數據蘊藏價值,但數據的價值需要用 IT 技術去發現、探索,可視化可以幫助人更好的去分析數據,信息的質量很大程度上依賴於其呈現方式。在數據分析上,熱力圖無疑是一種很好的方式。在很多行業中都有著廣泛的應用。最近剛好項目中需要用到 3D 熱力圖的效果展示。網上搜了相關資料,發現大多數是 2D 效果或者偽 ... ...
前言
數據蘊藏價值,但數據的價值需要用 IT 技術去發現、探索,可視化可以幫助人更好的去分析數據,信息的質量很大程度上依賴於其呈現方式。在數據分析上,熱力圖無疑是一種很好的方式。在很多行業中都有著廣泛的應用。
最近剛好項目中需要用到 3D 熱力圖的效果展示。網上搜了相關資料,發現大多數是 2D 效果或者偽 3D 的,而 3D 粒子效果對於性能上的體驗不是很好,於是取巧寫了個 3D 熱力圖的效果 。
Demo : http://www.hightopo.com/demo/heatMap3D/
部分效果圖:
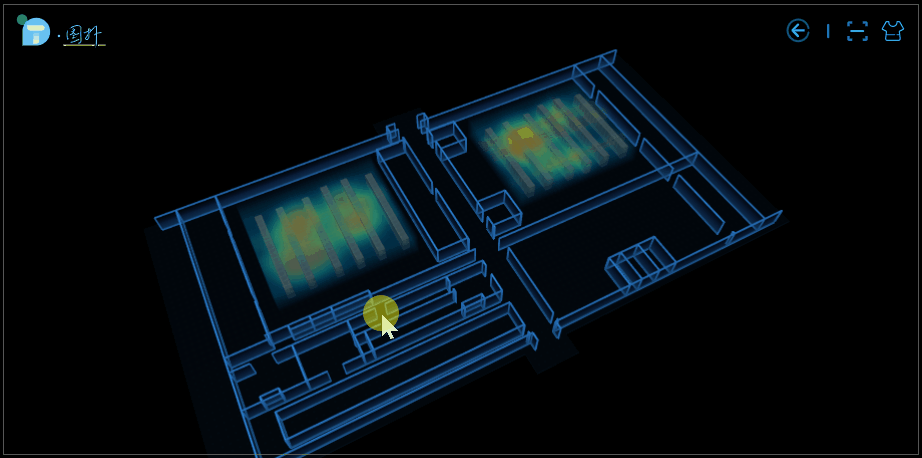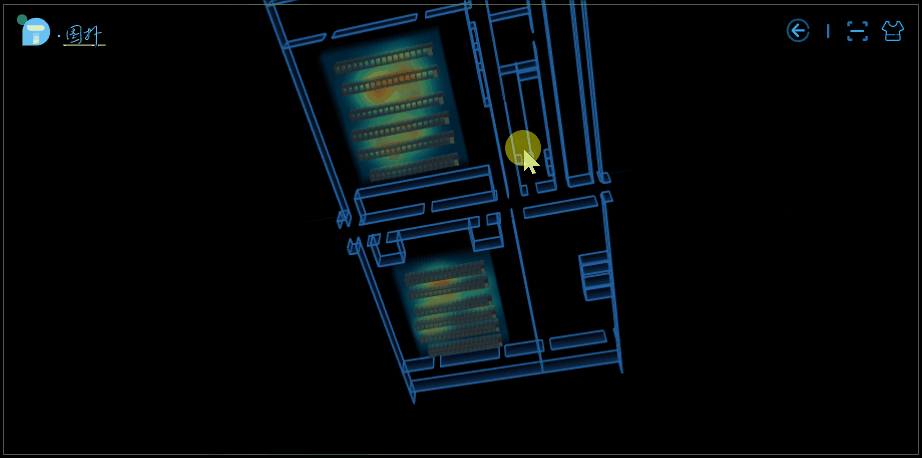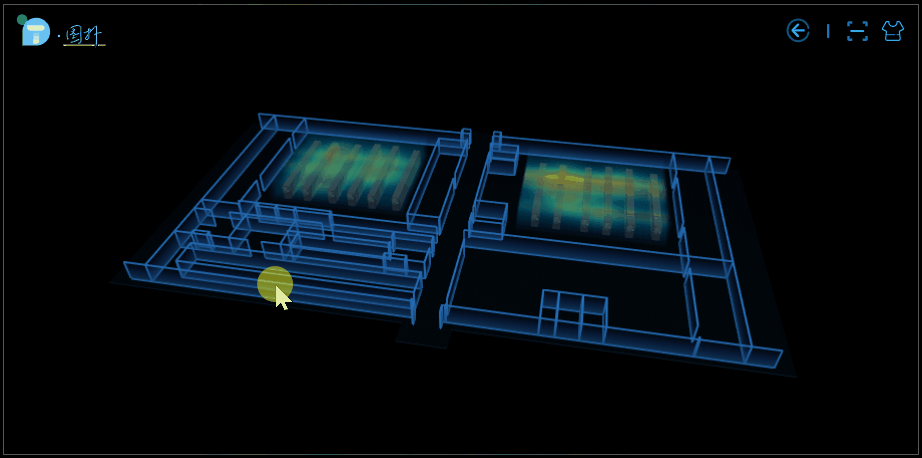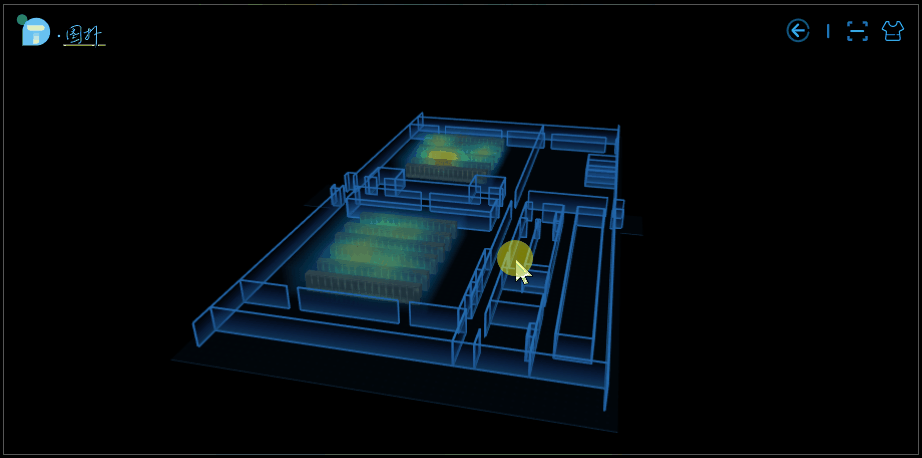
應用場景
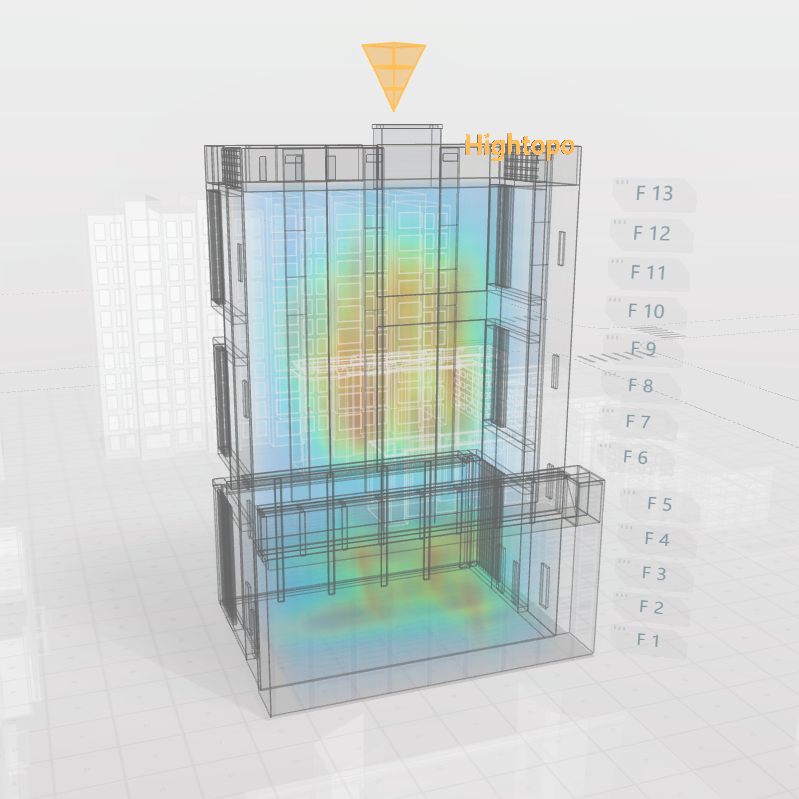
大樓內的人員分佈熱力圖。我們可以通過觀察到一個區域的顏色深淺來判斷該區域內實時的人員流動情況,知道哪個區域人多,哪個區域人少。該場景可適用於大樓內的警務監控,在發生突發事件時科學高效地制定分流疏導策略提供有力的幫助和支持,減少損失。亦可用於火險預警,監控區域實時溫度。
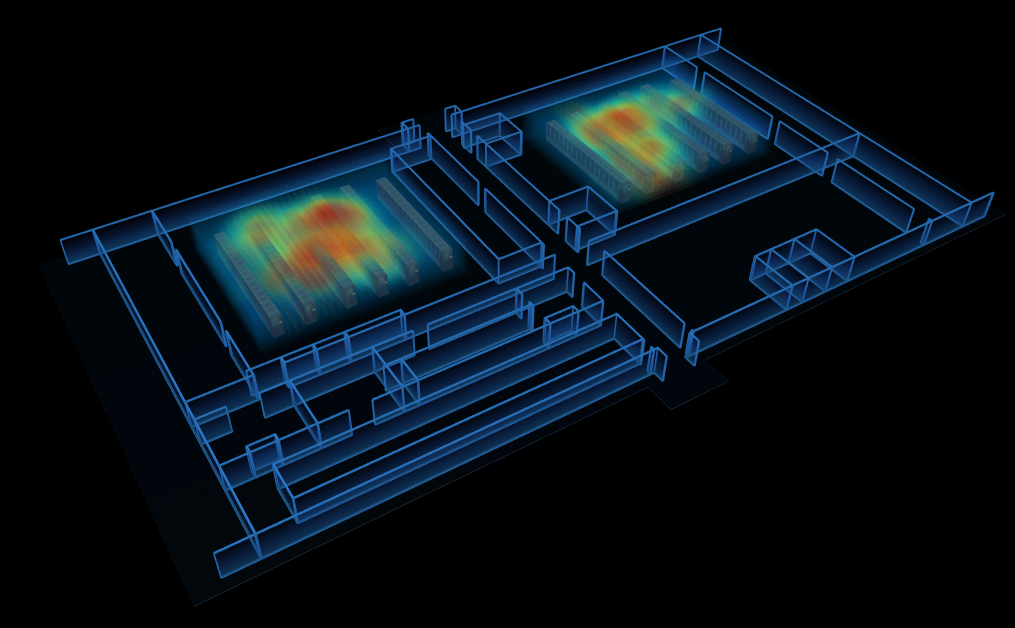
室內設備溫度熱力圖。傳統的數據中心彙報方式枯燥單調、真實感不強,互動性差等,藉助於 3D 熱力圖的可視化呈現方式,機房運維管理人員可大大提高工作效率及降低工作失誤的可能性。
整體思路
在場景反序列化之後,設置熱力圖的初始參數,初始化後得到的熱力圖模型添加進場景中,模擬 3D 熱力圖效果,最後再添加掃描、換膚、溫度提示等功能。
1.數據準備
在場景中畫出熱力圖的區域,如圖
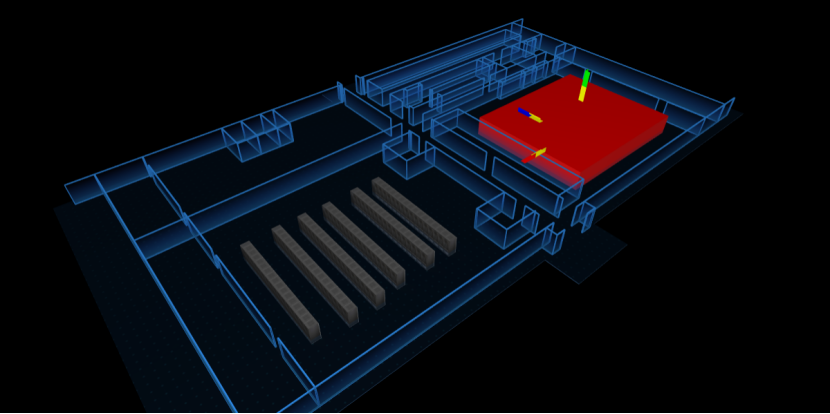
首先確定要生成熱力圖的區域 areaNode ,然後隨機生成 20 個點的信息,包含坐標 position (坐標是相對紅色長方體的某個頂點) 及熱力值 temperature 。
以下是該部分的主要代碼:
