File類和IO流 File類 概述 public class File 文件和目錄路徑名的抽象表示 文件和目錄是可以通過File封裝成對象的 封裝的不是文件,而是一個路徑(可以存在,也可以不存在);要通過具體的操作將這個路徑轉化為具體存在 public class FileDemo { publi ...
File類和IO流
File類
概述
- public class File
- 文件和目錄路徑名的抽象表示
- 文件和目錄是可以通過File封裝成對象的
- 封裝的不是文件,而是一個路徑(可以存在,也可以不存在);要通過具體的操作將這個路徑轉化為具體存在
public class FileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建一個路徑操作對象 路徑包括父路徑和子路徑
File f = new File("G:\\FileTest\\java.txt");
System.out.println(f);
//創建一個路徑操作對象 父路徑,子路徑
File f1 = new File("G:\\FileTest","java.txt");
System.out.println(f1);
//創建一個父路徑操作對象
File f2 = new File("G:\\FileTest");
//從父路徑和子路徑創建的路徑操作對象
File f3 = new File(f2,"java.txt");
System.out.println(f3);
}
}
運行結果:
//File類重寫了toString()
G:\FileTest\java.txt
G:\FileTest\java.txt
G:\FileTest\java.txt
File類創建功能
運行代碼之前
代碼
public class FileDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*在G:\FileTest目錄下,創建一個Hello.txt文件
如果文件不存在就創建文件,返回true
如果文件存在返回false*/
File f1 = new File("G:\\FileTest\\Hello.txt");
System.out.println(f1.createNewFile());
/*在G:\FileTest目錄下,創建一個Cat文件夾
如果文件不存在就創建文件,返回true
如果文件存在返回false*/
File f2 = new File("G:\\FileTest\\Cat");
System.out.println(f2.mkdir());
/*在G:\FileTest目錄下,創建一個多級目錄Eat\egg文件夾
如果文件不存在就創建文件,返回true
如果文件存在返回false*/
File f3 = new File("G:\\FileTest\\Eat\\egg");
System.out.println(f3.mkdirs());
}
}
運行結果
true
true
true
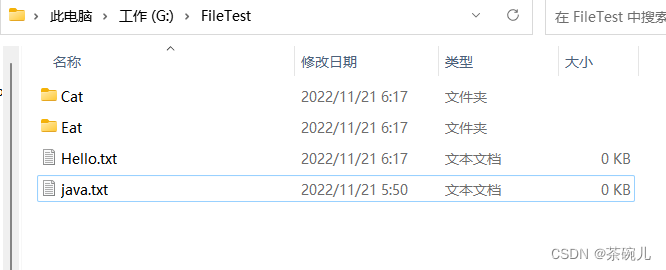
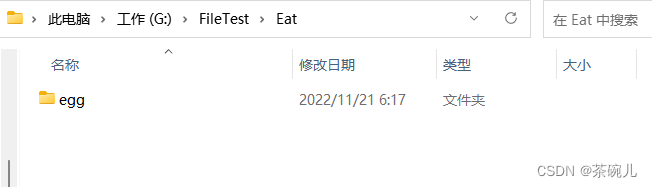
註意
- 如果同一目錄下存在同名的文件夾,createNewFile()創建文件時會失敗;要將同名的文件夾刪掉才會創建文件成功。
File類判斷和獲取功能
運行代碼之前,先在此位置創建一個java.txt文件
public class FileDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建File對象
File f = new File("idea_test\\java.txt");
//抽象路徑名錶示的File是否為目錄
System.out.println("是否為目錄:"+f.isDirectory());
//抽象路徑名錶示的File是否為文件
System.out.println("是否為文件:"+f.isFile());
//抽象路徑名錶示的File是否存在
System.out.println("是否存在:"+f.exists());
//返回此抽象路徑名的絕對路徑(字元串)
System.out.println("絕對路徑:"+f.getAbsolutePath());
//將此抽象路徑名轉化為字元串
System.out.println("抽象路徑:"+f.getPath());
//返回此抽象路徑名錶示的文件名或者目錄名
System.out.println("文件名或者目錄名:"+f.getName());
System.out.println("-------FileTest目錄-------------");
File f1 = new File("G:\\FileTest");
//返回此抽象路徑名錶示的目錄中的文件名和目錄的名稱字元串數組
String[] list = f1.list();
//遍歷字元串數組
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("---------FileTest目錄中的文件-----------");
//返回此抽象路徑名錶示的目錄中的文件名和目錄的File對象數組
File[] files = f1.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
//System.out.println(file);
//如果對象是一個文件,輸出文件名
if (file.isFile()){
System.out.println(file.getName());
}
}
}
}
運行結果:
是否為目錄:false
是否為文件:true
是否存在:true
絕對路徑:G:\Work_Basic\JavaSE_Code\idea_test\java.txt
抽象路徑:idea_test\java.txt
文件名或者目錄名:java.txt
-------FileTest目錄-------------
Cat
Eat
Hello.txt
java.txt
---------FileTest目錄中的文件-----------
Hello.txt
java.txt
File類刪除功能
創建一個hello.txt文件
public class FileDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//在當前模塊目錄下創建一個hello.txt文件
File f = new File("idea_test\\hello.txt");
//System.out.println(f.createNewFile());
//刪除當前模塊目錄下的hello.txt文件
System.out.println(f.delete());
}
}
運行結果:hello.txt文件已經刪除
true
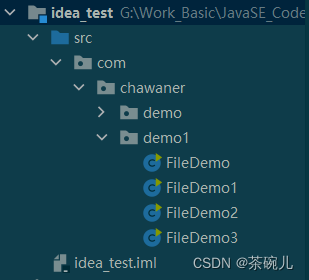
//在當前模塊目錄下創建一個"雀巢"文件夾
File f1 = new File("idea_test\\雀巢");
System.out.println(f1.mkdir());
運行結果:true
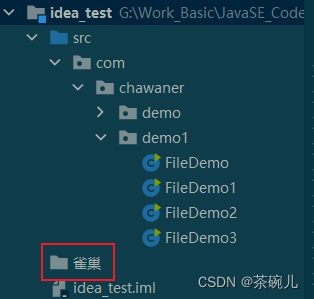
//刪除當前模塊目錄下的"雀巢"文件夾
System.out.println(f1.delete());
運行結果:true
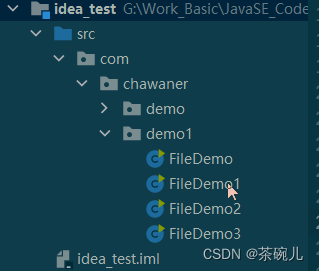
