Spring5相關的知識點,IOC,AOP,DI依賴註入,Bean的自動裝配,使用註解開發,spring整合mybatis等於Spring相關的知識都在這裡了 ...
1、Spring
1.1簡介
-
2002,首次退出來Spring框架的雛形:interface21框架
-
Spring框架即以interface21框架為基礎,經過重新設計,並不斷豐富其內涵,與2004年3月24日,發佈了1.0正式版
-
Rod Johnson,Spring framework創始人,著名作者。
-
spring理念:是現有的技術更加容易使用,本身是一個大雜燴
官網地址:
https://spring.io/projects/spring-framework
官方下載地址
https://repo.spring.io/ui/native/release/org/springframework/spring/
對應jar包的導入
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.22</version>
</dependency>
1.2優點
-
Spring是一個開源的免費的框架(容器)
-
Spring是一個輕量級的,非入侵式的框架(不會使項目因為導入改jar包而導致項目不能運行)
-
控制反轉(IOC),面向切麵編程(AOP)
-
支持事物的處理,對框架整合的支持
總結一句話:Spring就是一個輕量級的控制反轉(IOC)和麵向切麵編程(AOP)的框架!
1.3組成
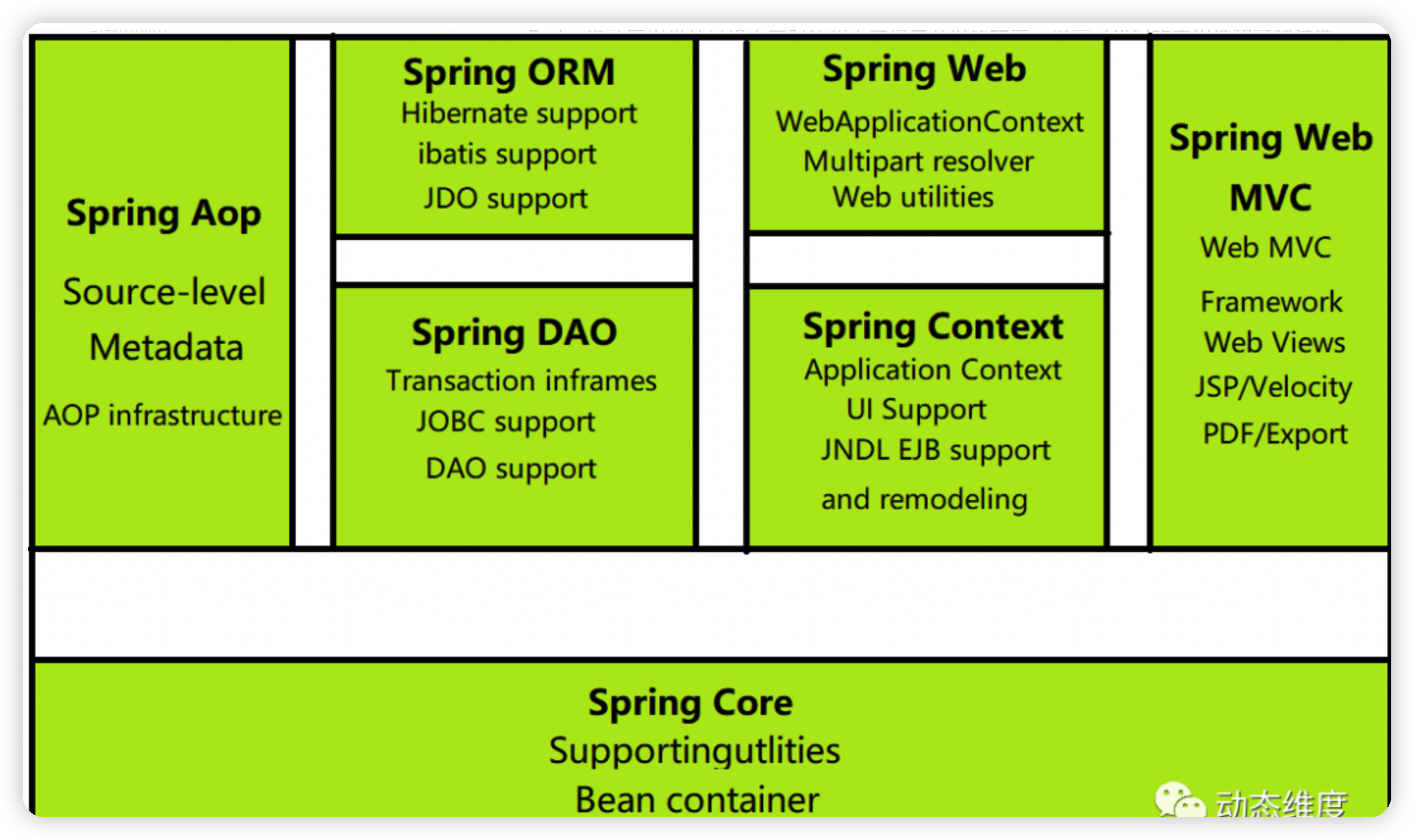
1.4拓展
在Spring的官網有這個介紹:現代化的Java開發!說白了就是基於Spring的開發
-
Spring Boot
- 一個快速開發的腳手架(用了SpringBoot之後就可以根據一個配置就可以開發一個網站)
- 基於SpringBoot可以快速的開發單個微服務
- 約定大於配置
-
Spring Cloud
- SpringCloud是基於SpringBoot實現的
因為現在大多數公司都在使用SpringBoot進行快速開發,學習SpringBoot的前提,需要完全掌握Spring及SpringMVC!承上啟下的作用
弊端:發展了太久之後,違背了原來的理念,配置十分繁瑣,人稱:“配置地獄”
2.IOC理論推導
2.1以前寫項目的過程
- UserDao介面
package com.tang.dao;
public interface UserDao {
public void getUser();
}
- UserDaoImpl實現類
package com.tang.dao;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
public void getUser() {
System.out.println("預設UserDao載入數據");
}
}
UserMysqlDaoImpl實現類
public class UserMysqlDaoImpl implements UserDao{
public void getUser() {
System.out.println("Mysql獲取數據");
}
}
- UserService業務介面
package com.tang.service;
public interface UserService {
public void getUser();
}
- UserServiceImpl業務實現類
package com.tang.service;
import com.tang.dao.UserDao;
import com.tang.dao.UserDaoImpl;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
//private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
//利用set進行動態實現指的註入
public void getUser() {
userDao.getUser();
}
}
模擬的用戶層
public class Mytest {
@Test
public void test(){
//用戶實體調用的是業務層,dao層他們不需要接觸
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
//控制權交給用戶,用戶想調用誰的實現類就直接new即可
((UserServiceImpl)userService).setUserDao(new UserMysqlDaoImpl());
userService.getUser();
}
}
測試結果
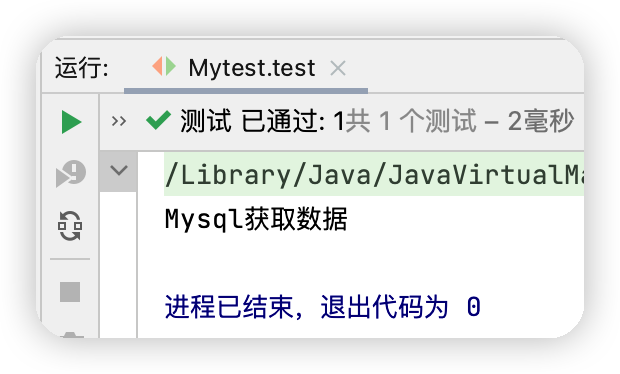
在我們之前的業務中,用戶的需求可能會影響我們原來的代碼,我們需要根據用戶的需求去修改源代碼,如果程式代碼量十分大,修改一次的成本代價十分昂貴
我們使用一個set介面實現,每當用戶更改之後,不用在業務層去修改源碼,只需要在用戶層,根據用戶所需調用相應的service層然後service層去調用dao層的代碼
