt-get update | 更新包索引信息 |
| apt-get upgrade | 更新已安裝軟體包 |
| apt-get clean | 清理緩存 |
shell腳本入門
腳本格式
腳本以#!/bin/bash開頭(指定解析器)
#!/bin/bash
使用shell輸出helloworld
- 新建文件
touch helloworld.sh
vi helloworld.sh
- 文件內容
#!/bin/bash
echo "helloworld!!!!"
- 運行
# 方式一
sh helloworld.sh
# 方式二,需要給許可權,chmod 777 helloworld.sh
chmod 777 helloworld.sh
./helloworld.sh
- 方式1,本質是bash解析器幫你執行腳本,所以腳本本身不需要執行許可權;
- 方式2,本質是腳本自己需要執行,所以需要執行許可權
多命令處理
在/tmp目錄下創建一個test.txt文件,併在文件中寫入1234567890
vi batch.sh
- 輸入
#!/bin/bash
cd /tmp
touch test.txt
echo "1234567890" >> test.txt
shell中的變數
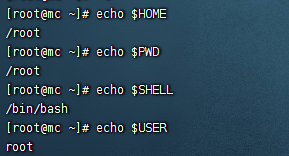
常用系統變數
$HOME
$PWD
$SHELL
$USER
[root@mc ~]# echo $HOME
/root
[root@mc ~]# echo $PWD
/root
[root@mc ~]# echo $SHELL
/bin/bash
[root@mc ~]# echo $USER
root
自定義變數
基本語法
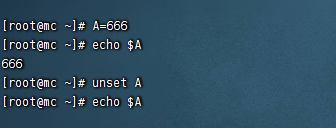
- 定義變數:變數=值 等號兩邊不能留有空格
- 撤銷變數:unset 變數
- 輸出變數:echo $變數
- 聲明靜態變數: readonly 變數,註意:不能unset
變數定義規則
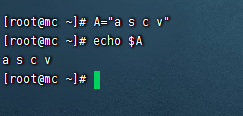
- 變數名稱可以由字母,數字和下劃線組成,不能以數字開頭,環境變數名建議大寫
- 等號兩側不能有空格
- 在bash中,變數預設類型都是字元串類型,無法直接進行數值運算
- 變數的值如果有空格,需要使用雙引號或單引號括起來
- 可把變數提升為全局變數,可供其他shell程式使用
export 變數
#!/bin/bash
echo "helloworld!!!!"
echo $A
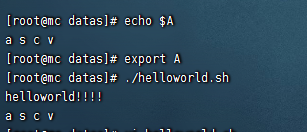
特殊變數
$n
- $n (描述:n為數字,$0代表腳本名稱,10以內參數用$1-9 表示 , 10以上的需要用大括弧包含 ,9表示,10以上的需要用大括弧包含,9表示,10以上的需要用大括弧包含,{10})
#!/bin/bash
echo "$0 $1 $2 $3"
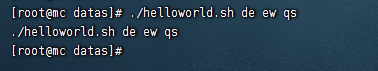
$#
- $# (功能描述:獲取所有輸入參數個數,常用於迴圈)
#!/bin/bash
echo "$0 $1 $2 $3"
echo $#
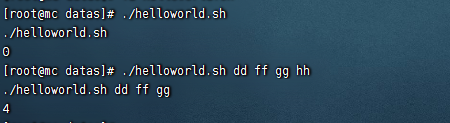
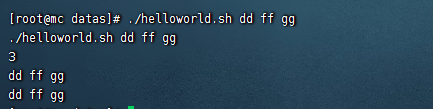
$* 和$@
- $* (描述:代表命令行中所有的參數,把所有參數看成一個整體)
- $@ (描述:也代表命令行中所有的參數,不過把每個參數區分對待)
#!/bin/bash
echo "$0 $1 $2 $3"
echo $#
echo $*
echo $@
$?
