一、Frame視窗 點擊查看代碼 package com.Tang.gui; import java.awt.*; public class TestFrame1 { public static void main(String[] args) { MyFrame myFrame1 = new My ...
一、Frame視窗
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
public class TestFrame1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
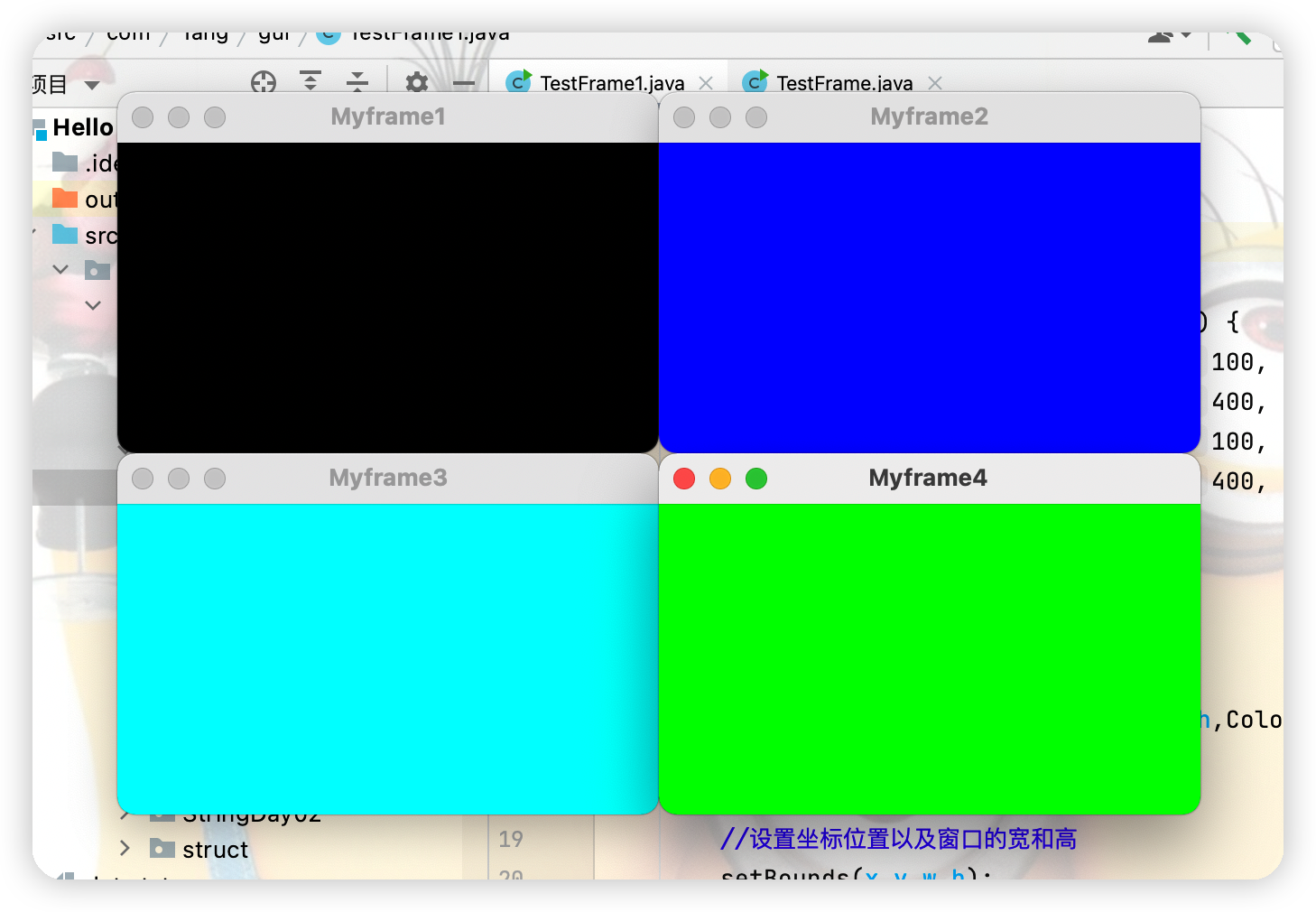
MyFrame myFrame1 = new MyFrame(100, 100, 300, 200, Color.black);
MyFrame myFrame2 = new MyFrame(400, 100, 300, 200, Color.blue);
MyFrame myFrame3 = new MyFrame(100, 300, 300, 200, Color.cyan);
MyFrame myFrame4 = new MyFrame(400, 300, 300, 200, Color.GREEN);
}
}
//將一個視窗的屬性封裝起來
class MyFrame extends Frame {
static int id =0;
public MyFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h,Color color){
//調用父類的有參構造
super("Myframe"+(++id));
//設置坐標位置以及視窗的寬和高
setBounds(x,y,w,h);
//設置視窗的背景顏色
setBackground(color);
////設置視窗可見性
setVisible(true);
}
}
二、Panel面板
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
//panel可以看成是一個空間,但是不能單獨存在
public class PanelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
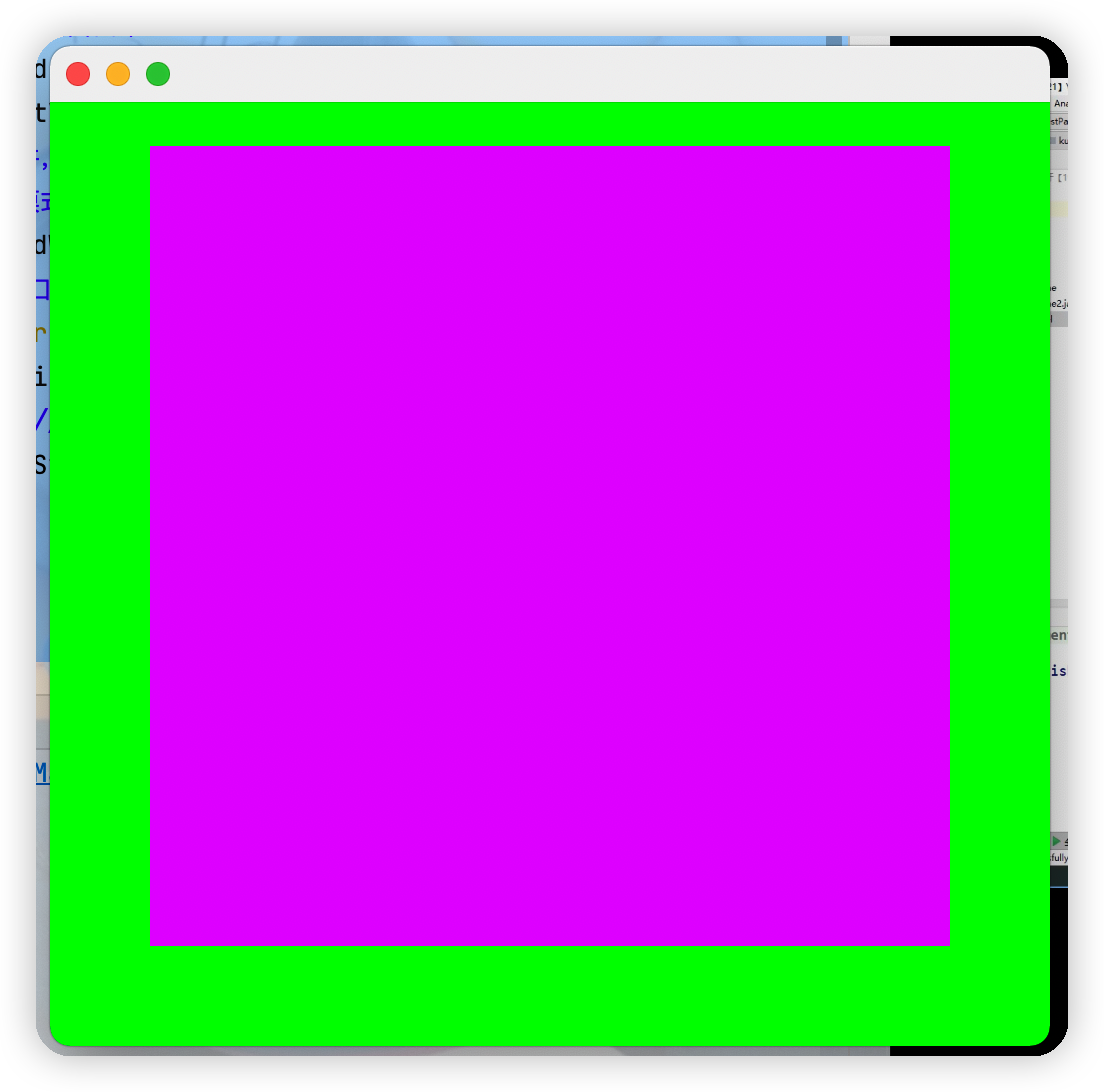
Frame frame = new Frame();
Panel panel = new Panel();
//設置佈局
frame.setLayout(null);
//坐標
frame.setBounds(300,300,500,500);
frame.setBackground(new Color(0, 255, 0));
//panel設置坐標,相對於frame而言
panel.setBounds(50,50,400,400);
panel.setBackground(new Color(211, 0, 255));
//將面板放入視窗中
frame.add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
//監聽事件,監聽視窗關閉事件,System.exit(0)
//適配器模式:利用WindowAdapter重寫自己需要的方法即可
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
//視窗點擊關閉的時候需要做的事情
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
//結束程式
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
三、佈局管理器
1.流式佈局
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class FlowLayoutTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
frame.setSize(200,200);
Button button1 = new Button("Button1");
Button button2 = new Button("Button2");
Button button3 = new Button("Button3");
//設置佈局,FlowLayout由源碼可知無參預設是居中模式
// frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
//在視窗里的按鈕統一靠左
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
frame.add(button1);
frame.add(button2);
frame.add(button3);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}

2.邊界佈局
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class BorderLayoutTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("Twq");
Button east = new Button("East");
Button west = new Button("West");
Button south = new Button("South");
Button north = new Button("North");
Button center = new Button("Center");
frame.add(east, BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(west,BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(south,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(north,BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(center,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setSize(200,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}

