什麼是API API (Application Programming Interface) :應用程式編程介面 java中的API 指的就是 JDK 中提供的各種功能的 Java類,這些類將底層的實現封裝了起來,我們不需要關心這些類是如何實現的,只需要學習這些類如何使用即可,我們可以通過幫助文檔來 ...
-
API (Application Programming Interface) :應用程式編程介面
-
java中的API
Math
-
1、Math類概述
-
Math 包含執行基本數字運算的方法
-
-
2、Math中方法的調用方式
-
Math類中無構造方法,但內部的方法都是靜態的,則可以通過 類名.進行調用
-
-
3、Math類的常用方法
| 說明 | |
|---|---|
| public static int abs(int a) | 返回參數的絕對值 |
| public static double ceil(double a) | 返回大於或等於參數的最小double值,等於一個整數 |
| public static double floor(double a) | 返回小於或等於參數的最大double值,等於一個整數 |
| public static int round(float a) | 按照四捨五入返回最接近參數的int |
| public static int max(int a,int b) | 返回兩個int值中的較大值 |
| public static int min(int a,int b) | 返回兩個int值中的較小值 |
| public static double pow (double a,double b) | 返回a的b次冪的值 |
| public static double random() |
package Nomal_API.APIdemo;
public class MathDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public static int abs(int a); //返回參數的絕對值
int abs = Math.abs(10);
System.out.println("abs的絕對值為:"+abs);
// public static double ceil(double a); //向上取整
double ceil = Math.ceil(10.1);
System.out.println("ceil的向上取整:"+ceil);
// public static double floor(double a); //向下取整
double floor = Math.floor(10.9);
System.out.println("floor的向下取整為:"+floor);
// public static int round(float a); //四捨五入
long round = Math.round(10.1);
System.out.println("round的四捨五入為:"+round);
long round1 = Math.round(1.9);
System.out.println("round1的四捨五入為:"+round1);
// public static int max(int a,int b); //返回兩個int值中的較大值
int max = Math.max(10, 20);
System.out.println("max的最大值為:"+max);
// public static int min(int a,int b); //返回兩個int值中的較小值
int min = Math.min(10, 20);
System.out.println("min的最小值為:"+min);
// public static double pow(double a,double b); //返回a的b次冪的值
double pow = Math.pow(2, 3);
System.out.println("pow的冪次方為:"+pow);
// public static double random(); //返回值為double的正值,[0.0,1.0)
System.out.println("隨機值【double類型】");
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) {
double random = Math.random();
System.out.println(random);
}
}
}
| 方法名 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public static void exit(int status) | 終止當前運行的 Java 虛擬機,非零表示異常終止 |
| public static long currentTimeMillis() |
package Nomal_API.APIdemo;
public class Systemdemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 獲取開始的時間節點
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("開始時間為"+start);
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
int c = 0;
c += i;
}
// 獲取代碼運行結束後的時間節點
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("結束時間為:"+end);
System.out.println("迴圈"+i+"共耗時:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");
}
}-
-
Object 是類層次結構的根,每個類都可以將 Object 作為超類。所有類都直接或者間接的繼承自該類,換句話說,該類所具備的方法,所有類都會有一份
-
-
查看方法源碼的方式
-
選中方法,按下Ctrl + B
-
-
重寫toString方法的方式
-
-
Alt + Insert 選擇toString
-
在類的空白區域,右鍵 -> Generate -> 選擇toString
-
-
-
toString方法的作用:
-
-
-
用於對象之間的比較,返回true和false的結果
-
舉例:s1.equals(s2); s1和s2是兩個對象
-
-
重寫equals方法的場景
-
不希望比較對象的地址值,想要結合對象屬性進行比較的時候。
-
-
重寫equals方法的方式
-
-
alt + insert 選擇equals() and hashCode(),IntelliJ Default,一路next,finish即可
-
-
-
-
package Nomal_API.APIdemo;
//讓student類繼承祖宗類object,不寫也是預設繼承他
class Student extends Object {
private String name;
private int age;
//生成空參構造方法
public Student() {
}
//生成有參構造方法
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//生成get方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