- $? (描述:最後一次執行命令的狀態,0:正確執行)
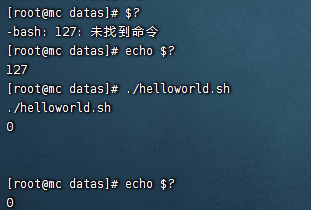
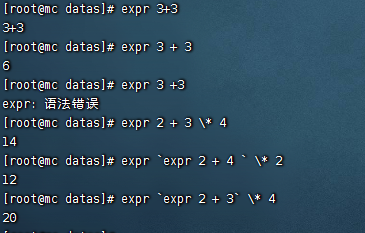
運算符
- $((運算式)) 或 $[運算式]
- expr +,-,*,/,% 加減乘除取餘
- expr運算符間要有空格
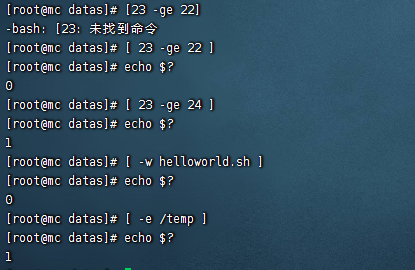
條件判斷
基本語法
- [condition] (註意 condition前後要有空格)
常用判斷條件
兩個整數之間比較
| 符號 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| -lt | less than)小於 |
| -le | (less equal) 小於等於 |
| -eq | (equal)等於 |
| -gt | (greater than) 大於 |
| -ge | (greater equal) 大於等於 |
| -ne | (not equal) 不等於 |
文件許可權判斷
| 符號 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| -r | 有讀的許可權(read) |
| -w | 有寫的許可權(write) |
| -x | 有執行的許可權(execute) |
文件類型判斷
| 符號 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| -f | 文件存在並且是一個常規文件(file) |
| -e | 文件存在(existence) |
| -d | 文件存在病是一個目錄(directory) |
多條件判斷
- &&
- ||
流程式控制制
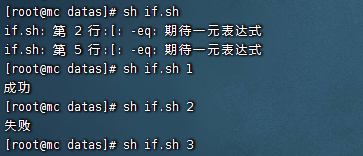
if判斷
#!/bin/bash
if [ $1 -eq 1 ]
then
echo "成功"
elif [ $1 -eq 2 ]
then
echo "失敗"
fi
註意事項:
(1)[ 條件判斷式 ],中括弧和條件判斷式之間必須有空格
(2)if後要有空格
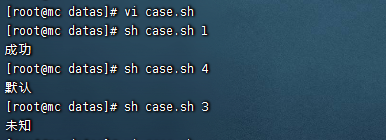
case 語句
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
1)
echo "成功"
;;
2)
echo "失敗"
;;
3)
echo "未知"
;;
*)
echo "預設"
;;
esac
註意事項:
- case行尾必須為單詞“in”,每一個模式匹配必須以右括弧“)”結束。
- 雙分號“;;”表示命令序列結束,相當於java中的break。
- 最後的“*)”表示預設模式,相當於java中的default。
for迴圈
- 語法1
- 從1加到100
#!/bin/bash
s=0
for((i=1;i<=100;i++))
do
s=$[$s + $i]
done
echo $s

- 語法2
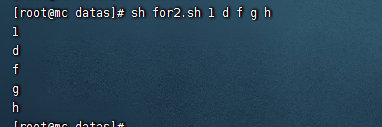
- 列印所有輸入參數
#!/bin/bash