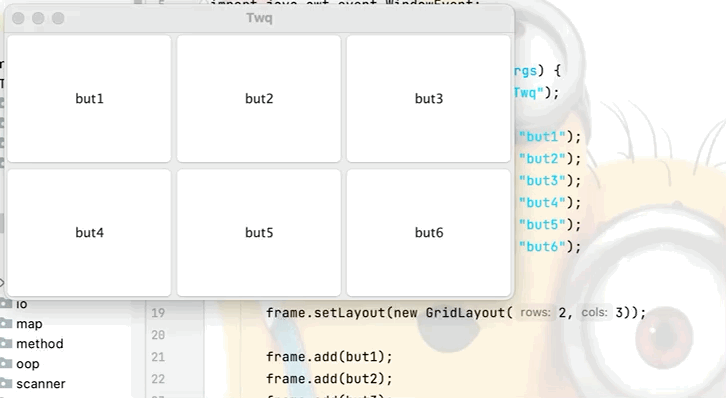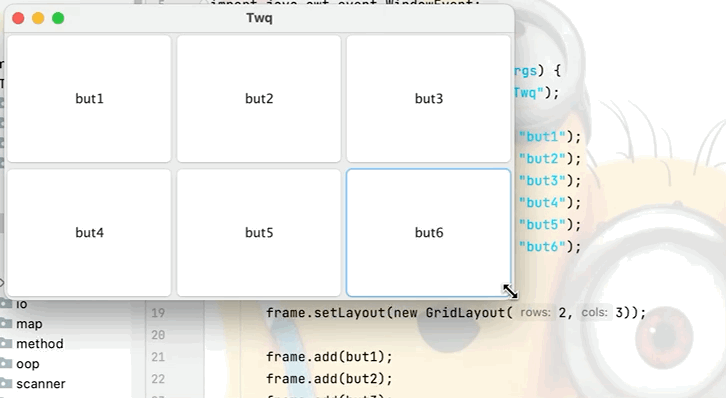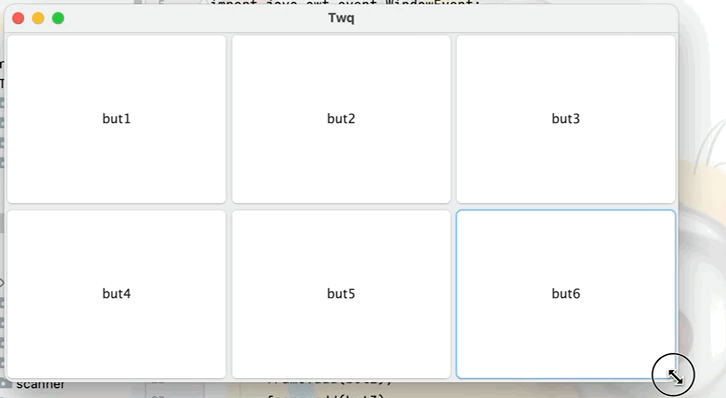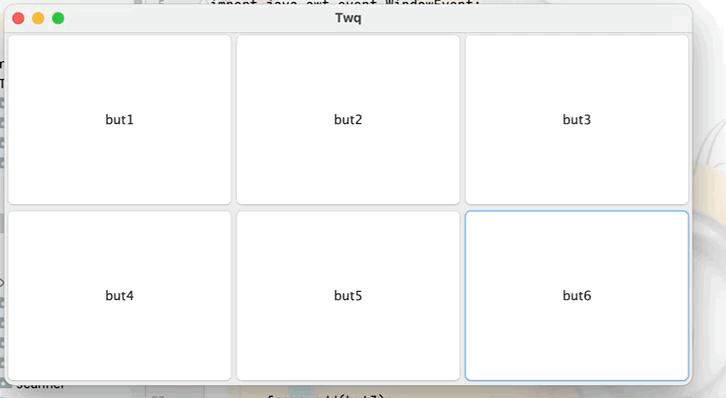
3.表格佈局
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class GridLayoutTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("Twq");
Button but1 = new Button("but1");
Button but2 = new Button("but2");
Button but3 = new Button("but3");
Button but4 = new Button("but4");
Button but5 = new Button("but5");
Button but6 = new Button("but6");
//設置表格佈局為兩行三列,還可在後面繼續加參數即上下的間隔
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,3));
frame.add(but1);
frame.add(but2);
frame.add(but3);
frame.add(but4);
frame.add(but5);
frame.add(but6);
//不用設置視窗的大小,視窗會根據所添加的東西自動分配空間大小
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
4.練習
實現下圖操作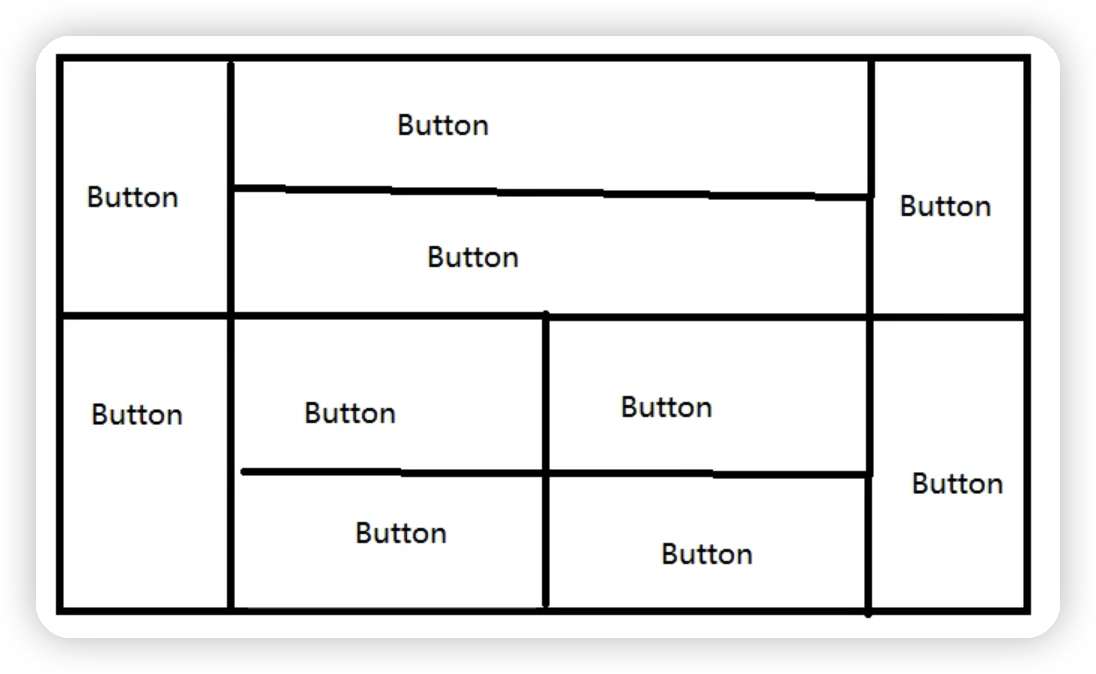
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class ExDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
Panel panel1 = new Panel();
Panel panel2 = new Panel();
//首先分為上下兩個結構,分別用面板來放置下麵的按鈕
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1));
frame.add(panel1);
frame.add(panel2);
//對於上半部分,使用borderLayout佈局,左右放button,中間放面板(以便在中間繼續放置按鈕)
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Panel panel3 = new Panel();
Button button4 = new Button("button4");
panel1.add(button1,BorderLayout.WEST);
panel1.add(panel3,BorderLayout.CENTER);
panel1.add(button4,BorderLayout.EAST);
//對於中間部分的panel3繼續採用表格佈局,上下方button
panel3.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1));
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
panel3.add(button2);
panel3.add(button3);
//然後對於下半部分,同理左右放置button,中間放置面板
Button button5 = new Button("button5");
Panel panel4 = new Panel();
Button button10 = new Button("button10");
panel2.add(button5,BorderLayout.WEST);
panel2.add(panel4,BorderLayout.CENTER);
panel2.add(button10,BorderLayout.EAST);
//對於中間部分的panel4繼續採用表格佈局2行2列
panel4.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,2));
Button button6 = new Button("button6");
Button button7 = new Button("button7");
Button button8 = new Button("button8");
Button button9 = new Button("button9");
panel4.add(button6);
panel4.add(button7);
panel4.add(button8);
panel4.add(button9);
frame.setSize(400,300);
frame.setLocation(300,400);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
運行結果如下圖

四、事件監聽
1.實現當點擊按鈕時控制台輸出aaa
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class ActionEventTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//按下按鈕,觸發一些事件
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button = new Button("Twq");
//因為addActionListener需要一個ActionListener,所以,我們需要構造一個ActionListener
//構造原則:是介面就實現其方法,是父類就繼承
