一、IO流概述 1.原理  2.流的分類 3.流的體系,藍底框為重點掌握的 二、IO流操作 1.節點流-字元流 ( ...
一、IO流概述
1.原理
2.流的分類
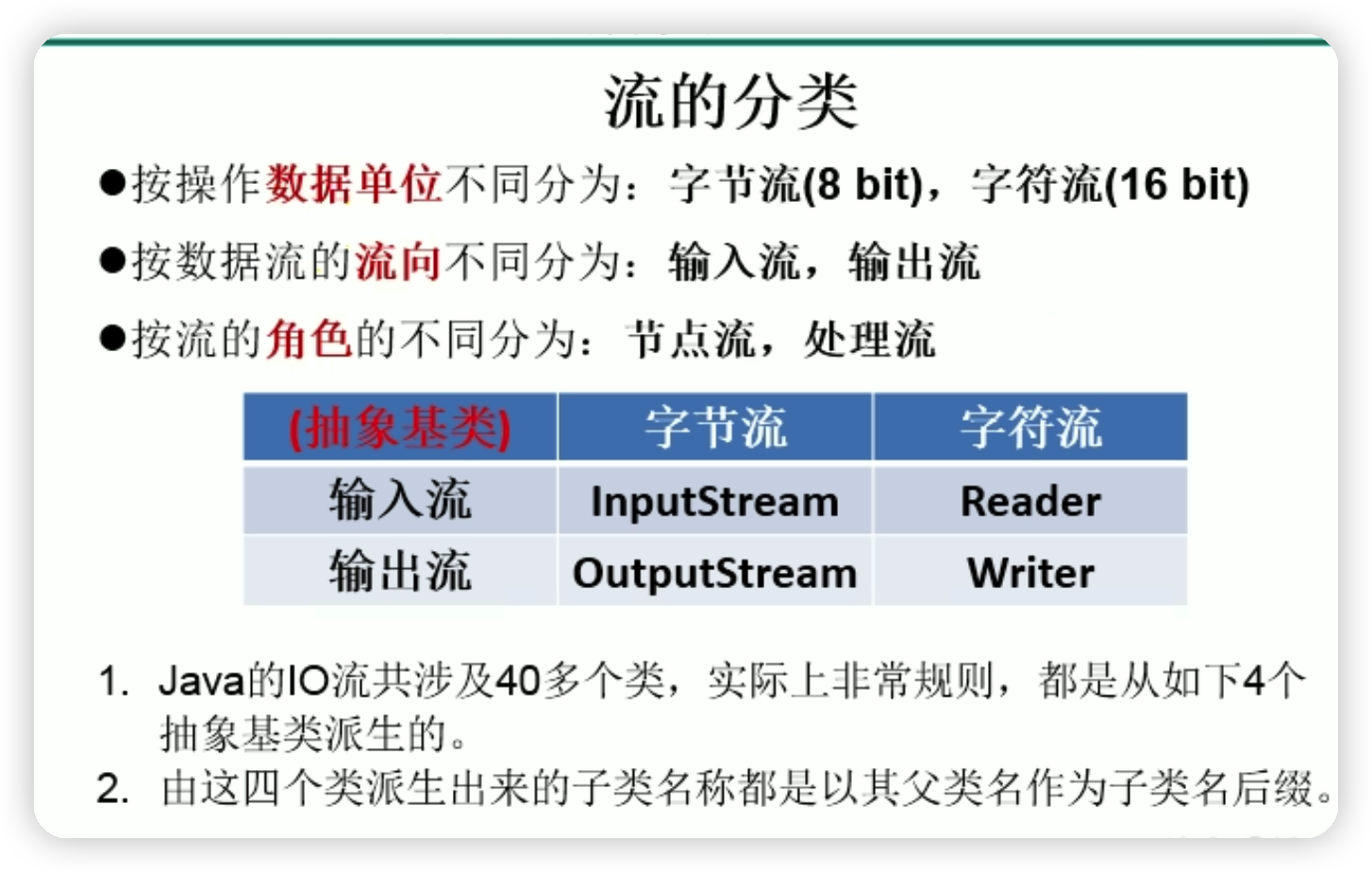
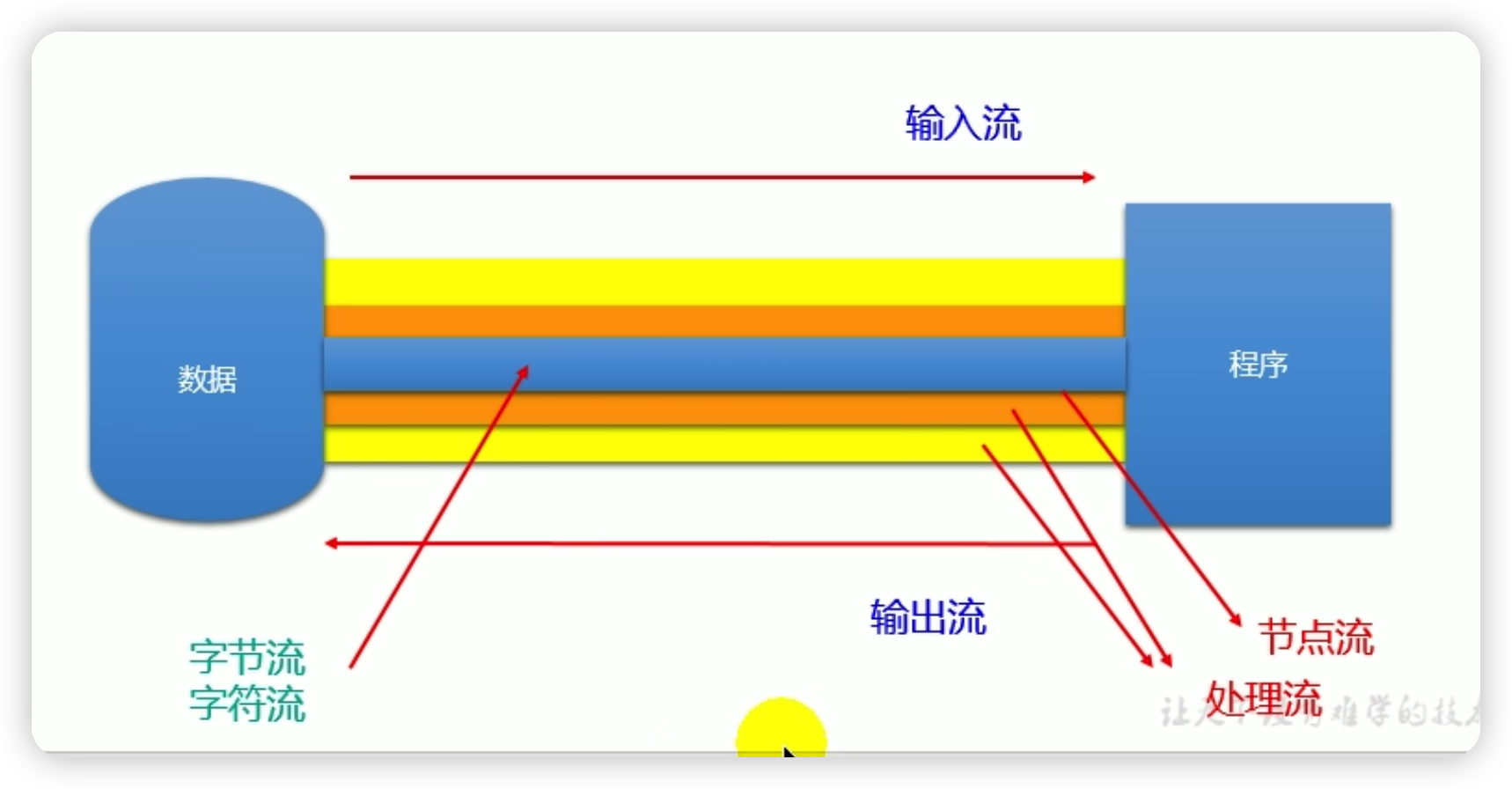
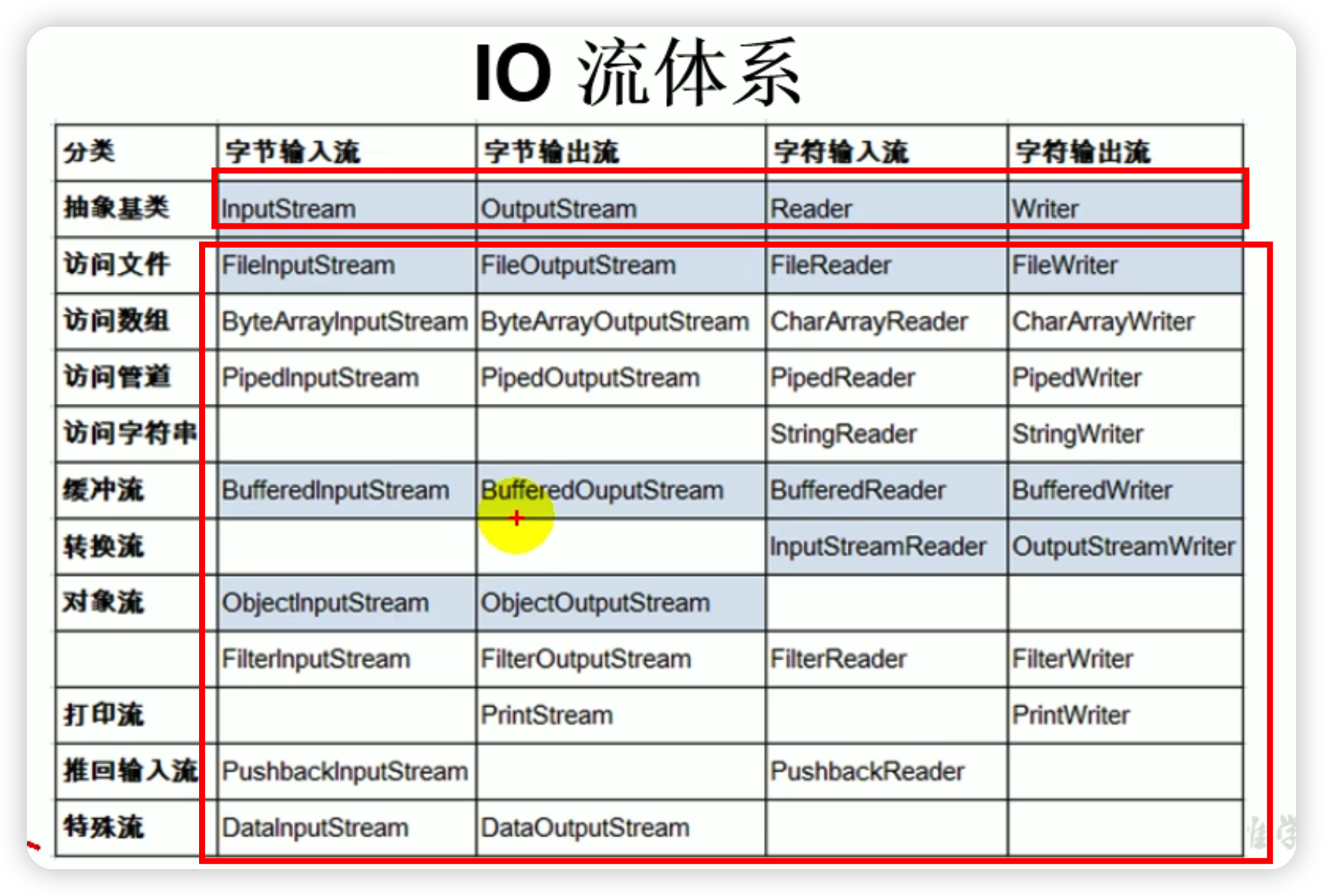
3.流的體系,藍底框為重點掌握的
二、IO流操作
1.節點流-字元流
(1).FileReader讀入數據的基本操作
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.io;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class IOTest {
@Test
public void test() {
FileReader fr = null;
//為了保證流資源一定可以執行關閉操作,需要使用try-catch-finally
//讀入的文件一定要存在,否則就會報FileNotFoundException。
try {
//將Hello工程下的hello.txt文件內容讀入程式中,並輸出到控制台
//1.實例化File類對象,指明要操作的文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//2.提供具體的流
fr = new FileReader(file);
//3.數據的讀入
//read():返回讀入的一個字元,如果達到文件末尾,返回-1;否則返回字元的Ascall值
int data = fr.read();
while(data != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);//讀取文件第一個字元
data = fr.read();//讀取文件下一個字元
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.流的關閉操作
try {
if(fr != null)
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
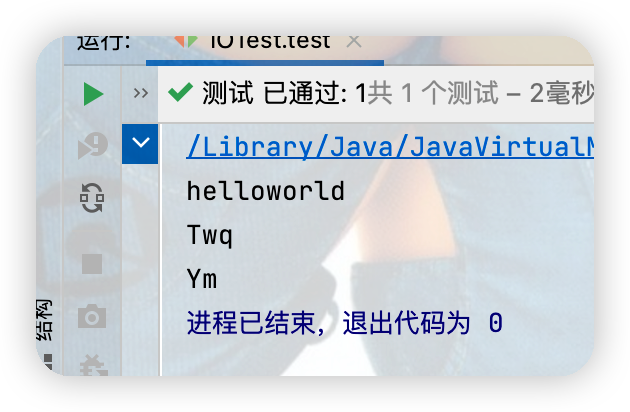
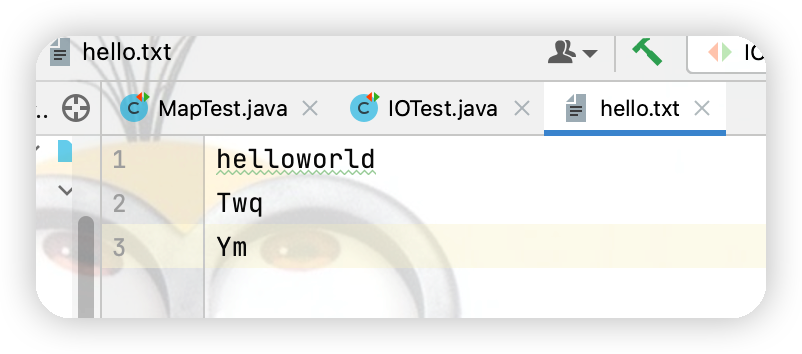
①.FileReader對read()操作升級:使用read的重載方法
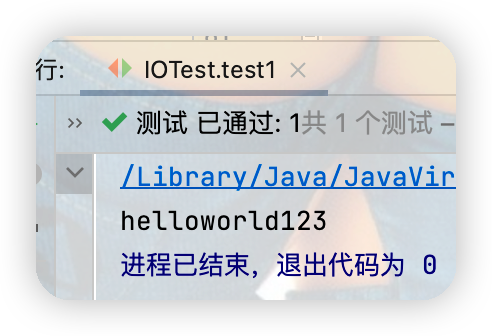
代碼中for迴圈處如果寫為i < cubf.length會出現一下問題 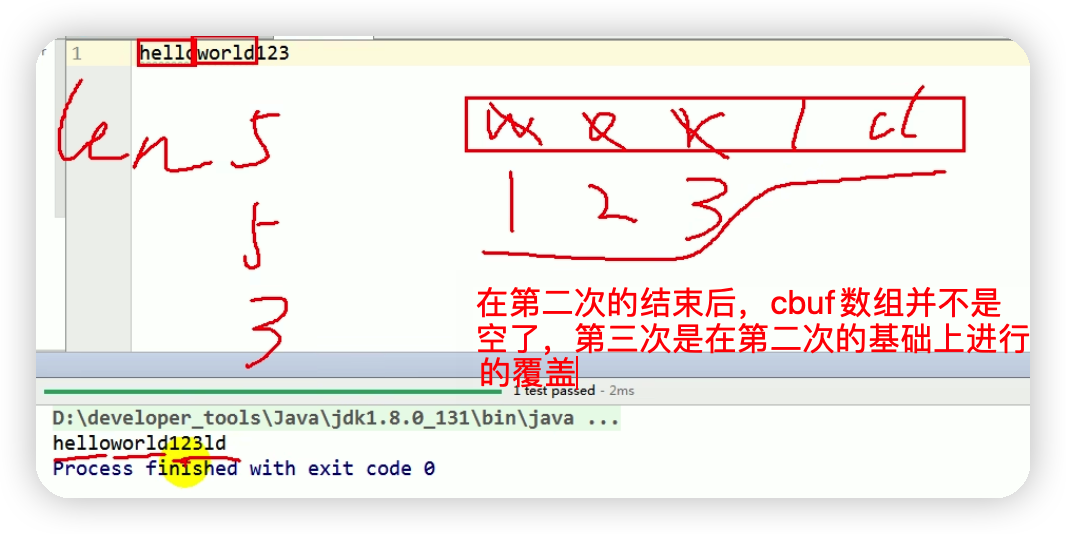點擊查看代碼
//對read()操作升級:使用read的重載方法
@Test
public void test1(){
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//1.File類的實例化