//在當前模塊目錄下創建一個"雀巢"文件夾,文件夾里有個java.txt文件
File f2 = new File("idea_test\\雀巢");
System.out.println(f2.mkdir());
File f3 = new File(f2, "java.txt");
System.out.println(f3.createNewFile());
運行結果:
true
true
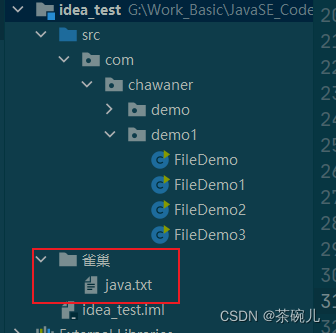
創建多級目錄文件
- 在創建文件之前,應該先創建上一級的目錄,否則會報錯
//刪除當前模塊目錄下的"雀巢"文件夾
System.out.println(f3.delete());
System.out.println(f2.delete());
運行結果:"雀巢"文件夾刪掉了
true
true
刪除文件夾
- 如果要刪除的文件夾下有文件,刪除操作會不成功,返回false
- 要先刪除該文件夾下的文件,之後才能刪除該文件夾
遞歸
方法中調用方法本身
思路:把一個複雜的問題,層層轉化為一個與原問題相似的規模較小的問題來求解,遞歸策略只需少量的程式就可描述出解題過程所需要的多次重覆計算。
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*不死神兔:求第20個月兔子的對數
* 每個月兔子的對數:1,1,2,3,5,8……*/
//創建長度為20的數組 索引0-19
int[] arr = new int[20];
//第一個月:1對
arr[0] = 1;
//第二個月:1對
arr[1] = 1;
//從第三個月(索引2)開始:兔子的對數等於前兩個月之和
for (int i = 2; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i - 1] + arr[i - 2];
}
//輸出第20個月(索引19)兔子的對數
System.out.println(arr[19]);
}
}
運行結果:
6765
使用遞歸來解決上述問題
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*不死神兔:求第20個月兔子的對數
* 每個月兔子的對數:1,1,2,3,5,8……*/
//第20個月,兔子的對數
System.out.println(f(20));
}
/**
* 遞歸:求第n個月兔子的對數
*
* @param n 第n個月
* @return 兔子的對數
* StackOverflowError 當由於應用程式而發生堆棧溢出時引發 遞歸太深。遞歸需要停止
*/
public static int f(int n) {
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
} else {
//從第3個月開始,每個月兔子的對數都是前兩個月之和
return f(n - 1) + f(n - 2);
}
}
}
運行結果:
6765
遞歸解決問題
- 遞歸出口:否則會出現記憶體溢出StackOverflowError
- 遞歸規則:與原問題相似的規模較小的問題
案例:遞歸求5的階乘
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//調用方法,求5的階乘
System.out.println(f(5));
}
/**
* 階乘
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static int f(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * f(n - 1);
}
}
}
運行結果:
120
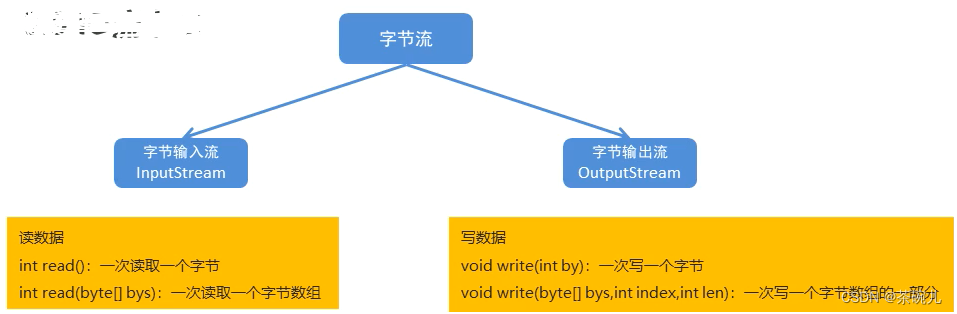
IO位元組流
IO流概述
- IO:輸入/輸出
- 流:數據傳輸
- IO流就是處理設備之間數據傳輸問題的(常見:文件複製,文件上傳,文件下載)
輸入:讀數據;硬碟到記憶體條
輸出:寫數據;記憶體條到硬碟
IO流的分類
- 按照數據的流向
- 輸入流:讀數據
- 輸出流:寫數據
- 按照數據類型
- 位元組流:位元組輸入流,位元組輸出流
- 字元流:字元輸入流,字元輸出流
使用場景
- 用記事本打開,能看懂的內容,使用字元流,否則使用位元組流。
- 如果不知道該使用哪種類型的流,就使用位元組流。
位元組流寫數據
位元組流抽象基類
- public abstract class InputStream:位元組輸入流的所有類的超類
- public abstract class OutputStream:位元組輸出流的所有類的超類
- 子類名稱特點:子類名稱都是以父類名作為子類命的尾碼
FileOutputStream:文件輸入流,用於將數據寫入File
- FileOutputStream(String name):將數據以指定的名稱寫入文件
使用位元組輸出流寫數據的步驟
- 創建位元組輸出流對象
- 調用系統功能創建了文件
- 創建位元組輸出流
- 讓位元組數流對象指向文件)
- 調用位元組輸出流對象的寫數據方法
- 釋放資源:關閉此文件的輸出流並釋放與此流關聯的任何系統資源
創建位元組輸出流對象的三種方式:
//創建位元組輸出流對象 第一種
FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt");
//創建位元組輸出流對象 第二種
File file = new File("idea_test\\java.txt");
FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream(file);
//創建位元組輸出流對象 第三種
FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream(new File("idea_test\\java.txt"));
案例:使用位元組輸出流寫數據的步驟
public class IoDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 創建位元組輸出流對象
* 1.調用系統功能創建了文件
* 2.創建了位元組輸出流對象
* 3.讓位元組輸出流對象指向創建好的文件
*/
FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt");
//void write(int b):將指定的位元組寫入此文件輸出流
fo.write(97);
//釋放資源:關閉此文件的輸出流並釋放與此流關聯的任何系統資源
fo.close();
}
}
運行結果:
位元組流寫數據的三種方式

//寫入abcde 第一種
fo.write(97);
fo.write(98);
fo.write(99);
fo.write(100);
fo.write(101);
//寫入abcde 第二種
byte[] b = {97,98,99,100,101};
//或者,返回字元串中的位元組數組
//byte[] b = "abcde".getBytes();
fo.write(b);
//寫入abcde 第三種
byte[] b = {97,98,99,100,101};
//參數:位元組數組 索引起始位置 索引結束位置
fo.write(b,0,b.length);
位元組流寫數據的兩個小問題
- 位元組流寫數據如何實現換行?