MyActionListener myActionListener = new MyActionListener();
button.addActionListener(myActionListener);
frame.add(button);
frame.setSize(300,200);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class MyActionListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("aaa");
}
}
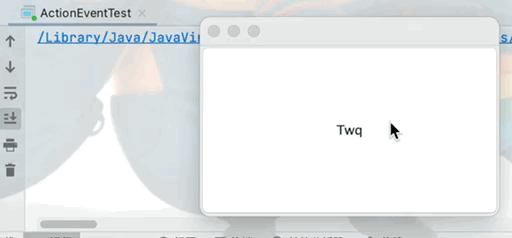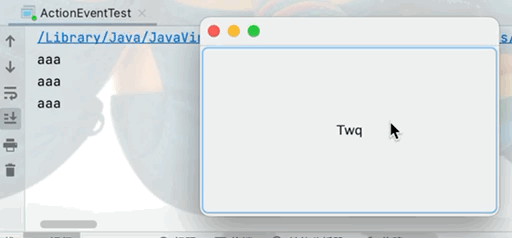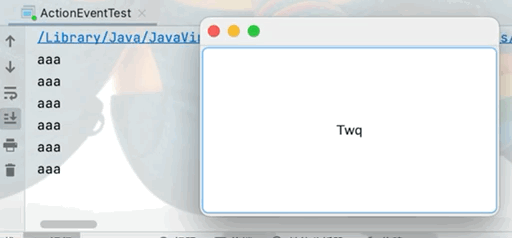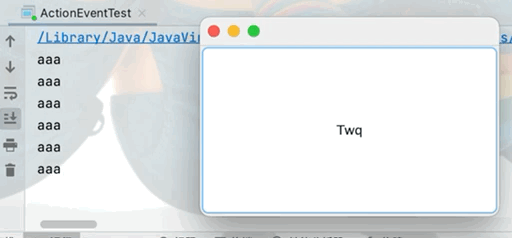
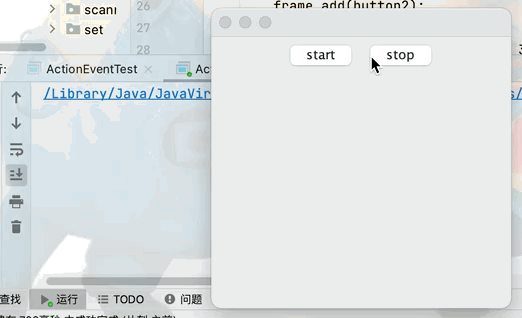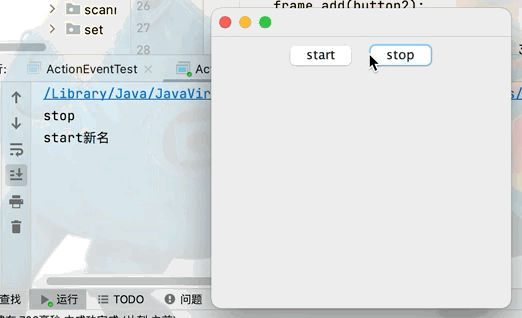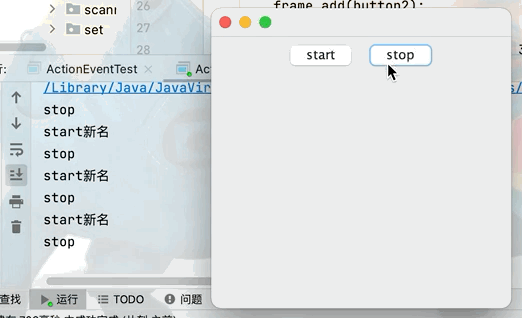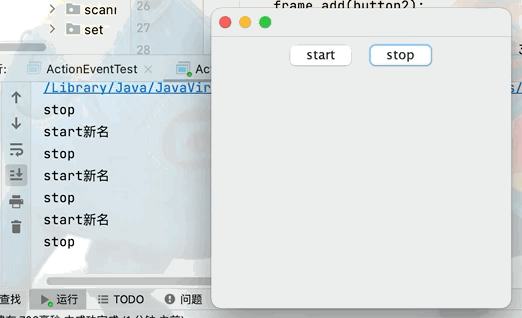
2.兩個按鈕實現同一個監聽
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class ActionMonitorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button1 = new Button("start");
Button button2 = new Button("stop");
//如果不顯示定義就會走預設的無參構造
button1.setActionCommand("start新名");
MyMonitr myMonitr = new MyMonitr();
button1.addActionListener(myMonitr);
button2.addActionListener(myMonitr);
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER));
frame.add(button1);
frame.add(button2);
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class MyMonitr implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//e.getActionCommand()獲取按鈕信息
System.out.println(e.getActionCommand());
}
}
4.輸入框事件的監聽
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class ActionEventTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyFrame1 myFrame1 = new MyFrame1();
//關閉事件
myFrame1.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class MyFrame1 extends Frame {
public MyFrame1(){
TextField textField = new TextField();
MyMoniter2 moniter2 = new MyMoniter2();
//每次通過回車觸發監視器
textField.addActionListener(moniter2);
// //在前臺實現輸入的內容為*,但是後臺獲取可以正常獲取輸入的數據
// textField.setEchoChar('*');
add(textField);
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
}
class MyMoniter2 implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Object source = e.getSource();
TextField tf = (TextField)source;
System.out.println(tf.getText());//獲取文本框的輸入的數據
tf.setText("");//每次回車之後將文本框內容清空
}
}
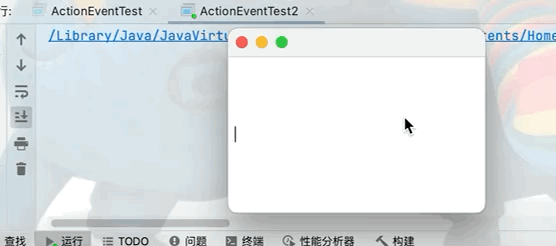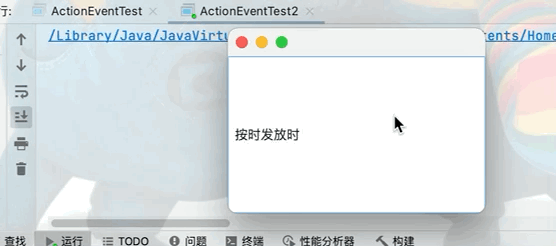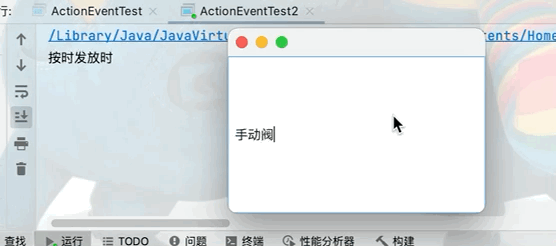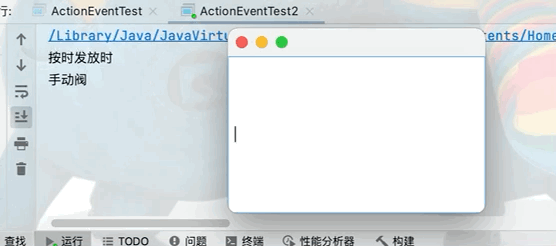
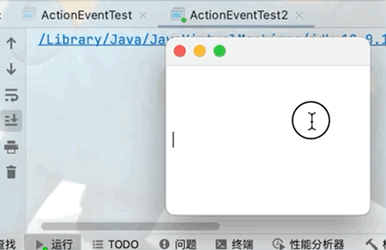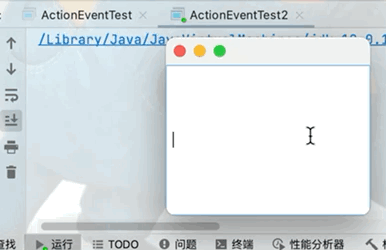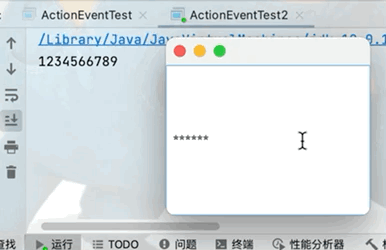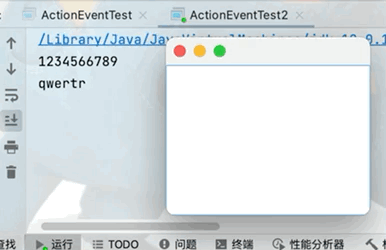
在前臺輸入框中不顯示輸入數據,但是在後臺可以正常獲取文本框中的數據
五、簡易計算器的實現
實現如下圖操作功能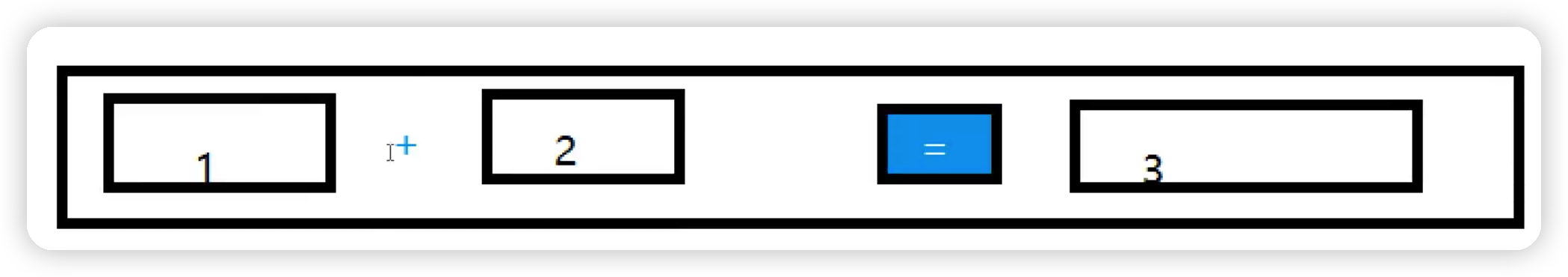
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class CalculateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame3();
}
}
class MyFrame3 extends Frame {
public MyFrame3(){
//3個文本框
TextField num1 = new TextField(10);
TextField num2 = new TextField(10);
TextField num3 = new TextField(20);
//1個按鈕
Button button = new Button("=");
//1個標簽