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//2.FileReader流的實例化
fr = new FileReader(file);
//3.讀入的操作
//read(char[] cbuf):返回每次讀入cbuf數組中的字元的個數,當讀到文件末尾時返回-1
char[] cbuf = new char[5];//相當於一個容量池,每次能從文件能讀出的最大字元數
int len;
while((len = fr.read(cbuf) )!= -1){
//方式一:
//錯誤寫法
// for (int i = 0; i <cbuf.length ; i++) {
// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);
// }
//正確寫法:每次讀到幾個字元就輸出幾個
// for (int i = 0; i <len; i++) {
// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);
// }
//方式二:
// 將數組轉化為字元,因為每一次讀到的字元都是在上一次數組上的覆蓋
//因此每次只需取出從數組開始位置到所能讀到的字元的即可結束
String str = new String(cbuf,0,len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fr != null){
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// fr.read(cbuf);
}
(2)FileWriter寫出數據的操作
點擊查看代碼
/*
1.輸出操作,對應的File可以不存在,並不會報異常
2.
File對應的硬碟中的文件如果不存在:在輸出的過程中,會自動創建此文件
File對應的硬碟中的文件如果存在:
如果流使用的構造器是FileWriter(file,false) / FileWriter(false):對原有文件的覆蓋
如果流使用的構造器是FileWriter(file,true) /:不會對原有文件覆蓋,而是在原有文件基礎上追加內容
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//1.提供File類的對象,指明寫出到的文件
File file = new File("hello1.txt");
//2.提供FileWriter的對象,用於數據的寫出
fw = new FileWriter(file);
//3.寫出的操作
fw.write("I have a dream\n");
fw.write("you need to hava a dream");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.流資源的關閉
if(fw != null){
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
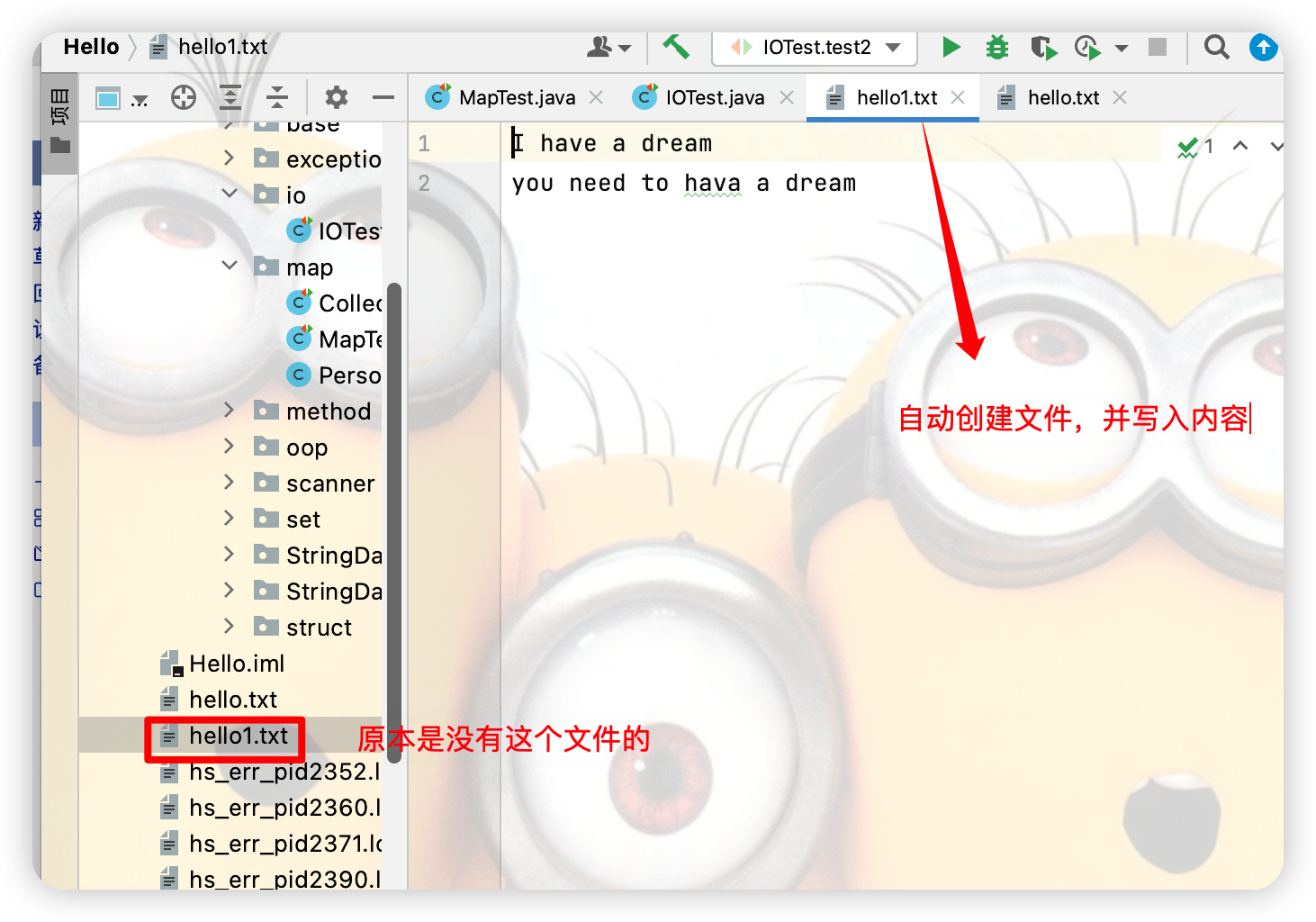