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
//以前就需要在業務層,每當用戶改變之後new 的實現類也必須隨之發生變化,加了個set之後就可以在用戶層根據所需通過service間接使用所需要的用戶層的實現類
//private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
//利用set進行動態實現指的註入
public void getUser() {
userDao.getUser();
}
}
-
之前,程式是主動創建對象,控制權在程式猿手上
-
使用set註入後,程式不再具有主動性,而是變成了被動的接收對象
這種思想,從本質上解決了問題,我們程式員不用再去管理對象的創建了,系統的耦合性大大降低,可以更加專註在業務的是線上,這是IOC的原型
2.2.IOC本質
控制反轉IoC(Inversion of Control),是一種設計思想,DI(依賴註入)是實現IoC的一種方法,也有人認為DI只是IoC的另一種說法。沒有IoC的程式中 , 我們使用面向對象編程 , 對象的創建與對象間的依賴關係完全硬編碼在程式中,對象的創建由程式自己控制,控制反轉後將對象的創建轉移給第三方,個人認為所謂控制反轉就是:獲得依賴對象的方式反轉了。
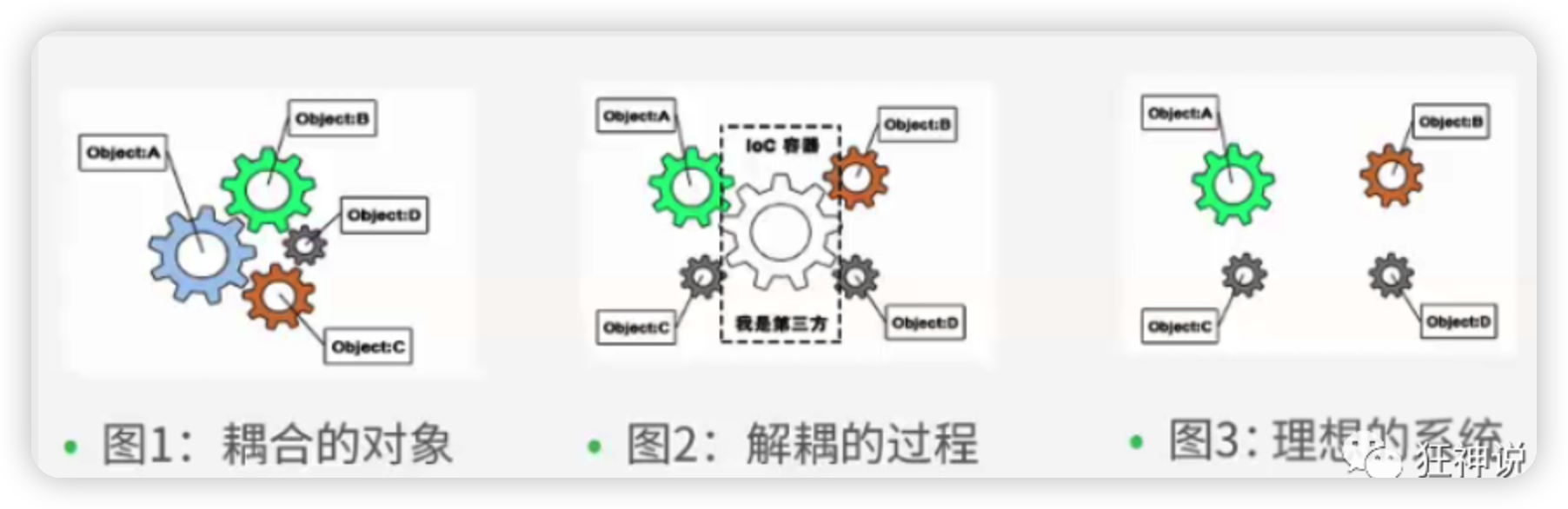
採用XML方式配置Bean的時候,Bean的定義信息是和實現分離的,而採用註解的方式可以把兩者合為一體,Bean的定義信息直接以註解的形式定義在實現類中,從而達到了零配置的目的。
控制反轉是一種通過描述(XML或註解)並通過第三方去生產或獲取特定對象的方式。在Spring中實現控制反轉的是IoC容器,其實現方法是依賴註入(Dependency Injection,DI)。
3.HelloSpring
bean.xml創建方式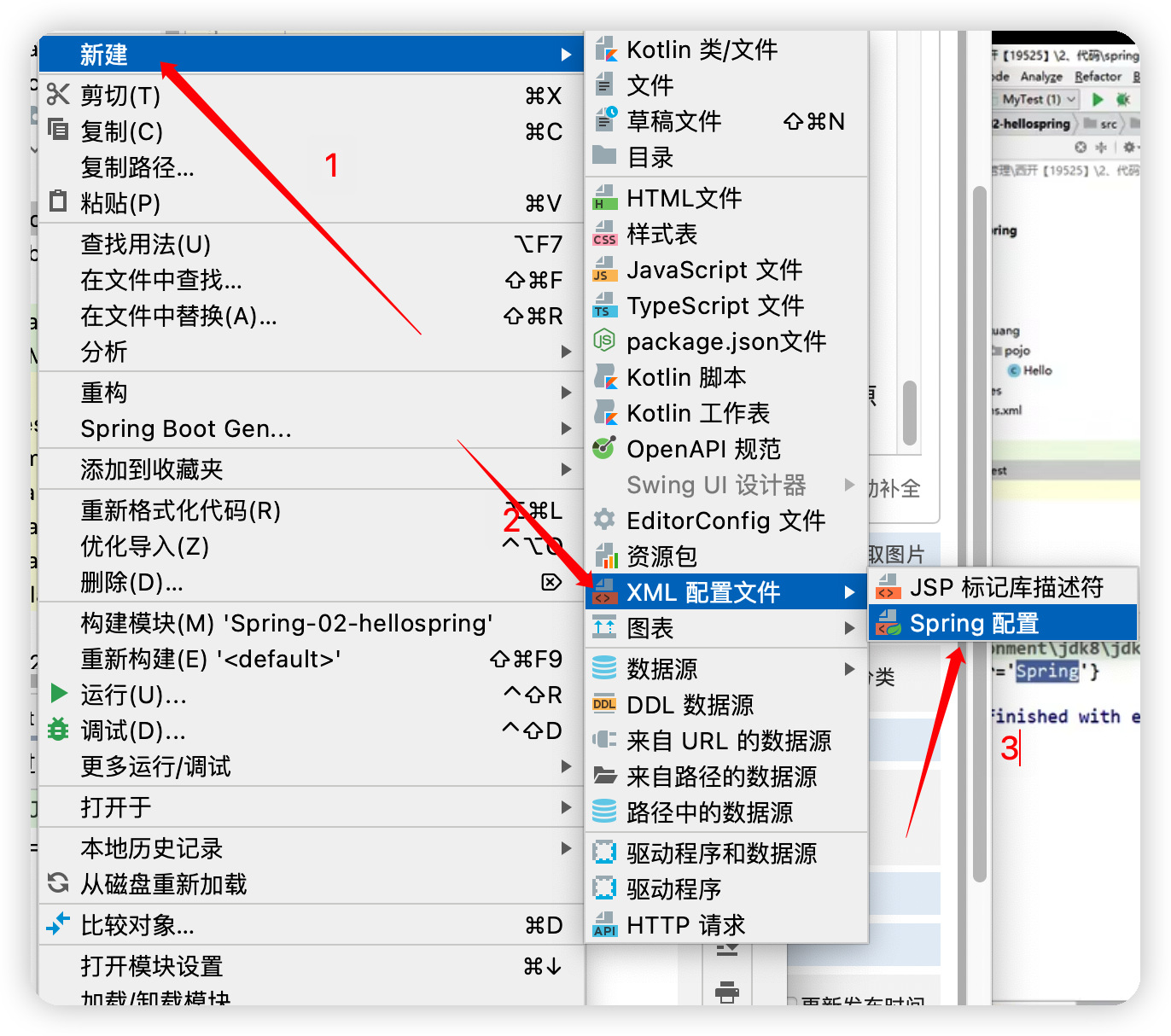
實體類User
package com.tang.pojo;
public class Hello {
private String str;
public Hello() {
}
public Hello(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
public String getStr() {
return str;
}
public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hello{" +
"str='" + str + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--bean = 對象-->
<!--id = 變數名-->
<!--class = new的對象-->
<!--property 相當於給對象中的屬性設值-->
<bean id="hello" class="com.tang.pojo.Hello">
<property name="str" value="Spring"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
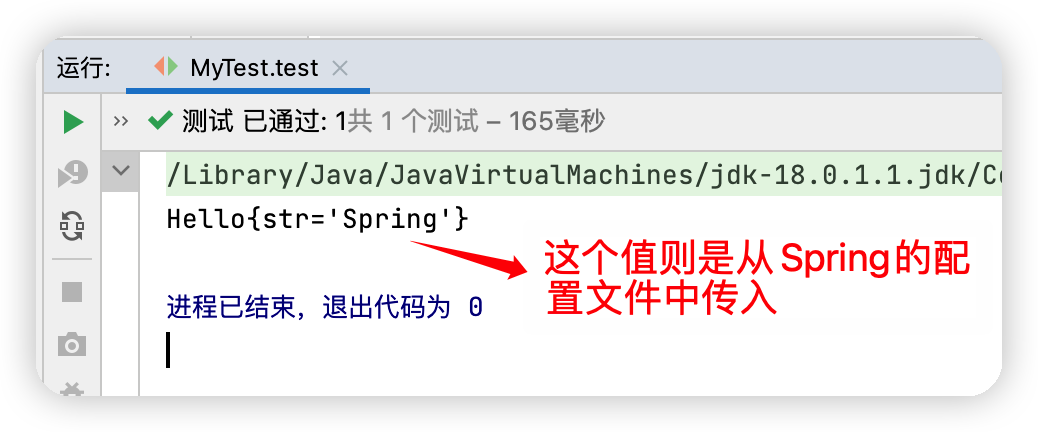
測試代碼
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test(){
//獲取Spring的上下文對象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//我們的對象現在都在Spring中管理了,我們要使用,直接去裡面取出來就可以了
Hello hello = (Hello) context.getBean("hello");//這裡就相當於new了一個對象
System.out.println(hello.toString());
}
}
運行結果圖
如果運行之後報這個錯IOException parsing XML document from class path resource [beans.xml]; nested exception is java.io.FileNotFoundException: class path resource [beans.xml] cannot be opened because it does not exist
可以將該項目的pom文件的打包方式設置為jar即可解決此問題,問題出現原因就是在target中沒有beans.xml文件導致
【思考問題?】
-
Hello對象是誰創建的?
hello對象是由Spring創建的 -
Hello對象的屬性是怎麼設置的?
- hello對象的屬性是由Spring容器設置的
這個過程就叫控制反轉:
控制:誰來控制對象的創建,傳統應用程式的對象是有程式本身控制創建的,使用Spring後,對象是由Spring來創建的
反轉:程式本身不創建對象,而變成不被動的接收對象
依賴註入:就是利用set方法來進行註入的