for i in $*
do
echo $i
done
比較$*和$@區別
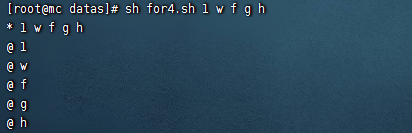
- $*和$@都表示傳遞給函數或腳本的所有參數,不被雙引號“”包含時,都以$1 $2 …$n的形式輸出所有參數。
#!/bin/bash
for i in $*
do
echo "* $i "
done
for j in $@
do
echo "@ $j"
done

- 當它們被雙引號“”包含時,“$*”會將所有的參數作為一個整體,以“$1 $2 …$n”的形式輸出所有參數;“$@”會將各個參數分開,以“$1” “$2”…”$n”的形式輸出所有參數。
#!/bin/bash
for i in "$*"
#$*中的所有參數看成是一個整體,所以這個for迴圈只會迴圈一次
do
echo "* $i"
done
for j in "$@"
#$@中的每個參數都看成是獨立的,所以“$@”中有幾個參數,就會迴圈幾次
do
echo "@ $j"
done
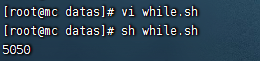
WHILE迴圈
- 從1加到100
#!/bin/bash
s=0
i=1
while [ $i -le 100 ]
do
s=$[$s + $i]
i=$[$i + 1]
done
echo $s
read讀取控制台輸入
基本語法
read(選項)(參數)
選項:
-p:指定讀取值時的提示符;
-t:指定讀取值時等待的時間(秒)。
參數
變數:指定讀取值的變數名
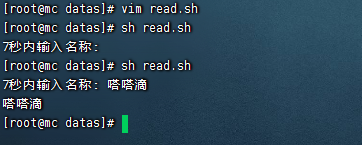
- 提示7秒內,讀取控制台輸入的名稱
#!/bin/bash
read -t 7 -p "7秒內輸入名稱:" NAME
echo $NAME
函數
系統函數
basename基本語法
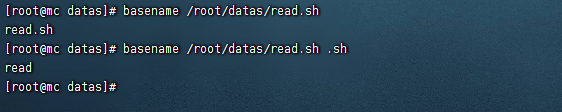
- basename [string / pathname] [suffix] (功能描述:basename命令會刪掉所有的首碼包括最後一個(‘/’)字元,然後將字元串顯示出來。
- 選項:suffix為尾碼,如果suffix被指定了,basename會將pathname或string中的suffix去掉。
# 用法一
[root@mc datas]# basename /root/datas/read.sh
read.sh
# 用法二
[root@mc datas]# basename /root/datas/read.sh .sh
read
dirname基本語法
- dirname 文件絕對路徑(功能描述:從給定的包含絕對路徑的文件名中去除文件名(非目錄的部分),然後返回剩下的路徑(目錄的部分))
[root@mc datas]# dirname /root/datas/read.sh
/root/datas
自定義函數
[ function ] funname[()]
{
Action;
[return int;]
}
funname
- 必須在調用函數地方之前,先聲明函數,shell腳本是逐行運行。不會像其它語言一樣先編譯。