(3).使用FileReader和FileWriter實現文本文件的複製
①一開始就按下方圖片的代碼去寫,然後選中除關閉流的以外的代碼按快捷鍵ctrl + alt + t生成 try - catch - finally然後將關閉流的代碼放入finally中並單獨生成 try - catch 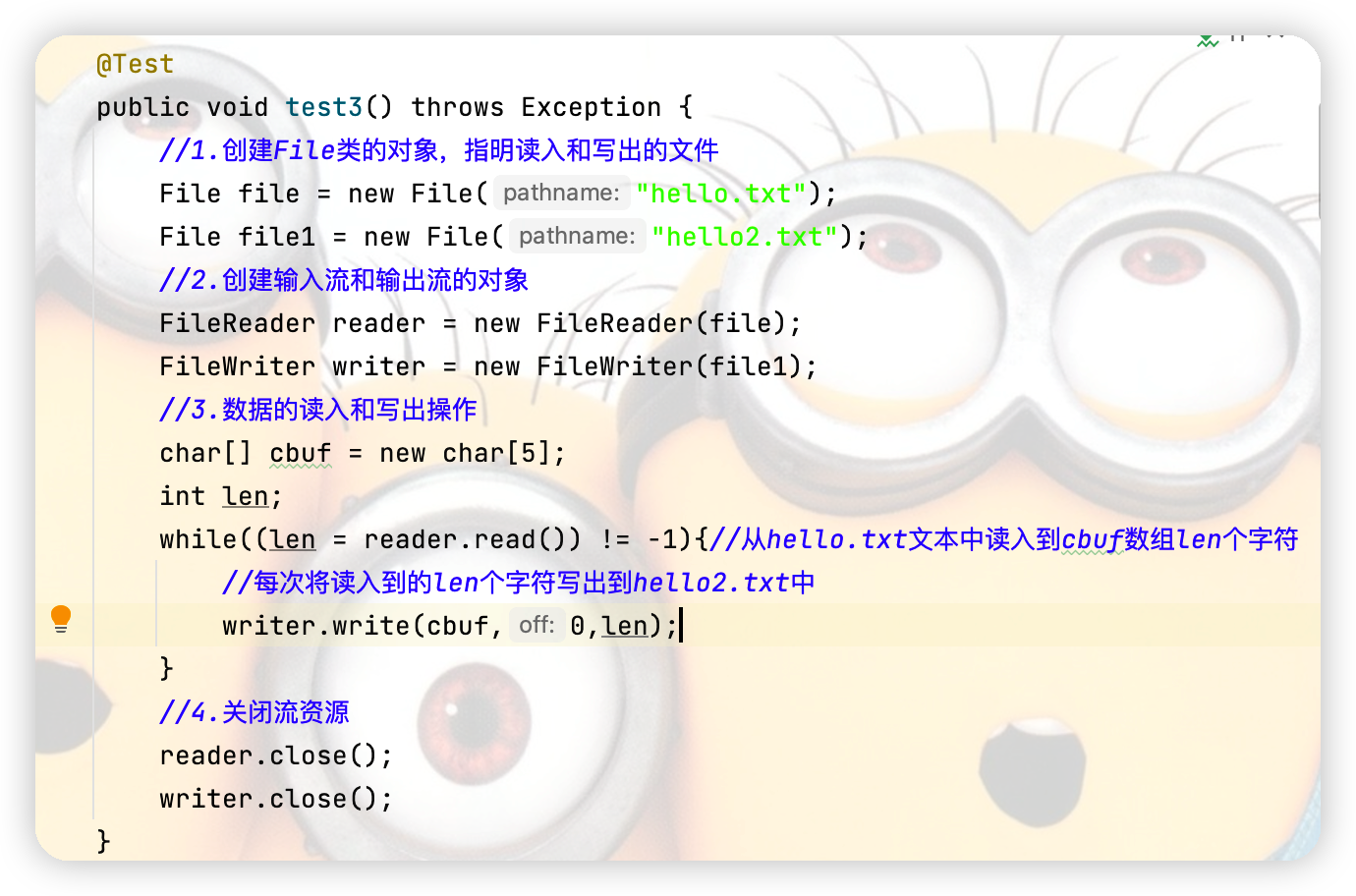點擊查看代碼
@Test
public void test3(){
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//1.創建File類的對象,指明讀入和寫出的文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");
File file1 = new File("hello2.txt");
//2.創建輸入流和輸出流的對象
fr = new FileReader(file);
fw = new FileWriter(file1);
//3.數據的讀入和寫出操作
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
int len;
while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){//從hello.txt文本中讀入到cbuf數組len個字元
//每次將讀入到的len個字元寫出到hello2.txt中
fw.write(cbuf,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.關閉流資源
try {
if(fw !=null)
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(fr != null)
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
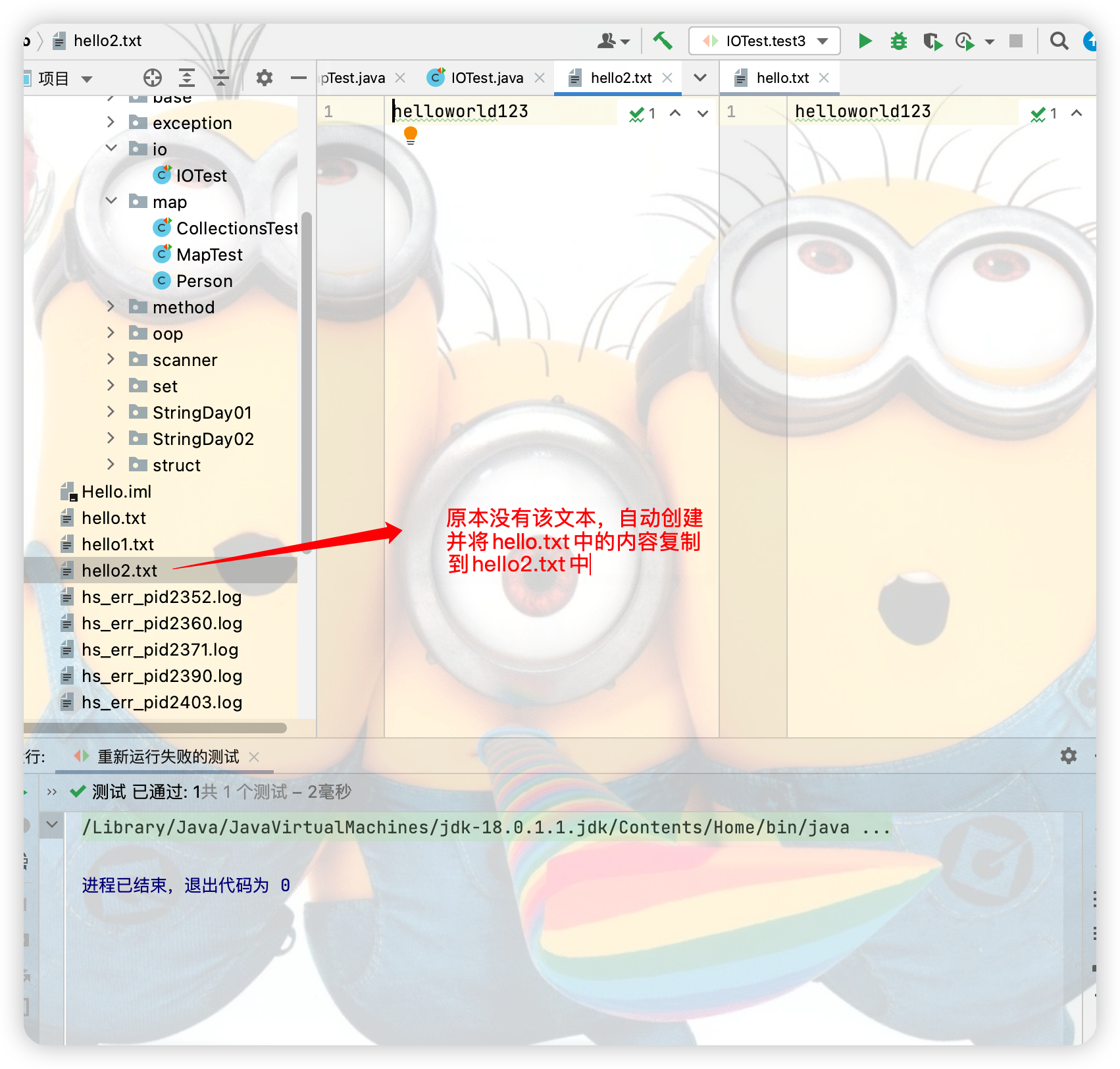
註意:字元流不能處理圖片文件的測試
2.節點流-位元組流
(1)FileInputStream的使用
①位元組流處理文本文件
點擊查看代碼
/*
結論:
1.對於文本文件(.txt , .java , .c , .cpp)使用字元流處理
2.對於非文本文件(.jpg, .mp3, .mp4, .doc, .ppt ......)使用位元組流處理
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
//使用位元組流FileInputStream處理文本文件,可能出現亂碼
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//2.造流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//3.讀數據
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
int len;//記錄每次讀取的位元組的個數