Label label = new Label("+");
MyMoniter3 m = new MyMoniter3(num1,num2,num3);
button.addActionListener(m);
pack();
add(num1);
add(label);
add(num2);
add(button);
add(num3);
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
setVisible(true);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class MyMoniter3 implements ActionListener{
//獲取三個文本框的值
private TextField num1,num2,num3;
public MyMoniter3(TextField num1,TextField num2,TextField num3) {
this.num1 = num1;
this.num2 = num2;
this.num3 = num3;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//1.獲得加數和被加數
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(num1.getText());
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(num2.getText());
//2.將兩個數相加之後的值放入第三個文本框
num3.setText(""+(i1+i2));
//3.清除前兩個框
num1.setText("");
num2.setText("");
}
}

代碼優化(轉換為面向對像)
點擊查看代碼
public class CalculateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Calculator().loadFrame();
}
}
class Calculator extends Frame {
//屬性
TextField num1,num2,num3;
//方法
public void loadFrame(){
//3個文本框
num1 = new TextField(10);
num2 = new TextField(10);
num3 = new TextField(20);
//1個按鈕
Button button = new Button("=");
//1個標簽
Label label = new Label("+");
MyMoniter3 m = new MyMoniter3(this);
button.addActionListener(m);
pack();
add(num1);
add(label);
add(num2);
add(button);
add(num3);
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
setVisible(true);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
class MyMoniter3 implements ActionListener{
//獲取計算器這個對象,在一個類中組合另一個類
Calculator calculator;
public MyMoniter3(Calculator calculator) {
this.calculator = calculator;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//1.獲得加數和被加數
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(calculator.num1.getText());
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(calculator.num2.getText());
//2.將兩個數相加之後的值放入第三個文本框
calculator.num3.setText(""+(i1+i2));
//3.清除前兩個輸入框
calculator.num1.setText("");
calculator.num2.setText("");
}
}
代碼進一步優化(將監聽器轉換為內部類)
點擊查看代碼
public class CalculateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Calculator().loadFrame();
}
}
class Calculator extends Frame {
//屬性
TextField num1,num2,num3;
//方法
public void loadFrame(){
//3個文本框
num1 = new TextField(10);
num2 = new TextField(10);
num3 = new TextField(20);
//1個按鈕
Button button = new Button("=");
//1個標簽
Label label = new Label("+");
MyMoniter3 m = new MyMoniter3();
button.addActionListener(m);
pack();
add(num1);
add(label);
add(num2);
add(button);
add(num3);
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
setVisible(true);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
//監聽器類,內部類最大的好處就是可以暢通無阻的訪問外部內的屬性和方法
class MyMoniter3 implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//1.獲得加數和被加數
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(num1.getText());