- Windows: \r\n
- Linux: \n (win11用這個也可以)
- Mac: \r
- 位元組流寫數據如何實現追加寫入?
- public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)
//追加寫入
public class IoDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//如果第二個參數為true,將在文件末尾追加內容
//如果第二個參數不為true(不寫或者false),將不是追加,而是從文件開頭開始覆蓋內容
FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt",true);
//FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt",false);
//寫入十次”hello“
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 寫入位元組流
// getBytes()返回字元串中的位元組數組
fo.write("hello".getBytes());
fo.write("\n".getBytes());
}
fo.close();
}
}
位元組流寫數據加異常處理
public class IoDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化為null
FileOutputStream fo = null;
try {
//可能出現異常的代碼
fo = new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt");
fo.write("世界盃".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
//異常處理的代碼
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {//被finally控制的語句,一定會執行,除非JVM退出
//null調方法會報空指針異常,所以fo不為null才能執行close()釋放資源操作
if (fo != null) {
try {
//close()有編譯時異常,用try...catch()處理一下
fo.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
位元組流讀數據(一次讀一個位元組)
FileInputStream:從文件系統中的文件獲取輸入位元組
- FileInputStream(String name):通過打開與實際文件的連接來創建一個FileInputStream,該文件由文件系統中的路徑名name命名。
使用位元組輸入流讀數據的步驟:
- 創建位元組輸入流對象
- 調用位元組輸入流對象的讀數據方法
- 釋放資源
一次讀取一個位元組 read(),如果返回-1說明到了文件末尾
public class IoDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:把文件java.txt中的內容讀取出來在控制台輸出
File file = new File("idea_test\\java.txt");
//初始化fi
FileInputStream fi = null;
try {
//創建位元組輸出流對象
fi = new FileInputStream(file);
//調用位元組輸入流對象的讀數據方法,一次讀取一個位元組
int read;
while ((read = fi.read()) != -1) {
//輸出
System.out.print((char) read);
}
//釋放資源
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fi != null) {
try {
fi.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
再補充一個一次性讀取文件全部內容的:
public class IoDemo {//throws拋出異常
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:把文件java.txt中的內容讀取出來在控制台輸出
File file = new File("idea_test\\java.txt");
//創建文件輸入流對象
FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream(file);
//file.length()返回值是long,但byte只能裝整形大小的空間,所以要強轉
byte[] buffer = new byte[(int) file.length()];
//調用位元組輸入流對象的讀數據方法,讀取文件全部內容
fi.read(buffer);
System.out.print(new String(buffer));
//釋放資源
fi.close();
}
}
註意:文件位元組流讀取文件,一次讀一個位元組,遇到中文會亂碼;一次讀取文件的所有內容,中文不會亂碼。
位元組流複製文本文件
思路:
- 根據數據源創建位元組輸入流對象
- 根據目的地創建位元組輸出流對象
- 讀寫數據,複製文本文件
- 釋放資源
public class IoDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:把文件G:\FileTest\Hello.txt中的內容複製到模塊目錄下的java.txt
//1.根據數據源創建輸入流對象
InputStream fo = new FileInputStream("G:\\FileTest\\Hello.txt");
//2.根據目的地創建輸出流對象
OutputStream fi = new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt");
//一次讀取一個位元組,一次寫入一個位元組
//3.讀文件
int read;
while ((read = fo.read()) != -1) {
//4.寫入文件
fi.write(read);
}
//5.釋放資源,先關閉輸出流,在關閉輸入流
fo.close();
fi.close();
}
}
位元組流讀數據(一次讀一個位元組數組)
使用位元組輸入流讀數據的步驟
- 創建位元組輸入流對象
- 調用位元組輸入流對象的讀數據方法
- 釋放資源
public class IoDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//創建位元組輸入流對象
InputStream fo = new FileInputStream("idea_test\\java.txt");
//創建一個位元組數組,長度一般為1024及其整數倍
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//創建位元組輸入流對象的讀數據方法,
// len 一次讀取的位元組數組的長度
int len;
while ((len = fo.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
//釋放資源
fo.close();
}
}
註意:讀含有中文的文件時,建議一次讀完。
因為一個漢字占2~3個位元組,如果正好讀了半個漢字,那就亂碼了(如圖)。
後面的內容用字元流就更方便了,因為一個漢字一個字母都是一個字元。
位元組流複製圖片
思路
- 根據數據源創建位元組輸入流對象
- 根據目的地創建位元組輸出流對象
- 讀寫數據,複製圖片
- 釋放資源
public class IoDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:把圖片G:\FileTest\dog.jpg複製到模塊目錄下的dog.jpg
//1.根據數據源創建輸入流對象
InputStream fo = new FileInputStream("G:\\FileTest\\dog.jpg");
//2.根據目的地創建輸出流對象
OutputStream fi = new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\dog.jpg");
//定義一個位元組數組
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//一次讀取一個位元組數組,一次寫入一個位元組數組
int len;
//3.迴圈讀寫圖片