while((len=fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
String str = new String(bytes,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {//4.關閉數據
try {
if(fis != null)
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
②位元組流處理非文本文件
點擊查看代碼
//實現對圖片的複製
@Test
public void test5() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
File file = new File("QQ20210927-0.jpg");
File file1 = new File("QQ20210927-1.jpg");
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
int len ;
while((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
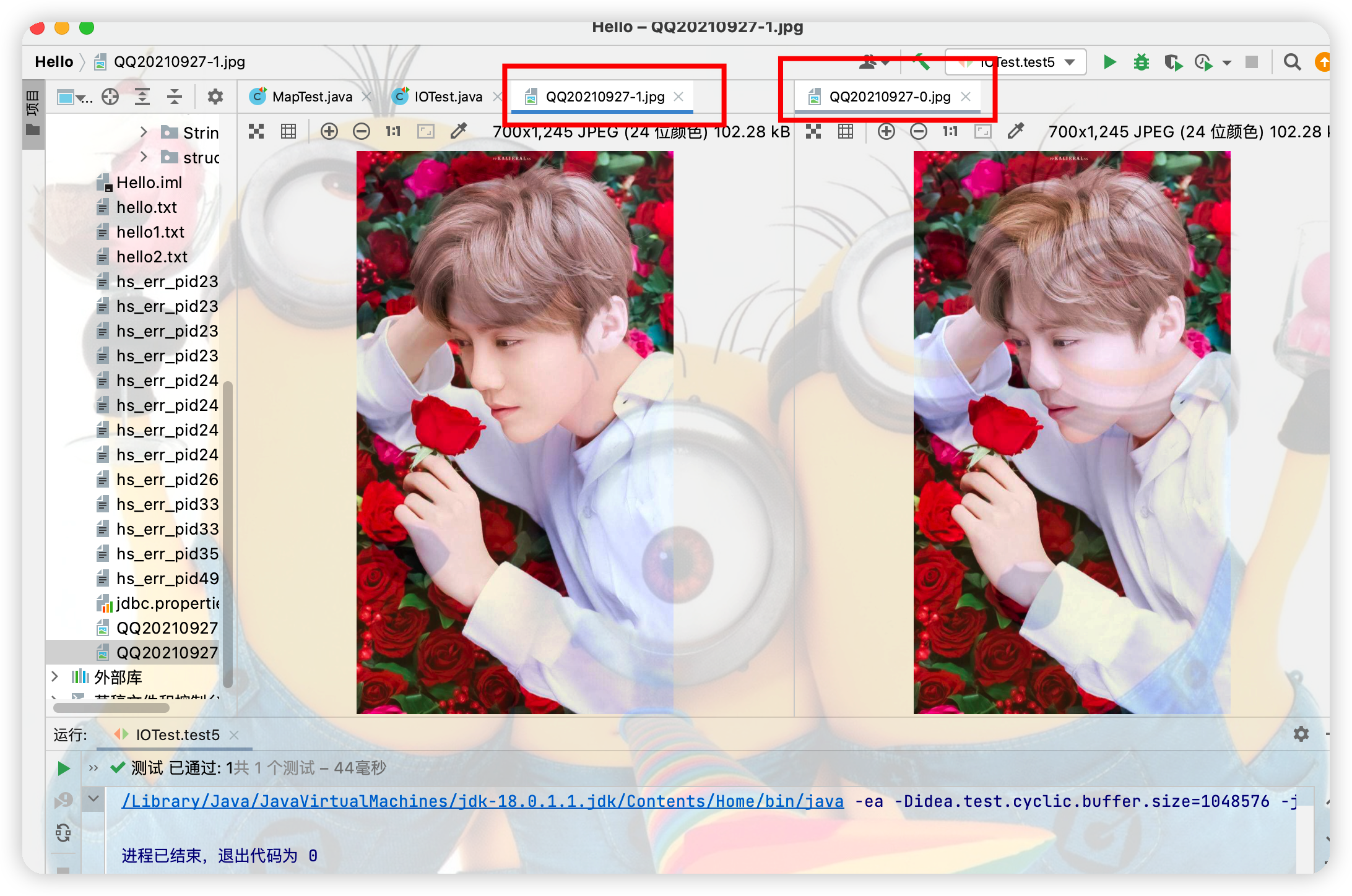
(2)FileInputStream和FileOutputStream複製文件的方法測試
點擊查看代碼
//指定路徑下的文件複製
public void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
File file = new File(srcPath);
File file1 = new File(destPath);
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len ;
while((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void test6(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String srcPath = "/Users/twq/Downloads/01.mp4";
String destPath = "/Users/twq/Downloads/03.mp4";
copyFile(srcPath,destPath);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
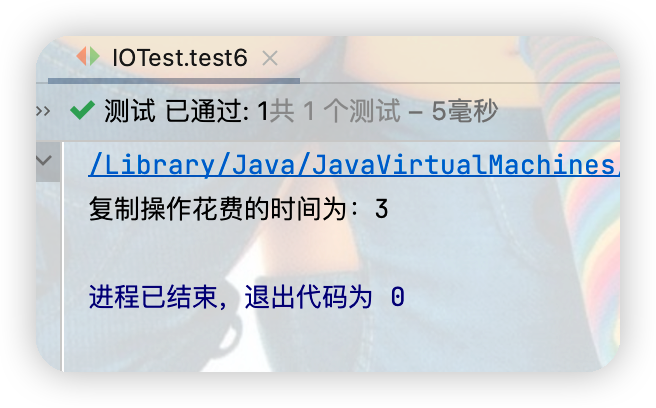
System.out.println("複製操作花費的時間為:"+(end - start));
}
3.緩衝流-位元組流
(1)實現非文本文件的複製
點擊查看代碼
/*
實現非文本文件的複製
*/
@Test
public void test7() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File file = new File("QQ20210927-0.jpg");