- 函數返回值,只能通過$?系統變數獲得,可以顯示加:return返回,如果不加,將以最後一條命令運行結果,作為返回值。return後跟數值n(0-255)
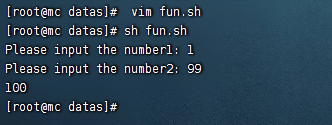
- 計算兩個輸入參數的和
#!/bin/bash
function sum()
{
s=0
s=$[ $1 + $2 ]
echo "$s"
}
read -p "請輸入第一個數: " n1;
read -p "請輸入第二個數: " n2;
sum $n1 $n2;
Shell工具
cut
- cut的工作就是“剪”,具體的說就是在文件中負責剪切數據用的。cut 命令從文件的每一行剪切位元組、字元和欄位並將這些位元組、字元和欄位輸出。
基本用法
cut [選項參數] filename
說明:預設分隔符是製表符
| 選項參數 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -f | 列號,提取第幾列 |
| -d | 分隔符,按照指定分隔符分割列 |
- 準備數據
vim cut.txt
dong shen
guan zhen
wo wo
lai lai
le le
- 切割cut.txt第一列
cut -d " " -f 1 cut.txt
- 切割cut.txt第二、三列
cut -d " " -f 2,3 cut.txt
- 在cut.txt文件中切割出guan
cat cut.txt | grep "guan" | cut -d " " -f 1
- 選取系統PATH變數值,第2個“:”開始後的所有路徑:
echo $PATH | cut -d: -f 2-
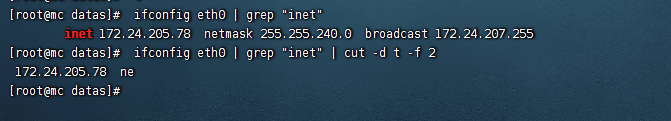
- 切割ifconfig 後列印的IP地址
ifconfig eth0 | grep "inet" | cut -d t -f 2
sed
- sed是一種流編輯器,它一次處理一行內容。處理時,把當前處理的行存儲在臨時緩衝區中,稱為“模式空間”,接著用sed命令處理緩衝區中的內容,處理完成後,把緩衝區的內容送往屏幕。接著處理下一行,這樣不斷重覆,直到文件末尾。文件內容並沒有改變,除非你使用重定向存儲輸出。
基本用法
sed [選項參數] ‘command’ filename
- 選項參數說明
| 選項參數 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -e | 直接在指令列模式上進行sed的動作編輯。 |
- 命令功能描述
| 命令 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| a | 新增,a的後面可以接字串,在下一行出現 |
| d | 刪除 |
| s | 查找並替換 |
將“mei nv”這個單詞插入到cut.txt第二行下,列印
sed '2a mei nv' cut.txt

刪除cut.txt文件所有包含wo的行
sed '/wo/d' cut.txt

將cut.txt文件中wo替換為ni
sed 's/wo/ni/g' cut.txt
- 註意:‘g’表示global,全部替換
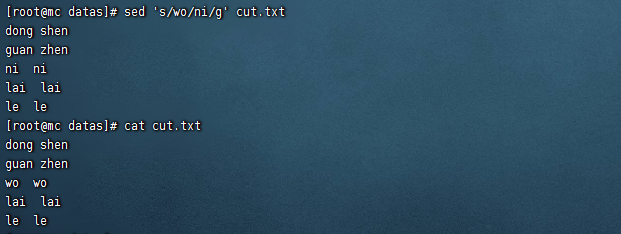