IOC是一種編程思想,由主動地編程變成被動的接收
可以通過new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext去瀏覽以下底層的源碼
OK,到了現在,我們徹底不用在程式中去改動了,要實現不同的操作,只需要在xml配置文件中進行修改,所謂的IOC一句話搞定:對象有Spring來創建,管理,裝配!
4.IOC創建對象的方式
4.1使用無參構造創建對象,預設
beans.xml
<!--這裡就相當於new了一個對象,不管用於不用,這裡都已經創建了一個對象-->
<bean id="user" class="com.tang.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="唐昊"></property>
</bean>
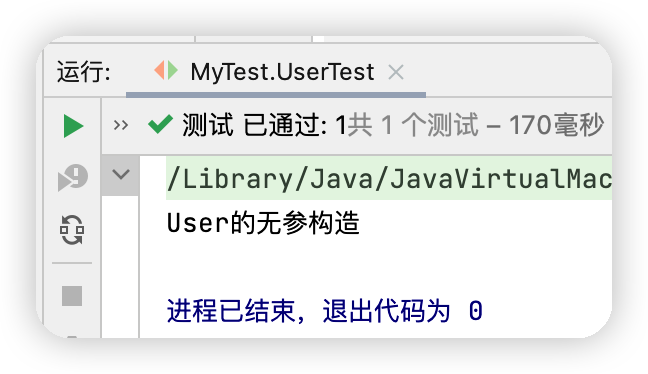
測試代碼
@Test
public void UserTest(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
User user = (User) context.getBean("user");
}
測試結果
4.2假設我們要使用了有參構造
下標賦值
<bean id="user" class="com.tang.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="User的有參構造"/>
</bean>
通過類型創建,不建議使用
<bean id="user" class="com.tang.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="User有參構造"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
通過參數名來設置
<bean id="user" class="com.tang.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="唐昊"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
5.Spring配置
5.1別名
<!--別名,如果添加了別名,我們也可以使用別名獲取到這個對象-->
<alias name="user" alias="fasdagsd"></alias>
@Test
public void UserTest(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
User user = (User) context.getBean("fasdagsd");
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
5.2Bean的配置
<!--
id:bean的唯一標識符,也就是相當於我們學的對象名
class: bean對象多對應的許可權定名:包名 + 類型
name:也是別名 而且name也可以同時取多個別名,每個別名之間可以用逗號,空格,分號等符號都可以實現,name起別名還是很強大的
-->
<bean id="user" class="com.tang.pojo.User" name="user2,twq">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="唐昊"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
5.3Import
這個import,一般用於團隊開發使用,他可以將多個配置文件,導入合併一個假設,現在項目中有多個人開發(張三,李四,王五),這三個人複製不同的類開發,不同的類需要註冊在不同的Bean中,我們可以利用import將多誘人的beans.xml合併為一個總的
使用的時候,直接使用總的配置就可以了
項目結構圖
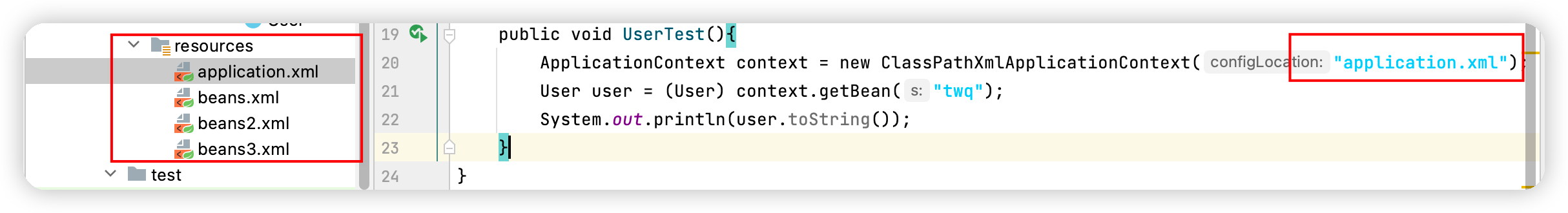
application.xml
<import resource="beans.xml"></import>
<import resource="beans2.xml"></import>
<import resource="beans3.xml"></import>
6.DI依賴註入
6.1Set方式註入(重點)
- 依賴註入:Set註入
- 依賴:bean對象的創建依賴於容器
- 註入:bean對象中的所有屬性,由容器註入
(1)環境搭建
複雜類型
public class Address {
private String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
真實測試對象
public class Student {
private String name;
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private String wife;
