一、流的概念 流:數據在數據源(文件)和程式(記憶體)之間經歷的路徑。 輸入流:數據從數據源(文件)到程式(記憶體)的路徑。 輸出流:數據從程式(記憶體)到數據源(文件)的路徑。 以記憶體為參照,如果數據向記憶體流動,則是輸入流,反之則是輸出流 位元組流:FileInputStream用來讀取文件 FileOu ...
一、流的概念
流:數據在數據源(文件)和程式(記憶體)之間經歷的路徑。
輸入流:數據從數據源(文件)到程式(記憶體)的路徑。
輸出流:數據從程式(記憶體)到數據源(文件)的路徑。
以記憶體為參照,如果數據向記憶體流動,則是輸入流,反之則是輸出流
位元組流:FileInputStream用來讀取文件
FileOutputStream用來寫入到文件
字元流:FileReader\BufferedReader用來讀取文件
FileWrite\BufferedWrite用來寫入到文件
二、操作用法
1.獲取文件對象,針對該對象進行一些基本操作

1 //創建一個文件對象 2 File f = new File("F:\\test\\sheet.xls"); 3 //得到文件的路徑 4 System.out.println("文件路徑"+f.getAbsolutePath()); 5 //得到文件的大小,位元組數 6 System.out.println("文件大小"+f.length()); 7 //可讀屬性 8 System.out.println("可讀"+f.canRead());View Code
2.創建文件(判斷該文件是否存在,若存在則彈出提示,若不存在則進行創建)

1 //創建文件 2 File f = new File("F:\\test\\test.txt"); 3 //判斷該文件是否存在 4 if(!f.exists()) 5 { 6 //可以創建 7 try { 8 f.createNewFile(); 9 } catch (IOException e) { 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 } 13 else 14 { 15 System.out.println("改文件已存在,創建失敗!"); 16 }View Code
3.創建文件夾(條件同上)

1 //創建文件夾 2 File f = new File("F:\\test"); 3 if (f.isDirectory())//判斷是不是一個文件夾 4 { 5 System.out.println("創建失敗"); 6 } else { 7 f.mkdir(); 8 }View Code
Tips:這裡寫明一下isFile()、exists()和isDirectory()的區別
isFile():判斷是否文件,也許可能是文件或者目錄。
exists():判斷是否存在,可能不存在。
isDirectory(): 判斷該對象是否是一個文件夾。
4.列出某文件夾下麵的所有文件(此時對象還是File,File沒有文件和文件夾之分,對電腦來講,文件夾只是一種特殊的文件)

1 File f = new File("F:\\testt"); 2 if (f.isDirectory()) { 3 File filelists[] = f.listFiles(); 4 for (int i = 0; i < filelists.length; i++) 5 { 6 System.out.println("文件名是:"+filelists[i].getName()); 7 } 8 }View Code
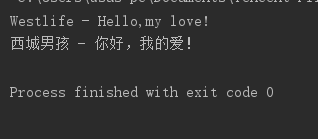
5.FileInputStream的使用

1 /** 2 * 演示FileInputStream類的使用 3 */ 4 package com.test2; 5 6 import java.io.*; 7 8 public class Demo11_2 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 11 //得到一個文件對象 12 File f = new File("F:\\tt\\test.txt"); 13 FileInputStream fis = null; 14 //因為file沒用讀寫的能力,所以需要使用FileInputStream 15 try { 16 fis = new FileInputStream(f); 17 18 //定義一個位元組數組(相當於一個緩存,如果你的對象"f"是一個很大的文件,記憶體不夠用,所以只能一點一點地讀取) 19 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; 20 //實際讀取到的位元組數 21 int n = 0; 22 //迴圈讀取 23 //如果read()返回-1,則說明讀取完畢 24 while ((n = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) { 25 //將位元組轉換成string 26 //此時實例化s時,要註意指定編碼格式,電腦上文檔預設的是GBK,而我這邊預設的是utf-8, 27 //所以如果不指定格式的話,最後輸出的中文會出現亂碼 28 String s = new String(bytes, 0, n,"GBK"); 29 System.out.println(s); 30 } 31 } catch (Exception e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } finally { 34 //關閉文件流(關鍵) 35 try { 36 if (fis != null) { 37 fis.close(); 38 } 39 } catch (IOException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 }View Code
讀取成功..
6.FileOutputStream的使用