function getTemplateList(areaNode, hot, num) {
let heatRect = areaNode.getRect();
let { width, height } = heatRect;
let rackTall = areaNode.getTall();
hot = hot + this.random(20);
let templateList = [];
for (let i = 0; i < num; i++) {
templateList.push({
position: {
x: 0.2 * width + this.random(0.6 * width),
y: 0.2 * height + this.random(0.6 * height),
z: 0.1 * rackTall + this.random(0.8 * rackTall)
},
temperature: hot
});
}
return templateList;
}
let heatMapArea_1 = dm.getDataByTag('heatMapArea_1');
let templateList_1 = this.getTemplateList(
heatMapArea_1,
70,
20
);
2.初始化
使用 ht-thermodynamic.js 插件來生成熱力圖。
發熱點的數據準備好後,接著配置熱力圖的參數,參數說明如下。
// 預設配置
let config = {
hot: 45,
min: 20,
max: 55,
size: 50,
pointNum: 20,
radius: 150,
opacity: 0.05,
colorConfig: {
0: 'rgba(0,162,255,0.14)',
0.2: 'rgba(48,255,183,0.60)',
0.4: 'rgba(255,245,48,0.70)',
0.6: 'rgba(255,73,18,0.90)',
0.8: 'rgba(217,22,0,0.95)',
1: 'rgb(179,0,0)'
},
colorStopFn: function (v, step) { return v * step * step },
};
// 獲取區域數據
let rackTall = areaNode.getTall();
let heatRect = areaNode.getRect();
let { width, height } = heatRect;
if (width === 0 || height === 0) return;
// 熱力圖初始化