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(num2.getText());
//2.將兩個數相加之後的值放入第三個文本框
num3.setText(""+(i1+i2));
//3.清除前兩個框
num1.setText("");
num2.setText("");
}
}
}
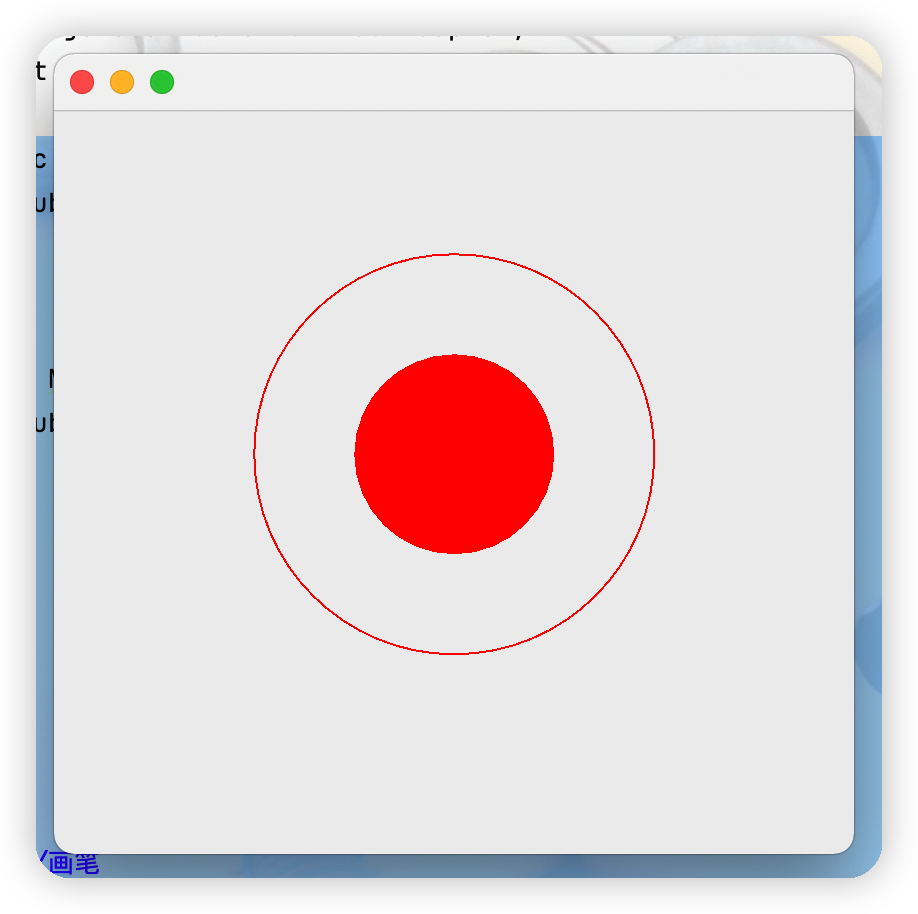
六、畫筆
1.畫筆的簡單使用
點擊查看代碼
public class PaintTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Mypaint().loadFrame();
}
}
class Mypaint extends Frame {
public void loadFrame(){
setVisible(true);
setBounds(200,200,400,400);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
//重寫畫筆方法
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
//設置畫筆顏色
g.setColor(Color.red);
//畫一個空心圓
g.drawOval(100,100,200,200);
//畫一個實心圓
g.fillOval(150,150,100,100);
//養成喜歡:畫筆用完,將它還原為最初的顏色
}
}
2.滑鼠監聽
目的:想要實現滑鼠畫畫點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class MouseistenerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame4("畫圖");
}
}
class MyFrame4 extends Frame {
//畫畫需要畫筆,需要監聽滑鼠當前的位置
//用集合數組存儲滑鼠當前點擊的位置
ArrayList points;
public MyFrame4(String title){
super(title);
setBounds(100,100,300,300);
points = new ArrayList();
//針對視窗的滑鼠的監聽器
addMouseListener(new MouseListenered());
setVisible(true);
setSize(300,300);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
//畫畫,監聽滑鼠的事件
Iterator iterator = points.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
//將當前獲取到的數組中的點轉換為一個點類
Point point = (Point)iterator.next();
//設置滑鼠點擊點的顏色
g.setColor(Color.CYAN);
//讓當前畫筆獲得滑鼠點擊的位置
g.fillOval(point.x,point.y,10,10);
}
}
//將獲取到的滑鼠的點存儲到數組裡
public void addPaint(Point point){
points.add(point);
}
//若採用實現MouseListener介面的話,就必須要重寫其介面內的所有方法
//所以可以採用適配器模式去重寫自己需要的方法,
class MouseListenered extends MouseAdapter {
//滑鼠有按下,彈起,按住不放
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
//在視窗上獲取當前滑鼠的位置
MyFrame4 frame =(MyFrame4) e.getSource();
frame.addPaint(new Point(e.getX(),e.getY()));
//每次點擊滑鼠都需要重新畫一遍
frame.repaint();//刷新
}
}
}
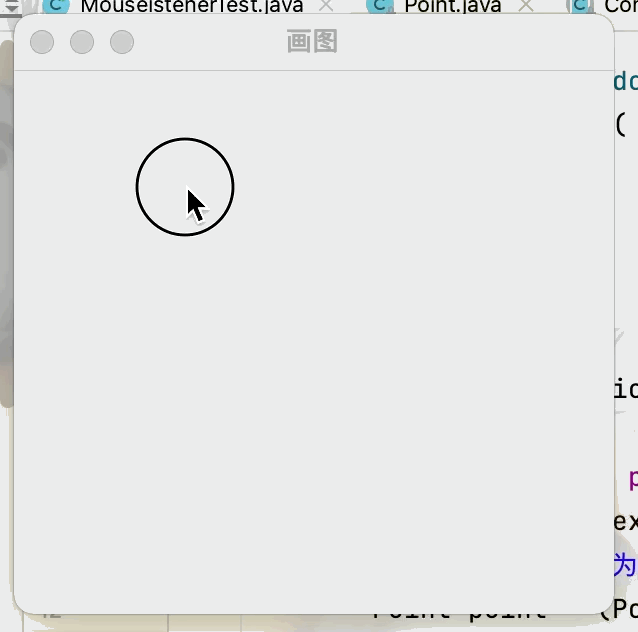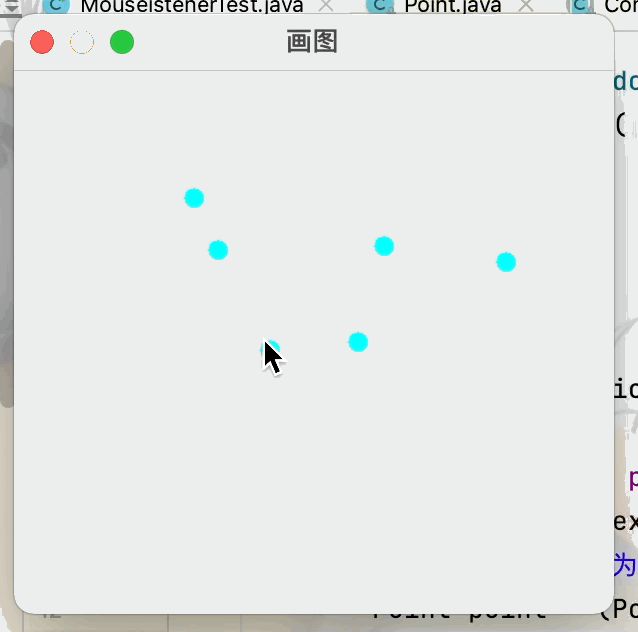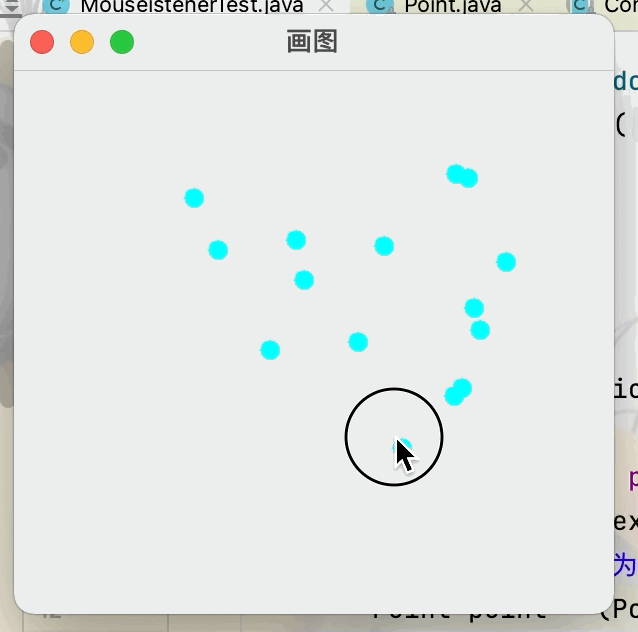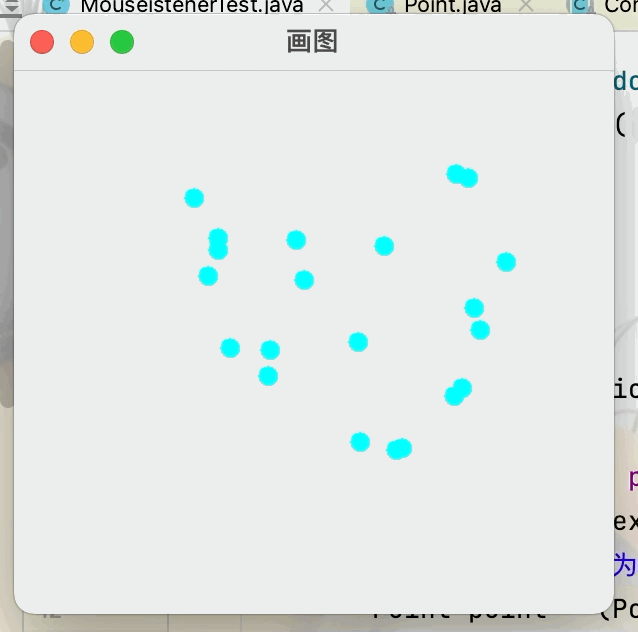
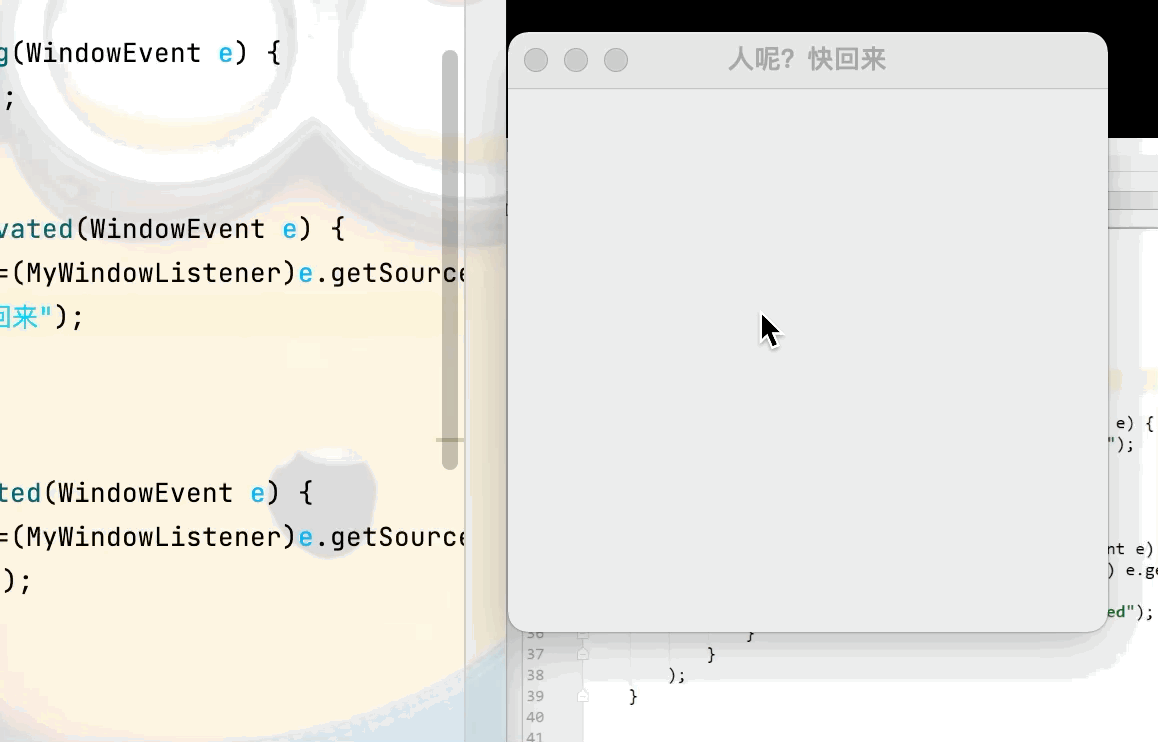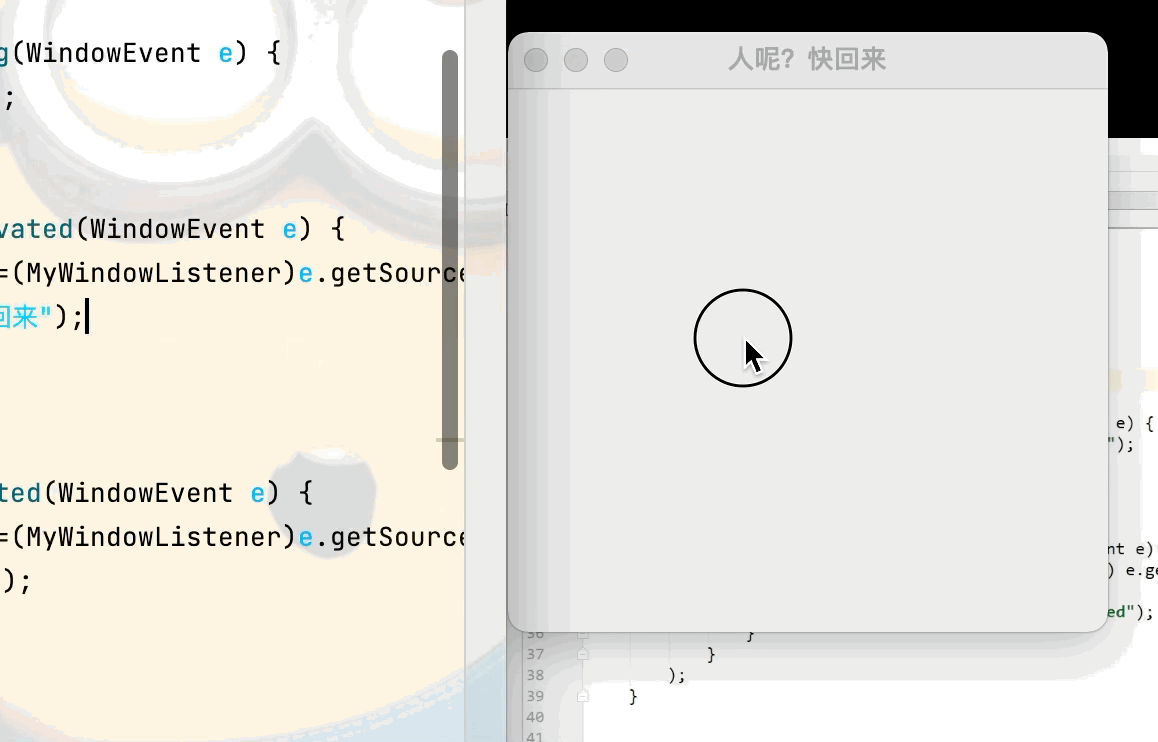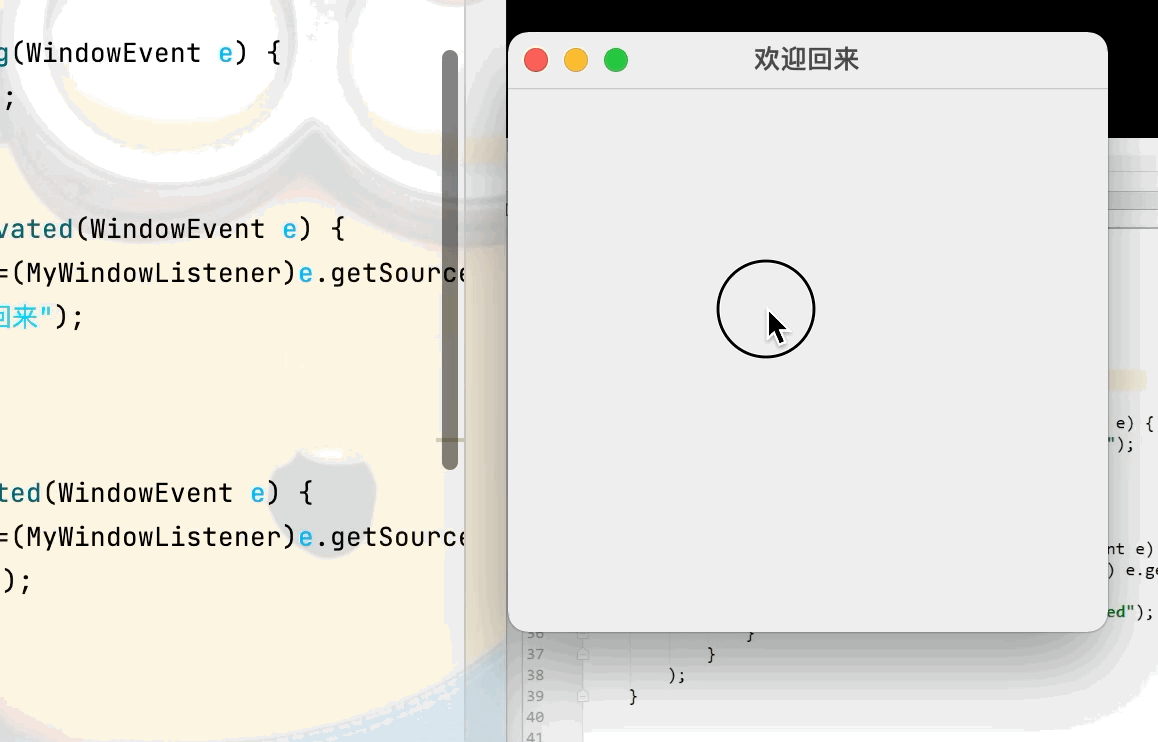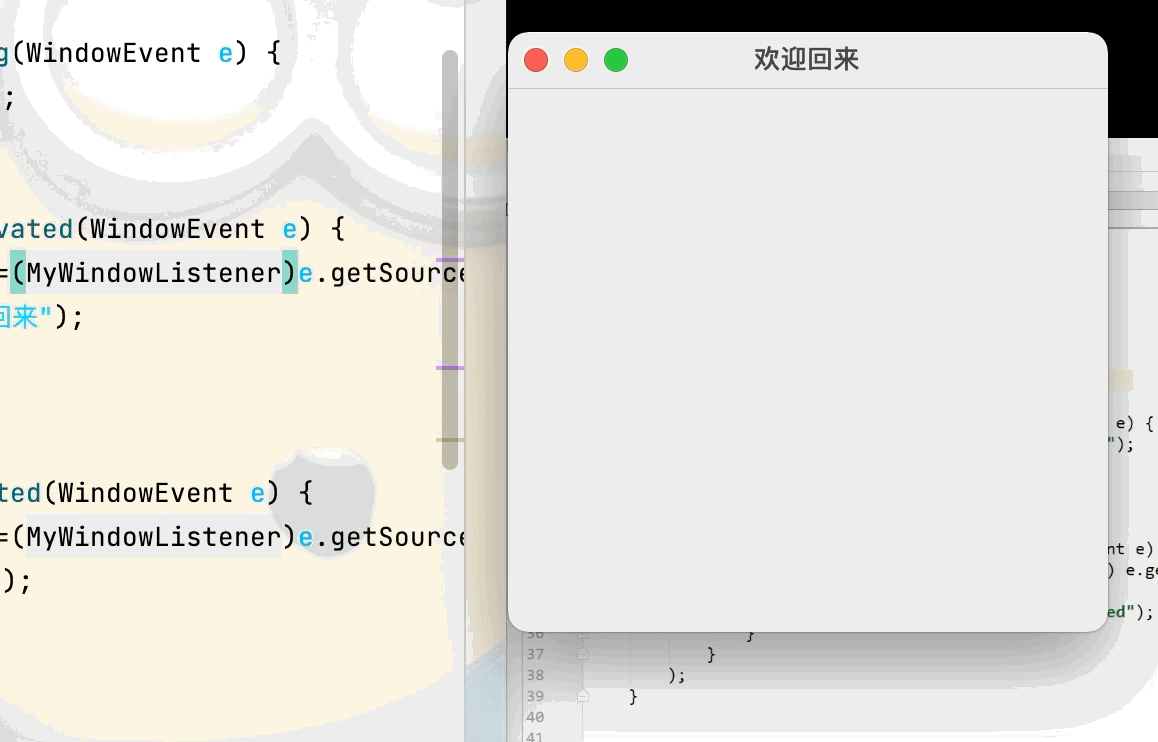
3.視窗監聽
目的:實現當 離開當前視窗後 視窗標題設置為“人呢?快回來”,回到當前視窗則視窗標題設置為“歡迎回來”點擊查看代碼
public class WindowListennerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyWindowListener();
}
}
class MyWindowListener extends Frame{
public MyWindowListener(){
setBounds(100,100,300,300);
setVisible(true);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
@Override
public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) {
MyWindowListener mw =(MyWindowListener)e.getSource();
mw.setTitle("人呢?快回來");
}
@Override
public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) {
MyWindowListener mw =(MyWindowListener)e.getSource();
mw.setTitle("歡迎回來");
}
});
}
}
4.鍵盤監聽