private Properties info;
//get,set方法這裡就不寫上了,可以自己寫上
}
beans.xml
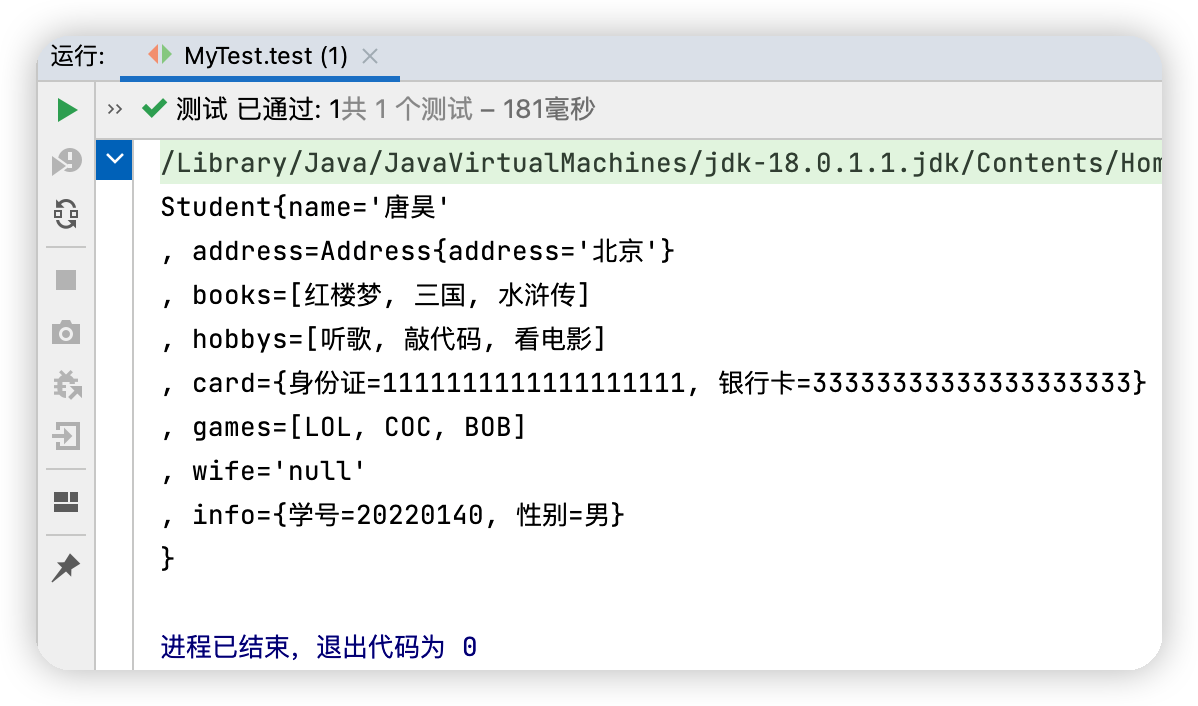
<bean id="student" class="com.tang.pojo.Student">
<!--第一種,普通的註入,value-->
<property name="name" value="唐昊"></property>
</bean>
測試類
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
完善註入信息
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="com.tang.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="北京"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.tang.pojo.Student">
<!--第一種,普通的註入,value-->
<property name="name" value="唐昊"></property>
<!--第二種,Bean註入,使用ref-->
<property name="address" ref="address"></property>
<!--第三種:數組的註入-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>紅樓夢</value>
<value>三國</value>
<value>水滸傳</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--第四種:list的註入-->
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>聽歌</value>
<value>敲代碼</value>
<value>看電影</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--第五種:map的註入-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="身份證" value="1111111111111111111"></entry>
<entry key="銀行卡" value="33333333333333333333"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--第六種:Set的註入-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>LOL</value>
<value>COC</value>
<value>BOB</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--第七種:null的註入-->
<property name="wife">
<null></null>
</property>
<!--第八種:Properties-->
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="學號">20220140</prop>
<prop key="性別">男</prop>
<prop key="學號">20220140</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
測試結果
7.Bean的自動裝配
7.1自動裝配
自動裝配是Spring滿足Bean依賴的一種方式spring會在上下文中自動尋找,並自動給Bean裝配屬性
在Spring中有三種裝配的方式
-
在xml中顯示的配置
-
在Java中顯示配置
-
隱式的自動裝配Bean【重要】
7.2測試
環境搭建:一個人有兩個寵物ByName自動裝配
<!--byName:會自動在容器上下文中查找,和自己對象set方法後面的值對應的beanid-->
<bean id="people" class="com.tang.pojo.People" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="twq"></property>
<!--<property name="dog" ref="dog"></property>-->
<!--<property name="cat" ref="cat"></property>-->
</bean>
ByType自動裝配
<bean id="cat" class="com.tang.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog111" class="com.tang.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<!--
byType:會自動在容器上下文中查找,和自己對象屬性類型相同的bean !