let thd = this.thd = new ht.thermodynamic.Thermodynamic3d(g3d, {
// 熱力圖所占用的空間
box: new ht.Math.Vector3(width, height, rackTall),
// 配置溫度的最小值和最大值
min: config.min,
max: config.max,
// 每一片的渲染間隔
interval: 40,
// 為false時,溫度區域交集時值不累加,取最高溫度
remainMax: false,
// 每一片的透明度
opacity: config.opacity,
// 顏色步進
colorStopFn: config.colorStopFn,
// 顏色範圍
gradient: config.colorConfig
});
3.載入熱力圖
將第一步生成的發熱點,設置 thd 的數據對象,調用 thd.createThermodynamicNode() 來生成熱力圖的 3D 圖元。設置其相關信息,將該圖元添加進 3D 場景中。這樣一個簡單的 3D 熱力圖就算完成了。
// 載入熱力圖
function loadThermodynamic(thd, areaNode, templateList, config) {
thd.setData(templateList);
// x,y,z面數
let node = this.heatNode = thd.createThermodynamicNode(config.size, config.size, config.size);
let p3 = areaNode.p3();
node.setAnchorElevation(0);
node.p3(p3);
node.s({
'interactive': true,
'preventDefaultWhenInteractive': false,
'3d.movable': false,
"wf.visible": false
});
g3d.dm().add(node);
}
主體介紹完了,現在開始講講該 demo 的幾個功能。
4.溫度提示
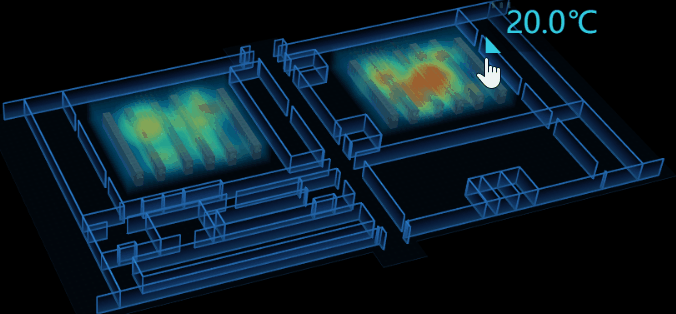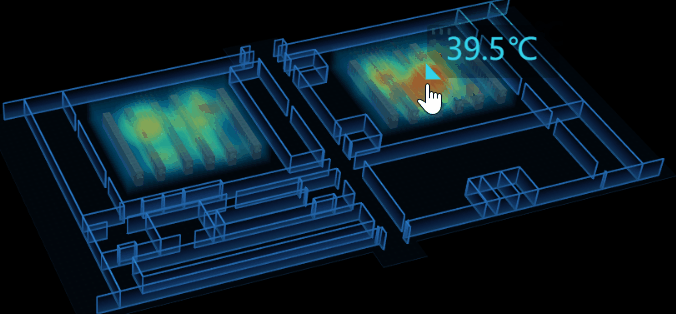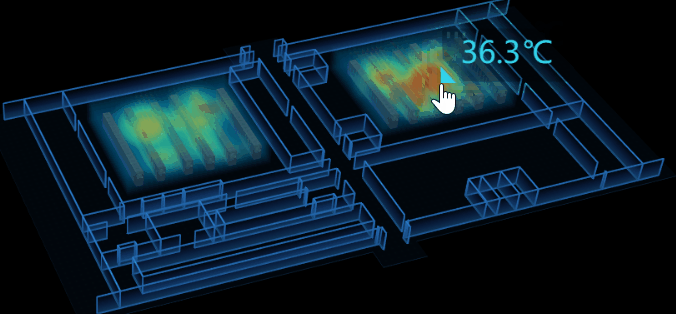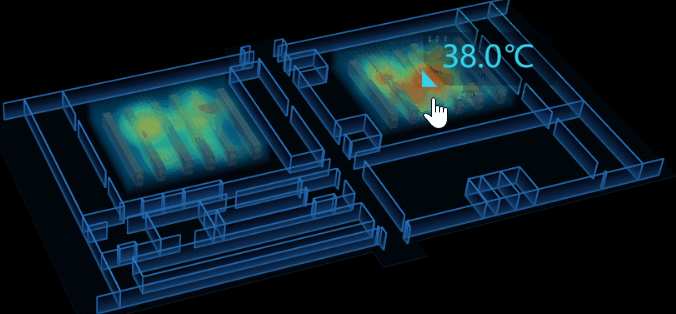
因為在 3D 場景中,我不好判斷當前滑鼠坐標(x,y,z),所以我將 tip 面板放在了 2D 圖紙上,將 2D 圖紙嵌在 3D 場景的上層。通過監聽 3D 場景中的 onMove 事件來控制 tip 面板的顯隱及值的變化。