while ((len = fo.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//4.寫入文件
fi.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//5.釋放資源,先關閉輸出流,在關閉輸入流
fo.close();
fi.close();
}
}
運行結果:
IO字元流
位元組緩衝流

位元組緩衝輸出流寫數據
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//位元組緩衝輸出流寫數據
//創建位元組緩衝輸出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//寫入數據
bos.write("hello\r\n".getBytes());
bos.write("java\r\n".getBytes());
//釋放資源
bos.close();
}
}
位元組緩衝輸入流讀數據
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//位元組緩衝輸入流讀數據
//創建位元組緩衝輸入流,一次性從文件中讀取8192個位元組
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//一次讀取的位元組流數組長度
//每次讀取的1024個位元組,是直接從位元組緩衝流那8192個位元組里拿的,拿完之後位元組緩衝流會再次從文件中一次性讀取8192個位元組
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//讀數據
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
//釋放資源
bis.close();
}
}
位元組流複製視頻
思路
- 根據數據源創建位元組輸入流對象
- 根據目的地創建位元組輸出流對象
- 讀寫數據,複製視頻
- 釋放資源
位元組緩衝流一次讀寫一個位元組數組
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//把G:\FileTest\video.avi複製到模塊目錄下idea_test\video.avi
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("G:\\FileTest\\video.avi"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\video.avi"));
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
//System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
速度:
- 基本位元組流一次讀寫一個位元組 < 基本位元組流一次讀寫一個位元組數組 < 位元組緩衝流一次讀寫一個位元組 < 位元組緩衝流一次讀寫一個位元組數組
為什麼出現字元流
- 位元組流操作中文不方便,所以Java提供了字元流
- 字元流 = 位元組流 + 編碼表
- 用位元組流每次讀寫一個位元組複製文本時,底層操作會自動進行位元組拼接中文
- 漢字在存儲的時候,無論選擇哪種編碼格式,第一個位元組都是負數
案例:
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s = "abc";
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes("UTF-8");
byte[] bytes1 = s.getBytes("GBK");
//[97, 98, 99]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
//[97, 98, 99]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1));
String s1 = "肥胖";
byte[] bytes2 = s1.getBytes("UTF-8");
byte[] bytes3 = s1.getBytes("GBK");
//[-24, -126, -91, -24, -125, -106]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes2));
//[-73, -54, -59, -42]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes3));
}
}
編碼表
- 電腦存儲數據是二進位的(0和1)
- 編碼和解碼
- 按照規則,將字元存儲到電腦中,稱為編碼;反之,將存儲到電腦中的二進位內容按照規則解析顯示出來,稱為解碼
- 編碼和解碼的規則必須一致,否則會出現亂碼
- 字元編碼
- 就是一套自然語言的字元與二進位數之間的對應關係。如(A,65)
字元集
- 是一個系統支持的所有字元集的集合,包括各國家文字,標點符號,圖形符號,數字等
- 電腦要存儲和識別各種字元集符號,就要進行字元編碼,一套字元集必然至少有一套字元編碼規則。常見的字元集有ASCII字元集,GBXXX字元集,Unicode字元集等



字元串中的編碼解碼問題
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String s = "接化發";
//預設規則編碼
byte[] bys = s.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bys));
//指定規則編碼
byte[] bys1 = s.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bys1));
//預設規則解碼
String s1 = new String(bys);
System.out.println(s1);
//指定規則解碼
String s2 = new String(bys1, "GBK");
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
運行結果:
[-26, -114, -91, -27, -116, -106, -27, -113, -111]
[-67, -45, -69, -81, -73, -94]
接化發
接化發
字元流中的編碼解碼問題
字元流抽象基類
- Reader:字元輸入流的抽象類
- Writer:字元輸出流的抽象類
InputStreamReader:是從位元組流到字元流的橋梁
OutputStreamWriter:是從字元流到位元組流的橋梁
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//字元輸出流對象 預設編碼格式
//OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//字元輸出流對象 指定編碼格式
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"),"UTF-8");
osw.write("蔬菜");
osw.close();
//字元輸入流對象 指定編碼格式
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"),"UTF-8");
//一次讀取一個字元
int ch;
while ((ch = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
isr.close();
}
}
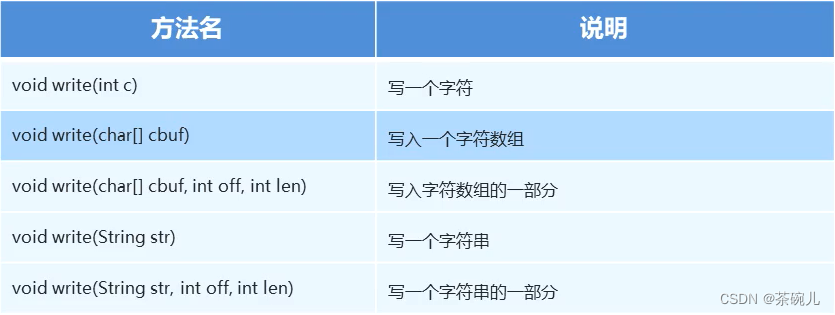
字元流寫數據的5種方式
flush()和close()的區別
- flush()刷新流,刷新之後還可以寫數據
- close()關閉流,關閉流之前會自動執行刷新流操作,關閉之後就不能再繼續寫數據了
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"));
osw.write(97);
/**
* 刷新緩衝
* 字元流寫數據如果不刷新流,那麼數據就在緩衝區中,沒close()之前,打開文件java.txt看不到數據
* 字元流相對於位元組流是有緩衝的,真正寫數據是位元組流
*/
osw.flush();
//close():關閉流之前會自動執行刷新流操作
//flush()刷新流之後還可以繼續寫數據,但是close()關閉流之後就不能繼續寫數據了
osw.close();
}
}