File file1 = new File("QQ20210927-2.jpg");
//2.造流
//2.1造節點流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);
//2.2造緩衝流:處理流是包裝在節點流之上的
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//3.複製的細節:讀取、寫入
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bytes))!= -1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bis != null){
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(bos != null){
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//4.資源關閉
//要求:先關閉外層的流,在關閉內層的流
//關閉外層流的同時,內層流也會自動進行關閉,關於內層流的關閉我們可以省略
// fos.close();
// fis.close();
}
(2)緩衝流相較於節點流的優勢
點擊查看代碼
/*
實現非文本文件的複製
*/
@Test
public void test7() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String srcPath = "/Users/twq/Downloads/01.mp4";
String destPath = "/Users/twq/Downloads/02.mp4";
copyFileBuffer(srcPath,destPath);
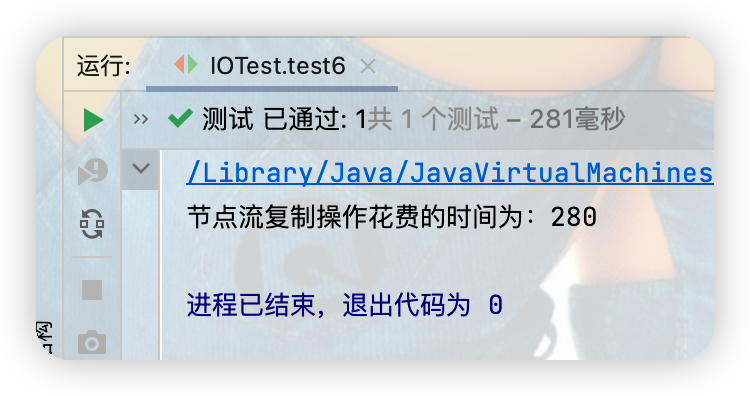
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("緩衝流複製操作花費的時間為:"+(end - start));
}
//指定路徑下的文件複製
public void copyFileBuffer(String srcPath,String destPath){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File file = new File(srcPath);
File file1 = new File(destPath);
//2.造流
//2.1造節點流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);
//2.2造緩衝流:處理流是包裝在節點流之上的
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//3.複製的細節:讀取、寫入