tip 顯隱控制:當滑鼠移入進熱力圖區域時,tip 顯示,反之則隱藏。在這我遇到了個問題,因為我把除了熱力圖區塊以外的設置成不可交互的,當滑鼠移出區域後,無法監聽到 onMove 事件,導致 bug,tip 面板始終存在著。我使用了 setTimeout 來解決這問題,延時1s後自動隱藏,但後來發現完全沒必要濫用 setTimeout ,只要監聽 onLeave 時隱藏 tip 就行了。
tip 值控制:調用 ht-thermodynamic.js 的方法可以獲取到當前滑鼠相對熱力圖區域的溫度值 thd.getHeatMapValue(e.event,'middle'),實時改變 tip 面板的 value 屬性 。
代碼如下:
// 交互效果
g3d.mi(e => {
if (e.kind === 'onMove') {
let { clientX, clientY } = e.event;
if (this.templateTip) {
let value1 = this.thd1.getHeatMapValue(e.event, 'middle');
let value2 = this.thd2.getHeatMapValue(e.event, 'middle');
if (value1 || value1 === 0 || value2 || value2 === 0) {
let position = g2d.getLogicalPoint({ x: clientX, y: clientY })
this.templateTip.a('value', value1 || value2 || 0)
let { width, height } = this.templateTip.getRect()
this.templateTip.setPosition({ x: position.x + width / 2, y: position.y - height / 2 })
}
}
} else if (kind === 'onLeave') {
let tag = data.getTag()
if (tag && tag.hasOwnProperty('hoverBlock') > -1) {
this.g2d.getView().style.cursor = 'default';
}
this.templateTip && this.setVisible(this.templateTip, false)
}
})
5.掃描