//生成set方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//重寫object祖宗類的toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
//重寫equals方法,如果不重寫equals方法,那麼他們的比較是比較地址是否相同,跟 ‘ = = ‘ 是同樣的效果
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
//this -- s ,this代表的是調用者
//o -- s2 , o代表的是與調用者相比較的對象
if (this == o) return true; // 如果他們地址相等的話,返回TRUE
// getClass()方法的作用:通過返回的Class對象獲取Person的相關信息,比如:獲取Person的構造方法,方法,屬性有哪些等等信息。
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; // 如果被比較者為空,或者他們的類對象不相等,則返回為FALSE
//將o對象賦為student,
Student student = (Student) o; //student -- s2
// 如果調用者的age不等於被比較者的age,返回為FALSE
if (age != student.age) return false;
// 三元比較:name不等於null為TRUE-->調用者與被比較者比較,否則被比較者的name也為null
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
}
public class ObjectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.setName("李思思");
s.setAge(30);
System.out.println(s);
// 列印重寫的toString方法
System.out.println(s.toString());
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setName("李思思");
s2.setAge(30);
//需求:比較兩個對象的內容是否相同,重寫之後比較他們的內容是否相同,而不是比較地址了
System.out.println(s.equals(s2));
}
}| 方法名 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| public static String toString (對象) | 返回參數中對象的字元串表示形式。 |
| public static String toString(對象, 預設字元串) | 返回對象的字元串表示形式。 |
| public static Boolean isNull(對象) | 判斷對象是否為空 |
| public static Boolean nonNull(對象) |
package Nomal_API.APIdemo.objects;
package Nomal_API.APIdemo.objects;
class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
import java.util.Objects;
public class MyObjectsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public static String toString(對象): 返回參數中對象的字元串表示形式。
Student s1 = new Student("小小同學",50);
String result1 = Objects.toString(s1);
System.out.println(result1); // 列印toString方法
System.out.println(s1);
// public static String toString(對象, 預設字元串): 返回對象的字元串表示形式。如果對象為空,那麼返回第二個參數.
Student s2 = new Student("小花同學",23);
Student s3 = null;
String result2 = Objects.toString(s3, "隨便寫一個");
System.out.println(result2);
// public static Boolean isNull(對象): 判斷對象是否為空
Student s4 = null;
Student s5 = new Student();
boolean result3 = Objects.isNull(s5);
System.out.println("對象是否為空:"+result3);
// public static Boolean nonNull(對象): 判斷對象是否不為空
Student s6 = new Student();
Student s7 = null;
boolean result4 = Objects.nonNull(s6); // 判斷對象是否不為空
System.out.println("對象是否不為空"+ result4);
}
}-
可以用來進行精確計算
-
-
方法名 說明 BigDecimal(double val) 參數為double BigDecimal(String val)
-
說明 public BigDecimal add(另一個BigDecimal對象) 加法 public BigDecimal subtract (另一個BigDecimal對象) 減法 public BigDecimal multiply (另一個BigDecimal對象) 乘法 public BigDecimal divide (另一個BigDecimal對象) 除法 public BigDecimal divide (另一個BigDecimal對象,精確幾位,舍入模式)
-
BigDecimal是用來進行精確計算的
-
創建BigDecimal的對象,構造方法使用參數類型為字元串的。
-
BigDecimal divide = bd1.divide(參與運算的對象,小數點後精確到多少位,舍入模式);
參數1 ,表示參與運算的BigDecimal 對象。
參數2 ,表示小數點後面精確到多少位
參數3 ,舍入模式
BigDecimal.ROUND_UP 進一法
BigDecimal.ROUND_FLOOR 去尾法
BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP 四捨五入package Nomal_API.APIdemo.bigdecimal;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BigdecimalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("10.0");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("0.4");
System.out.println("字元串數字"+bd1);
System.out.println(bd2);
// BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal(0.1);
// BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal(0.2);
BigDecimal bd3 = new BigDecimal("0.1");