字元流寫數據的5種方式:
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//1.寫入一個字元:a
osw.write(97);
//2.寫入一個字元數組:abcde
char[] chs = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'};
osw.write(chs);
//3.寫入一個字元數組的一部分:abc
osw.write(chs, 0, 3);
//4.寫入一個字元串:世界盃
String s = "世界盃";
osw.write(s);
//5.寫入一個字元串的一部分:界
osw.write(s,1,1);
osw.flush();
osw.close();
}
}
字元流讀數據的2種方式
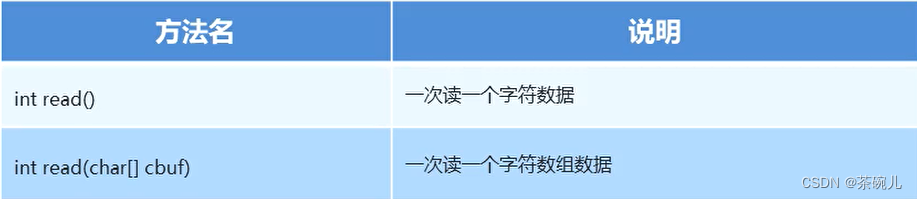
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//創建字元輸入流對象
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//1.一次讀一個字元
int ch;
while ((ch = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) ch);
}
//2.一次讀取一個字元數組
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(chs)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(chs,0,len));
}
isr.close();
}
}
字元流複製Java文件
思路:
- 根據數據源創建字元輸入流對象
- 根據目的地創建字元輸出流對象
- 讀寫數據,複製文件
- 釋放資源
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:將模塊下的idea_test\java.txt,複製到idea_test\java1.txt
//創建字元輸入流對象
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//創建字元輸出流對象
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("idea_test\\java1.txt"));
//讀寫數據,複製文件
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(chs)) != -1) {
osw.write(chs,0,len);
}
osw.close();
isr.close();
}
}
字元流複製Java文件(改進版)

思路:
- 根據數據源創建字元輸入流對象
- 根據目的地創建字元輸出流對象
- 讀寫數據,複製文件
- 釋放資源
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:將模塊下的idea_test\java.txt,複製到idea_test\java1.txt
//創建字元輸入流對象
FileReader fr = new FileReader("idea_test\\java.txt");
//創建字元輸出流對象
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("idea_test\\java2.txt");
//讀寫數據,複製文件
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) {
fw.write(chs,0,len);
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}
字元緩衝流

構造方法
- BufferedWriter(Writer out)
- BufferedReader(Reader in)
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("idea_test\\java.txt"));
bw.write("hello\n");
bw.write("world\r");
bw.write("java\r\n");
bw.write(97);
bw.write(98);
bw.write(99);
bw.close();
//緩衝流預設一次從文件里讀取8192個字元
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("idea_test\\java1.txt"));
//每次讀取的1024個字元,是直接從緩衝流那8192個字元里拿的,拿完之後緩衝流會再次從文件中一次性讀取8192個字元
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = br.read(chs)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(chs, 0, len));
}
br.close();
}
}
換行
- /r Mac
- /n Unix/Linux
- /r/n Windows
- 不過我在windows11上測試換行,以上三種都可以。
字元緩衝流複製Java文件
思路:
- 根據數據源創建字元緩衝輸入流對象
- 根據目的地創建字元緩衝輸出流對象
- 讀寫數據,複製文件
- 釋放資源
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:java字元緩衝流複製文件,從idea_test\java.txt複製到idea_test\java3.txt
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("idea_test\\java.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("idea_test\\java3.txt"));
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = br.read(chs)) != -1){
bw.write(chs,0,len);
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
字元緩衝流特有功能

newLine():就是根據系統,自動識別的換行符
readLine():一次讀一行數據,如果讀到了結尾則返回null;只讀每行的內容,不讀行尾終止符
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//寫數據
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("idea_test\\java.txt"));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
bw.write("hello-"+i);
//換行
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
//讀數據
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("idea_test\\java.txt"));
String s;
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(s);
}
br.close();
}
}
字元緩衝流特有功能複製Java文件
思路:
- 根據數據源創建字元緩衝輸入流對象
- 根據目的地創建字元緩衝輸出流對象
- 讀寫數據,複製文件(使用字元緩衝流特有功能)
- 釋放資源
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:java字元緩衝流(特有功能)複製文件,從idea_test\java.txt複製到idea_test\java3.txt
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("idea_test\\java.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("idea_test\\java4.txt"));
char[] chs = new char[1024];
String s;
while ((s = br.readLine())!=null){
//每寫一行數據,換行,刷新