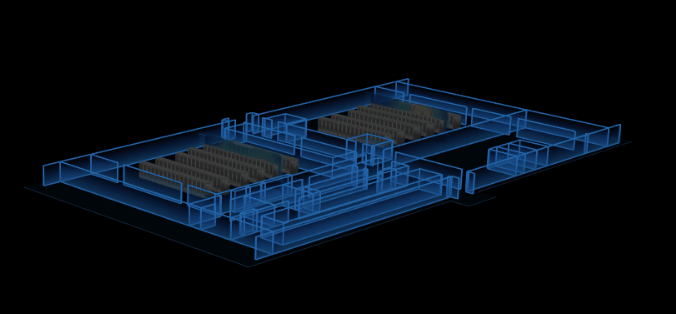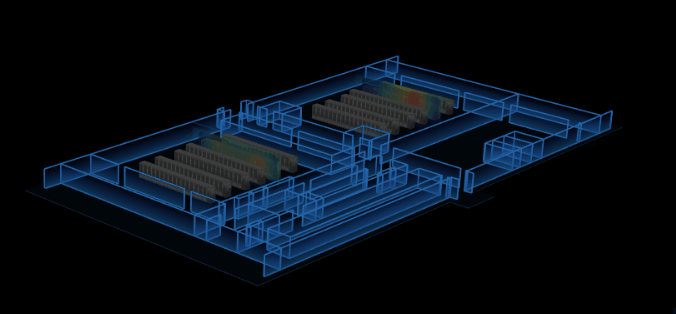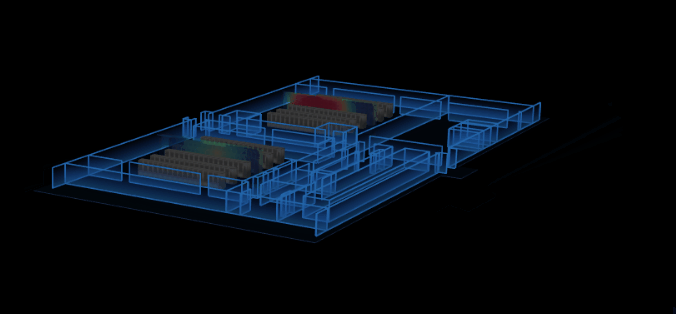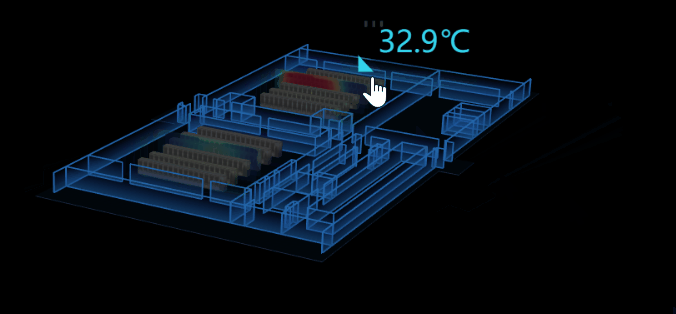
將第三步中的 thd.createThermodynamicNode() 替換。在生成熱力圖對象時,不直接返回一個模型,而是選擇某一個方向進行“切割”,將這一方向的長度均分為 n 份,通過 thd.getHeatMap() 方法來獲取每一片的熱成像。n 的值理論上可以取任意值,但為了渲染效果更好一點,這裡我取的是 50,不至於太多而導致首次渲染時間過長。每切出一個面,我們就在熱力區域的相對位置上動態創建一個 ht.Node ,接著使用 ht.Default.setImage() 將切出來的面註冊成圖片,去設置成該 node 的貼圖(只需設置切割方向上的兩個面就行)。最後將所有的 node 添加進 dataModel ( ht 中承載 Data 數據的模型)。
掃描功能,有兩種方案。第一種是在步驟 3 切割貼片時,不去創建 n 個 node ,而是只創建一個,然後動態去設置該 node 的貼圖及坐標,模擬掃描效果;第二種依舊創建 n 個 node,然後全部隱藏,通過不同時刻來控制讓其中某一個節點顯示,模擬掃描功能。這裡我採用了第二種,因為第一種要去頻繁的修改多種屬性才能達到效果,第二種的話只要控制其 '3d.visible'。
主要代碼如下:
let length;
if (dir === 'z') {
length = rackTall;
}
else if (dir === 'x') {
length = width;
}
else if (dir === 'y') {
length = height;
}
let size = config.size;
for (let index = 0; index < size; index++) {
// 熱力切圖間隔
const offset = length / size;
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
let ctx = thd.getHeatMap(index * offset, dir, colorConfig);
let floor = this.getHeatFloor(
areaNode,
dir,
ctx,
index,
size,
config
);
this.floors.push(floor);