-->
<bean id="people" class="com.tang.pojo.People" autowire="byType">
<property name="name" value="twq"></property>
<!--<property name="dog" ref="dog"></property>-->
<!--<property name="cat" ref="cat"></property>-->
</bean>
小結:
-
byName的時候,需要保證所有bean的id唯一,並且這個bean需要和自動註入的屬性的set方法的值一致
-
byType的時候,需要保證所有bean的class唯一,並且這個bean需要和自動註入的屬性的類型一致
7.3使用註解實現自動裝配
要使用註解須知:-
導入約束:context約束
-
配置註解的支持
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置註解支持-->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<bean id="cat" class="com.tang.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog111" class="com.tang.pojo.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="people" class="com.tang.pojo.People"></bean>
</beans>
在實體類上使用註解即可
public class People {
@Autowired
private Cat cat;
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
private String name;
}
測試代碼
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
People people = context.getBean("people", People.class);
people.getDog().shot();
people.getCat().shot();
}
運行結果圖
@Autowired
直接在屬性山使用即可,也可以在set方法上使用使用@Autowired我們可以不用編寫set方法了,前提是你這個自動裝的屬性在IOC(Spring)容器中存在,且符合名字byname
8.使用註解開發
在Spring4之後,要使用註解開發,必須要保證aop的包導入了
使用註解需要導入context約束,增加註解的支持
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
</beans>
8.1.屬性如何註入
//等價於<bean id="user" class="com.tang.pojo.User"></bean>
//@Component組件,放在類上,說明這個類被Spring管理了,就是bean
@Component
public class User {
// public String name ="唐昊";
//相當於 <property name="name" value="唐昊"/>
@Value("唐昊")//給name賦值
public String name;
}
8.2衍生的註解
@Component有幾個衍生註解,我們在web開發中,會按照mvc三層架構分層
-
dao【@Repository】
-
service【@Service】
-
controller【@Controller】
這四個註解功能都是一樣的,都是代表某個類註冊到Spring中,裝配Bean
8.3小結
xml與註解:-
xml更加萬能,適用於任何場合!維護簡單方便
-
註解不是自己的類使用不了,維護相對複雜
最佳實踐:
-
xml用來管理bean
-
註解只負責完成屬性的註入
-
我們在使用的過程中,只需要註意一個問題,必須讓註解生效,就需要開啟註解的支持
<!--指定要掃描的包,這個包下的註解就會生效--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.tang.pojo"></context:component-scan> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
9.使用Java的方式配置Spring
我們現在要完全不使用Spring的xml配置了,全權交給java來做JavaConfig是Spring的一個子項目,在Spring4之後,他就成為了一個核心功能
User實體類代碼
//這裡這個註解的意思,就是說明這個類被Spring接管了,註冊到了容器中
@Component
public class User {
@Value("唐三")//將name的值設置為唐三
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Config類
/*
* 這個也會被Spring容器托管,註冊倒容器中,因為他本愛就是一個@Component
* @Confguration代表這是一個配置類,就是我們之前看的beans.xml*/
@Configuration
@Component("com.tang.pojo")
public class TangConfig {
//註冊一個bean,就相當於我們之前寫的一個bean標簽
//這個方法的名字,就相當於bean標簽的id屬性
//這個方法的返回值,就相當於bean標簽中class屬性
@Bean
public User getUser(){
return new User();//就是要返回要註入到bean的對象
}
測試類
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test(){
//如果完全使用了配置類方式去做,我們就只能通過AnnotationConfig上下文
// 來獲取容器,通過配置類的class對象載入
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TangConfig.class);
User getUser = context.getBean("getUser", User.class);//取得getUser是TangConfig中經過Bean註冊過的
System.out.println(getUser.getName());
}
這種純java的配置方式,在SpringBoot中隨處可見
10.代理模式
為什麼要學習代理模式? 因為這就是SpringAOP的底層!【SpringAOP和SpringMVC面試必問】代理模式的分類:
-
靜態代理
-
動態代理
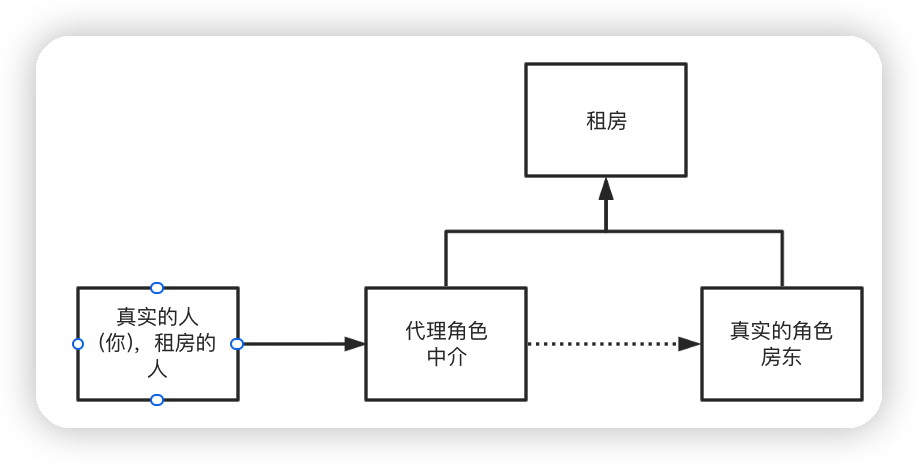
10.1靜態代理
角色分析:-
存在一個抽象角色(比如上圖中介和房東共同完成租房這個事件):一般會使用介面或者抽象類來解決
-
真是角色:被代理的角色
-
代理角色:代理真是角色,代理真實角色後,我們一般會做一些附屬操作
-
客戶:訪問代理對象的人
代碼步驟:
①.介面
//租房
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}
②.真實角色(房東)
//房東
public class Host implements Rent {
public void rent(){
System.out.println("房東要出租房子");
}
}
③.代理角色
//代理(中介幫房東出租房子)
public class Proxy implements Rent{
private Host host;//中介得找到房東
public Proxy() {
}
public Proxy(Host host) {
this.host = host;
}
public void rent() {
host.rent();
seeHouse();
