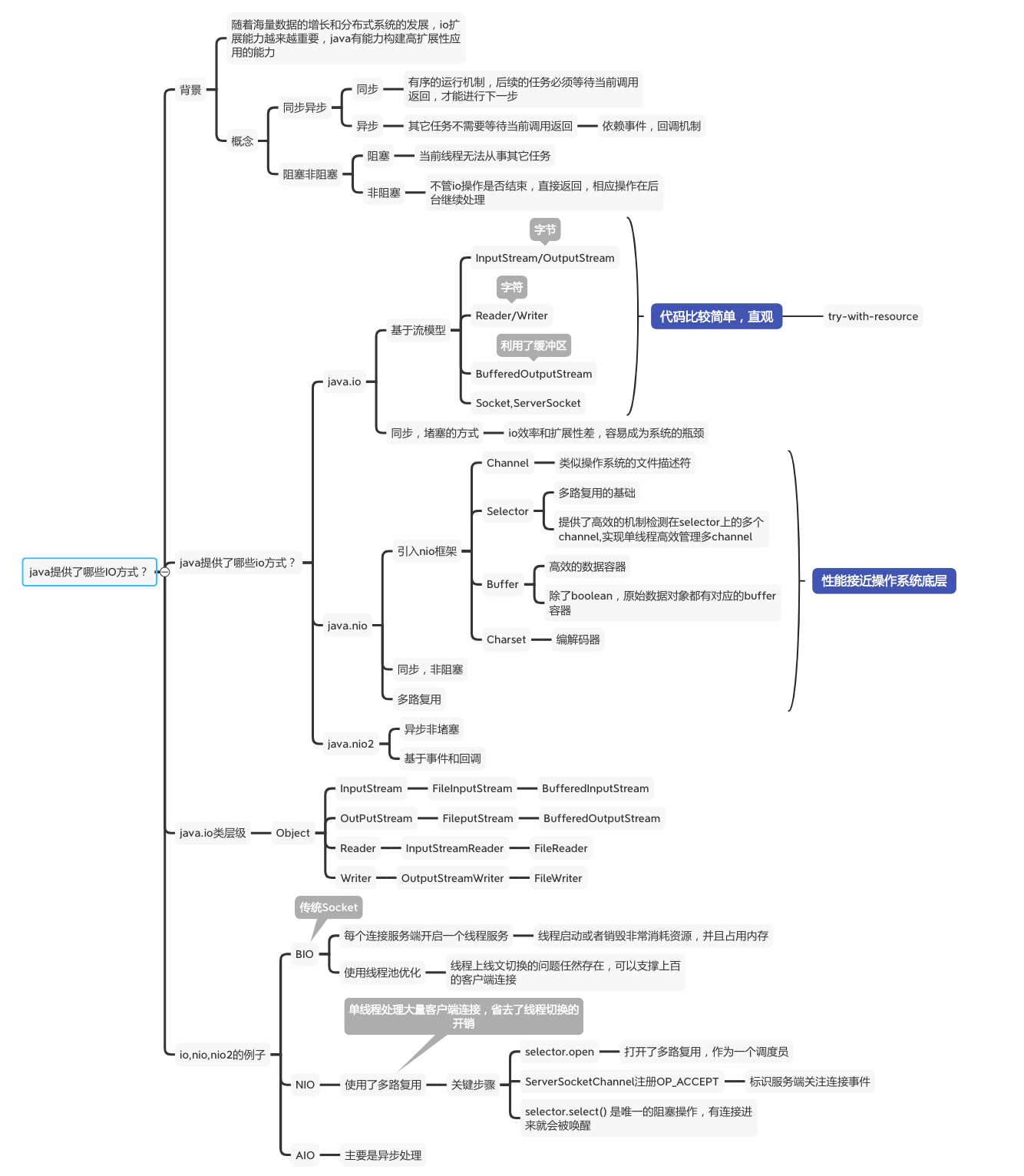
隨著分散式技術的普及和海量數據的增長,io的能力越來越重要,java提供的io模塊提供了足夠的擴展性來適應。 我是李福春,我在準備面試,今天的問題是: java中的io有哪幾種? java中的io分3類: 1,BIO ,即同步阻塞IO,對應java.io包提供的工具;基於流模型,雖然直觀,代碼實現也 ...