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
IO流小結
1.位元組流
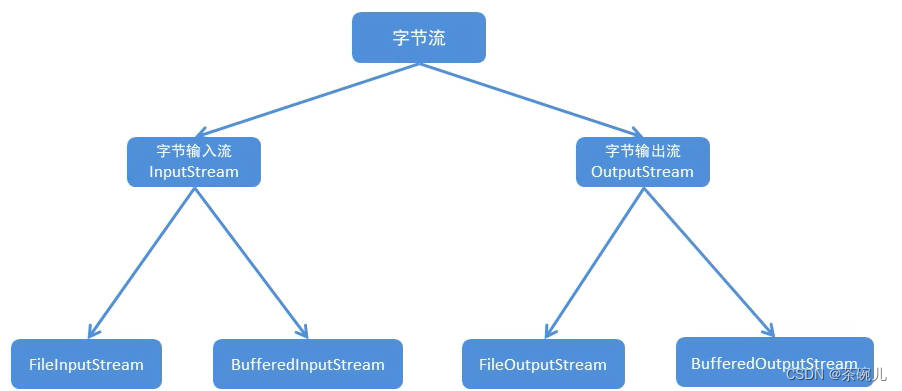
位元組流小結
- 位元組流可以複製【任意文件】數據,有四種方式,一般採用位元組緩衝流一次讀寫一個位元組數組的方式
2.字元流
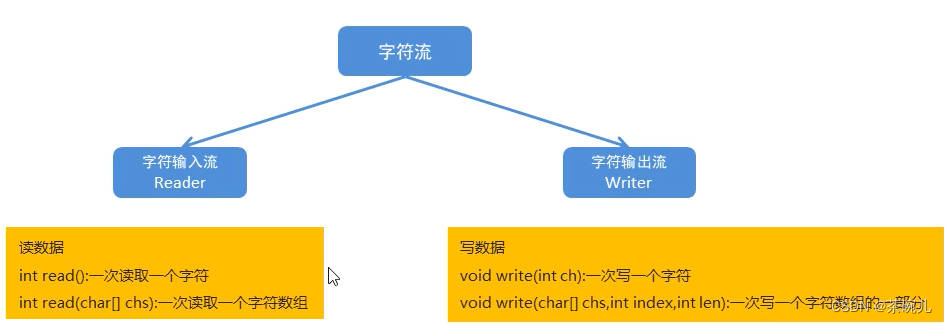
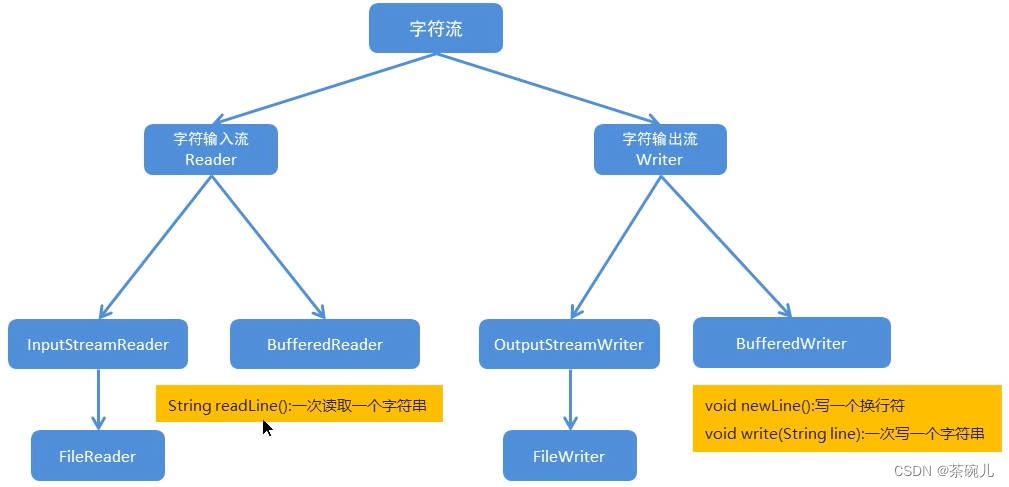
字元流小結
- 字元流只能複製【文本數據】,有五種方式,一般採用字元緩衝流的特有功能
IO練習
1.集合到文件
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:將ArrayList集合中的字元串數據寫入到文本文件。要求每一個字元串元素作為文件中的一行數據
//1.創建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//2.向集合中創建字元串元素
list.add("hello");
list.add("world");
list.add("java");
list.add("世界盃");
//3.創建字元緩衝流輸入對象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//4.遍歷集合,得到每一個字元串數據
for (String s : list) {
//5.調用字元緩衝流對象的方法寫數據
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
//6.釋放資源
bw.close();
}
}
運行結果:
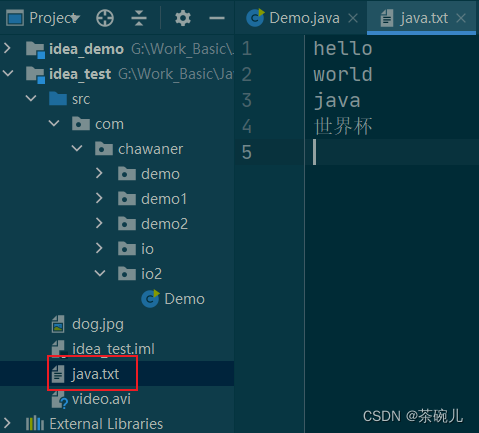
2.文件到集合
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:把文本文件中的數據讀取到集合中,並遍歷集合。要求:文本中每一行數據是一個集合元素
//1.創建字元緩衝輸入流對象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//2.創建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//3.調用字元緩衝輸入流對象的方法讀數據
String s;
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
//4.把讀到的字元串數據存儲到集合
list.add(s);
}
//5.釋放資源
br.close();
//6.遍歷集合
for (String s1 : list) {
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
}
運行結果:
hello
world
java
世界盃
3.點名器
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:文件中存儲了班級同學的姓名,每一個姓名占一行,要求通過程式實現隨機點名
//1.創建字元緩衝輸入流對象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//2.創建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//3.調用字元緩衝輸入流對象的方法讀數據
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
//4.把讀到的字元串數據存儲到集合
list.add(line);
}
//5.釋放資源
br.close();
//6.使用Random產生一個隨機數,隨機數的範圍在:[0,集合長度)
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(list.size());
//7.把產生的隨機數作為索引,在集合中獲取值
String s = list.get(i);
//8.將獲取到的值輸出到控制台
System.out.println(s);
}
}
4.集合到文件(改進版)
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:將ArrayList集合中的學生數據寫入到文本文件。要求每一個向何生對象的數據作為文件中的一行數據
//格式:學號,姓名,年齡,居住地
//1.定義學生類
//2.創建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
//3.創建學生對象
Student s1 = new Student("初二001", "小明", 15, "西安");
Student s2 = new Student("初二002", "小紅", 16, "北京");
Student s3 = new Student("初二003", "小軍", 17, "上海");
Student s4 = new Student("初二004", "白展堂", 14, "雲南");
Student s5 = new Student("初二005", "史珍香", 13, "廣州");
//4.把學生對象添加到集合中
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
list.add(s4);
list.add(s5);
//5.創建字元緩衝輸出流對象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//6.遍歷集合,得到每一個學生對象
for (Student stu : list) {
//7.把學生對象的數據拼接成指定格式的字元串
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append(stu.getId() + "," + stu.getName() + "," + stu.getAge() + "," + stu.getAddress());
//8.調用字元緩衝輸出流對象的方法寫數據
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
//9.釋放資源
bw.close();
}
}
5.文件到集合(改進版)
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 需求:把文本文件中的數據讀取到集合中,並遍歷集合。
* 要求:文本中每一行數據是一個學生對象的成員變數值
* 格式:學號,姓名,年齡,居住地
*/
//1.定義學生類
//2.創建字元緩衝輸入流對象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("idea_test\\java.txt"));
//3.創建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
String line;
//4.調用字元緩衝輸入流對象的方法讀數據
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
//5.把讀取到的字元串用split分割,得到一個字元串數組
String[] s = line.split(",");
//6.創建學生對象
Student stu = new Student();
//7.把字元串數組中的每一個元素取出來,賦值給學生對象的成員變數
stu.setId(s[0]);
stu.setName(s[1]);
stu.setAge(Integer.parseInt(s[2]));
stu.setAddress(s[3]);
//8.把學生對象添加到集合
list.add(stu);
}
//9.釋放資源
br.close();
//10.遍歷集合
for (Student s : list) {
//直接輸出,因為Student類中重寫了toString()
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
運行結果:
Student{id='初二001', name='小明', age=15, address='西安'}
Student{id='初二002', name='小紅', age=16, address='北京'}
Student{id='初二003', name='小軍', age=17, address='上海'}
Student{id='初二004', name='白展堂', age=14, address='雲南'}