contract();
fees();
}
//看房
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("中介帶你看房");
}
//簽合同
public void contract(){
System.out.println("簽租賃合同");
}
//收中介費
public void fees(){
System.out.println("收中介費");
}
}
④.客戶訪問dialing角色
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Host host = new Host();//房東要出租房子
//中介幫房東出租房子,但是dialing角色一般會有一些附屬操作
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(host);
//你不用面對房東,直接找中介租房
proxy.rent();
}
}
代理模式的好處
-
可以使真實角色的操作更加純粹!不用去關註一些公共的業務
-
公共業務就交給代理角色!實現業務的分工
-
公共業務發生擴展的時候,方便集中管理
缺點:
- 一個真是角色就會產生一個代理角色;代碼量會翻倍-開發效率低
10.2加深理解
目的:在每次調用增刪改查的時候列印一個日誌,表明當前調用的是哪個操作,在公司里在原來的代碼上修改是大忌,這時就可以採用代理模式來實現UserService介面
public interface UserService {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void query();
}
UserServiceImpl代碼
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
public void add() {
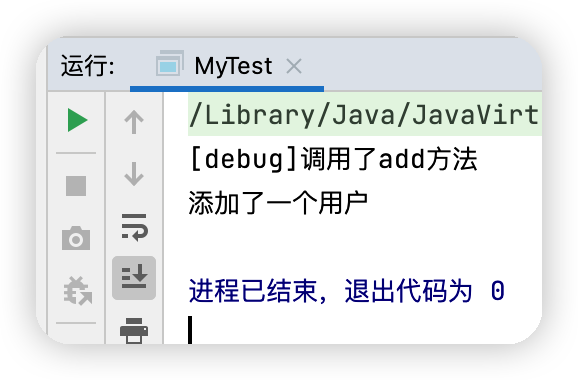
System.out.println("添加了一個用戶");
}
public void delete() {
System.out.println("刪除了一個用戶");
}
public void update() {
System.out.println("修改了一個用戶");
}
public void query() {
System.out.println("查詢了一個用戶");
}
}
UserServiceProxy代理代碼
public class UserServiceProxy implements UserService{
private UserServiceImpl userServiceimpl;
public void setUserServiceimpl(UserServiceImpl userServiceimpl) {
this.userServiceimpl = userServiceimpl;
}
public void add() {
log("add");
userServiceimpl.add();
}
public void delete() {
log("delete");
userServiceimpl.delete();
}
public void update() {
log("update");
userServiceimpl.update();
}
public void query() {
log("query");
userServiceimpl.query();
}
public void log(String name){
System.out.println("[debug]調用了"+name+"方法");
}
}
測試代碼
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
UserServiceProxy userServiceProxy = new UserServiceProxy();
userServiceProxy.setUserServiceimpl(userService);
userServiceProxy.add();
}
}
測試結果
10.3動態代理
-
動態代理和靜態代理角色一樣
-
動態代理的代理類是動態生成的,不是我們直接寫好的
-
動態dialing分為兩大類:基於介面的代理,基於類的動態代理
- 基於介面---JDK動態代理
- 基於類:cglib
- java位元組碼實現:javAssist
需要瞭解兩個類:Proxy:代理,InvocationHandler:調用處理程式
租房介面類
//租房
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}
真實角色Host房東
//房東
public class Host implements Rent {
public void rent(){
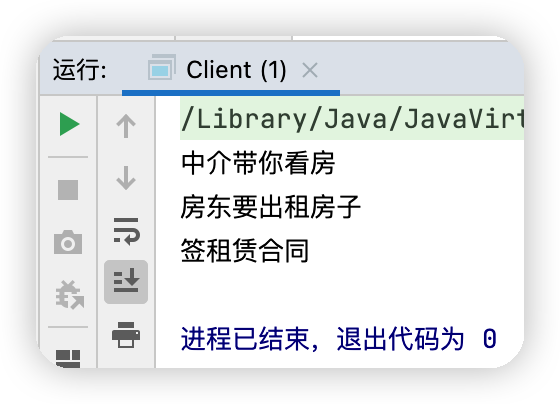
System.out.println("房東要出租房子");
}
}
動態生成代理ProxyInvocationHandler
//等會這裡會用這個類,自動生成代理類
public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//被代理的介面
private Rent rent;
public void setRent(Rent rent) {
this.rent = rent;
}
//生成得到代理類
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), rent.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
}
//處理代理實例,並返回結果
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
seeHouse();
//動態代理的本質,就是使用反射機制實現
Object result = method.invoke(rent, args);
contract();
return result;
}
//看房
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("中介帶你看房");
}
//簽合同
public void contract(){
System.out.println("簽租賃合同");
}
}
用戶類
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//真實角色
Host host = new Host();
//代理角色:現在沒有
ProxyInvocationHandler pih = new ProxyInvocationHandler();
//通過調用程式處理鴃舌來處理我們要調用的介面對象
pih.setRent(host);
Rent proxy = (Rent) pih.getProxy();//這裡的Proxy就是動態生成的,我們並沒有寫
proxy.rent();
}
}
測試結果
將ProxyInvocationHandler提取為工具類,並實現增刪改查的時候列印日誌的操作
項目結構圖
ProxyInvocationHandler代碼
package com.tang.demo04;
import com.tang.demo03.Rent;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
//等會我們會用這個類,自動生成代理類
public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//被代理的介面
private Object target;
public void settarget(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//生成得到代理類
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