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bytes))!= -1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bis != null){
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(bos != null){
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//4.資源關閉
//要求:先關閉外層的流,在關閉內層的流
//關閉外層流的同時,內層流也會自動進行關閉,關於內層流的關閉我們可以省略
// fos.close();
// fis.close();
}
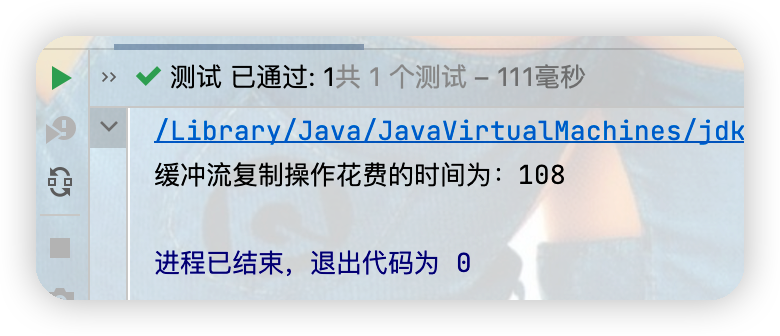
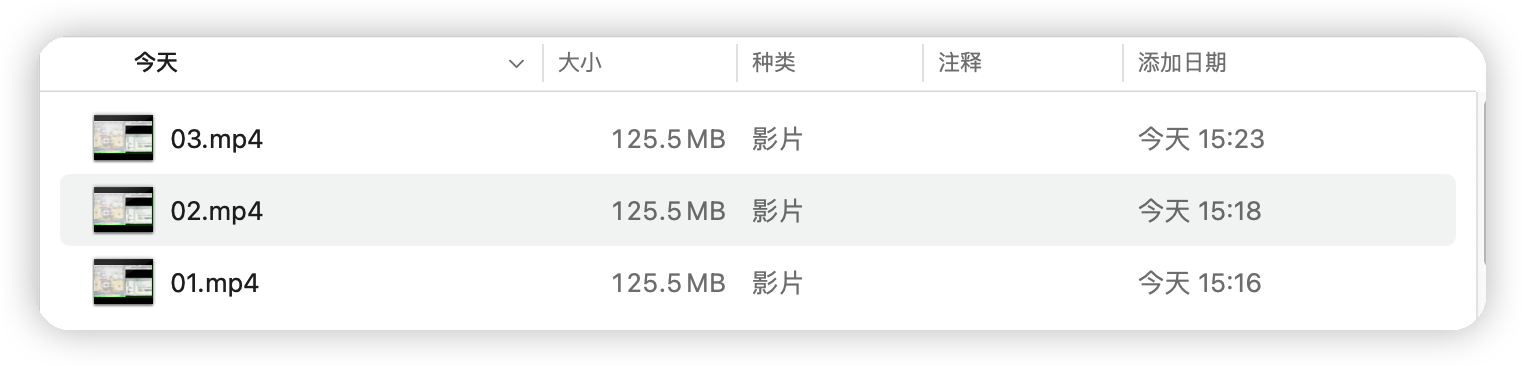
緩衝流能提高讀寫速度的原因:內部提供了一個緩衝區
4.緩衝流-字元流
使用BufferReader和BufferWriter實現文本文件的複製點擊查看代碼
//使用BufferReader和BufferWriter實現文本文件的複製
@Test
public void test8() {
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
//創建文件和相應的流
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("hello.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("hello3.txt")));
//讀
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len ;
while((len = br.read(chars))!= -1){
bw.write(chars,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(br != null){
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(bw != null){
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}

5.圖片的加解密
相同的代碼在運行一次就可以進行解密,主要是因為兩次相同的異或之後可以得到運來的數據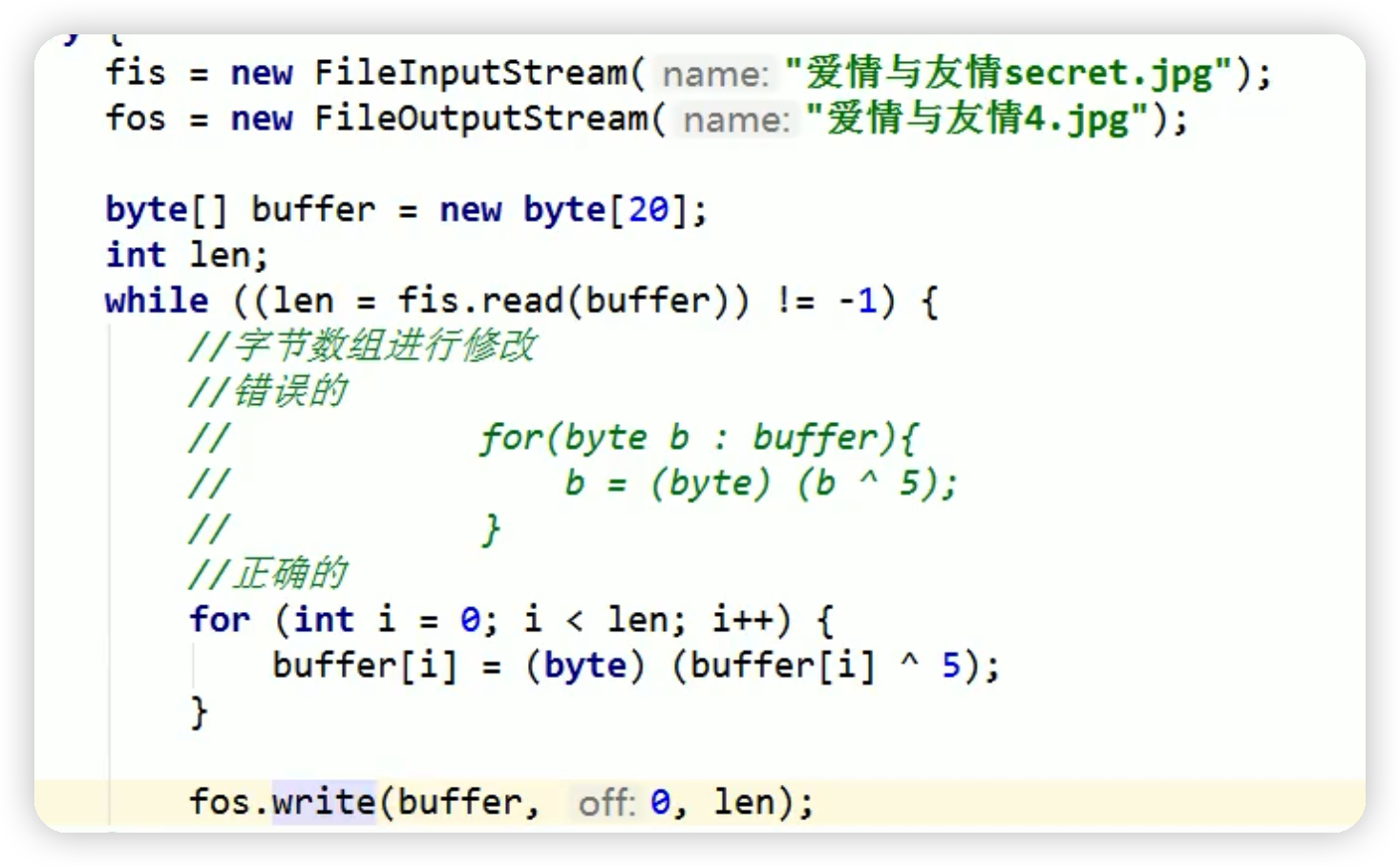
6.轉換流
(1)InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter都屬於字元流,作用都是提供位元組流與字元流之間的轉換①InputStreamReader:將一個位元組的輸入流轉換為字元的輸入流
點擊查看代碼
@Test
public void test() {
InputStreamReader isr = null;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("hello.txt");
