說明: 本文基於Spring-Framework 5.1.x版本講解 概述 說起生命周期, 很多開源框架、中間件的組件都有這個詞,其實就是指組件從創建到銷毀的過程。 那這裡講Spring Bean的生命周期,並不是講Bean是如何創建的, 而是想講下Bean從實例化到銷毀,Spring框架在Bean ...
說明: 本文基於Spring-Framework 5.1.x版本講解
概述
說起生命周期, 很多開源框架、中間件的組件都有這個詞,其實就是指組件從創建到銷毀的過程。 那這裡講Spring Bean的生命周期,並不是講Bean是如何創建的, 而是想講下Bean從實例化到銷毀,Spring框架在Bean的各個階段給我們提供了哪些拓展點。 Bean本身有三個大的階段: 實例化、初始化、銷毀。
Spring的強大就是提供了非常多的拓展點, 我們可以基於這些拓展點實現不同的需求。 回到主題,Spring容器圍繞著生命周期的各個階段提供了不同功能的拓展點如下圖:
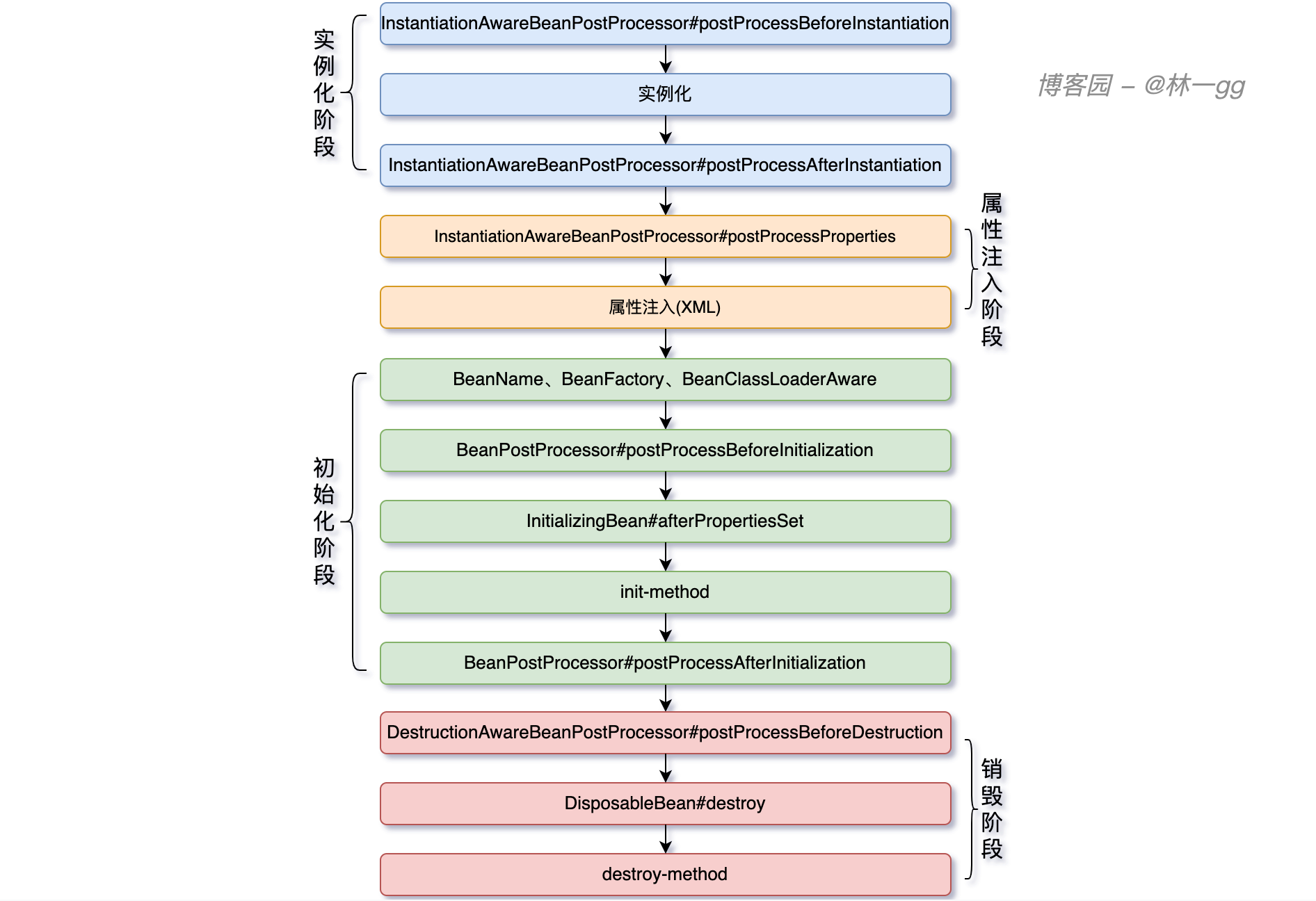
從上圖可以看到,整個生命周期涉及到的介面(當然這不是所有介面,只是日常中可以用到的,還有一部分是Spring內部的介面)分成了4個階段:
1. 實例化階段: 主要是以不同方式實例化Bean
2. 屬性註入階段:IOC的過程
3. 初始化階段:初始化Bean的內部組件、生成代理對象等都在這裡
4. 銷毀階段: 釋放資源
下麵我們對這些核心的介面進行簡單的介紹
介面介紹
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}返回值Object: 返回null值則執行Spring提供給我們的Bean實例化、屬性註入、初始化階段, 這是對於大多數Bean的選擇; 返回非null值則跳過Bean實例化、屬性註入、初始化階段,因為Spring會認為IOC等階段由使用者管理,所以在這種情況下後續會直接調用BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization介面, 進而有可能提前結束標準IOC流程, 為什麼說有可能呢? 因為還需取決於BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization的返回值。
使用場景: 使用頻率比較低,實際沒有用到過。不過在Spring-Framework的AOP源碼中有用到,見AbstractAutoProxyCreator
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation
default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}返回值boolean: true則執行Spring的屬性註入功能 , 大多數情況返回true即可,除非你有定製化的需求;返回false跳過Spring屬性註入功能,意味著@Resource、@Autowired等註解失效,也意味著xml文件中<property>標簽失效。
使用場景: 比較少, Spring-Framework源碼中也沒有用到
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}返回值PropertyValues: 一般返回入參pvs即可, Spring後續會使用返回值進行屬性註入。 尤其對於SpringBoot這種純JavaConfig配置的方式, 參數pvs一般為Empty(註意與null區分)
使用場景:標註@Resource、@Autowired等註解的屬性都在這個方法實現註入,比較核心, 詳見: CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
如果postProcessProperties方法返回null,Spring也會調用postProcessPropertyValues方法實現同樣的效果,不過這個方法是老版本中的,已經棄用掉的,不推薦使用.