dm.add(floor);
}, 0);
this.timers.push(timer);
}
function start() {
this.hide();
this.anim = true;
this.count = 0;
let frames = this.floors.length;
let params = {
frames, // 動畫幀數
interval: 50, // 動畫幀間隔毫秒數
easing: t => {
return t;
},
finishFunc: () => {
if (this.anim) {
this.start();
}
},
action: (v, t) => {
this.count++;
this.show(this.count);
}
};
this.scanning = ht.Default.startAnim(params);
}
function hide(index) {
if (index || index === 0) {
this.floors.forEach((i, j) => {
if (index === j) {
i.s('3d.visible', false);
}
else {
i.s('3d.visible', true);
}
});
}
else {
this.floors.forEach(i => {
i.s('3d.visible', false);
});
}
}
function show(index) {
if (index || index === 0) {
this.floors.forEach((i, j) => {
if (index === j) {
i.s('3d.visible', true);
}
else {
i.s('3d.visible', false);
}
});
}
else {
this.floors.forEach(i => {
i.s('3d.visible', true);
});
}
}
第一種方式實現主要代碼:
getHeatFloor(node, dir, config) {
let { width, height } = node.getRect();
let rackTall = node.getTall();
let s3 = [1, rackTall, height];
let floor = new ht.Node();
floor.setTag('hotspot');
floor.setAnchor3d({
x: 0.5,
y: 0.5,
z: 0.5
});
floor.s3(s3);
floor.s({
