前言 在Python中 in 操作符可以用於判斷某個元素是否存在於當前對象中,而對於不同的Python對象,使用 in 操作符的處理效率是不一樣的。 今天我們主要針對 4 種不同的Python數據類型進行學習:list列表、tuple元組、set集合、dict字典。 測試過程 我們用於測試的 4 種 ...
前言
在Python中 in 操作符可以用於判斷某個元素是否存在於當前對象中,而對於不同的Python對象,使用 in 操作符的處理效率是不一樣的。
今天我們主要針對 4 種不同的Python數據類型進行學習:list列表、tuple元組、set集合、dict字典。
測試過程
我們用於測試的 4 種Python數據類型,分別為 tmp_list 、tmp_tuple、tmp_set、tmp_dict,測試過程中,它們所包含的元素都是相同的,均通過 random.randint(0, num) 隨機生成,但它們的長度均為 num - 3 ,也就是說在 [0, num] 範圍內,將有3個整數不在上面的對象中,我們需要把這3個整數找出來。
測試代碼如下:
import time
import random
def demo(target, num):
time1 = time.time()
res = []
for i in range(num):
if i not in target:
res.append(i)
time2 = time.time()
print("結果:{},當前類型:{},耗時:{}".format(res, type(target), time2 - time1))
num = 500
tmp_set = set()
while len(tmp_set) <= num - 3:
tmp_set.add(random.randint(0, num))
tmp_list = list(tmp_set)
tmp_tuple = tuple(tmp_set)
tmp_dict = {key: "" for key in tmp_set}
demo(tmp_list, num)
demo(tmp_tuple, num)
demo(tmp_set, num)
demo(tmp_dict, num)
當 num = 50 時,得到如下結果:
不包含的整數:[25, 31, 36],當前類型:<class 'list'>,耗時:0.0
不包含的整數:[25, 31, 36],當前類型:<class 'tuple'>,耗時:0.0
不包含的整數:[25, 31, 36],當前類型:<class 'set'>,耗時:0.0
不包含的整數:[25, 31, 36],當前類型:<class 'dict'>,耗時:0.0
當 num = 500 時,得到如下結果:
不包含的整數:[114, 329, 355],當前類型:<class 'list'>,耗時:0.0059354305267333984
不包含的整數:[114, 329, 355],當前類型:<class 'tuple'>,耗時:0.0052182674407958984
不包含的整數:[114, 329, 355],當前類型:<class 'set'>,耗時:0.0
不包含的整數:[114, 329, 355],當前類型:<class 'dict'>,耗時:0.0
當 num = 5000 時,得到如下結果:
不包含的整數:[445, 850, 3547],當前類型:<class 'list'>,耗時:0.3342933654785156
不包含的整數:[445, 850, 3547],當前類型:<class 'tuple'>,耗時:0.39918947219848633
不包含的整數:[445, 850, 3547],當前類型:<class 'set'>,耗時:0.00099945068359375
不包含的整數:[445, 850, 3547],當前類型:<class 'dict'>,耗時:0.0
當 num = 50000 時,得到如下結果:
不包含的整數:[9296, 18652, 32281],當前類型:<class 'list'>,耗時:26.92029118537903
不包含的整數:[9296, 18652, 32281],當前類型:<class 'tuple'>,耗時:25.956974506378174
不包含的整數:[9296, 18652, 32281],當前類型:<class 'set'>,耗時:0.009968996047973633
不包含的整數:[9296, 18652, 32281],當前類型:<class 'dict'>,耗時:0.009973287582397461
當 num = 55000 時,得到如下結果:
不包含的整數:[16086, 33891, 46161],當前類型:<class 'list'>,耗時:52.91718029975891
不包含的整數:[16086, 33891, 46161],當前類型:<class 'tuple'>,耗時:52.84810948371887
不包含的整數:[16086, 33891, 46161],當前類型:<class 'set'>,耗時:0.009554624557495117
不包含的整數:[16086, 33891, 46161],當前類型:<class 'dict'>,耗時:0.007979393005371094
當 num = 75000 時,得到如下結果:
不包含的整數:[23057, 35827, 69232],當前類型:<class 'list'>,耗時:75.57932734489441
不包含的整數:[23057, 35827, 69232],當前類型:<class 'tuple'>,耗時:64.49729013442993
不包含的整數:[23057, 35827, 69232],當前類型:<class 'set'>,耗時:0.005983591079711914
不包含的整數:[23057, 35827, 69232],當前類型:<class 'dict'>,耗時:0.005979776382446289
當 num = 100000 時,得到如下結果:
'''
學習中遇到問題沒人解答?小編創建了一個Python學習交流群:711312441
尋找有志同道合的小伙伴,互幫互助,群里還有不錯的視頻學習教程和PDF電子書!
'''
不包含的整數:[22499, 22800, 29652],當前類型:<class 'list'>,耗時:110.19707798957825
不包含的整數:[22499, 22800, 29652],當前類型:<class 'tuple'>,耗時:109.08251285552979
不包含的整數:[22499, 22800, 29652],當前類型:<class 'set'>,耗時:0.011965036392211914
不包含的整數:[22499, 22800, 29652],當前類型:<class 'dict'>,耗時:0.009937524795532227
結論
通過上面的測試,我們可以看到,總體來說,list、tuple它們使用 in 操作符的查找效率相差不多,set、dict它們使用 in 操作符的查找效率相差不多,但隨著查找數據量的增大,list、tuple的處理效率變得越來越慢,而set、dict的處理效率,將遠遠優於list及tuple。
list列表、tuple元組、set集合、dict字典,使用 in 操作符查找的平均時間複雜度如下:
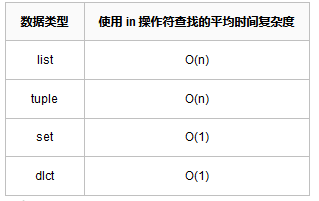
當我們在處理數據量大且需頻繁查找元素時,最好使用 set、dict ,這樣將會大幅度提升處理速度。