1 /** 2 * 演示FileOutputStream的使用 3 */ 4 package com.test2; 5 6 import java.io.*; 7 8 public class Demo11_3 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 File f = new File("F:\\tt\\test.txt"); 11 //位元組輸出流 12 FileOutputStream fos = null; 13 14 try { 15 fos = new FileOutputStream(f); 16 17 String s = "Westlife - Better man\r\n西城男孩 - 更完美的人"; 18 19 fos.write(s.getBytes()); 20 } catch (Exception e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } finally { 23 try { 24 if (fos != null) { 25 fos.close(); 26 } 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 } 31 32 } 33 }View Code
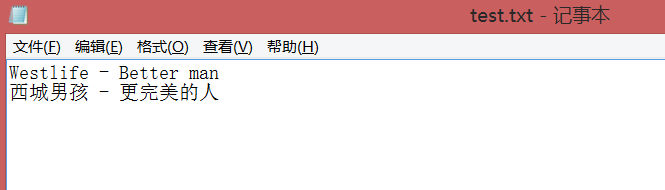
寫入成功..
7.位元組流的操作(通過寫入寫出來實現圖片的拷貝,操作byte)

1 /** 2 * 圖片拷貝 3 */ 4 package com.test2; 5 6 import java.io.*; 7 8 public class Demo11_4 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 //先把圖片讀入到記憶體,再寫到某個文件 11 //因為是二進位文件,因此只能用位元組流完成 12 File f = new File("F:\\tt\\Westlife.jpg"); 13 //輸入流 14 FileInputStream fis = null; 15 //輸出流 16 FileOutputStream fos = null; 17 18 try { 19 fis = new FileInputStream(f); 20 //或者省略上面實例化File,直接在這裡fis = new FileInputStream("F:\tt\Westlife.jpg");也可以 21 22 fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\練習\\Westlife.jpg"); 23 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; 24 int n = 0;//記錄實際讀取到的位元組數 25 //迴圈讀取 26 while ((n = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) { 27 //輸出到指定文件 28 fos.write(bytes); 29 } 30 } catch (Exception e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } finally { 33 //關閉打開的文件流 34 if (fos != null) { 35 try { 36 fos.close(); 37 } catch (IOException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 } 41 42 if (fis != null) { 43 try { 44 fis.close(); 45 } catch (IOException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 }View Code
8.字元流的操作(操作char)

1 /** 2 * 字元流操作 3 */ 4 package com.test2; 5 6 import java.io.*; 7 8 public class Demo11_5 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 //文件取出字元流對象(輸入流) 11 FileReader fr = null; 12 //寫入到文件(輸出流) 13 FileWriter fw = null; 14 15 //創建一個fr對象 16 try { 17 //創建輸入對象 18 fr = new FileReader("F:\\tt\\test.txt"); 19 //創建輸出對象 20 fw = new FileWriter("D:\\練習\\test2.txt"); 21 22 23 //讀入到記憶體 24 int n = 0;//記錄實際讀取到的字元數 25 char c[] = new char[1024]; 26 while ((n = fr.read(c)) != -1) { 27 //輸入 28 // String s = new String(c,0,n); 29 // System.out.println(s); 30 //輸出 31 //方法一:fw.write(c); 32 方法二://指定輸出的起始位置 33 fw.write(c, 0, n); 34 } 35 } catch (Exception e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } finally { 38 //關閉文件流 39 if (fr != null) { 40 try { 41 fr.close(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 } 46 47 if (fw != null) { 48 try { 49 fw.close(); 50 } catch (IOException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 } 57 }View Code
9.緩衝字元流(提高了效率,直接操作String)

1 /** 2 * 緩衝字元流操作 3 */ 4 package com.test2; 5 6 import java.io.*; 7 8 public class Demo11_6 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 BufferedReader br = null; 11 BufferedWriter bw = null; 12 13 //先創建FileReader對象 14 FileReader fr = null; 15 16 //創建FileWriter對象 17 FileWriter fw = null; 18 try { 19 fr = new FileReader("F:\\tt\\test.txt"); 20 br = new BufferedReader(fr); 21 22 23 fw = new FileWriter("D:\\練習\\test3.txt"); 24 bw = new BufferedWriter(fw); 25 26 //迴圈讀取文件 27 String s = ""; 28 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 29 //讀取到記憶體 30 //System.out.println(s); 31 32 //輸出到磁碟 33 bw.write(s+"\r\n"); 34 } 35 } catch (Exception e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } finally { 38 //註:如果文件流不關閉的話會影響後續對該文件的操作,比如可能讀不到該文件的數據 39 if (br != null) { 40 try { 41 { 42 br.close(); 43 } 44 } catch (IOException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 } 48 49 if (bw != null) { 50 try { 51 { 52 bw.close(); 53 } 54 } catch (IOException e) { 55 e.printStackTrace(); 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 }View Code