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//使用系統預設的字元集
//參數2指明瞭字元集,具體使用那個字元集,取決於文件hello.txt保存時使用的字元集
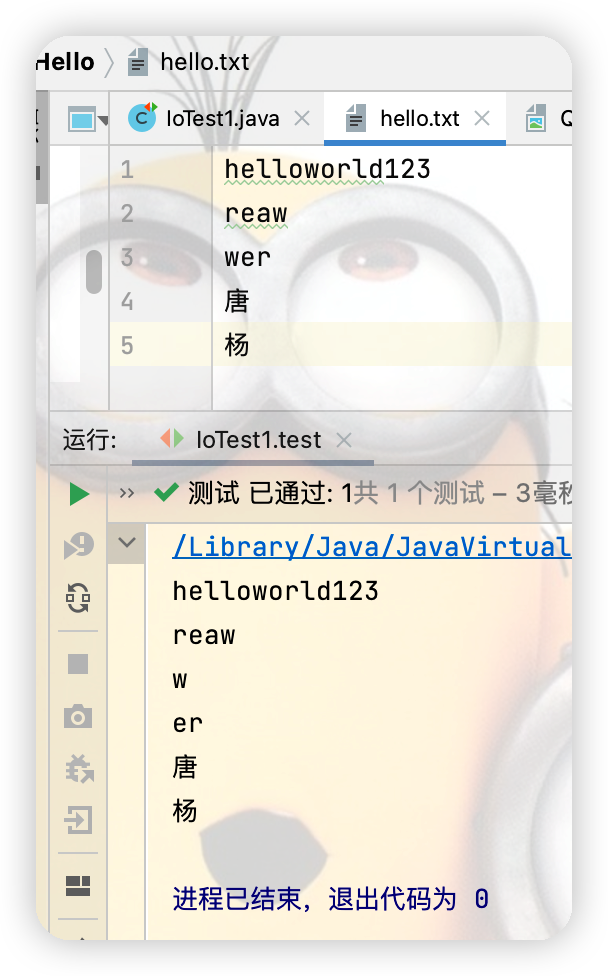
isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8");
char[] chars = new char[20];
int len ;
while((len = isr.read(chars))!= -1){
String s = new String(chars, 0, len);
System.out.println(s);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(isr != null){
try {
isr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
②OutputStreamWriter:將一個字元的輸出流轉為位元組的輸出流
(2)綜合使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
點擊查看代碼
@Test
public void test1(){
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
try {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
File file1 = new File("hello4.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);
isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");
char[] chars = new char[20];
int len;
while((len = isr.read(chars)) != -1){
osw.write(chars,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(isr != null){
try {
isr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(osw != null){
try {
osw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
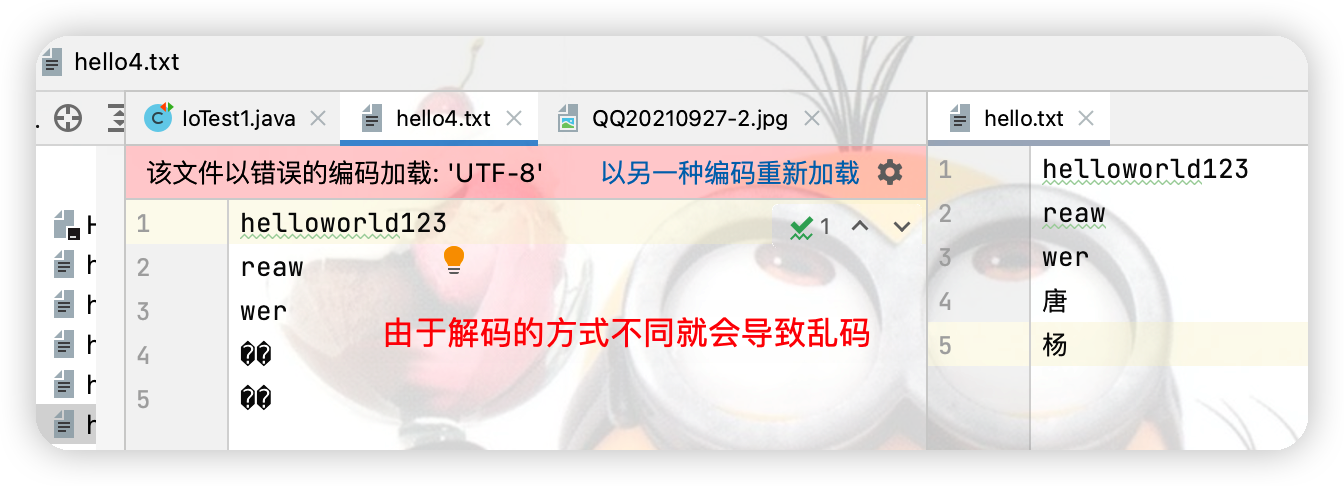
7.數據流
(1)DataInputStream 和 DataOutputStream作用:擁有讀取或寫出基本數據類型的變數或字元串點擊查看代碼
將文件中存儲的基本數據類型變數和字元串讀取到記憶體中,保存在變數中
註意點:讀取不同類型的數據要與當初寫入文件時,保存的數據的順序一致!