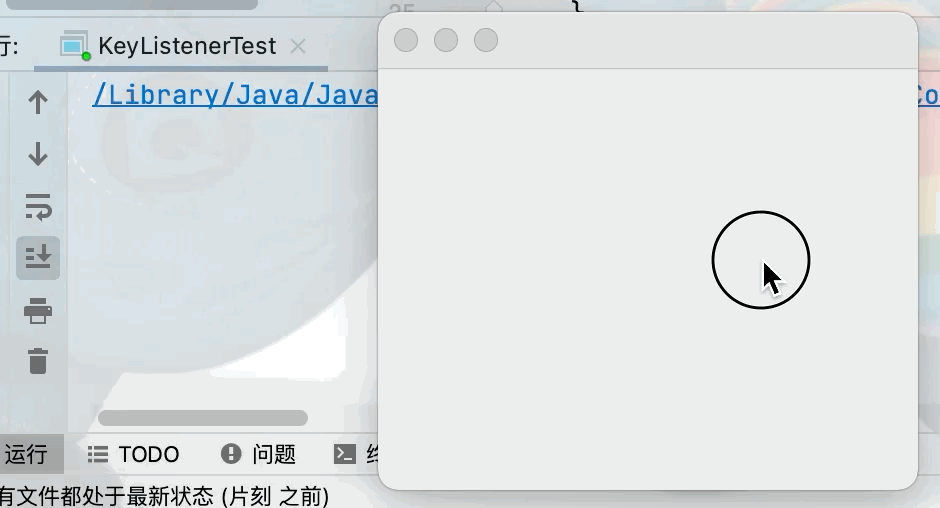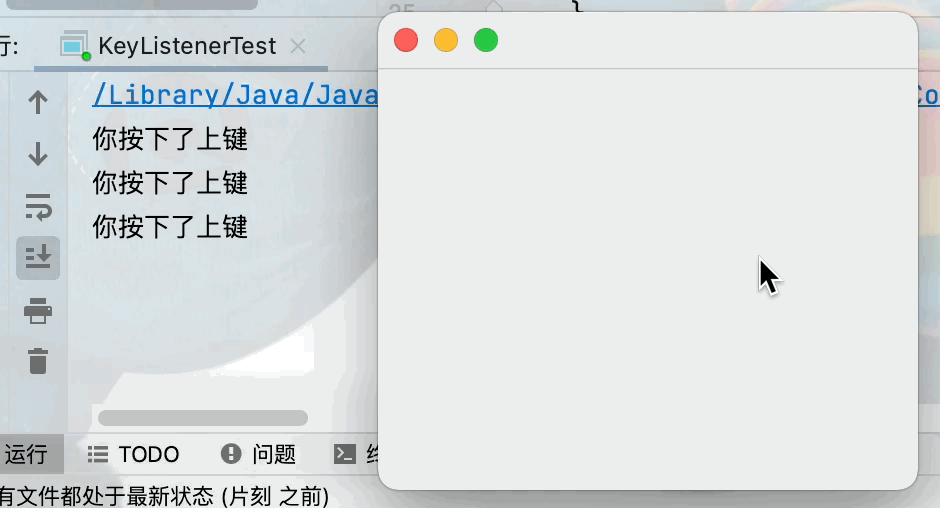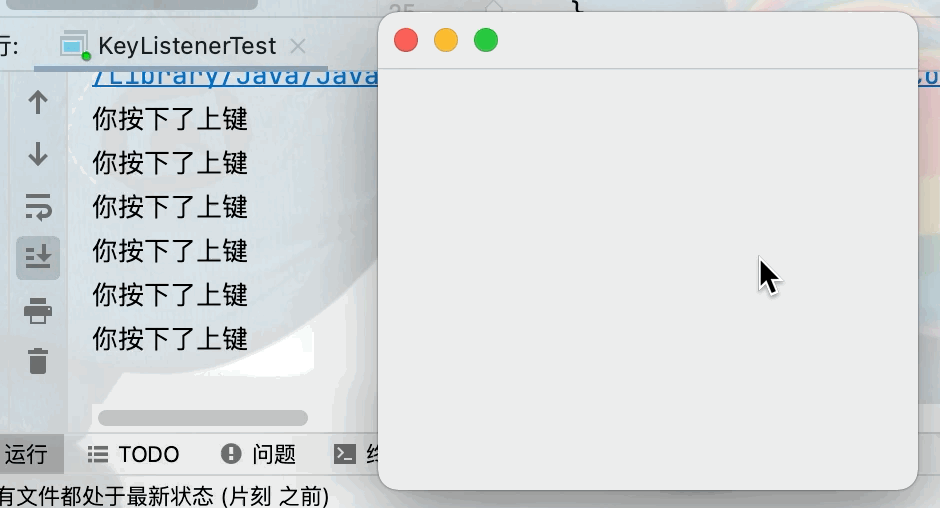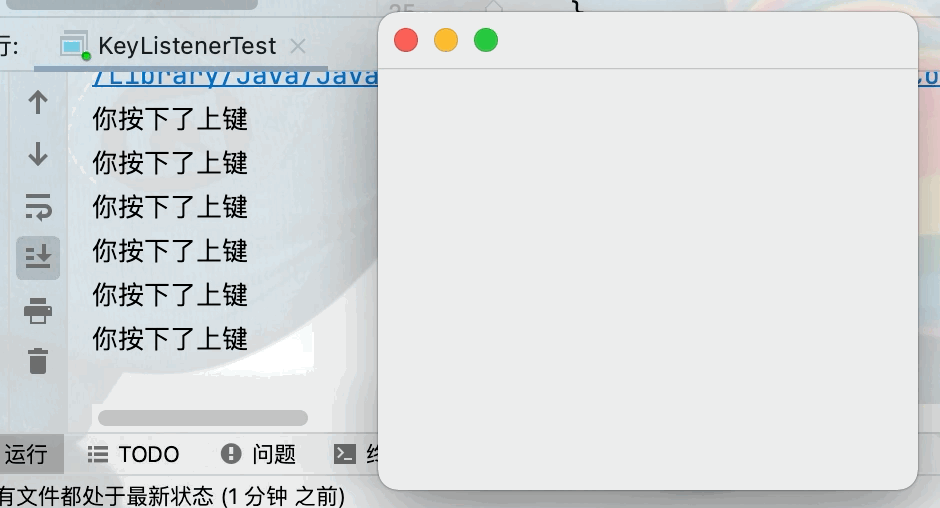
目的:實現當在視窗中按下鍵盤的上鍵,則輸出你按下了上鍵點擊查看代碼
public class KeyListenerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new KeyFrame();
}
}
class KeyFrame extends Frame {
public KeyFrame(){
setVisible(true);
setSize(300,300);
addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
int keyCode = e.getKeyCode();
if(keyCode == KeyEvent.VK_UP){
System.out.println("你按下了上鍵");
}
}
});
}
}
七、GUI-Swing窗體
1.JFrame窗體
看其源碼可知JFrame和Frame 還是有很大聯繫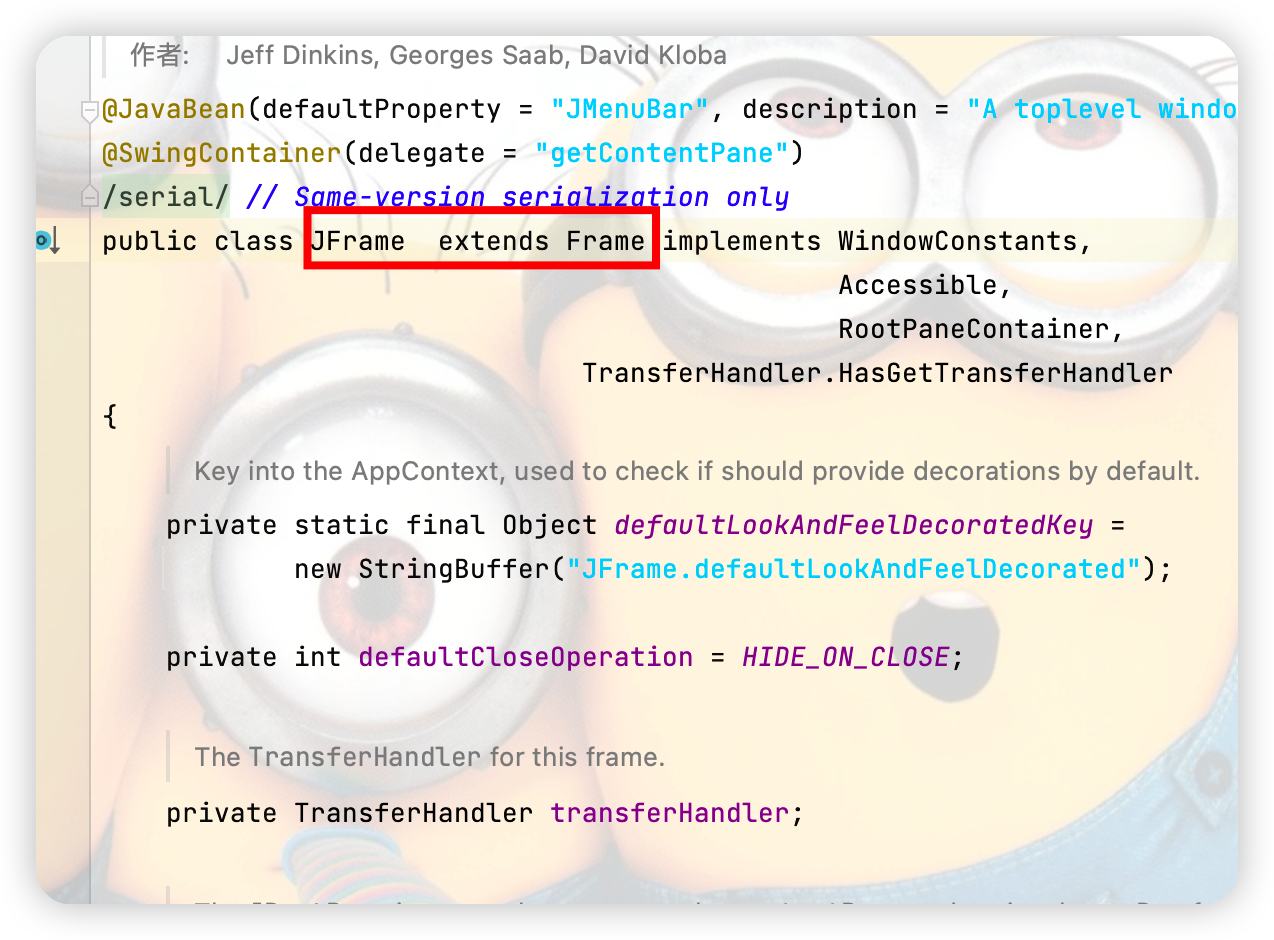
點擊查看代碼
public class JFrameTest {
//init()用於視窗的初始化操作
public void init(){
//頂級視窗
JFrame jf = new JFrame("這是一個JFrame視窗");
JLabel label = new JLabel("歡迎進入Twq的博客,歡迎點贊加關註");
jf.add(label);
//讓標簽居中顯示
label.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
//由於JFrame設計到容器的概念,所有東西要放在容器里去實現
//jf.setBackground(Color.gray);這樣寫並不能實現背景的設置
jf.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.cyan);
//視窗關閉
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
jf.setBounds(100,100,300,300);
jf.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JFrameTest().init();
}
}

2.彈窗
點擊查看代碼
//主視窗
public class DialogTest extends JFrame{
public DialogTest() {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
JButton button = new JButton("點擊出現彈窗");
button.setSize(200,50);
add(button);
//添加按鈕監聽事件
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
new MyDialog();//當按鈕被點擊後新建一個視窗
}
});
setLayout(null);
setBounds(80,80,300,300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new DialogTest();
}
}
//彈窗視窗
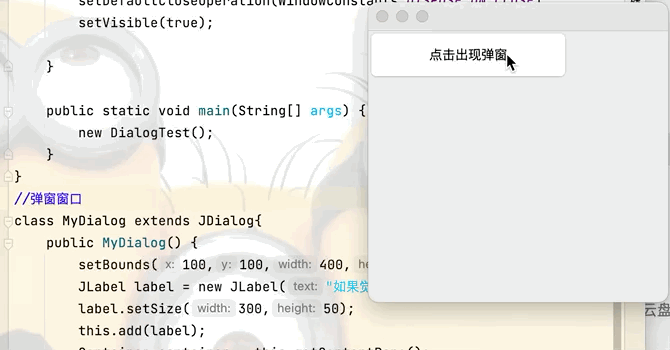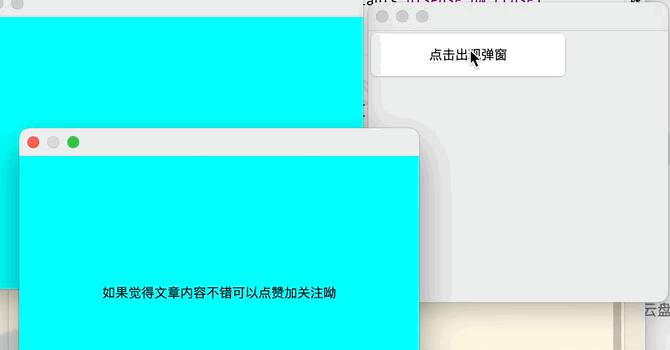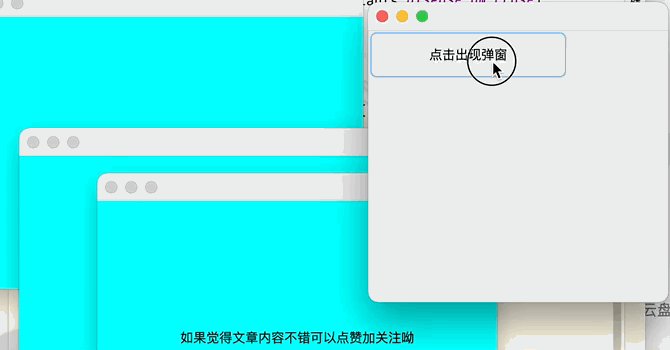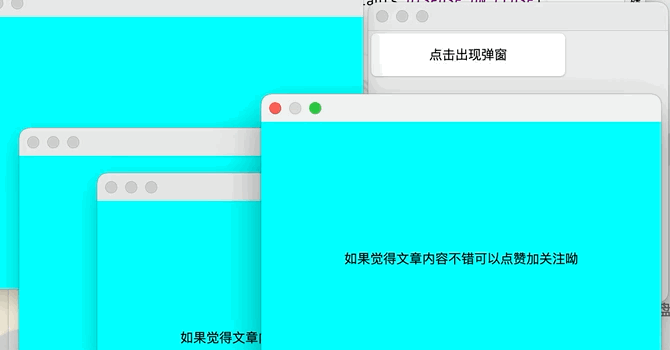
class MyDialog extends JDialog{
public MyDialog() {
setBounds(100,100,400,300);
JLabel label = new JLabel("如果覺得文章內容不錯可以點贊加關註呦");
label.setSize(300,50);
this.add(label);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
label.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
container.setBackground(Color.CYAN);
//彈窗預設就可以進行關閉操作,不需要在進行關閉操作
//setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
}
}
3.標簽之Icon
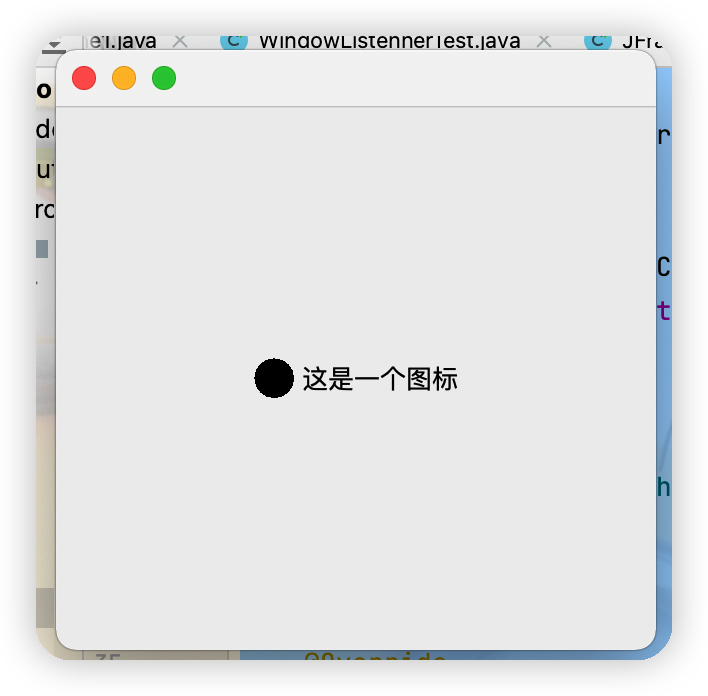
(1)圖標Icon點擊查看代碼
public class IconTest extends JFrame implements Icon {
private int width,height;
public IconTest() {
}
public IconTest(int width,int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public void init(){
IconTest iconTest = new IconTest(20,20);
//圖標放在標簽上,也可以放在按鈕上
JLabel label = new JLabel("這是一個圖標",iconTest,SwingConstants.CENTER);
Container container = getContentPane();
container.add(label);
setBounds(100,100,300,300);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) {
g.fillOval(x,y,width,height);
}
@Override
public int getIconWidth() {
return this.width;