將cut.txt文件中的第二行刪除並將wo替換為ni
sed -e '2d' -e 's/wo/ni/g' cut.txt

awk
一個強大的文本分析工具,把文件逐行的讀入,以空格為預設分隔符將每行切片,切開的部分再進行分析處理。
基本用法
awk [選項參數] ‘pattern1{action1} pattern2{action2}...’ filename
pattern:表示AWK在數據中查找的內容,就是匹配模式
action:在找到匹配內容時所執行的一系列命令
- 選項參數說明
| 選項參數 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -F | 指定輸入文件折分隔符 |
| -v | 賦值一個用戶定義變數 |
- 數據準備
sudo cp /etc/passwd ./
- 搜索passwd文件以root關鍵字開頭的所有行,並輸出該行的第7列。
awk -F: '/^root/{print $7}' passwd
- 搜索passwd文件以root關鍵字開頭的所有行,並輸出該行的第1列和第7列,中間以“_”號分割
awk -F: '/^root/{print $1"_"$7}' passwd
- 只顯示/etc/passwd的第一列和第七列,以逗號分割,且在所有行前面添加列名user,shell在最後一行添加"dahaige,/bin/zuishuai"。
awk -F : 'BEGIN{print "user, shell"} {print $1","$7} END{print "dahaige,/bin/zuishuai"}' passwd
註意:BEGIN 在所有數據讀取行之前執行;END 在所有數據執行之後執行。
- 將passwd文件中的用戶id增加數值1並輸出
awk -v i=1 -F: '{print $3+i}' passwd
awk的內置變數
| 變數 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| FILENAME | 文件名 |
| NR | 已讀的記錄數 |
| NF | 瀏覽記錄的域的個數(切割後,列的個數) |
- 統計passwd文件名,每行的行號,每行的列數
awk -F: '{print "filename:" FILENAME ", linenumber:" NR ",columns:" NF}' passwd
- 切割IP
ifconfig eth0 | grep "inet" | awk -F t '{print $2}' | awk -F " " '{print $1}'

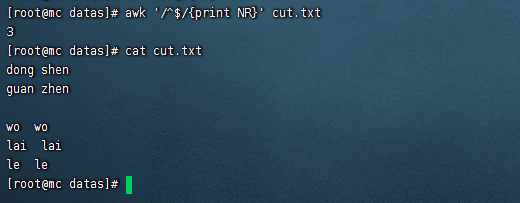
- 查詢cut.txt中空行所在的行號
awk '/^$/{print NR}' sed.txt
sort
sort命令是在Linux里非常有用,它將文件進行排序,並將排序結果標準輸出。
基本語法
sort(選項)(參數)
| 選項 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| -n | 依照數值的大小排序 |
| -r | 以相反的順序來排序 |
| -t | 設置排序時所用的分隔字元 |