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
DataInputStream dis = null;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.txt"));
String name = dis.readUTF();
int age = dis.readInt();
boolean isMale = dis.readBoolean();
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println("isMale = " + isMale);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(dis != null){
try {
dis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void test2() {
DataOutputStream dos = null;
try {
dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.txt"));
dos.writeUTF("唐昊");
dos.flush();//刷新操作,將記憶體中的數據寫入文件
dos.writeInt(23);
dos.flush();
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(dos != null){
try {
dos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
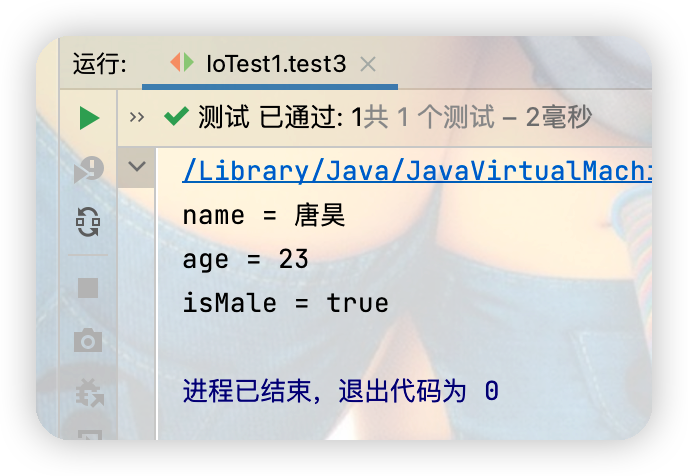
註意:需要先運行向文件里寫的操作,才能繼續運行讀的操作,並且讀的順序必須與寫的順序一致,否則就會報EOFException異常
8.對象流
(1)ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream:用於存儲和讀取基本數據類型數據或對象的處理流
①序列化與反序列化
點擊查看代碼
/*
反序列化:將磁碟文件的對象還原為記憶體中的一個Java對象
使用ObjectInputStream來實現
*/
@Test
public void test6(){
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("Object.txt"));
Object o = ois.readObject();
String str = (String)o;
Person p =(Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(p);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ois != null){
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/*
序列化過程:將記憶體中的Java對象保存到磁碟中或通過網路傳輸出去
使用ObjectOutputStream實現
*/
@Test
public void test5(){
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Object.txt"));
oos.writeObject(new String("北京天安門"));
oos.flush();//刷新操作
//要想一個Java對象時可序列化的,需要滿足相應的要求,見Person.java
oos.writeObject(new Person("王名",23));
oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(oos != null){
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
②自定義類的序列化與反序列化
Person類代碼如下點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.io;
import java.io.Serializable;
/*
Person需要滿足如下的要求,方可序列化
1.需要實現介面:Seriallizabe
2.當前類提供一個全局常量:serialVersionUID
3.除了當前Person類需要實現Serializable介面之外,還必須保證其內部所有屬性也必須是可序列化的(預設情況下:基本數據類型可序列化
*/
public class Person implements Serializable {
public static final long serialVersionUID = 3476465475L;
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
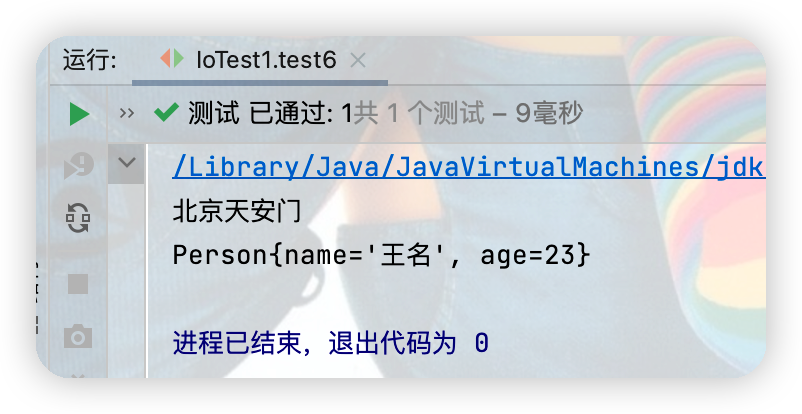
註:代碼的運行得先運行序列化的代碼然後再運行反序列化的代碼
③public static final long serialVersionUID :這個id如果沒有寫的話,就進行的序列化操作(沒有進行反序列化),然後對類進行一些修改之後,在進行反序列化就會報錯,起初定義好序列化id是為了反序列化能根據此id進行無差錯的反序列化
9.RandomAccessFile的使用
(1)實現非文本文件的複製
點擊查看代碼
/*
RandomAccessFile的使用
1.RandomAccessFile直接繼承與Java.lang.object類,實現了DataInput和DataOutput介面
2.RandomAccessFile既可以作為一個輸入流,又可以作為一個輸出流
*/
@Test
public void test7(){
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
RandomAccessFile rw = null;
try {
raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"), "r");
rw = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello1.txt"), "rw");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = raf.read(bytes))!= -1){
rw.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(raf != null){
try {
raf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(rw != null){
try {
rw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(2)單獨作為輸出流時
點擊查看代碼
/*
如果RandomAccessFile作為輸出流時,寫出到的文件如果不存在,則在執行過程中自動創建
如果寫到的文件存在,則會對原有文件從頭開始覆蓋
*/
@Test
public void test8(){
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
try {
raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"),"rw");
raf.write("xyz".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(raf != null){
try {
raf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
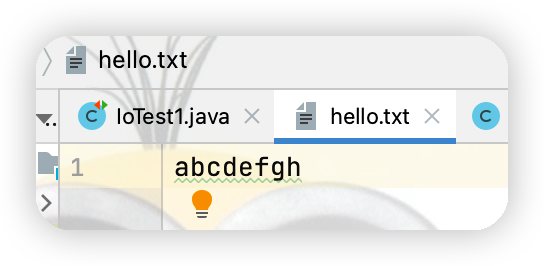
上述代碼運行之後hello.txt 中的內容如下
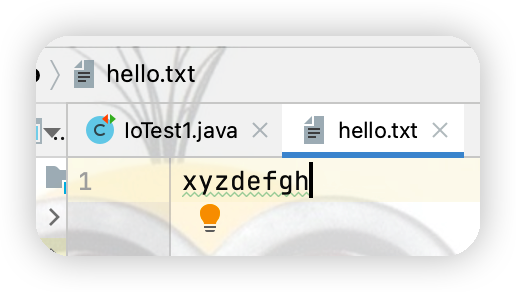
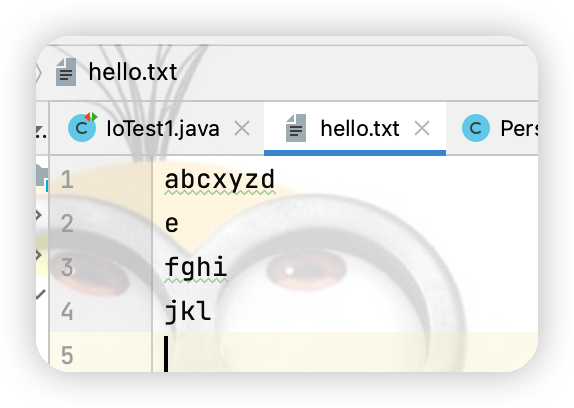
(3)實現在文件指定位置插入數據
點擊查看代碼
@Test
public void test8(){
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
try {
raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"),"rw");
raf.seek(3);//將指針調到角標為3的位置
//保存指針3後面的所有數據到StringBuilder中
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder((int) new File("hello.txt").length());
byte[] bytes = new byte[20];
int len;
while((len = raf.read(bytes))!= -1){
builder.append(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
//調回指針寫入"xyz"
raf.seek(3);
raf.write("xyz".getBytes());
//將StringBuilder 中的數據寫入到文件中
raf.write(builder.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(raf != null){
try {
raf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
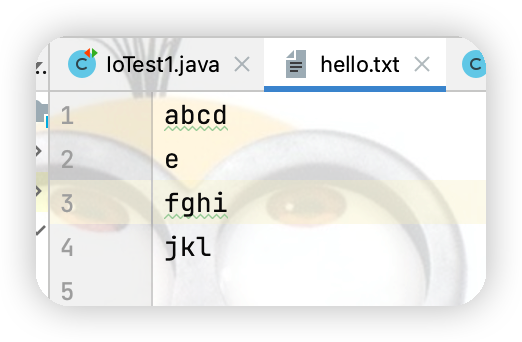
運行代碼在文件內容角標為3的位置插入xyz之後結果如下