BigDecimal bd4 = new BigDecimal("0.2");
// public BigDecimal add(另一個BigDecimal對象) 加法
BigDecimal add = bd3.add(bd4); // 加法
System.out.println("和為" + add);
//System.out.println(0.1 + 0.2);
// public BigDecimal subtract (另一個BigDecimal對象) 減法
BigDecimal subtract = bd3.subtract(bd4);
System.out.println("差為" + subtract);
// public BigDecimal multiply (另一個BigDecimal對象) 乘法
BigDecimal multiply = bd1.multiply(bd2);
System.out.println("積為" + multiply);
// public BigDecimal divide (另一個BigDecimal對象) 除法
BigDecimal divide = bd1.divide(bd2); // 除出來為無理數則會報錯
System.out.println("商為" + divide);
}
}
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class MyBigDecimalDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("0.3");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("4"); //0.075
/* BigDecimal divide = bd1.divide(bd2);
System.out.println(divide);*/
//參數一:表示參數運算的另一個對象
//參數二:表示小數點後精確到多少位
//參數三:舍入模式
//進一法 BigDecimal.ROUND_UP
//去尾法 BigDecimal.ROUND_FLOOR
//四捨五入 BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP
BigDecimal divide = bd1.divide(bd2, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
System.out.println(divide);
}
}基本類型包裝類(記憶)
-
基本類型包裝類的作用
將基本數據類型封裝成對象的好處在於可以在對象中定義更多的功能方法操作該數據
常用的操作之一:用於基本數據類型與字元串之間的轉換
-
基本類型對應的包裝類
-
包裝類 byte Byte short Short int Integer long Long float Float double Double char Character boolean
| 說明 | |
|---|---|
| public Integer(int value) | 根據 int 值創建 Integer 對象(過時) |
| public Integer(String s) | 根據 String 值創建 Integer 對象(過時) |
| public static Integer valueOf(int i) | 返回表示指定的 int 值的 Integer 實例 |
| public static Integer valueOf(String s) |
自動拆箱和自動裝箱
-
自動裝箱
把基本數據類型轉換為對應的包裝類類型
-
自動拆箱
把包裝類類型轉換為對應的基本數據類型
package Nomal_API.APIdemo.basicInterger;
public class IntergerDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = 100;
// 對象 = 預設是一個基本數據類型
// jdk1.5的特性 --- 自動裝箱
//裝箱: 把一個基本數據類型 變數對應的包裝類.
//自動: Java底層會幫我們自動的調用valueof方法.
System.out.println("自動裝箱i1為interger:"+i1);
//jdk1.5的特性 --- 自動拆箱
//拆箱: 把一個包裝類型 變成對應的基本數據類型
int i2 = i1;
System.out.println("自動拆箱i2為int:"+i2);
Integer i3 = 100; //自動裝箱機制
i3 += 200;//i3 = i3 + 200;
//會把i3這個對象變成基本數據類型100.
//100 + 200 = 300
//把基本數據類型300再次自動裝箱變成Integer對象賦值給i3
System.out.println("自動拆裝箱,最後i3為Interger類型:"+i3);
//細節:
Integer i4 = null;
if (i4 != null) {
i4 += 200;
System.out.println(i4);
}
}
}數組的高級操作-二分查找思路分析
查找指定元素在數組中的位置時,以前的方式是通過遍歷,逐個獲取每個元素,看是否是要查找的元素,這種方式當數組元素較多時,查找的效率很低
前提條件
數組內的元素一定要按照大小順序排列,如果沒有大小順序,是不能使用二分查找法的
二分查找的實現步驟
1,定義兩個變數,表示要查找的範圍。預設min = 0 , max = 最大索引
2,迴圈查找,但是min <= max
3,計算出mid的值
4,判斷mid位置的元素是否為要查找的元素,如果是直接返回對應索引
5,如果要查找的值在mid的左半邊,那麼min值不變,max = mid -1.繼續下次迴圈查找
6,如果要查找的值在mid的右半邊,那麼max值不變,min = mid + 1.繼續下次迴圈查找
7,當 min > max 時,表示要查找的元素在數組中不存在,返回-1.
package Nomal_API.APIdemo.MyBinarySearchDemo;
public class MybinarySearchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int number = 11;
//1,現在要幹嘛? --- 二分查找
//2.這件事情需要什麼? --- 數組 元素
//3,幹完了, 要不要把結果返回調用者 --- 把索引返回給調用者
int index = binarySearchForIndex(arr, number);
System.out.println(index);
}
private static int binarySearchForIndex(int[] arr, int number) {
//1,定義查找的範圍
int min = 0;
int max = arr.length - 1;
//2.迴圈查找 min <= max
while (min <= max) {
//3.計算出中間位置 mid
int mid = (min + max) >> 1;
//mid指向的元素 > number
if (arr[mid] > number) {
//表示要查找的元素在左邊.
max = mid - 1;
} else if (arr[mid] < number) {
//mid指向的元素 < number
//表示要查找的元素在右邊.
min = mid + 1;
} else {
//mid指向的元素 == number
return mid;
}
}
//如果min大於了max就表示元素不存在,返回-1.