}
//處理代理實例,並返回結果
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
log(method.getName());//得到當前執行方法的名字
//動態代理的本質,就是使用反射機制實現
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
return result;
}
public void log(String msg){
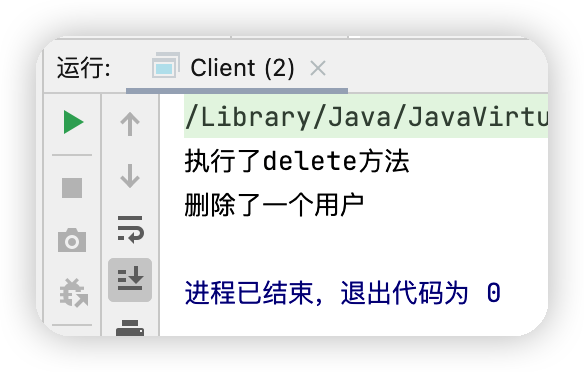
System.out.println("執行了"+msg+"方法");
}
}
測試代碼
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//真實角色
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
//代理角色,不存在
ProxyInvocationHandler pih = new ProxyInvocationHandler();
pih.settarget(userService);//設置要代理的對象
//動態生成代理類
UserService proxy = (UserService) pih.getProxy();
proxy.delete();
}
}
測試結果
動態代理的好處:
-
可以使真實角色的操作更加純粹!不用去關註一些公共的業務
-
公共業務就交給代理角色!實現業務的分工
-
公共業務發生擴展的時候,方便集中管理
*一個動態代理類處理的是一個介面,一般就是對應的一類業務
- 一個動態代理類可以代理多個類,只要是實現類同一個介面即可
11.AOP
11.1什麼是AOP
在軟體業,AOP為Aspect Oriented Programming的縮寫,意為:面向切麵編程,通過預編譯方式和運行期間動態代理實現程式功能的統一維護的一種技術。AOP是OOP的延續,是軟體開發中的一個熱點,也是Spring框架中的一個重要內容,是函數式編程的一種衍生範型。利用AOP可以對業務邏輯的各個部分進行隔離,從而使得業務邏輯各部分之間的耦合度降低,提高程式的可重用性,同時提高了開發的效率。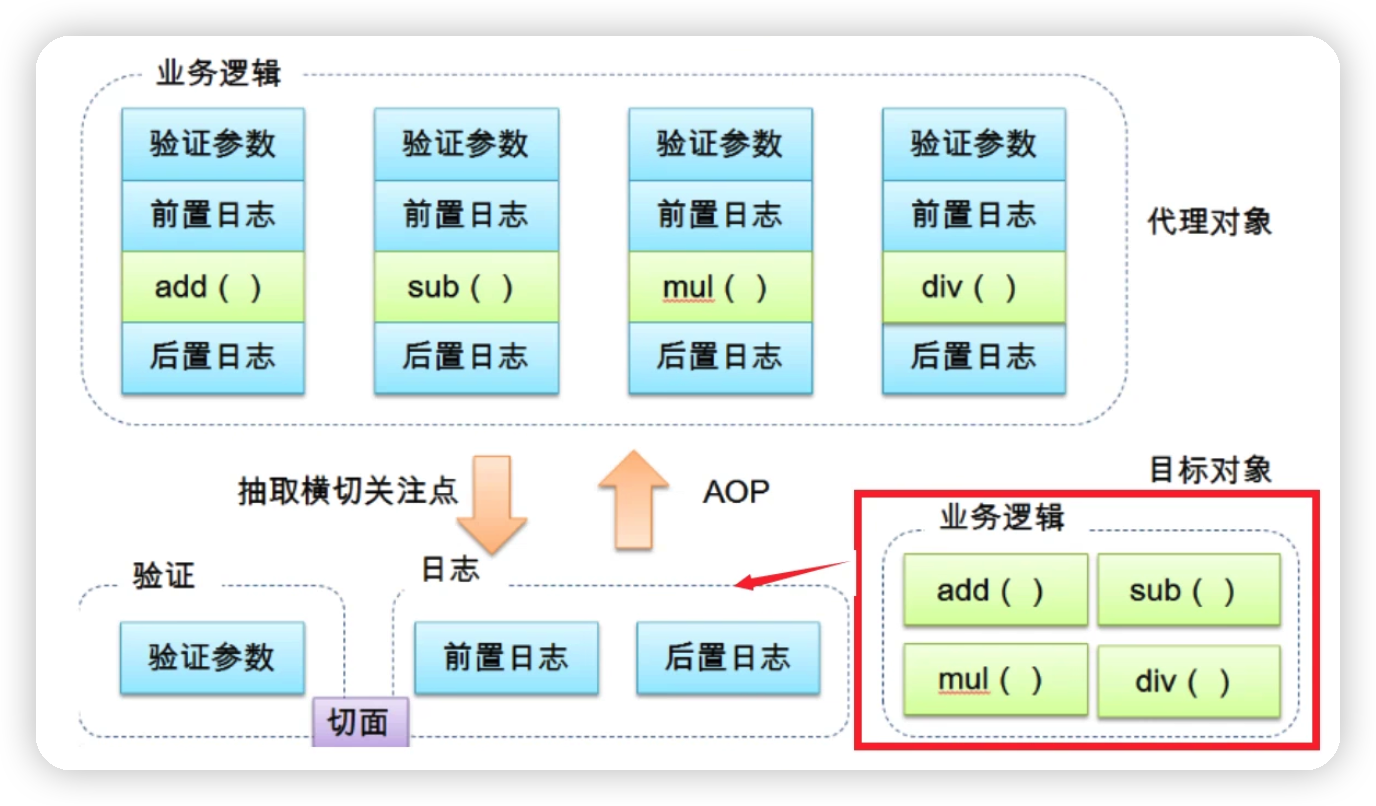
11.2AOP在Spring中的作用
提供聲明式事務;允許用戶自定義切麵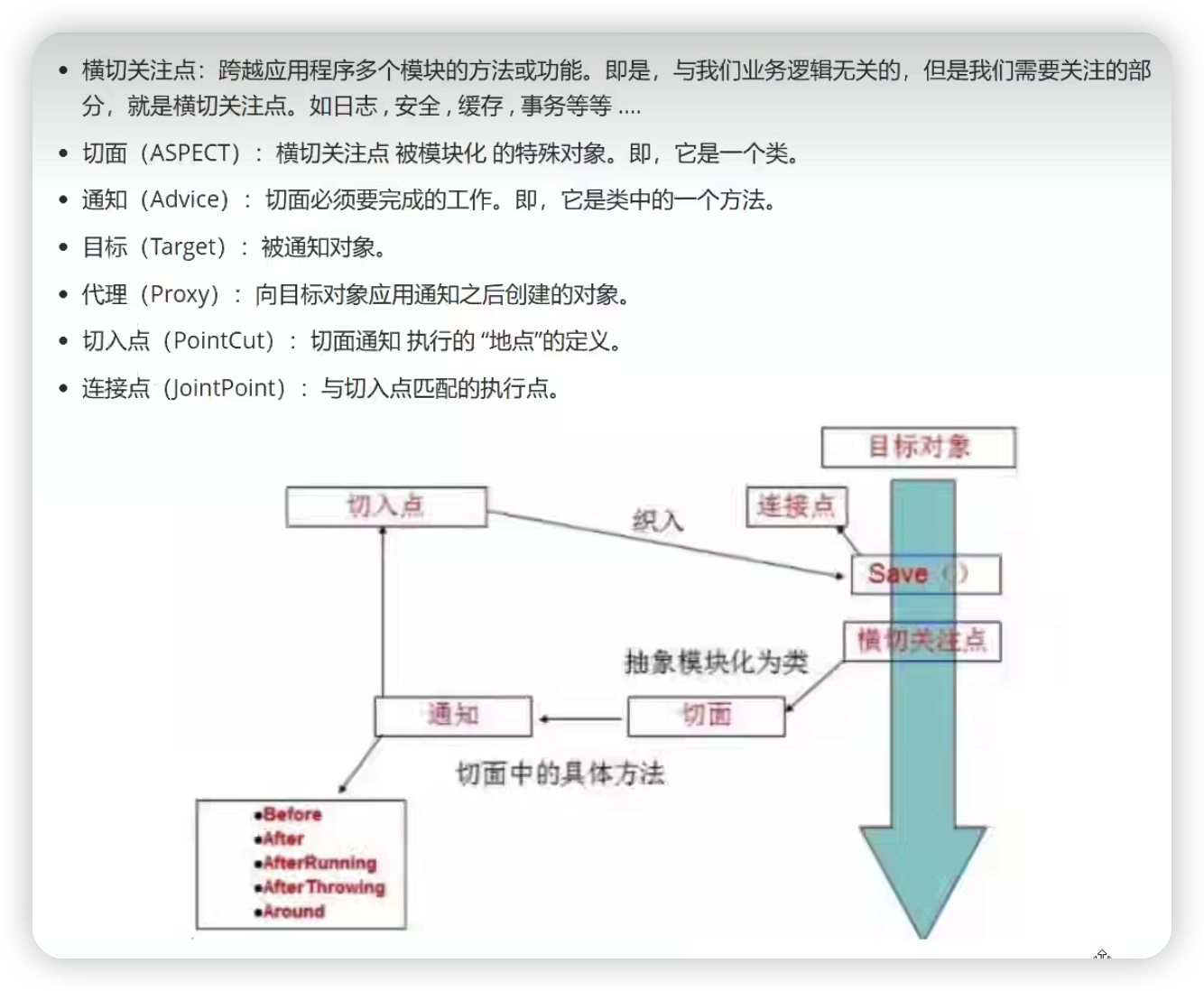
11.3使用Spring實現Aop
【重點】使用AOP織入,需要導入一個依賴包<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.9.1</version>
</dependency>
①使用Spring的API介面
UserService介面public interface UserService {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void select();
}
UserServiceImpl代碼
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
public void add() {
System.out.println("添加了一個用戶");
}
public void delete() {
System.out.println("刪除了一個用戶");
}
public void update() {
System.out.println("修改了一個用戶");
}
public void select() {
System.out.println("查詢了一個用戶");
}
}
Log代碼
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
//method:要執行的目標對象的方法
//args:參數
//target:目標對象
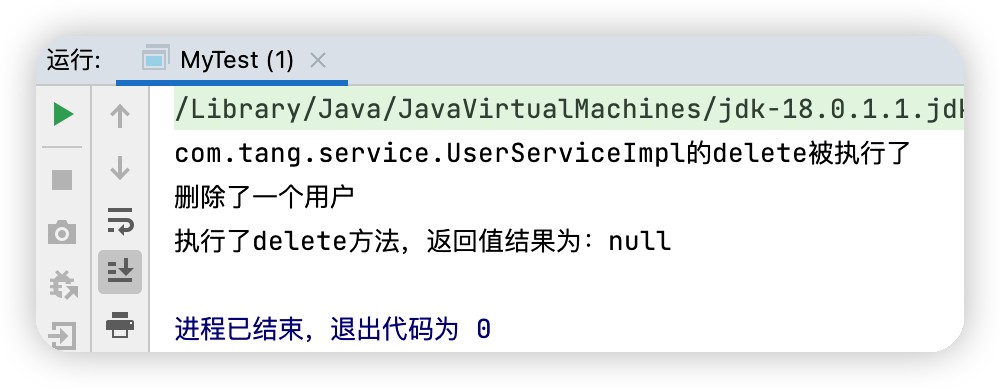
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"被執行了");
}
}
AfterLog代碼
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("執行了"+method.getName()+"方法,返回值結果為:"+returnValue);
}
}
applicationContext.xml代碼
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--註冊bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.tang.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="log" class="com.tang.log.Log"></bean>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.tang.log.AfterLog"></bean>
<!--方式一:使用原生Spring API介面 -->
<!--配置aop:需要導入aop的約束-->
<aop:config>
<!--切入點:expression:表達式,execution(需要執行的位置)-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.tang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--執行環繞增強-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"></aop:advisor>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
測試代碼
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//動態代理代理的是介面
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.delete();
}
}
測試結果
②自定義來實現AOP
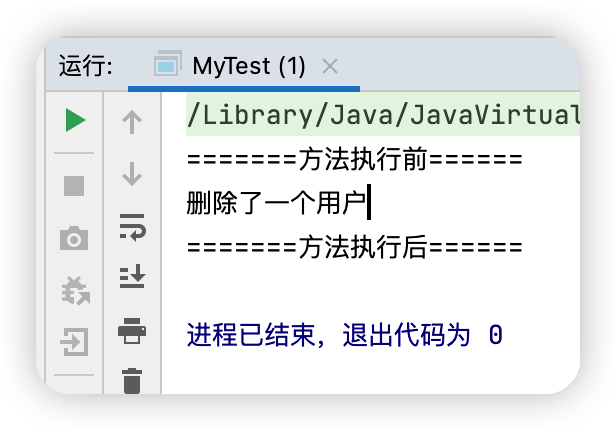
diy下的DiyPointCut類的代碼public class DiyPointCut {
public void before(){
System.out.println("=======方法執行前======");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("=======方法執行後======");
}
}
applicationContext.xml核心代碼
<!--方式二:自定義類-->
<bean id="diy" class="com.tang.diy.DiyPointCut"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="diy">
<!--切入點-->
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* com.tang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--通知-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
其它代碼同方式一使用Spring的API介面代碼相同就不在寫了
測試結果
③使用註解來實現AOP
beas.xml核心代碼<!--方式三:使用註解實現AOP-->
<bean id="annotationPoinCut" class="com.tang.diy.AnnotationPointCut"/>