Student{id='初二005', name='史珍香', age=13, address='廣州'}
標準流和列印流
集合到文件數據排序(改進版)
定義學生類:
public class Student {
private String name;
private int yuwen;
private int shuxue;
private int yingyu;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int yuwen, int shuxue, int yingyu) {
this.name = name;
this.yuwen = yuwen;
this.shuxue = shuxue;
this.yingyu = yingyu;
}
//定義獲取總分的方法
public int getSum() {
return this.yuwen + this.shuxue + this.yingyu;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getYuwen() {
return yuwen;
}
public void setYuwen(int yuwen) {
this.yuwen = yuwen;
}
public int getShuxue() {
return shuxue;
}
public void setShuxue(int shuxue) {
this.shuxue = shuxue;
}
public int getYingyu() {
return yingyu;
}
public void setYingyu(int yingyu) {
this.yingyu = yingyu;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", yuwen=" + yuwen +
", shuxue=" + shuxue +
", yingyu=" + yingyu +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (yuwen != student.yuwen) return false;
if (shuxue != student.shuxue) return false;
if (yingyu != student.yingyu) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + yuwen;
result = 31 * result + shuxue;
result = 31 * result + yingyu;
return result;
}
}
測試類:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 需求:鍵盤錄入幾個學生信息(姓名,語文成績,數學成績,英語成績)
* 要求:按照成績總分由高到低寫入文件(排序規則)
*/
Set<Student> list = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
//匿名內部類重寫排序方法
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
//總分從低到高
int num = o2.getSum() - o1.getSum();
//如果總分相同,按照語文成績從高到低
int num1 = num == 0 ? o1.getYuwen() - o2.getYuwen() : num;
//如果總分相同,語文成績也相同,按照數學成績從高到低
int num2 = num1 == 0 ? o1.getShuxue() - o2.getShuxue() : num1;
//如果總分相同,語文成績也相同,數學成績也相同,說明英語成績肯定相同,那就按照姓名的字母排序
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) : num2;
return num3;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入第" + (i + 1) + "學生信息:");
System.out.println("姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入語文成績:");
int yuwen = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("請輸入數學成績:");
int shuxue = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("請輸入英語成績:");
int yingyu = sc.nextInt();
Student s = new Student(name, yuwen, shuxue, yingyu);
list.add(s);
}
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("idea_test\\java.txt"));
for (Student stu : list) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(stu.getName() + "," + stu.getYuwen() + "," + stu.getShuxue() + "," + stu.getYingyu() + ",總分:" + stu.getSum());
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
}
}
運行結果:總分從高到低排序
關羽,89,94,1,總分:184
孫權,1,99,3,總分:103
張飛,1,88,9,總分:98
caocao,1,55,9,總分:65
劉備,1,2,3,總分:6
複製單級文件夾
單級文件夾:文件夾中只有文件,沒有文件夾
數據源目錄
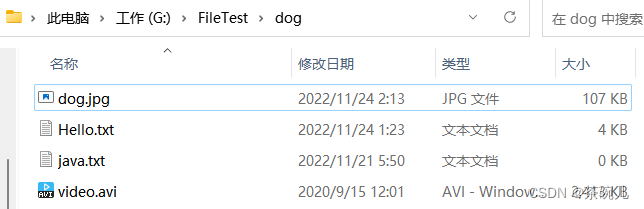
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 需求複製單級文件夾及其內容
*/
//1.創建數據源目錄
File file = new File("G:\\FileTest\\dog");
//2.獲取創建數據源目錄的名稱
String name = file.getName();
//3.創建目的地File對象
File file1 = new File("idea_test", name);
//4.判斷目的地是否已經存在該名稱的文件夾
if (!file1.exists()) {
//5.在目的地創建該名稱的文件夾
file1.mkdir();
}
//6.獲取數據源文件夾下的所有文件
File[] files = file.listFiles();
//7.遍曆數組,得到每一個文件對象
for (File fi : files) {
//8.獲取文件名稱
String fiName = fi.getName();
//9.在目的地文件夾中,創建fiName同名稱的文件
File fil = new File(file1, fiName);
//10.複製文件內容:將數據源文件內容複製到目的地文件中
copyFile(fi, fil);
}
}
/**
* 位元組緩衝流複製文件內容
* @param f1 數據源文件
* @param f2 目的地文件
*/
public static void copyFile(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {
//緩衝位元組輸入流對象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));
//緩衝位元組輸出流對象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2));
//讀寫文件
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
運行結果:
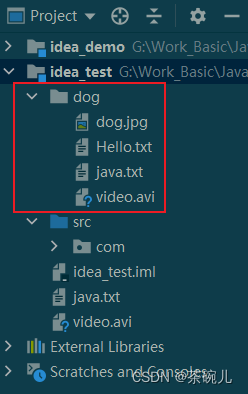
複製多級文件夾
多級文件夾:文件夾下還有文件夾
數據源文件夾:
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.創建數據源目錄
File srcFile = new File("G:\\FileTest");
//2.創建目的地File對象
File destFile = new File("D:\\");