interactive: true,
preventDefaultWhenInteractive: false,
'3d.selectable': true,
'3d.movable': false,
'all.visible': false,
[Top + '.visible']: true,
[Top + '.opacity']: config.opacity,
[Top + '.transparent']: true,
[Top + '.reverse.flip']: true,
[Top + '.color']: 'rgba(51,255,231,0.10)'
});
return floor
}
getHeatFloorInfo(node, dir, ctx, index, size, config) {
let { width, height } = node.getRect();
let rackTall = node.getTall();
let point = node.getPosition3d();
let part = 0;
let p3, s3;
let Top = 'top';
if (!dir) {
dir = 'z';
}
// 熱力圖的yz方向與ht的yz方向相反 dir=z代表的是豎直方向
if (dir === 'x') {
Top = 'left';
part = (width / size) * index;
p3 = [
point[0] - width / 2 + part,
point[1] + rackTall / 2,
point[2]
];
// p3 = [point[0] + part, point[1], point[2]];
s3 = [1, rackTall, height];
}
else if (dir === 'y') {
Top = 'front';
part = (height / size) * index;
p3 = [
point[0],
point[1] + rackTall / 2,
point[2] - height / 2 + part
];
s3 = [width, rackTall, 1];
}
else if (dir === 'z') {
Top = 'top';
part = (rackTall / size) * index;
p3 = [point[0], point[1] + part, point[2]];
s3 = [width, 1, height];
}
let heatName = this.generateUUID();