@Deprecated
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}BeanName、BeanFactory、BeanClassLoaderAware
public interface BeanNameAware extends Aware {
void setBeanName(String name);
}
public interface BeanClassLoaderAware extends Aware {
void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader);
}
public interface BeanFactoryAware extends Aware {
void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}這三個介面就比較簡單了,就是給我們的Bean註入BeanName、ClassLoader、BeanFactory屬性, 他的調用時機在實例化、屬性註入之後,是初始化階段的第一步
BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}返回值Object: 一般情況返回入參的bean即可。
需要註意幾點:
1. 如果返回null,則後續所有實現該介面的Processor都不會執行,且返回上個Processor的返回值;
2. 上個Processor的返回值會作為下個Processor的入參。
3. 最後一個Processor的返回值會代替原來的Bean(返回入參Bean的情況可以忽略這一條)進行後續處理(包含Bean初始化、以及最終暴露到Spring容器中)
這裡比較難理解,貼下源碼
/**
* 執行Bean的初始化步驟
*/
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 此處省略不關鍵的部分代碼
Object wrappedBean = bean;
// 調用所有實現BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization介面的方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
// 使用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法的返回值當做入參進行Bean初始化
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
// 使用postProcessBeforeInitialization方法的返回值當做入參進行Bean初始化的後置處理
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
return wrappedBean;
}
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
// getBeanPostProcessors() 返回的Processors是有有優先順序順序的
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result; // 如果為null , 這裡直接退出該方法並返回上次Processor返回的結果
}
result = current; // 上個Processor執行的結果作為下個Processor處理的入參
}
return result;
}使用場景:1. 標註@PostConstruct註解的方法都在該介面實現調用, 詳見InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 2. 各種Aware介面的調用入口,詳見ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}Bean初始化資源的回調介面 , 與@PostConstruct一樣的作用 ,但要註意的是幾個初始化方法調用的順序:1.@PostConstruct2. afterPropertiesSet 3. init-method
使用場景: 資源初始化、可以使用回調的特性實現策略模式等,實際工作中用的較多
init-method
XML配置文件中init-method屬性或者@Bean註解initMethod屬性指定的方法 , 比較簡單不多說了
BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}返回值Object: 一般情況返回入參的bean即可。
與postProcessBeforeInitialization方法的調用邏輯一樣,需要註意幾點:
1. 如果返回null,則後續所有實現該介面的Processor都不會執行,且返回上個Processor的返回值;
2. 上個Processor的返回值會作為下個Processor的入參。
3. 最後一個Processor的返回值會代替原來的Bean(返回入參Bean的情況可以忽略這一條)進行後續處理(包含Bean初始化、以及最終暴露到Spring容器中)
使用場景:AOP生成代理的入口,詳見AbstractAutoProxyCreator
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeDestruction
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given bean instance before its
* destruction, e.g. invoking custom destruction callbacks.
* <p>Like DisposableBean's {@code destroy} and a custom destroy method, this
* callback will only apply to beans which the container fully manages the
* lifecycle for. This is usually the case for singletons and scoped beans.
* @param bean the bean instance to be destroyed
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean#destroy()
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#setDestroyMethodName(String)
*/
void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;用於處理Bean銷毀前的一些前置工作,可實現批量處理。
使用場景:標註@PreDestroy註解的方法都在該介面實現調用, 詳見InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
DisposableBean#destroy
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} on destruction of a bean.
* @throws Exception in case of shutdown errors. Exceptions will get logged
* but not rethrown to allow other beans to release their resources as well.
*/
void destroy() throws Exception;Bean直接實現該介面即可,同時也註意這幾個銷毀方法的調用順序: 1.@PreDestroy2. destroy 3. destroy-method
使用場景:釋放Bean本身持有的資源,如連接池Bean資源等 ,單個處理。
destroy-method
XML配置文件中destroy-method屬性或者@Bean註解destroyMethod屬性指定的方法 , 比較簡單不多說了
小結
圍繞生命周期Spring容器給我們提供的介面就簡單介紹到這,實際上除了上面列舉的介面之外,還有一些不常用的介面我沒有列舉出來,如:SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor、MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor等。對於以上介面,個人理解沒有必要像八股文一樣死記硬背每個介面的作用,甚至嘗試記住介面的名稱,關鍵在於設計的思想,開頭也說過,其他框架的組件也有生命周期的實現,Spring與這些框架實現上有什麼不同,這才是應該瞭解的;當然完全不瞭解其介面的作用也是不行的,這裡強調的是不用刻意去死記硬背介面的含義, 在工作中多看看別人、別的框架的使用方式更有利於加深理解。
本文來自博客園,作者:林一gg,轉載請註明原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/linyigg/p/16948294.html