隨著分散式技術的普及和海量數據的增長,io的能力越來越重要,java提供的io模塊提供了足夠的擴展性來適應。
我是李福春,我在準備面試,今天的問題是:
java中的io有哪幾種?
java中的io分3類:
1,BIO ,即同步阻塞IO,對應java.io包提供的工具;基於流模型,雖然直觀,代碼實現也簡單,但是擴展性差,消耗資源大,容易成為系統的瓶頸;
2,NIO,同步非阻塞io,對應java.nio包提供的工具,基於io多路復用;
核心類: Channel ,Selector , Buffer , Charset
selector是io多路復用的基礎,實現了一個線程高效管理多個客戶端連接,通過事件監聽處理感興趣的事件。
3,AIO,即非同步非阻塞io, 基於事件和回調
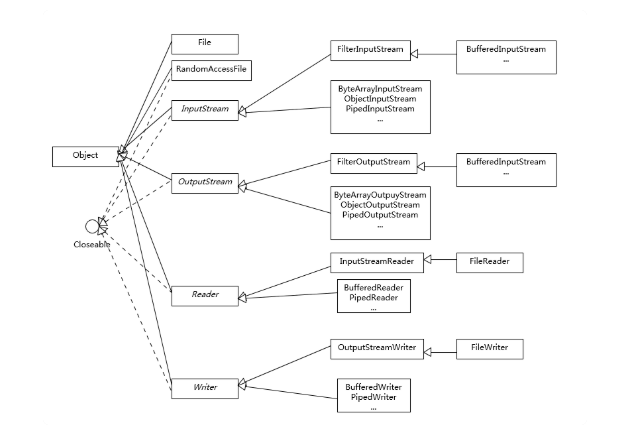
io的類層級
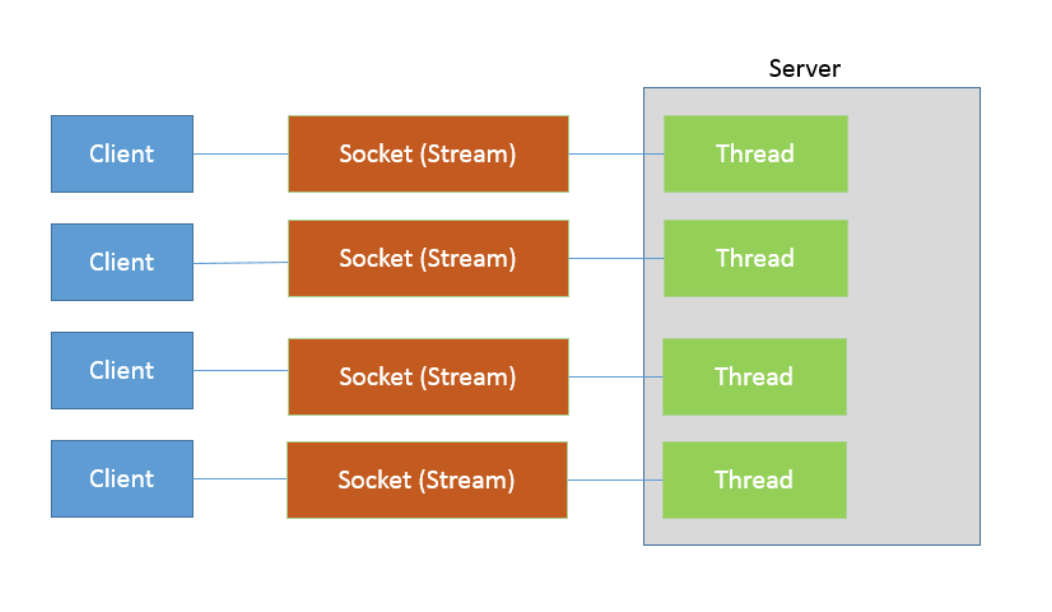
java各種IO的例子
java.io客戶端連接服務端例子
package org.example.mianshi.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* 說明:傳統流式io 客戶端連接服務端例子
* @author carter
* 創建時間: 2020年03月25日 9:58 下午
**/
public class JavaIOApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Server server = new Server();
new Thread(server).start();
try (
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), server.getPort());
) {
final BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
bufferedReader.lines().forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static class Server implements Runnable {
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
public int getPort() {
return serverSocket.getLocalPort();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(0);) {
this.serverSocket = serverSocket;
while (true) {
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
new RequestHandler(socket).start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private class RequestHandler extends Thread {
private Socket socket;
public RequestHandler(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (
final PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream());
) {
printWriter.write("hello world");
printWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
使用連接池優化
package org.example.mianshi.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* 說明:傳統流式io 客戶端連接服務端例子
* @author carter
* 創建時間: 2020年03月25日 9:58 下午
**/
public class ThreadPoolJavaIOApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Server server = new Server();
new Thread(server).start();
try (
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), server.getPort());
) {
final BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
bufferedReader.lines().forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static class Server implements Runnable {
private ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
public int getPort() {
return serverSocket.getLocalPort();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(0);) {
this.serverSocket = serverSocket;
while (true) {
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
threadPool.submit(new RequestHandler(socket));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