}
@Override
public int getIconHeight() {
return this.height;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new IconTest().init();
}
}
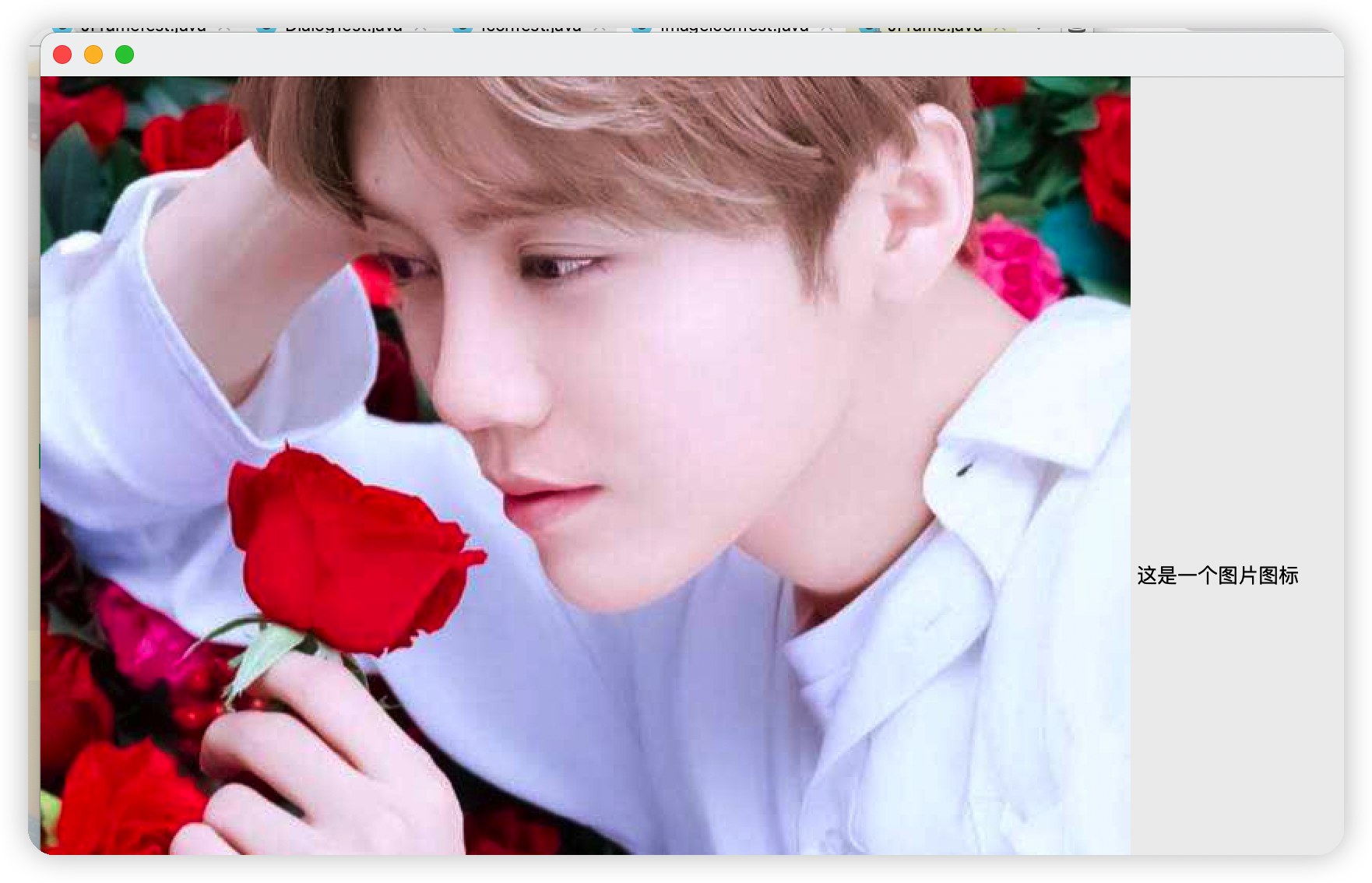
(2)圖片Icon
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui.swing;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.net.URL;
public class ImageIconTest extends JFrame {
public ImageIconTest(){
//獲取圖片地址
URL url = ImageIconTest.class.getResource("tx的副本.jpg");
JLabel label = new JLabel("這是一個圖片圖標");
//圖片圖標獲取圖片的路徑
ImageIcon imageIcon = new ImageIcon(url);
//將圖片放入標簽中
label.setIcon(imageIcon);
Container container = getContentPane();
container.add(label);
setBounds(100,100,300,200);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ImageIconTest();
}
}
4.面板
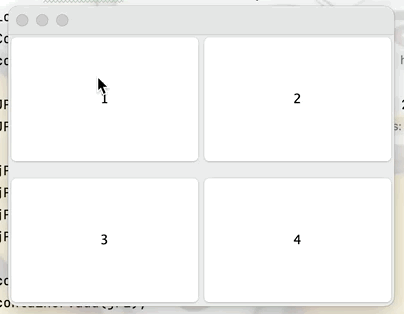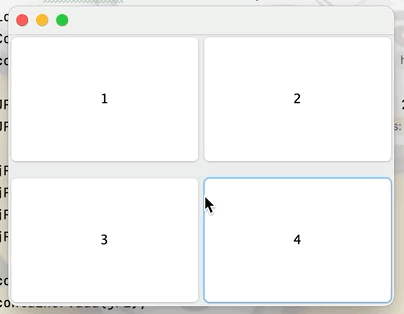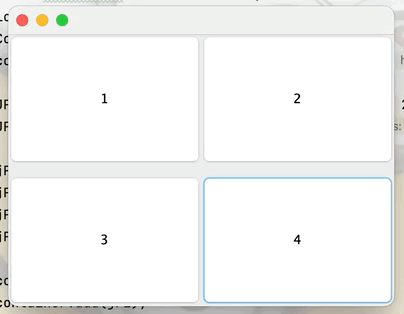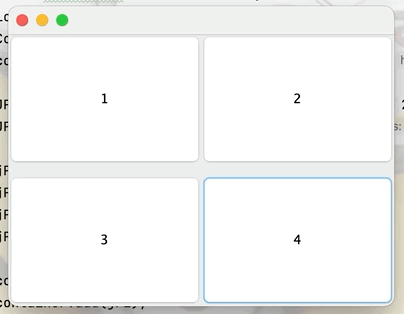
(1)普通面板
點擊查看代碼
package com.Tang.gui.swing;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JPanneltest extends JFrame {
public JPanneltest(){
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1,10,10));
JPanel jP = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,2));
JPanel jP1 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,2));
jP.add(new JButton("1"));
jP.add(new JButton("2"));
jP1.add(new JButton("3"));
jP1.add(new JButton("4"));
container.add(jP);
container.add(jP1);
this.setBounds(200,200,300,300);
this.setVisible(true);
//設置關閉視窗操作
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JPanneltest();
}
}
(2)JScroll(滾輪)面板
點擊查看代碼
public class ScrollPanelTest extends JFrame {
public ScrollPanelTest() {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
//文本域:在文本框中輸入的時候可以進行換行操作
JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea();
//設置滾動面板,並將文本域放到面板中
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea);
//將滾動面板添加到視窗中
container.add(scrollPane);
//設置視窗的初始狀態
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(200,200,300,300);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ScrollPanelTest();
}
}

5.按鈕
(1)圖片按鈕
目的:實現將一張圖片變成圖標,並放在按鈕上,並且當滑鼠放在按鈕上停留時顯示文字點擊查看代碼
public class ButtonImageTest extends JFrame {
public ButtonImageTest() {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
URL url = ButtonImageTest.class.getResource("tx的副本.jpg");
Icon icon = new ImageIcon(url);
JButton button = new JButton();
//將圖片放入按鈕中
button.setIcon(icon);
//當滑鼠在按鈕上停留的時候就會顯示下方設置的文字
button.setToolTipText("圖片按鈕");
container.add(button);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100,100,200,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ButtonImageTest();
}
}
(2)單選框按鈕
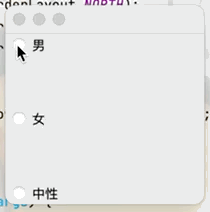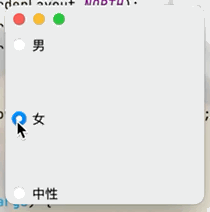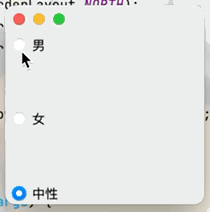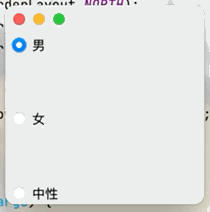
目的:實現單選框只能選擇一個選項的功能點擊查看代碼