ht.Default.setImage('heatMap' + heatName, ctx);
this.heatFloorInfo.push(
{
img: 'heatMap' + heatName,
p3
}
)
}
show(index){
let info = this.heatFloorInfo[index]
this.floor.p3(info.p3)
this.floor.s('3d.visible', true);
this.floor.s('top.image', info.img);
// 手動刷新
this.floor.iv();
}
6.換膚
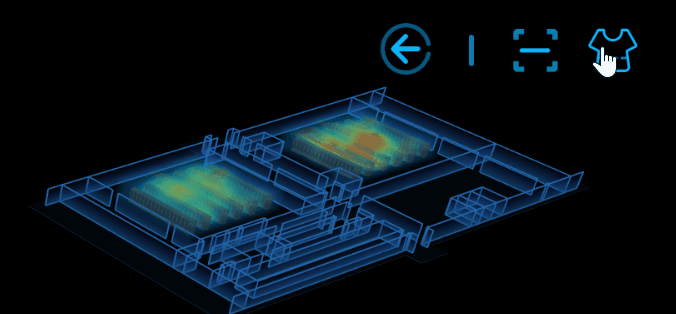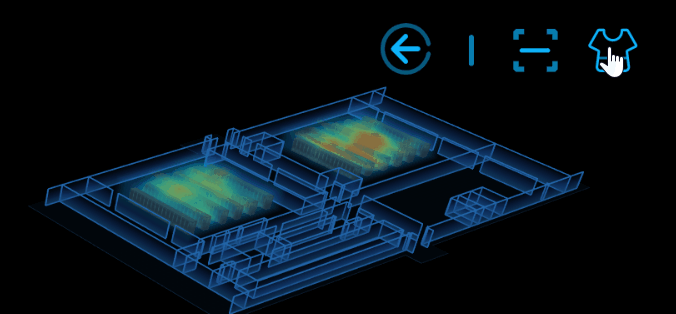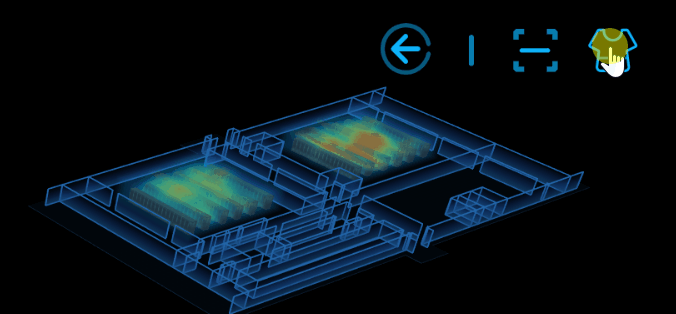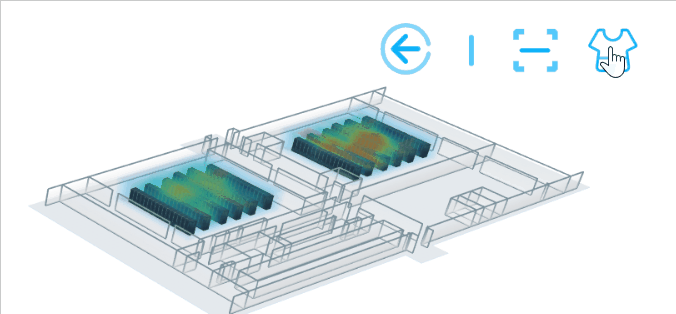
換膚的實現原理:根據不同的場景值去動態修改 ht.graph3d.Graph3dView 的背景色及牆的顏色等。
代碼:
function changeSkin() {
let backgroundColor = this.g3d.dm().getBackground(),
dark_bg = this.g3d.dm().getDataByTag('dark_skin'),
light_bg = this.g3d.dm().getDataByTag('light_skin');
if (backgroundColor !== 'rgb(255,255,255)') {
this.g3d.dm().setBackground('rgb(255,255,255)');
} else {
this.g3d.dm().setBackground('rgb(0,0,0)');
}
dark_bg.s('2d.visible', !dark_bg.s('2d.visible'));
dark_bg.s('3d.visible', !dark_bg.s('3d.visible'));
light_bg.s('2d.visible', !light_bg.s('2d.visible'));
light_bg.s('3d.visible', !light_bg.s('3d.visible'));
}
本篇就介紹到了,目前 ht-thermodynamic.js 還處於測試階段,待到相對成熟後再更新該 demo ,有興趣瞭解更多關於 2D/3D 可視化的構建,可翻閱其他文章的例子,HT 會給你很多不可思議的東西。