| -k | 指定需要排序的列 |
參數:指定待排序的文件列表
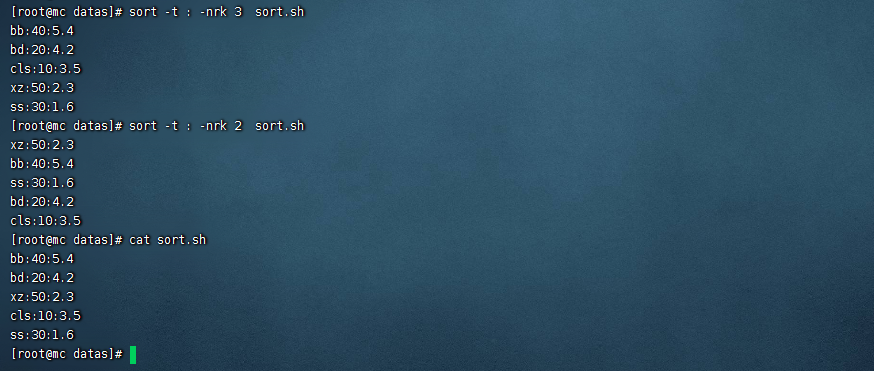
- 數據準備
vim sort.sh
bb:40:5.4
bd:20:4.2
xz:50:2.3
cls:10:3.5
ss:30:1.6
- 按照“:”分割後的第三列倒序排序。
sort -t : -nrk 3 sort.sh
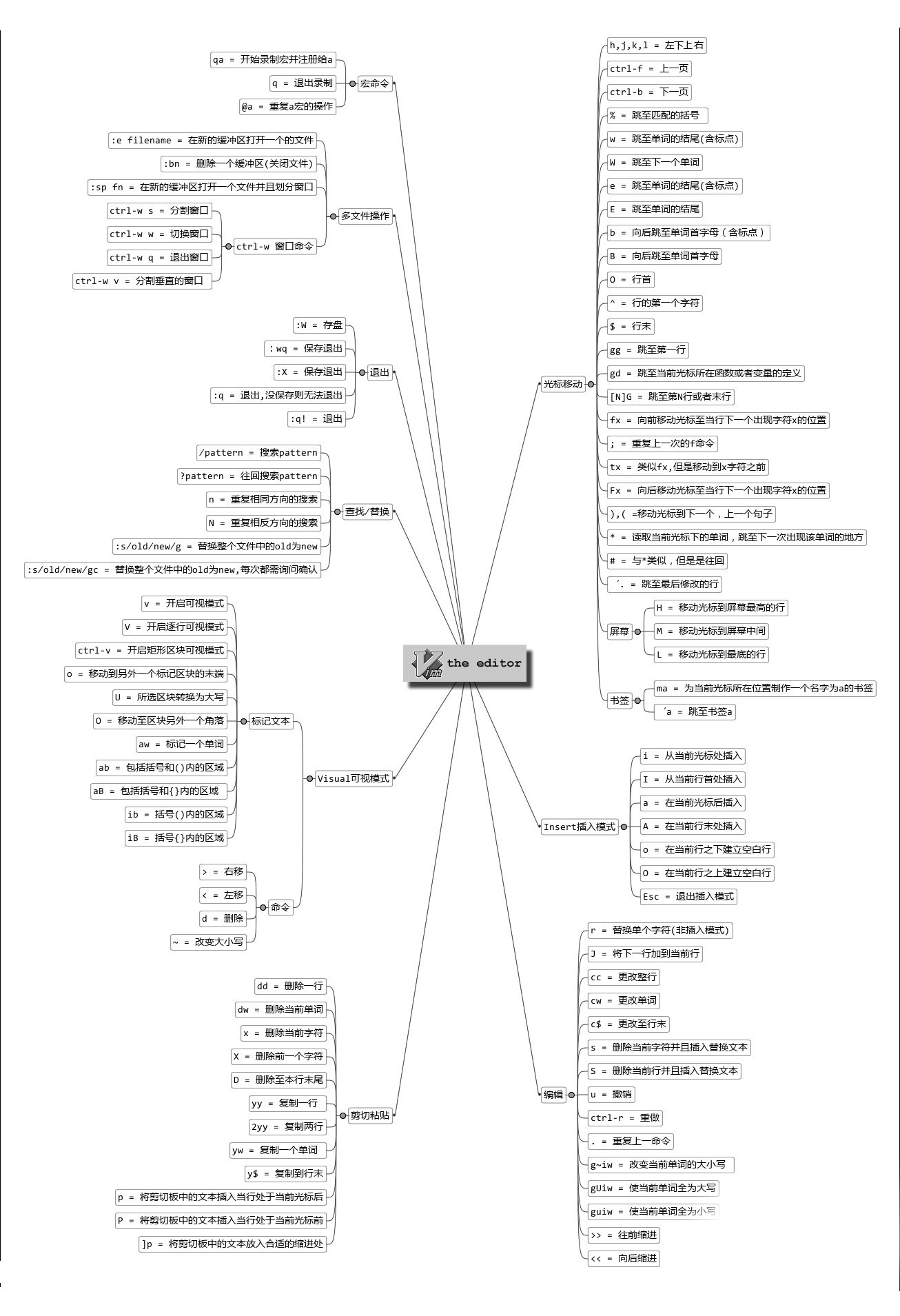
vim常用快捷鍵
grep常見用法
查找目錄
ls | grep logs
查找文件(字元串)
ls | grep "for"
# 查找wo
grep 'wo' cut.txt
# 查找空格
grep " " cut.txt
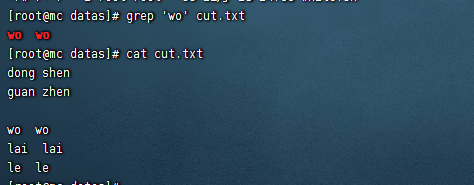
查找多個字元串
grep -e 'wo' -e 'zhen' cut.txt
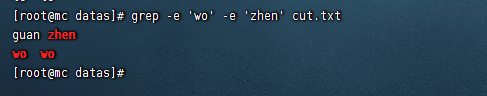
搜索包含兩個連續的“d”字母的字元串
egrep -E d\{2} cut.txt
grep -E d\{2} cut.txt
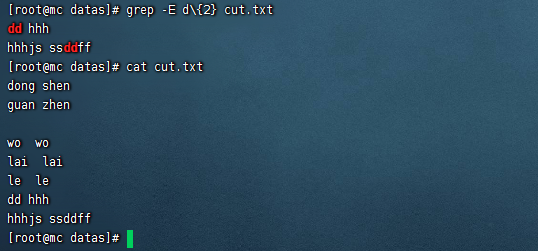
[]括弧用於匹配一組字元中的任何一個。
grep "[1358]" cut.txt
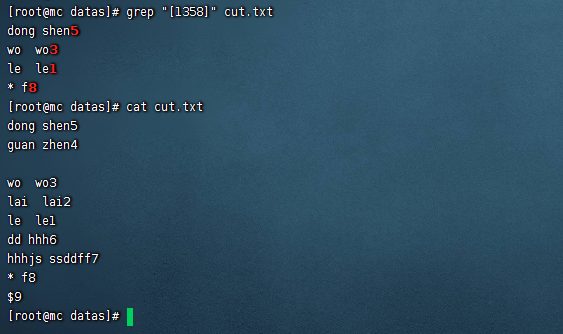
[-]括弧可用於指定數字或字母字元範圍
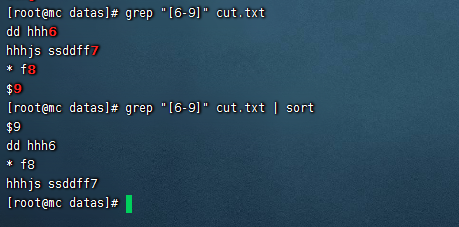
grep "[6-9]" cut.txt
^脫字元號用於搜索只出現在行的開頭的模式
grep ^d cut.txt
帶方括弧的脫字元號用於從搜索模式中排除字元
grep "[^6-9]" cut.txt
$符號用於搜索只出現在行的末尾的模式
grep "9$" cut.txt
** or條件**
grep -E '8|9' cut.txt
egrep '8|9' cut.txt
忽略大小寫 -i
grep -i 'dong' cut.txt
搜索時區分大小寫
- 如果我們要搜索一個字元串,其中第一個可以是大寫或小寫,但字元串的其餘部分應該是小寫怎麼辦?在這種情況下,無法使用-i 忽略大小寫,所以一種簡單的方法是使用方括弧。
grep '[Dd]ong' cut.txt
帶行號 -n
grep -n 'wo' cut.txt
輸出前後行 -C
輸出之前行-B
輸出之後行-A
grep -A 1 'la' cut.txt
grep -B 1 'la' cut.txt
grep -C 1 'la' cut.txt
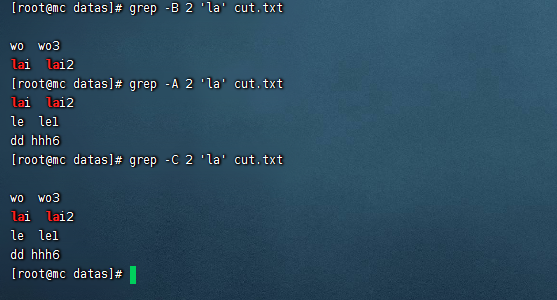
對結果排序
grep "[6-9]" cut.txt | sort
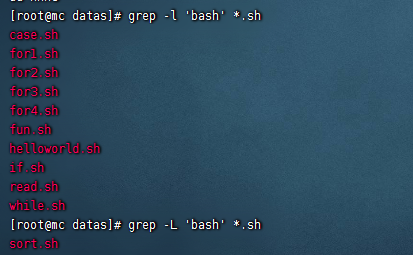
多文件查找-l與-L
# 包含使用-l
grep -l 'bash' *.sh
# 不包含使用-L
grep -L 'bash' *.sh
精確搜索
- 通過使用<和>來準確匹配到了 bin 這個詞
grep "\<bin\>" /etc/passwd