private class RequestHandler implements Runnable {
private Socket socket;
public RequestHandler(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (
final PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream());
) {
printWriter.write("hello world");
printWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
java.nio例子
package org.example.mianshi.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* 說明:nio的客戶端連接服務端例子
* @author carter
* 創建時間: 2020年03月25日 10:32 下午
**/
public class JavaNioApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server().start();
try (
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8888);
) {
final BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
bufferedReader.lines().forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static class Server extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8888));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
final Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
selector.select();
selector.selectedKeys().forEach(selectionKey -> {
sayHelloWorld((ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel());
});
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void sayHelloWorld(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
try (SocketChannel socketChannel = channel.accept()) {
socketChannel.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hello world nio"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
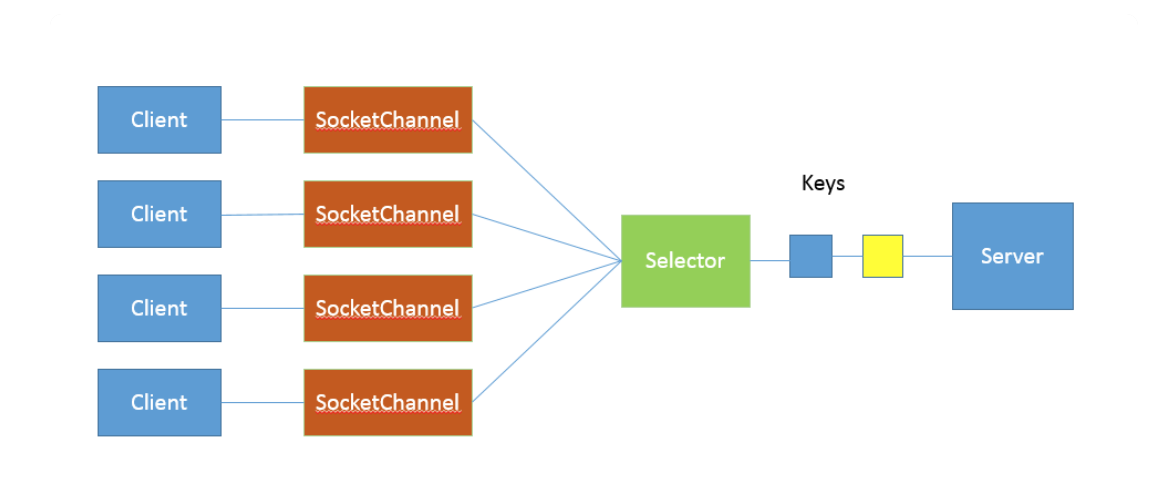
java.nio2例子
package org.example.mianshi.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* 說明:TODO
* @author carter
* 創建時間: 2020年03月25日 10:54 下午
**/
public class JavaNio2App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server().start();
try (
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
) {
final BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
bufferedReader.lines().forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static class Server extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999));
serverSocketChannel.accept(serverSocketChannel, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel,
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel1) {
// serverSocketChannel1.accept(socketChannel, this);
socketChannel.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hello world nio2 "));
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, AsynchronousServerSocketChannel attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
本例子暫時無法運行。只為展示過程;
小結
本篇主要介紹了java提供的3中io,即 BIO,NIO,AIO ; 並提供了一些示例代碼輔助理解。
原創不易,轉載請註明出處。