return -1;
}
}
-
-
把一個複雜的問題層層轉化為一個與原問題相似的規模較小的問題來求解
-
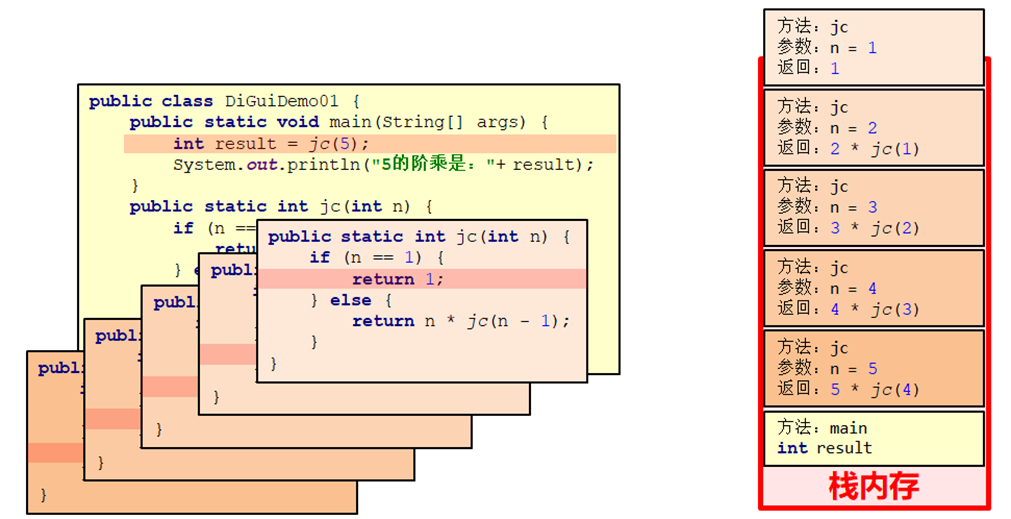
package Nomal_API.APIdemo.MyFactorialDemo;
//遞歸:求階乘
public class factorialDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//調用方法
int result = jc(5);
//輸出結果
System.out.println("5的階乘是:" + result);
}
//定義一個方法,用於遞歸求階乘,參數為一個int類型的變數
public static int jc(int n) {
//在方法內部判斷該變數的值是否是1
if (n == 1) {
//是:返回1
return 1;
} else {
//不是:返回n*(n-1)!
return n * jc(n - 1);
}
}
}冒泡排序概述
一種排序的方式,對要進行排序的數據中相鄰的數據進行兩兩比較,將較大的數據放在後面,依次對所有的數據進行操作,直至所有數據按要求完成排序
如果有n個數據進行排序,總共需要比較n-1次
每一次比較完畢,下一次的比較就會少一個數據參與
package Nomal_API.APIdemo.BubbleSortDemo;
//冒泡排序
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 5, 2, 1, 4};
//1 2 3 4 5
bubbleSort(arr);
}
private static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
//外層迴圈控制的是次數 比數組的長度少一次.
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
//記憶體迴圈就是實際迴圈比較的
//-1 是為了讓數組不要越界
//-i 每一輪結束之後,我們就會少比一個數字.
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
printArr(arr);
}
private static void printArr(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}Arrays的常用方法
| 說明 | |
|---|---|
| public static String toString(int[] a) | 返回指定數組的內容的字元串表示形式 |
| public static void sort(int[] a) | 按照數字順序排列指定的數組 |
| public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) |
-
構造方法用 private 修飾
-
package Nomal_API.APIdemo.ArrayDemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArraysDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public static String toString(int[] a) 返回指定數組的內容的字元串表示形式
int [] arr1 = {3,2,4,6,7};
System.out.println("返回數組的內容字元串:"+Arrays.toString(arr1));
// public static void sort(int[] a) 按照數字順序排列指定的數組
int [] arr2 = {3,2,4,6,7};
Arrays.sort(arr2);
System.out.println("進行從小到大順序排序:"+Arrays.toString(arr2));
// public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) 利用二分查找返回指定元素的索引:key為要查找的值
int[] arr3 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr3, 0);
System.out.println(index);
//1,數組必須有序
//2.如果要查找的元素存在,那麼返回的是這個元素實際的索引
//3.如果要查找的元素不存在,那麼返回的是 (-插入點-1)
//插入點:如果這個元素在數組中,他應該在哪個索引上.
}
}本文來自博客園,作者:link-零,轉載請註明原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/e-link/p/16758757.html❤❤❤