<!--開啟註解支持 JDK(預設 proxy-target-class="false") cglib(proxy-target-class="true")-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
AnnotationPointCut代碼
//方式三:使用註解方式實現AOP
@Aspect
public class AnnotationPointCut {
@Before("execution(* com.tang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("=======方法執行前======");
}
@After("execution(* com.tang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("=========方法執行後==========");
}
//在環繞增強中,我們可以給定一個參數,代表我們要獲取處理切入的點
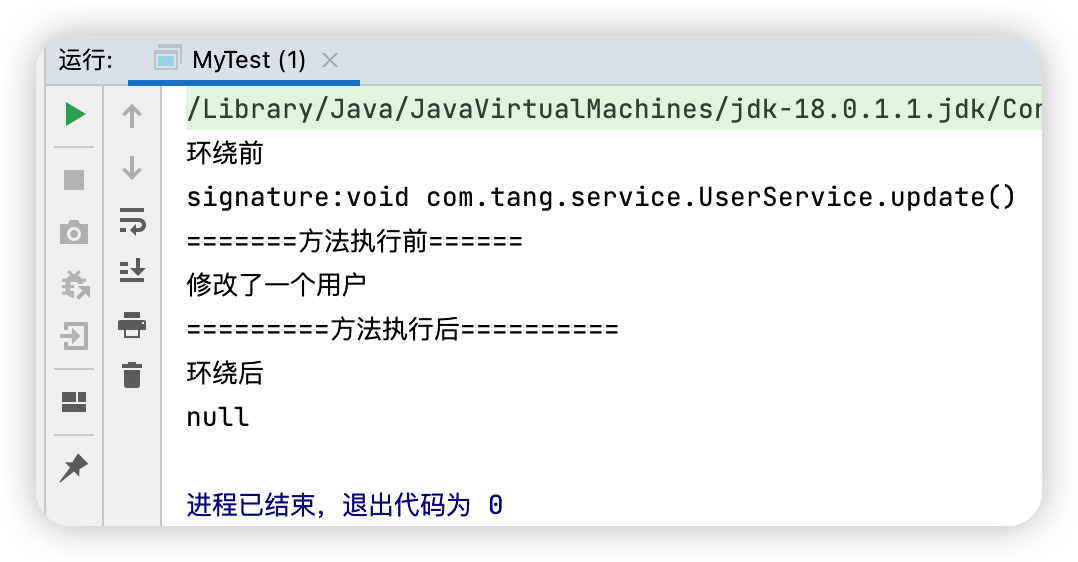
@Around("execution(* com.tang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("環繞前");
Signature signature = jp.getSignature();//獲得簽名
System.out.println("signature:"+signature);
Object proceed = jp.proceed();//執行方法
System.out.println("環繞後");
System.out.println(proceed);
}
}
測試結果
12.整合Mybatis
12.1步驟
①導入相關jar包
-
junit
-
mybatis
-
mysql資料庫
-
spring相關的
-
aop織入
-
mybatis-spring
②編寫配置文件
③測試
12.2回憶mybatis
步驟:- 編寫實體類
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
}
- 編寫核心配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--核心配置文件-->
<configuration>
<!--引入外部配置文件-->
<!-- <properties resource="db.properties"/>-->
<!--可以給實體類起別名-->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.tang.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- &在xml文件中與符號需要這樣來轉義-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.tang.mapper.UserMapper"></mapper>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 編寫介面
UserMapper介面代碼
public interface UserMapper {
public List<User> selectUser();
}
- 編寫mapper.xml
<!--核心配置文件-->
<mapper namespace="com.tang.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectUser" resultType="user">
select * from mybatis.user
</select>
</mapper>
- 測試
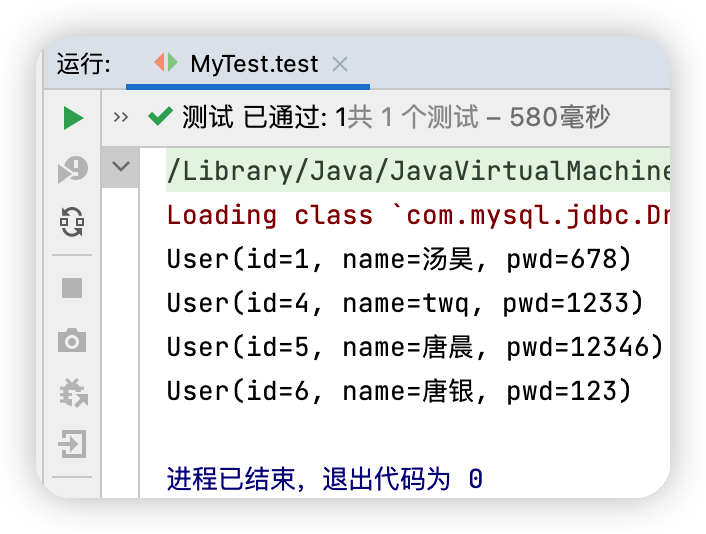
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
String resources ="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resources);
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession(true);
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> userList = mapper.selectUser();
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
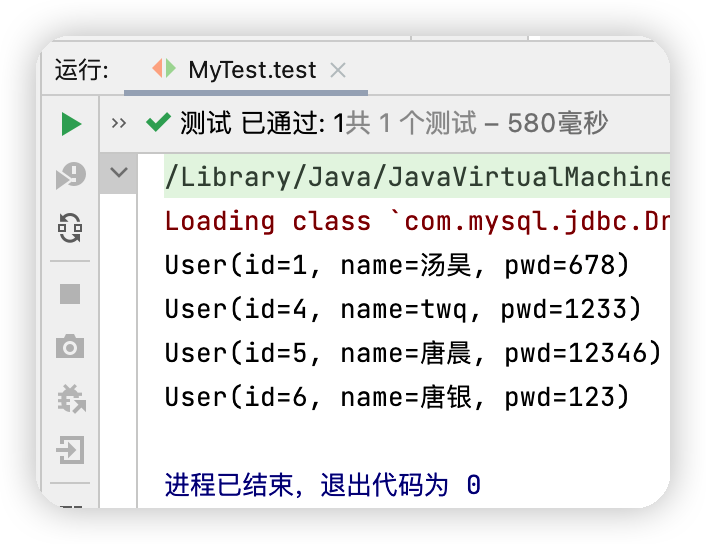
測試結果:
12.2Mybatis-spring
項目結構圖
①編寫數據源配置
<!--DataSource:使用Spring的數據源替換Mybatis的配置 c3p0 dbcpp druid
我們這裡使用Spring的JDBC
-->
<bean id="datasource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root123456"/>
</bean>
②sqlSessionFactory
<!--slqSessionFactory-->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="datasource"/>
<!--綁定Mybatis配置文件-->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/tang/mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
③sqlSessionTemplate
<!--SqlSessionTemplate:就是我們使用的sqlSession-->
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<!--只能使用構造器註入sqlSessionFactory,因為它沒有set方法-->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
④需要給介面加實現類
public class UserMapperImpl implements UserMapper{
//我們的所有操作,都使用sqlSession來執行,在原來,現在都使用SqlSessionTemplate;
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession;
public void setSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
}
public List<User> selectUser() {
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
return mapper.selectUser();
}
}
⑤將自己寫的實現類,註入到Spring中
<bean id="userMapper" class="com.tang.mapper.UserMapperImpl">
<property name="sqlSession" ref="sqlSession"/>
</bean>
⑥測試使用即可
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-dao.xml");
UserMapper userMapper = context.getBean("userMapper", UserMapper.class);
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectUser();
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
測試結果