//複製文件夾,參數為數據源File對象 和 目的地File對象
copyFolder(srcFile,destFile);
}
/**
* 複製文件夾
* @param srcFile 數據源文件夾操作對象
* @param destFile 目的地文件夾操作對象
*/
private static void copyFolder(File srcFile,File destFile) throws IOException {
//判斷數據源是否是目錄,如果是目錄
if (srcFile.isDirectory()){
//獲取數據源文件夾名稱
String srcFileName = srcFile.getName();
//目的地文件夾名稱
File destFileName = new File(destFile, srcFileName);
//判斷新文件夾名稱在目的地是否存在
if(!destFileName.exists()){
destFileName.mkdir();
}
//獲取數據源文件夾下的文件
File[] files = srcFile.listFiles();
//遍歷該數組,得到每一個元素對象
for (File file : files) {
//file可能是文件,也可能是文件夾;所以遞歸調用複製文件夾方法
copyFolder(file,destFileName);
}
}else {//如果數據源不是目錄
File newFile = new File(destFile, srcFile.getName());
copyFile(srcFile,newFile);
}
}
/**
* 複製文件內容
* @param f1 數據源文件操作對象
* @param f2 目的地文件操作對象
*/
public static void copyFile(File f1, File f2) throws IOException {
//緩衝位元組輸入流對象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));
//緩衝位元組輸出流對象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2));
//讀寫文件
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
目的地文件夾:
複製文件的異常處理
案例:複製文件;以下是幾種處理異常的方法
- 拋出處理
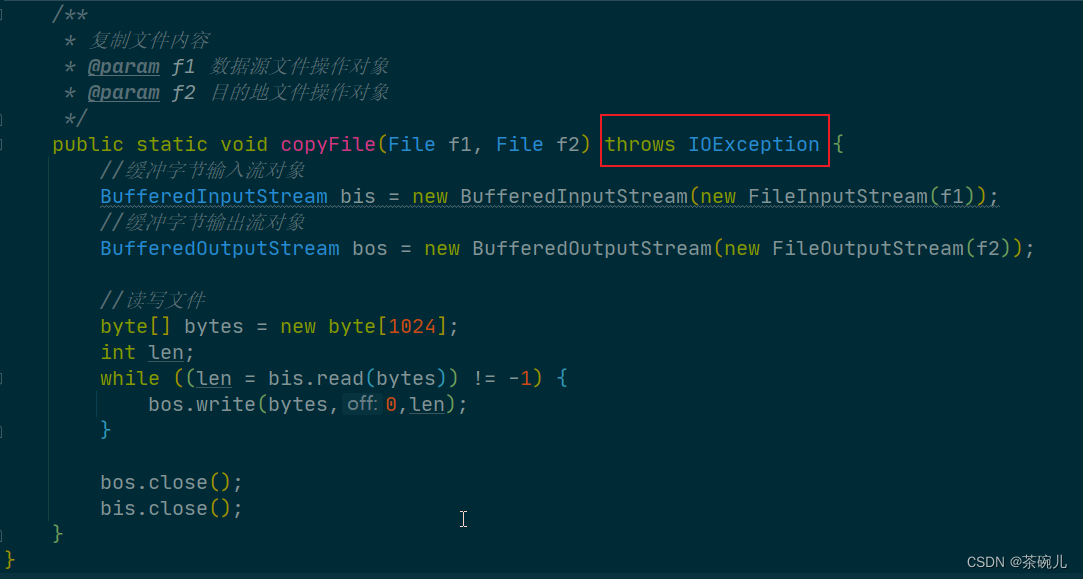
- try...catch...finally...處理

/**
* 複製文件內容
*
* @param f1 數據源文件操作對象
* @param f2 目的地文件操作對象
*/
public static void copyFile(File f1, File f2) {
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//緩衝位元組輸入流對象
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));
//緩衝位元組輸出流對象
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2));
//讀寫文件
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (bos != null) {
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (bis != null) {
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- JDK7的改進方案

/**
* 位元組緩衝流複製文件內容
* @param f1 數據源文件
* @param f2 目的地文件
* JDK7之後的寫法,會自動釋放資源,不需要close()
*/
public static void copyFile1(File f1, File f2) {
//註意try後面的的小括弧
try(//緩衝位元組輸入流對象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));
//緩衝位元組輸出流對象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2))) {
//讀寫文件
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- JDK9的改進方案

/**
* 位元組緩衝流複製文件內容
* @param f1 數據源文件
* @param f2 目的地文件
*/
public static void copyFile2(File f1, File f2) throws FileNotFoundException {
//緩衝位元組輸入流對象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1));
//緩衝位元組輸出流對象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2));
try(bis;bos) {
//讀寫文件
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
標準輸入流
System類中有兩個靜態成員變數
- public static final InputStream in:“標準”輸入流。此流已經 打開並準備提供輸入數據。通常此流 對應於鍵盤輸入或由 指定的其他輸入源 主機環境或用戶。
- public static final PrintStream out:“標準”輸出流。此流已經 打開並準備接受輸出數據。通常此流 對應於顯示輸出或其他輸出目標 由主機環境或用戶指定。
- 自己實現輸入操作
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("請輸入一個字元串:");
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println("你輸入的字元串是:" + line);
System.out.println("請輸入一個整數:");
System.out.println("你輸入的整數是:"+Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()));
}
}
運行:
請輸入一個字元串:
hello
你輸入的字元串是:hello
請輸入一個整數:
123
你輸入的整數是:123
- Java提供的輸入類Scanner
//自己實現輸入操作太麻煩,所以Java提供了一個類
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
標準輸出流
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.print("hello");
out.println("world");
out.println(100);
/**
* System.out的本質是一個位元組輸出流
* print()必須有參數
* println()可以沒有參數
* PrintStream類有的方法,System.out都可以調用
*/
System.out.println();
System.out.print("世界盃");
System.out.println(123);
}
}
運行:
helloworld
100
世界盃123
位元組列印流
列印流分類:
- 位元組列印流:PrintStream
- 字元列印流:PrintWriter
列印流的特點:
- 只負責輸出數據,不負責讀取數據
- 有自己的特有方法
位元組列印流
- PrintStream(String fileName):使用指定的文件名創建新的列印流
- 使用繼承父類的方法寫數據,查看的時候會轉碼;使用自己的特有方法寫數據,查看的數據原樣輸出
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
//創建位元組列印流對象
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("idea_test\\java1.txt");
//寫數據
// 1.位元組輸出流寫數據
//使用繼承父類的方法寫數據,查看的時候會轉碼
ps.write(97);
ps.write(98);
ps.println();
// 2.位元組列