public class JButtonTest02 extends JFrame {
public JButtonTest02() {
Container container = getContentPane();
JRadioButton radioButton1 = new JRadioButton("男");
JRadioButton radioButton2 = new JRadioButton("女");
JRadioButton radioButton3 = new JRadioButton("中性");
//由於單選框只能選擇一個,將三個按鈕放入一個組中就可以實現只選一個
ButtonGroup group = new ButtonGroup();
//將三個按鈕放入一個組中
group.add(radioButton1);
group.add(radioButton2);
group.add(radioButton3);
container.add(radioButton1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
container.add(radioButton2,BorderLayout.CENTER);
container.add(radioButton3,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100,100,200,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonTest02();
}
}
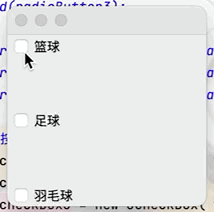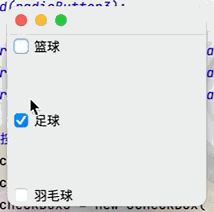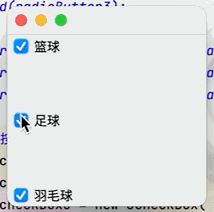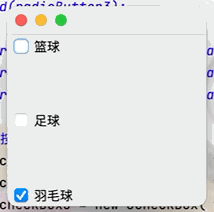
(3)覆選框按鈕
目的:實現多項選擇的功能點擊查看代碼
public class JButtonTest02 extends JFrame {
public JButtonTest02() {
Container container = getContentPane();
JRadioButton radioButton1 = new JRadioButton("男");
JRadioButton radioButton2 = new JRadioButton("女");
JRadioButton radioButton3 = new JRadioButton("中性");
//實現覆選框按鈕
JCheckBox checkBox1 = new JCheckBox("籃球");
JCheckBox checkBox2 = new JCheckBox("足球");
JCheckBox checkBox3 = new JCheckBox("羽毛球");
container.add(checkBox1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
container.add(checkBox2,BorderLayout.CENTER);
container.add(checkBox3,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100,100,200,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonTest02();
}
}
(4)下拉框選項
點擊查看代碼
public class JButtonTest02 extends JFrame {
public JButtonTest02() {
Container container = getContentPane();
//創建一個下拉框
JComboBox statue = new JComboBox();
//提供下拉選項
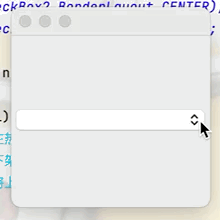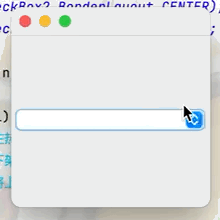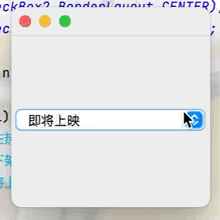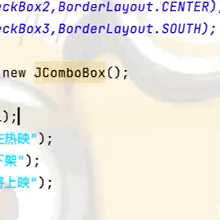
statue.addItem(null);
statue.addItem("正在熱映");
statue.addItem("已下架");
statue.addItem("即將上映");
container.add(statue);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100,100,200,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonTest02();
}
}
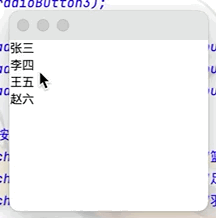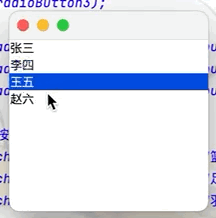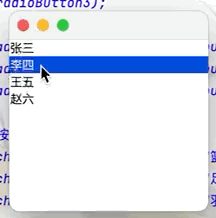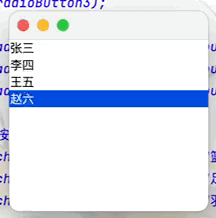
(5)列表框(如QQ好友列表)
點擊查看代碼
public class JButtonTest02 extends JFrame {
public JButtonTest02() {
Container container = getContentPane();
//實現列表框
Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.add("張三");
vector.add("李四");
vector.add("王五");
vector.add("趙六");
//將vector集合中的內容放入列表框中
JList jList = new JList(vector);
container.add(jList);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100,100,200,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonTest02();
}
}